文章目录
- 4 格式化输入输出
-
- 4.1 格式化写 fprintf
- 4.2 格式化读 fscanf
- 4.3 数据转化为字符串 sprintf
- 4.3 字符串的数据还原 sscanf
4 格式化输入输出
前边介绍的方法都是字符的读写,
而fprintf 和fscanf是对数据进行格式读写,
除此之外还有sscanf和sprintf
我们可以来对比一下这几个函数:
scanf从标准输入流读取格式化的数据。printf向标准输出流写格式化的数据。fscanf适用于所有输入流的格式化输入函数fprintf适用于所有输出流的格式化输出函数sprintf将格式化的数据写入到字符串中(将格式化的数据转化为字符串),可以将任何类型的数据转换成字符串;sscanf将转换成字符串的数据还原 ,(sprintf将数据转换成字符串,sscanf将数据还原。)
4.1 格式化写 fprintf
fprintf 适用于所有输出流的格式化输出函数
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
struct S {
int a;
float s;
};
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("data.txt", "w");//注意,读写时操作不同,注意修改
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
struct S s = { 100,3.14f };
//写入到文本
fprintf(pf, "%d %f", s.a, s.s);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}它可以将不同格式的数据输出到指定位置。fprintf 和printf很类似,就是前边加上输出的位置。
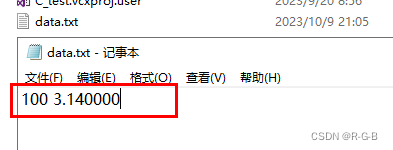
运行成功后,打开文件就可以看到100,3.140000出现在文件中。
4.2 格式化读 fscanf
fscanf 适用于所有输入流的格式化输入函数。
既然有格式化输出,那就必然有从文件中输入。
cpp
struct S {
int a;
float s;
};
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("data.txt", "r");
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
struct S s = { 0 };
fscanf(pf, "%d %f", &(s.a), &(s.s));
printf("%d %f", s.a, s.s);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
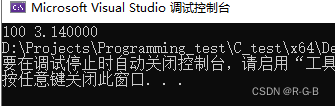
}读取之前保存的数据,屏幕上就会输出文件中的数据。
fscanf和我们经常适用的scanf也很相似,只是多了一个读取数据的位置。
4.3 数据转化为字符串 sprintf
sprintf 将格式化的数据写入到字符串中(将格式化的数据转化为字符串),可以将任何类型的数据转换成字符串;
cpp
struct S {
int a;
float s;
char str[20];
};
int main()
{
char ch[30] = { 0 };
struct S s = { 100,3.14f,"hello world" };
sprintf(ch, "%d %f %s", s.a, s.s, s.str);
return 0;
}通过调试,观察ch中的数据:
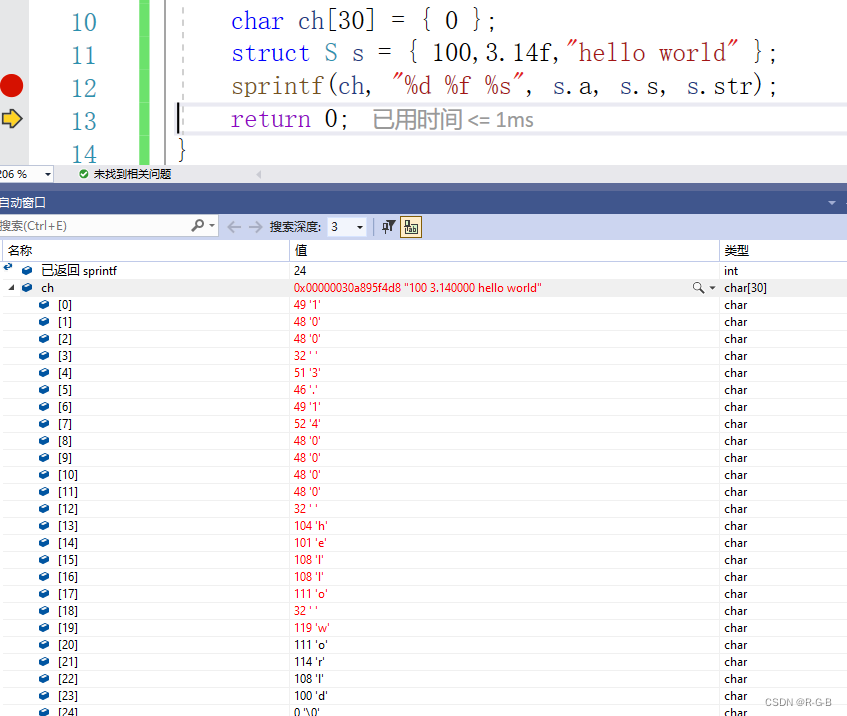
可以观察到它确实将数据转化成了字符串,并存放到了数组当中。
sprintf和printf也很类似,只需在前边添加要存放的数组。
4.3 字符串的数据还原 sscanf
sprintf 将数据转换成字符串,sscanf将数据还原。通过结构体访问成员进而输出。
cpp
struct S {
int a;
float s;
char str[20];
};
int main()
{
char ch[30] = { 0 };
struct S s = { 100,3.14f,"hello world" };
struct S t = { 0 };
sprintf(ch, "%d %f %s", s.a, s.s, s.str);
sscanf(ch, "%d %f %s", &(t.a), &(t.s), &(t.str));
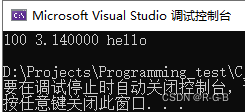
printf("%d %f %s\n", t.a, t.s, t.str);
return 0;
}
sscanf其实也是和scanf很像,它仅仅是在前边添加了一个转换的数组地址。