一.运行工程
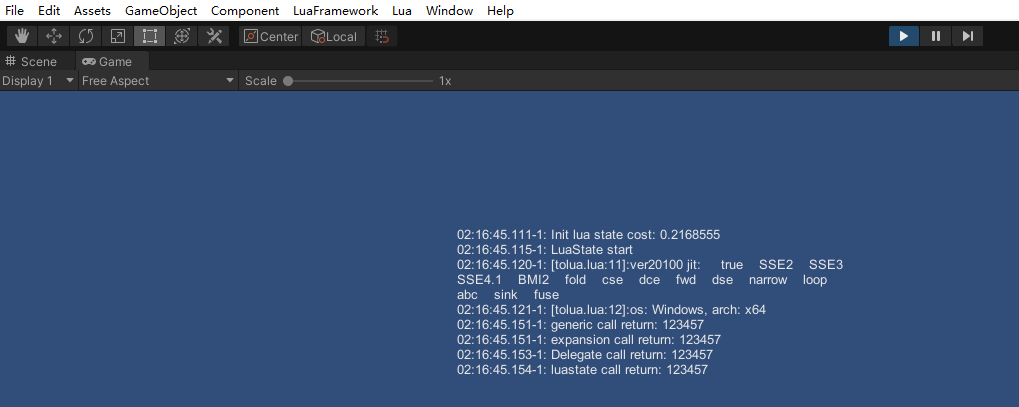
本例展示如何用C#调用Lua函数,运行表现很简单,打印几行文本,我们关注打印的最后4行
二.代码分析
2.1 代码展示
cs
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
using System;
public class CallLuaFunction : MonoBehaviour
{
private string script =
@" function luaFunc(num)
return num + 1
end
test = {}
test.luaFunc = luaFunc
";
LuaFunction luaFunc = null;
LuaState lua = null;
string tips = null;
void Start ()
{
#if UNITY_5 || UNITY_2017 || UNITY_2018
Application.logMessageReceived += ShowTips;
#else
Application.RegisterLogCallback(ShowTips);
#endif
new LuaResLoader();
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
DelegateFactory.Init();
lua.DoString(script);
//Get the function object
luaFunc = lua.GetFunction("test.luaFunc");
if (luaFunc != null)
{
int num = luaFunc.Invoke<int, int>(123456);
Debugger.Log("generic call return: {0}", num);
num = CallFunc();
Debugger.Log("expansion call return: {0}", num);
Func<int, int> Func = luaFunc.ToDelegate<Func<int, int>>();
num = Func(123456);
Debugger.Log("Delegate call return: {0}", num);
num = lua.Invoke<int, int>("test.luaFunc", 123456, true);
Debugger.Log("luastate call return: {0}", num);
}
lua.CheckTop();
}
void ShowTips(string msg, string stackTrace, LogType type)
{
tips += msg;
tips += "\r\n";
}
#if !TEST_GC
void OnGUI()
{
GUI.Label(new Rect(Screen.width / 2 - 200, Screen.height / 2 - 150, 400, 300), tips);
}
#endif
void OnDestroy()
{
if (luaFunc != null)
{
luaFunc.Dispose();
luaFunc = null;
}
lua.Dispose();
lua = null;
#if UNITY_5 || UNITY_2017 || UNITY_2018
Application.logMessageReceived -= ShowTips;
#else
Application.RegisterLogCallback(null);
#endif
}
int CallFunc()
{
luaFunc.BeginPCall();
luaFunc.Push(123456);
luaFunc.PCall();
int num = (int)luaFunc.CheckNumber();
luaFunc.EndPCall();
return num;
}
}2.2 ToLua 部分API用法
下面给出README(LuaFramework\ToLua\Examples\README.md)文档中的解释
tolua# 简化了lua函数的操作,通过LuaFunction封装(并缓存)一个lua函数,并提供各种操作, 建议频繁调用函数使用无GC方式。<br>
* LuaState.GetLuaFunction 获取并缓存一个lua函数, 此函数支持串式操作, 如"test.luaFunc"代表test表中的luaFunc函数。<br>
* LuaState.Invoke 临时调用一个lua function并返回一个值,这个操作并不缓存lua function,适合频率非常低的函数调用。<br>
* LuaFunction.Call() 不需要返回值的函数调用操作<br>
* LuaFunction.Invoke() 有一个返回值的函数调用操作 <br>
* LuaFunction.BeginPCall() 开始函数调用 <br>
* LuaFunction.Push() 压入函数调用需要的参数,通过众多的重载函数来解决参数转换gc问题 <br>
* LuaFunction.PCall() 调用lua函数 <br>
* LuaFunction.CheckNumber() 提取函数返回值, 并检查返回值为lua number类型 <br>
* LuaFunction.EndPCall() 结束lua函数调用, 清楚函数调用造成的堆栈变化 <br>
* LuaFunction.Dispose() 释放LuaFunction, 递减引用计数,如果引用计数为0, 则从_R表删除该函数 <br>
> **注意:** 无论Call还是PCall只相当于lua中的函数'.'调用。<br>
请注意':'这种语法糖 self:call(...) == self.call(self, ...) <br>
c# 中需要按后面方式调用, 即必须主动传入第一个参数self <br>
2.3 调用Lua写法分析
首先我们将代码进行整理,可以看出有如下4种调用Lua函数的做法
cs
LuaState lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
LuaFunction luaFunc = lua.GetFunction("test.luaFunc");
//style1
int num = luaFunc.Invoke<int, int>(123456);
Debugger.Log("generic call return: {0}", num);
//style2
num = CallFunc();
Debugger.Log("expansion call return: {0}", num);
//style3
Func<int, int> Func = luaFunc.ToDelegate<Func<int, int>>();
num = Func(123456);
Debugger.Log("Delegate call return: {0}", num);
//style4
num = lua.Invoke<int, int>("test.luaFunc", 123456, true);
Debugger.Log("luastate call return: {0}", num);
int CallFunc()
{
luaFunc.BeginPCall();
luaFunc.Push(123456);
luaFunc.PCall();
int num = (int)luaFunc.CheckNumber();
luaFunc.EndPCall();
return num;
}先分析style1,在Invoke按F12跳转
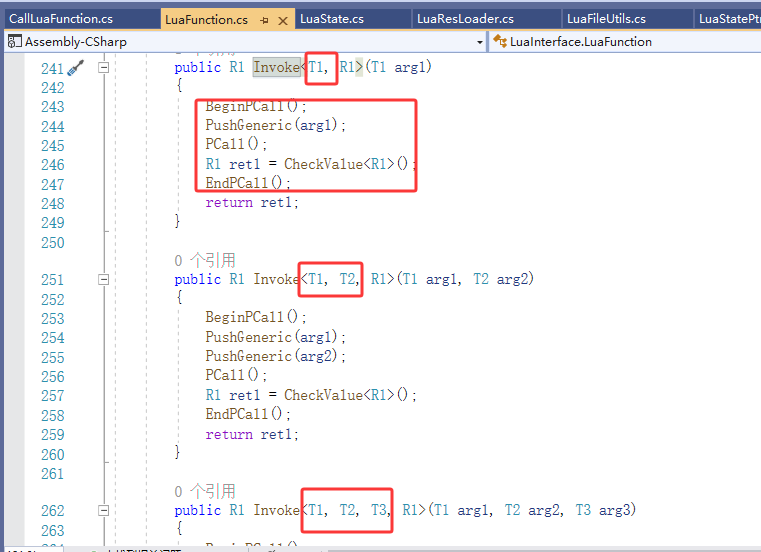
- 可以看到Invoke是泛型方法,内部的调用和style2的做法本质上是一样的;
- 根据要调用方法的参数类型和数量,选择不同的泛型方法
style2和style1本质一样,使用style1简化的写法即可
style3是委托式写法,应该和style1也是相同的
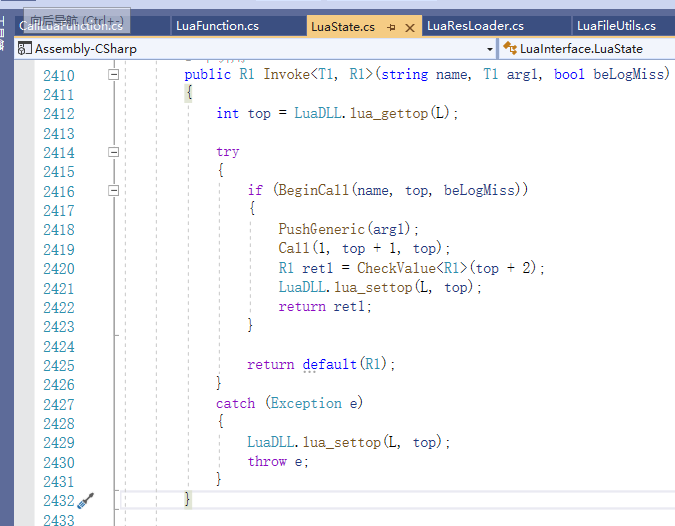
style4使用的是LuaState的Invoke方法,看上去和style1很像,但是README里说style4适合低频率调用的情况,因此谨慎使用
三.C#调用Lua方法小结
step1:通过LuaState.GetFunction获取LuaFunction对象
step2:通过Luafunction.Invoke泛型方法,调用Lua函数
cs
private string script =
@" function luaFunc(num)
return num + 1
end
test = {}
test.luaFunc = luaFunc
";
//step1:获取LuaFunction对象
LuaFunction luaFunc = lua.GetFunction("test.luaFunc");
if (luaFunc != null)
{
//step2:调用Invoke方法
int num = luaFunc.Invoke<int, int>(123);
Debugger.Log("generic call return: {0}", num);
}