提问
-
setState是怎么刷新页面的?
-
setState为什么有些情况下使用会带来不必要的开销?
-
flutter的渲染机制是什么?
-
带着这几个疑问读一下系统源码
- setState入手
- 补充flutter启动流程,runApp入手
- binding过程,补充window概念
- 回来以后整体看一下,然后补充Vsync概念
setState入手
typescript
@protected
void setState(VoidCallback fn) {
final Object? result = fn() as dynamic;
_element!.markNeedsBuild();
}markNeedsBuild
csharp
void markNeedsBuild() {
if (dirty) {
return;
}
_dirty = true;
owner!.scheduleBuildFor(this);
}scheduleBuildFor
ini
void scheduleBuildFor(Element element) {
if (element._inDirtyList) {
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = true;
return;
}
if (!_scheduledFlushDirtyElements && onBuildScheduled != null) {
_scheduledFlushDirtyElements = true;
onBuildScheduled!();
}
_dirtyElements.add(element);
element._inDirtyList = true;
}onBuildScheduled调到了哪?这个得从runApp入手
- 先补充一下window的概念,再走一下runapp流程
window
- 不管是安卓、ios、flutter,都是把操作系统抽象成一块屏幕,framework层就是和屏幕交互

- flutter中这块屏幕对应的就是window类
dart
@Native("Window,DOMWindow")
class Window extends EventTarget implements WindowEventHandlers, WindowBase GlobalEventHandlers,
_WindowTimers, WindowBase64 {
// 当前设备的DPI,即一个逻辑像素显示多少物理像素,数字越大,显示效果就越精细保真。
// DPI是设备屏幕的固件属性,如Nexus 6的屏幕DPI为3.5
double get devicePixelRatio => _devicePixelRatio;
// Flutter UI绘制区域的大小
Size get physicalSize => _physicalSize;
// 当前系统默认的语言Locale
Locale get locale;
// 当前系统字体缩放比例。
double get textScaleFactor => _textScaleFactor;
// 当绘制区域大小改变回调
VoidCallback get onMetricsChanged => _onMetricsChanged;
// Locale发生变化回调
VoidCallback get onLocaleChanged => _onLocaleChanged;
// 系统字体缩放变化回调
VoidCallback get onTextScaleFactorChanged => _onTextScaleFactorChanged;
// 绘制前回调,一般会受显示器的垂直同步信号VSync驱动,当屏幕刷新时就会被调用
FrameCallback get onBeginFrame => _onBeginFrame;
// 绘制回调
VoidCallback get onDrawFrame => _onDrawFrame;
// 点击或指针事件回调
PointerDataPacketCallback get onPointerDataPacket => _onPointerDataPacket;
// 调度Frame,该方法执行后,onBeginFrame和onDrawFrame将紧接着会在合适时机被调用,
// 此方法会直接调用Flutter engine的Window_scheduleFrame方法
void scheduleFrame() native 'Window_scheduleFrame';
// 更新应用在GPU上的渲染,此方法会直接调用Flutter engine的Window_render方法
void render(Scene scene) native 'Window_render';
// 发送平台消息
void sendPlatformMessage(String name,
ByteData data,
PlatformMessageResponseCallback callback) ;
// 平台通道消息处理回调
PlatformMessageCallback get onPlatformMessage => _onPlatformMessage;
... //其它属性及回调
} flutter启动时的runAapp,就是建立与window的联系
java
void runApp(Widget app) {
final WidgetsBinding binding = WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
_runWidget(binding.wrapWithDefaultView(app), binding, 'runApp');
}WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized()
scala
class WidgetsFlutterBinding extends BindingBase with GestureBinding, SchedulerBinding, ServicesBinding, PaintingBinding, SemanticsBinding, RendererBinding, WidgetsBinding {
static WidgetsBinding ensureInitialized() {
if (WidgetsBinding._instance == null) {
WidgetsFlutterBinding();
}
return WidgetsBinding.instance;
}
}binding中mixin过程
BindingBase:抽象基类
WidgetsBinding:绑定组件树
RendererBinding:绑定渲染树
SemanticsBinding:绑定语义树,跟无障碍模式有关,定义界面元素的功能和含义,如按钮、输入框、标题、返回等
PaintingBinding:绑定绘制操作
SchedulerBinding:绑定帧绘制回调函数,以及widget生命周期相关事件
ServicesBinding:绑定平台服务消息,注册Dart层和C++层的消息传输服务;
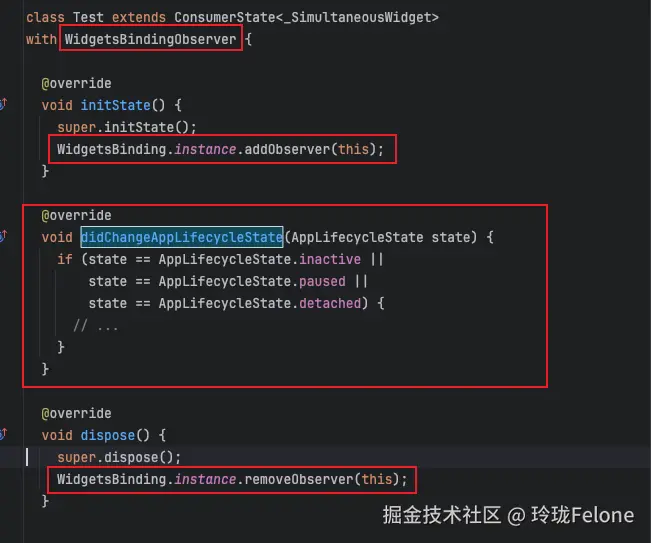
GestureBinding:绑定手势事件,用于检测应用的各种手势相关操作;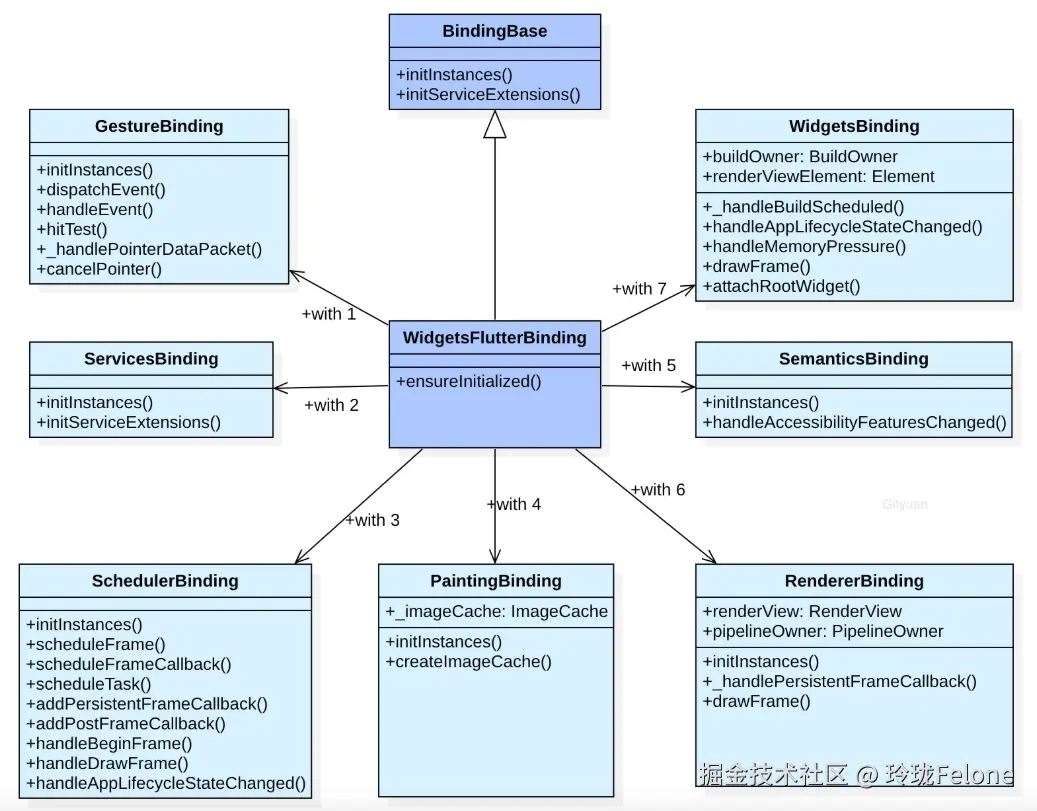
回到onBuildScheduled的调用,就注册在WidgetsBinding
ini
mixin WidgetsBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding, SchedulerBinding, GestureBinding, RendererBinding, SemanticsBinding {
@override
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances();
_instance = this;
_buildOwner = BuildOwner();
buildOwner!.onBuildScheduled = _handleBuildScheduled;
platformDispatcher.onLocaleChanged = handleLocaleChanged;
SystemChannels.navigation.setMethodCallHandler(_handleNavigationInvocation);
SystemChannels.backGesture.setMethodCallHandler(
_handleBackGestureInvocation,
);
platformMenuDelegate = DefaultPlatformMenuDelegate();
}buildOwner!.onBuildScheduled = _handleBuildScheduled;
ini
mixin WidgetsBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding, SchedulerBinding, GestureBinding, RendererBinding, SemanticsBinding {
@override
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances();
_instance = this;
_buildOwner = BuildOwner();
buildOwner!.onBuildScheduled = _handleBuildScheduled;
platformDispatcher.onLocaleChanged = handleLocaleChanged;
SystemChannels.navigation.setMethodCallHandler(_handleNavigationInvocation);
SystemChannels.backGesture.setMethodCallHandler(
_handleBackGestureInvocation,
);
platformMenuDelegate = DefaultPlatformMenuDelegate();
}
void _handleBuildScheduled() {
ensureVisualUpdate();
}
}ensureVisualUpdate
csharp
void ensureVisualUpdate() {
switch (schedulerPhase) {
case SchedulerPhase.idle:
case SchedulerPhase.postFrameCallbacks:
scheduleFrame();
return;
case SchedulerPhase.transientCallbacks:
case SchedulerPhase.midFrameMicrotasks:
case SchedulerPhase.persistentCallbacks:
return;
}
}scheduleFrame
ini
void scheduleFrame() {
if (_hasScheduledFrame || !framesEnabled) {
return;
}
ensureFrameCallbacksRegistered();
platformDispatcher.scheduleFrame();
_hasScheduledFrame = true;
}scheduleFrame,到native了,这里补充一下Vsync的概念
csharp
void scheduleFrame() => _scheduleFrame();
@Native<Void Function()>(symbol: 'PlatformConfigurationNativeApi::ScheduleFrame')
external static void _scheduleFrame();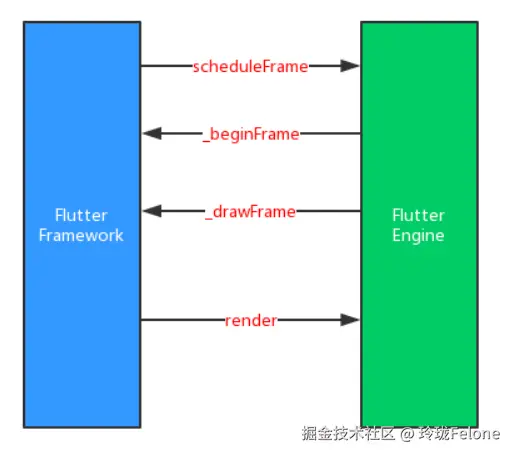
Vsync垂直同步
● buffer传递的过程是binder+共享内存,因为buffer特别大
为什么不是固定16ms一次?
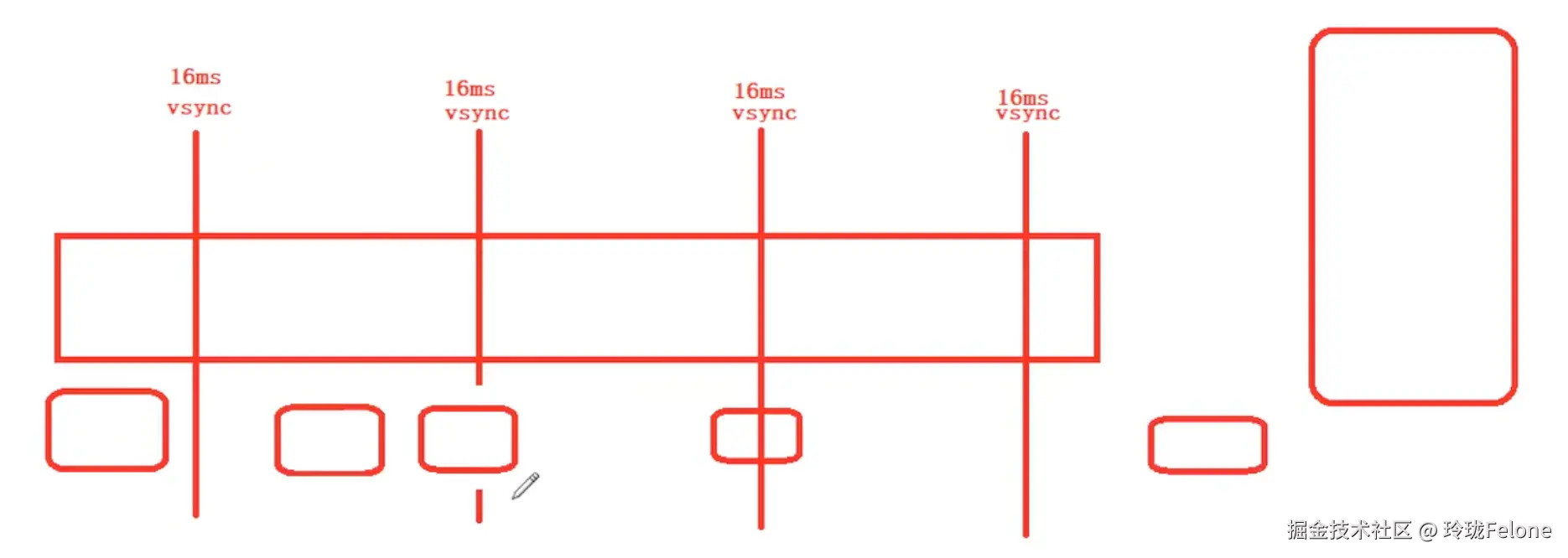
实际的Vsync是这样
ensureFrameCallbacksRegistered中注册了回调
typescript
@protected
void ensureFrameCallbacksRegistered() {
platformDispatcher.onBeginFrame ??= _handleBeginFrame;
platformDispatcher.onDrawFrame ??= _handleDrawFrame;
}handleBeginFrame和handleDrawFrame就是处理三个回调队列
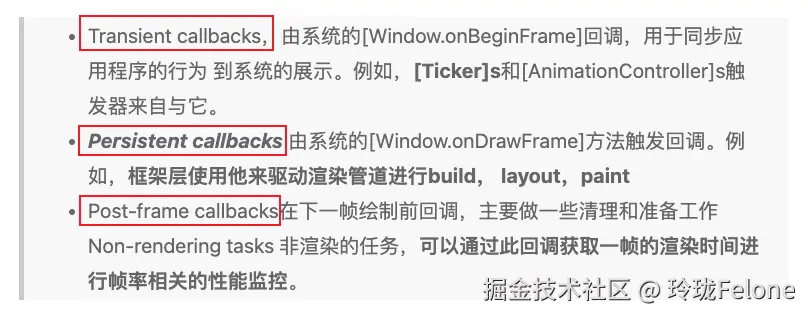
ini
void handleBeginFrame(Duration? rawTimeStamp) {
_frameTimelineTask?.start('Frame');
_firstRawTimeStampInEpoch ??= rawTimeStamp;
_currentFrameTimeStamp = _adjustForEpoch(rawTimeStamp ?? _lastRawTimeStamp);
if (rawTimeStamp != null) {
_lastRawTimeStamp = rawTimeStamp;
}
_hasScheduledFrame = false;
try {
// TRANSIENT FRAME CALLBACKS
_frameTimelineTask?.start('Animate');
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.transientCallbacks;
final Map<int, _FrameCallbackEntry> callbacks = _transientCallbacks;
_transientCallbacks = <int, _FrameCallbackEntry>{};
callbacks.forEach((int id, _FrameCallbackEntry callbackEntry) {
if (!_removedIds.contains(id)) {
_invokeFrameCallback(callbackEntry.callback, _currentFrameTimeStamp!, callbackEntry.debugStack);
}
});
_removedIds.clear();
} finally {
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.midFrameMicrotasks;
}
}
void handleDrawFrame() {
_frameTimelineTask?.finish(); // end the "Animate" phase
try {
// PERSISTENT FRAME CALLBACKS
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.persistentCallbacks;
for (final FrameCallback callback in List<FrameCallback>.of(_persistentCallbacks)) {
_invokeFrameCallback(callback, _currentFrameTimeStamp!);
}
// POST-FRAME CALLBACKS
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.postFrameCallbacks;
final List<FrameCallback> localPostFrameCallbacks =
List<FrameCallback>.of(_postFrameCallbacks);
_postFrameCallbacks.clear();
for (final FrameCallback callback in localPostFrameCallbacks) {
_invokeFrameCallback(callback, _currentFrameTimeStamp!);
}
} finally {
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.idle;
_frameTimelineTask?.finish(); // end the Frame
_currentFrameTimeStamp = null;
}
}
@pragma('vm:notify-debugger-on-exception')
void _invokeFrameCallback(FrameCallback callback, Duration timeStamp, [ StackTrace? callbackStack ]) {
try {
callback(timeStamp);
} catch (exception, exceptionStack) {
}
}重点追踪一下persistentCallbacks,怎么触发渲染流程的
ini
mixin RendererBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding, SchedulerBinding, GestureBinding, SemanticsBinding, HitTestable {
@override
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances();
_instance = this;
_rootPipelineOwner = createRootPipelineOwner();
platformDispatcher
..onMetricsChanged = handleMetricsChanged
..onTextScaleFactorChanged = handleTextScaleFactorChanged
..onPlatformBrightnessChanged = handlePlatformBrightnessChanged;
// 在这里add了一个回调
addPersistentFrameCallback(_handlePersistentFrameCallback);
initMouseTracker();
if (kIsWeb) {
addPostFrameCallback(_handleWebFirstFrame, debugLabel: 'RendererBinding.webFirstFrame');
}
rootPipelineOwner.attach(_manifold);
}_handlePersistentFrameCallback
scss
void _handlePersistentFrameCallback(Duration timeStamp) {
drawFrame();
_scheduleMouseTrackerUpdate();
}
@protected
void drawFrame() {
rootPipelineOwner.flushLayout();
rootPipelineOwner.flushCompositingBits();
rootPipelineOwner.flushPaint();
if (sendFramesToEngine) {
for (final RenderView renderView in renderViews) {
renderView.compositeFrame(); // this sends the bits to the GPU
}
rootPipelineOwner.flushSemantics(); // this sends the semantics to the OS.
_firstFrameSent = true;
}
}WidgetsBinding继承RendererBinding,重写drawFrame
typescript
mixin WidgetsBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding, SchedulerBinding, GestureBinding, RendererBinding, SemanticsBinding {
@override
void drawFrame() {
try {
if (rootElement != null) {
buildOwner!.buildScope(rootElement!);
}
super.drawFrame();
buildOwner!.finalizeTree();
} finally {
}
}buildScope
ini
@pragma('vm:notify-debugger-on-exception')
void buildScope(Element context, [ VoidCallback? callback ]) {
if (callback == null && _dirtyElements.isEmpty) {
return;
}
try {
_scheduledFlushDirtyElements = true;
if (callback != null) {
Element? debugPreviousBuildTarget;
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = false;
try {
// runApp时调用
callback();
} finally {
}
}
_dirtyElements.sort(Element._sort);
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = false;
int dirtyCount = _dirtyElements.length;
int index = 0;
while (index < dirtyCount) {
// 重点
final Element element = _dirtyElements[index];
try {
element.rebuild();
} catch (e, stack) {
}
if (isTimelineTracked) {
FlutterTimeline.finishSync();
}
index += 1;
}
} finally {
for (final Element element in _dirtyElements) {
assert(element._inDirtyList);
element._inDirtyList = false;
}
_dirtyElements.clear();
_scheduledFlushDirtyElements = false;
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = null;
}
}rebuild --> performRebuild --> build
- 查看StatelessElement和StatefulElement共同祖先CompantElement中的实现
ini
void performRebuild() {
Widget? built;
try {
built = build();
} catch (e, stack) {
built = ErrorWidget.builder();
}
try {
_child = updateChild(_child, built, slot);
} catch (e, stack) {
built = ErrorWidget.builder();
_child = updateChild(null, built, slot);
}
}updateChild分四种情况
- 官方注释:

ini
Element? updateChild(Element? child, Widget? newWidget, Object? newSlot) {
if (newWidget == null) {
if (child != null) {
// 移除,递归操作
deactivateChild(child);
}
return null;
}
final Element newChild;
if (child != null) {
bool hasSameSuperclass = true;
if (hasSameSuperclass && child.widget == newWidget) {
if (child.slot != newSlot) {
// 更新角标,比如row、column中子元素位置改变
updateSlotForChild(child, newSlot);
}
newChild = child;
// canUpdate:是否能对比更新
} else if (hasSameSuperclass && Widget.canUpdate(child.widget, newWidget)) {
if (child.slot != newSlot) {
updateSlotForChild(child, newSlot);
}
child.update(newWidget);
newChild = child;
} else {
//移除并建个新的
deactivateChild(child);
newChild = inflateWidget(newWidget, newSlot);
}
} else {
newChild = inflateWidget(newWidget, newSlot);
}
return newChild;
}update递归更新,不同element不同实现,以StatulElement为例
- 可以看出setState的一个弊端,在顶层widget更新,会递归build所有子widget,会有不小的开销
typescript
@override
void update(StatefulWidget newWidget) {
super.update(newWidget);
final StatefulWidget oldWidget = state._widget!;
state._widget = widget as StatefulWidget;
//先调用didUpdateWidget:我们可以在state中重写这个方法
final Object? debugCheckForReturnedFuture = state.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget) as dynamic;
rebuild(force: true);
}
void rebuild({bool force = false}) {
try {
//走到子widget的performRebuild,跟上面流程一样,继续递归rebuild --> performRebuild --> build
performRebuild();
} finally {
}
}还差一个render收尾
前面有个RendererBinding.class
scss
@protected
void drawFrame() {
rootPipelineOwner.flushLayout();
rootPipelineOwner.flushCompositingBits();
rootPipelineOwner.flushPaint();
if (sendFramesToEngine) {
for (final RenderView renderView in renderViews) {
// 将合成后的图层树提交给引擎
renderView.compositeFrame(); // this sends the bits to the GPU
}
rootPipelineOwner.flushSemantics(); // this sends the semantics to the OS.
_firstFrameSent = true;
}
}
//应用启动时,可能需要等待一些关键资源(如初始化配置、主题数据、字体加载)准备完成后再显示第一帧,
//避免用户看到不完整的界面。
//第一帧没发,且需要延迟时不发生帧数据
bool get sendFramesToEngine => _firstFrameSent || _firstFrameDeferredCount == 0;
scss
void compositeFrame() {
try {
// 图层合成
final ui.SceneBuilder builder = ui.SceneBuilder();
final ui.Scene scene = layer!.buildScene(builder);
if (automaticSystemUiAdjustment) {
// 更新系统UI、状态栏导航栏等
_updateSystemChrome();
}
// 发送到native
_view.render(scene, size: configuration.toPhysicalSize(size));
scene.dispose();
} finally {
}
}
sql
@Native<Void Function(Int64, Pointer<Void>, Double, Double)>(symbol: 'PlatformConfigurationNativeApi::Render')
external static void _render(int viewId, _NativeScene scene, double width, double height);回顾一下
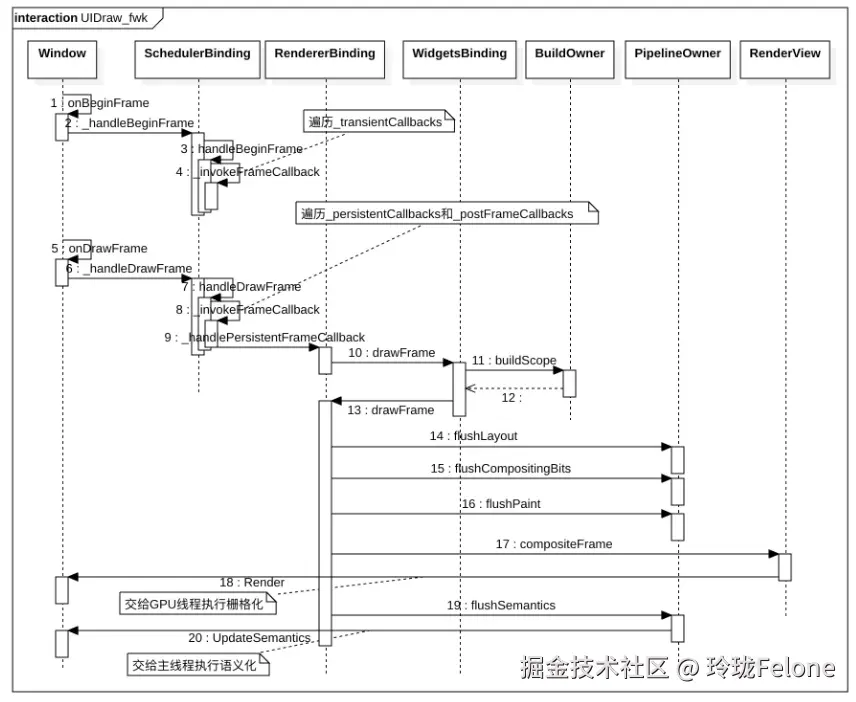
提问与收获
- renderViews什么时候构建的
- render怎么加进来的?如何保证绘制顺序
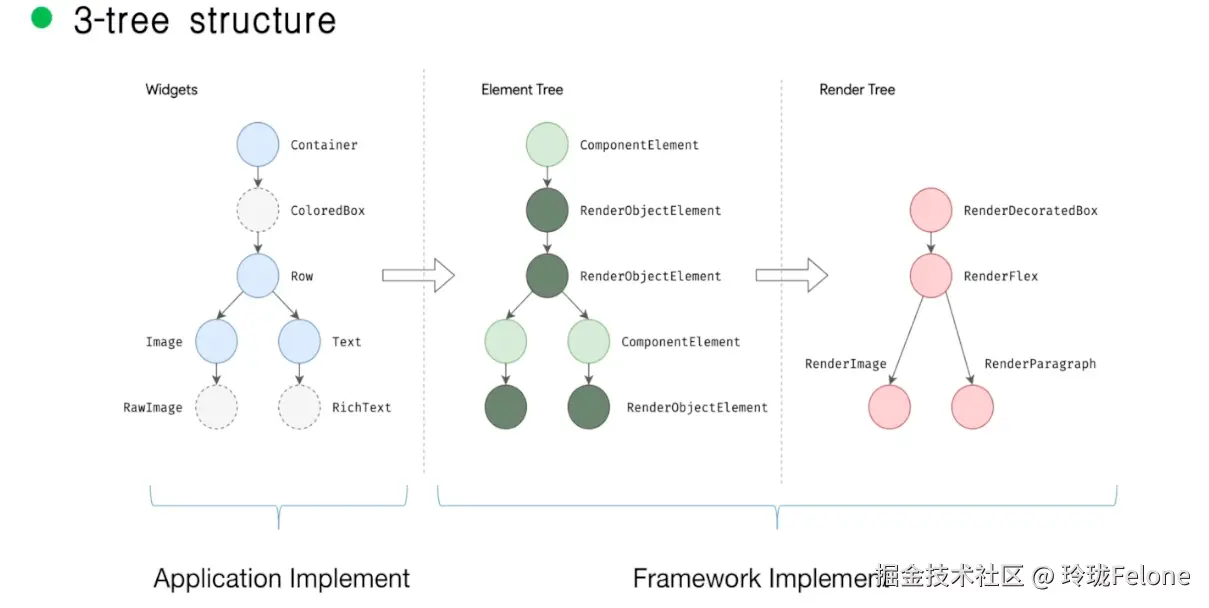
- 三棵树的形成?之间是什么样的依赖关系?
- setState的弊端?
- element复用时的diff过程是怎样的?
- flutter常用的页面的生命周期是的监听是哪来的?
flutter三棵树建立
-
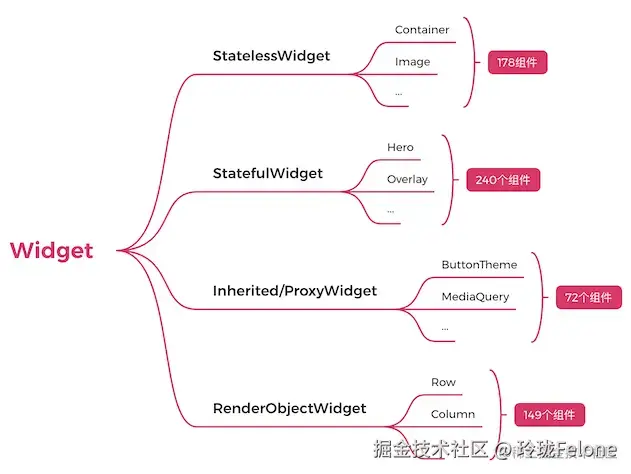
组合型widget
- stless
- stful
-
功能型widget
- 不在屏幕上画东西,但是影响在屏幕上画的东西,比如inheritwidget,用来做数据传递
-
展示型widget
- 只有renderobjectrenderwidget会创建renderobject
屏幕生命周期就是window传过来的