Compose 动画 + KMM 跨平台开发:从传统View到现代声明式UI动画
本文将深入探讨Compose动画技术和KMM跨平台开发,通过实战项目案例,带你掌握从基础到高级的动画开发技巧,以及如何用一套代码实现Android和iOS的跨平台动画效果,并分享性能优化和最佳实践。(由于需要在公司内部做技术分享,所以暂时不把demo代码地址放出,后续分享之后会贴上github地址)
🎬 动画效果预览
图:层次递进式动画演示 - 从基础波纹到烟花闪烁的完整动画效果
目录
技术背景与概述
为什么选择Compose动画?
传统View动画的痛点
kotlin
// 传统View动画 - 命令式编程
val animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "scaleX", 1f, 1.5f)
animator.duration = 300
animator.interpolator = BounceInterpolator()
animator.start()
// 需要手动管理生命周期、状态同步、内存泄漏等问题Compose动画的优势
kotlin
// Compose动画 - 声明式编程
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (isClicked) 1.5f else 1f,
animationSpec = spring(dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioMediumBouncy)
)
Box(modifier = Modifier.scale(scale)) {
// UI内容
}Compose动画的核心特性
- 声明式:描述"是什么"而不是"怎么做"
- 状态驱动:动画自动响应状态变化
- 可组合:动画组件可复用和组合
- 类型安全:编译时检查,减少运行时错误
- 性能优化:智能重组,只更新必要的部分
Compose动画API体系
动画API层次结构
scss
Compose 动画 API
├── 高级API (开箱即用)
│ ├── AnimatedVisibility // 显示/隐藏动画
│ ├── AnimatedContent // 内容切换动画
│ └── Crossfade // 淡入淡出切换
│
├── 中级API (灵活控制)
│ ├── animate*AsState // 状态驱动动画
│ ├── rememberInfiniteTransition // 无限循环动画
│ └── updateTransition // 多状态转换
│
└── 低级API (完全自定义)
├── Animatable // 手动控制动画
├── AnimationSpec // 自定义动画规格
└── Canvas + 手动绘制 // 完全自定义绘制1. 高级API - 开箱即用
AnimatedVisibility - 显示隐藏动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun AnimatedVisibilityDemo() {
var visible by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Column {
Button(onClick = { visible = !visible }) {
Text("切换显示")
}
AnimatedVisibility(
visible = visible,
enter = slideInVertically() + fadeIn(),
exit = slideOutVertically() + fadeOut()
) {
Card {
Text("我是动画内容!", modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp))
}
}
}
}AnimatedContent - 内容切换动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun AnimatedContentDemo() {
var count by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
Column {
Button(onClick = { count++ }) {
Text("增加计数")
}
AnimatedContent(
targetState = count,
transitionSpec = {
slideInVertically { height -> height } + fadeIn() togetherWith
slideOutVertically { height -> -height } + fadeOut()
}
) { targetCount ->
Text(
text = "计数: $targetCount",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineMedium
)
}
}
}2. 中级API - 灵活控制
animate*AsState - 状态驱动动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun StateBasedAnimationDemo() {
var isExpanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// 多个属性同时动画
val size by animateDpAsState(
targetValue = if (isExpanded) 200.dp else 100.dp,
animationSpec = spring(
dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioMediumBouncy,
stiffness = Spring.StiffnessLow
)
)
val color by animateColorAsState(
targetValue = if (isExpanded) Color.Red else Color.Blue,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 500)
)
val rotation by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (isExpanded) 180f else 0f,
animationSpec = spring(stiffness = Spring.StiffnessMedium)
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(size)
.rotate(rotation)
.background(color, CircleShape)
.clickable { isExpanded = !isExpanded }
)
}rememberInfiniteTransition - 无限循环动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun InfiniteAnimationDemo() {
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition()
// 脉冲效果
val scale by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 1f,
targetValue = 1.2f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
animation = tween(1000),
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse
)
)
// 旋转效果
val rotation by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0f,
targetValue = 360f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
animation = tween(2000, easing = LinearEasing),
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Restart
)
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.scale(scale)
.rotate(rotation)
.background(Color.Blue, CircleShape)
)
}3. 低级API - 完全自定义
Animatable - 手动控制动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun ManualAnimationDemo() {
val animatable = remember { Animatable(0f) }
val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope()
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
// 复杂的动画序列
animatable.animateTo(1f, tween(1000))
animatable.animateTo(0.5f, spring())
animatable.animateTo(1f, tween(500))
}
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.scale(animatable.value)
.background(Color.Green, CircleShape)
.clickable {
coroutineScope.launch {
// 手动触发动画
animatable.animateTo(
targetValue = if (animatable.value == 1f) 0.5f else 1f,
animationSpec = spring(
dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioHighBouncy
)
)
}
}
)
}项目实战案例分析
项目架构概览
我们的动画演示项目包含5个渐进式的动画阶段:
scss
动画演示项目
├── 第1阶段:基础波纹效果 (BaseRippleEffect)
├── 第2阶段:彩虹色彩层 (RainbowLayerEffect)
├── 第3阶段:表情包粒子效果 (EmojiParticleEffect)
├── 第4阶段:旋转表情包效果 (RotatingParticleEffect)
└── 第5阶段:烟花闪烁效果 (FireworkEffect)案例1:基础波纹效果 (BaseRippleEffect)
动画效果演示
图:第1阶段 - 基础波纹扩散动画效果
技术要点
- 使用
mutableStateOf管理波纹列表 LaunchedEffect响应点击事件- 协程 +
delay实现平滑动画 - 动态列表更新和清理
核心实现
kotlin
@Composable
fun BaseRippleEffect(clickCount: Int) {
var allRipples by remember { mutableStateOf<List<RippleEffect>>(emptyList()) }
val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope()
fun emitNewRipple() {
val currentRippleId = clickCount
val newRipple = RippleEffect(
id = currentRippleId,
scale = 1f,
alpha = 0.6f
)
allRipples = allRipples + newRipple
// 启动动画协程
coroutineScope.launch {
repeat(180) { step ->
val progress = step / 180f
val rippleScale = 1f + progress * 1.5f
val rippleAlpha = 0.6f - progress * 0.6f
// 更新特定波纹的状态
allRipples = allRipples.map { ripple ->
if (ripple.id == currentRippleId) {
ripple.copy(scale = rippleScale, alpha = rippleAlpha)
} else {
ripple
}
}
delay(16L) // 60fps
}
// 动画完成后清理
allRipples = allRipples.filter { it.id != currentRippleId }
}
}
// 渲染波纹
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
allRipples.forEach { ripple ->
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(60.dp)
.scale(ripple.scale)
.alpha(ripple.alpha)
.background(Color.Blue.copy(alpha = 0.3f), CircleShape)
.align(Alignment.Center)
)
}
}
}数据模型
kotlin
data class RippleEffect(
val id: Int,
val scale: Float,
val alpha: Float
)案例2:彩虹色彩层效果 (RainbowLayerEffect)
动画效果演示
图:第2阶段 - 彩虹渐变色彩动画效果
技术要点
- 使用
rememberInfiniteTransition实现无限循环动画 - 彩虹色彩渐变计算
- 多层色彩叠加效果
- 平滑的颜色过渡
核心实现
kotlin
@Composable
fun RainbowLayerEffect(clickCount: Int) {
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition()
// 彩虹色彩循环
val hue by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0f,
targetValue = 360f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
animation = tween(3000, easing = LinearEasing),
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Restart
)
)
// 透明度脉冲效果
val alpha by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0.3f,
targetValue = 0.8f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
animation = tween(1500, easing = FastOutSlowInEasing),
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse
)
)
// 缩放效果
val scale by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0.8f,
targetValue = 1.2f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
animation = tween(2000, easing = FastOutSlowInEasing),
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse
)
)
// 计算彩虹颜色
val rainbowColor = Color.hsv(hue, 0.8f, 1f)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(120.dp)
.scale(scale)
.alpha(alpha)
.background(
brush = Brush.radialGradient(
colors = listOf(
rainbowColor.copy(alpha = 0.6f),
rainbowColor.copy(alpha = 0.2f),
Color.Transparent
),
radius = 200f
),
shape = CircleShape
)
.align(Alignment.Center)
)
}案例3:表情包粒子系统 (EmojiParticleEffect)
动画效果演示
图:第3阶段 - 表情包粒子发射动画效果
技术特点
- 物理模拟:模拟粒子的抛物线运动
- 批量管理:一次创建多个粒子
- 生命周期管理:自动清理过期粒子
- 随机化:随机方向、距离、表情
核心实现
kotlin
@Composable
fun EmojiParticleEffect(clickCount: Int) {
var allParticles by remember { mutableStateOf<List<EmojiParticle>>(emptyList()) }
val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope()
fun createEmojiParticles() {
val newParticles = (1..18).map { // 增加粒子数量
val angle = (it * 20f + Random.nextFloat() * 40f) * kotlin.math.PI / 180f
val distance = 150f + (Random.nextFloat() * 200f) // 增加发射距离
EmojiParticle(
id = clickCount * 100 + it,
emoji = listOf("❤️", "💖", "💕", "💗", "💓", "💝").random(),
startX = 0f,
startY = 0f,
targetX = (kotlin.math.cos(angle) * distance).toFloat(),
targetY = (kotlin.math.sin(angle) * distance).toFloat(),
progress = 0f,
alpha = 1f
)
}
allParticles = allParticles + newParticles
// 启动粒子动画
coroutineScope.launch {
repeat(60) { step -> // 减少动画帧数,提高速度
val progress = step / 60f
allParticles = allParticles.map { particle ->
if (particle.id / 100 == clickCount) {
// 抛物线运动计算
val currentX = particle.startX + particle.targetX * progress
val currentY = particle.startY + particle.targetY * progress -
50f * progress * (1f - progress) // 重力效果
particle.copy(
currentX = currentX,
currentY = currentY,
progress = progress,
alpha = 1f - progress
)
} else {
particle
}
}
delay(12L) // 更快的帧率
}
// 延迟清理
delay(200L)
allParticles = allParticles.filter { it.id / 100 != clickCount }
}
}
// 响应点击事件
LaunchedEffect(clickCount) {
if (clickCount > 0) {
createEmojiParticles()
}
}
// 渲染粒子
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
allParticles.forEach { particle ->
if (particle.alpha > 0.1f) {
Text(
text = particle.emoji,
fontSize = 16.sp,
modifier = Modifier
.offset(
x = particle.currentX.dp,
y = particle.currentY.dp
)
.alpha(particle.alpha)
.align(Alignment.Center)
)
}
}
}
}粒子数据模型
kotlin
data class EmojiParticle(
val id: Int,
val emoji: String,
val startX: Float,
val startY: Float,
val targetX: Float,
val targetY: Float,
val currentX: Float = startX,
val currentY: Float = startY,
val progress: Float,
val alpha: Float
)案例4:旋转表情包效果 (RotatingParticleEffect)
动画效果演示
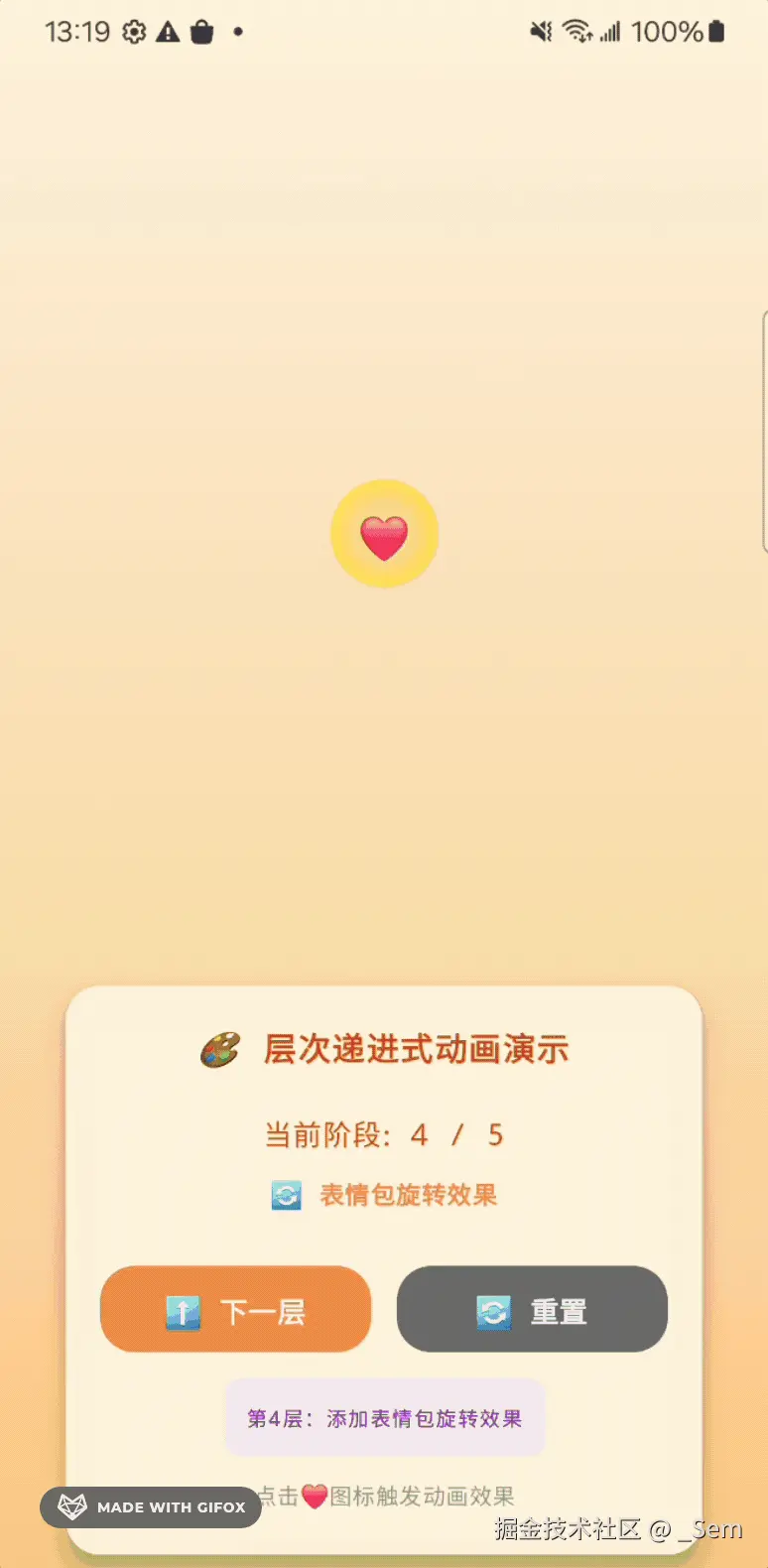
图:第4阶段 - 表情包旋转动画效果
技术特点
- 旋转动画:表情包围绕中心点旋转
- 连接线效果:粒子之间用线条连接
- 网络状结构:形成动态的粒子网络
- 同步旋转:所有粒子同步旋转
核心实现
kotlin
@Composable
fun RotatingParticleEffect(clickCount: Int) {
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition()
// 旋转角度
val rotation by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0f,
targetValue = 360f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
animation = tween(4000, easing = LinearEasing),
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Restart
)
)
// 粒子位置计算
val particles = remember {
(1..8).map { index ->
val angle = (index * 45f) * kotlin.math.PI / 180f
val radius = 80f
RotatingEmojiParticle(
id = index,
emoji = listOf("😊", "😍", "🥰", "😘", "🤗", "😚", "😙", "😋")[index - 1],
baseAngle = angle,
radius = radius
)
}
}
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
// 绘制连接线
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
val centerX = size.width / 2
val centerY = size.height / 2
particles.forEach { particle ->
val currentAngle = particle.baseAngle + rotation * kotlin.math.PI / 180f
val x = centerX + kotlin.math.cos(currentAngle) * particle.radius
val y = centerY + kotlin.math.sin(currentAngle) * particle.radius
// 绘制到中心的连接线
drawLine(
color = Color.White.copy(alpha = 0.3f),
start = Offset(centerX, centerY),
end = Offset(x.toFloat(), y.toFloat()),
strokeWidth = 2.dp.toPx()
)
}
}
// 渲染旋转的粒子
particles.forEach { particle ->
val currentAngle = particle.baseAngle + rotation * kotlin.math.PI / 180f
val x = kotlin.math.cos(currentAngle) * particle.radius
val y = kotlin.math.sin(currentAngle) * particle.radius
Text(
text = particle.emoji,
fontSize = 20.sp,
modifier = Modifier
.offset(x = x.dp, y = y.dp)
.align(Alignment.Center)
)
}
}
}旋转粒子数据模型
kotlin
data class RotatingEmojiParticle(
val id: Int,
val emoji: String,
val baseAngle: Float,
val radius: Float
)案例5:高性能烟花效果 (FireworkEffect)
动画效果演示

图:第5阶段 - 烟花闪烁动画效果 (请观察四周烟花部分)
性能优化亮点
- 独立动画状态 :每个烟花使用独立的
Animatable - 避免列表重组 :使用
derivedStateOf计算属性 - 内存管理:限制最大烟花数量,自动清理
- 条件渲染:只渲染可见的烟花
核心实现
kotlin
@Composable
fun FireworkEffect(clickCount: Int) {
var activeFireworks by remember { mutableStateOf<List<Int>>(emptyList()) }
val maxFireworks = 10 // 性能限制
// 响应点击,创建新烟花
LaunchedEffect(clickCount) {
if (clickCount > 0) {
val newFireworkId = clickCount
activeFireworks = (activeFireworks + newFireworkId).takeLast(maxFireworks)
}
}
// 渲染所有活跃的烟花
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
activeFireworks.forEach { fireworkId ->
SingleFirework(
fireworkId = fireworkId,
onComplete = {
// 烟花完成后从列表中移除
activeFireworks = activeFireworks.filter { it != fireworkId }
}
)
}
// 调试信息
Text(
text = "活跃烟花: ${activeFireworks.size}",
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.TopEnd),
color = Color.White
)
}
}
@Composable
private fun SingleFirework(
fireworkId: Int,
onComplete: () -> Unit
) {
// 创建烟花数据(只在首次创建时计算)
val firework = remember(fireworkId) { createRandomFirework(fireworkId) }
// 独立的动画状态
val progress = remember { Animatable(0f) }
// 使用 derivedStateOf 避免不必要的重组
val scale by remember {
derivedStateOf {
val p = progress.value
when {
p < 0.3f -> 0.5f + (p / 0.3f) * 1.0f
p < 0.7f -> 1.5f
else -> 1.5f - ((p - 0.7f) / 0.3f) * 1.0f
}
}
}
val alpha by remember {
derivedStateOf {
val p = progress.value
when {
p < 0.2f -> (p / 0.2f) * 1.0f
p < 0.6f -> 1.0f
else -> 1.0f - ((p - 0.6f) / 0.4f) * 1.0f
}
}
}
// 启动动画
LaunchedEffect(fireworkId) {
try {
progress.animateTo(
targetValue = 1f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 2000)
)
} finally {
onComplete()
}
}
// 条件渲染:只有当透明度大于阈值时才渲染
if (alpha > 0.01f) {
Text(
text = firework.emoji,
fontSize = 20.sp,
fontFamily = FontFamily.Monospace,
modifier = Modifier
.offset(x = firework.x.dp, y = firework.y.dp)
.scale(scale)
.alpha(alpha)
)
}
}烟花数据模型
kotlin
data class FireworkAnimation(
val id: Int,
val emoji: String,
val x: Float,
val y: Float,
val color: Color
)
private fun createRandomFirework(id: Int): FireworkAnimation {
val emojis = listOf("✨", "🎆", "🎇", "💫", "⭐", "🌟")
val colors = listOf(
Color.Red, Color.Blue, Color.Green,
Color.Yellow, Color.Magenta, Color.Cyan
)
return FireworkAnimation(
id = id,
emoji = emojis.random(),
x = (-100..100).random().toFloat(),
y = (-100..100).random().toFloat(),
color = colors.random()
)
}核心动画技术详解
1. 动画规格 (AnimationSpec)
Spring 弹簧动画
kotlin
// 不同的弹簧效果
val bouncySpring = spring(
dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioHighBouncy,
stiffness = Spring.StiffnessLow
)
val smoothSpring = spring(
dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioNoBouncy,
stiffness = Spring.StiffnessMedium
)
val quickSpring = spring(
dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioMediumBouncy,
stiffness = Spring.StiffnessHigh
)Tween 补间动画
kotlin
// 线性动画
val linearTween = tween<Float>(
durationMillis = 1000,
easing = LinearEasing
)
// 缓动动画
val easeTween = tween<Float>(
durationMillis = 1000,
easing = FastOutSlowInEasing
)
// 自定义贝塞尔曲线
val customTween = tween<Float>(
durationMillis = 1000,
easing = CubicBezierEasing(0.25f, 0.46f, 0.45f, 0.94f)
)Keyframes 关键帧动画
kotlin
val keyframesSpec = keyframes<Float> {
durationMillis = 2000
0f at 0 using LinearEasing
0.5f at 500 using FastOutSlowInEasing
1.2f at 1000 using LinearOutSlowInEasing
1f at 2000
}2. 状态管理模式
单一状态源
kotlin
@Composable
fun AnimationController() {
// 单一状态控制多个动画
var animationPhase by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = when (animationPhase) {
0 -> 1f
1 -> 1.2f
2 -> 0.8f
else -> 1f
}
)
val rotation by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = animationPhase * 90f
)
val color by animateColorAsState(
targetValue = when (animationPhase) {
0 -> Color.Blue
1 -> Color.Red
2 -> Color.Green
else -> Color.Gray
}
)
}复合状态管理
kotlin
@Stable
class AnimationState {
var isExpanded by mutableStateOf(false)
var isHighlighted by mutableStateOf(false)
var currentPhase by mutableIntStateOf(0)
fun nextPhase() {
currentPhase = (currentPhase + 1) % 4
}
fun reset() {
isExpanded = false
isHighlighted = false
currentPhase = 0
}
}
@Composable
fun ComplexAnimation() {
val animationState = remember { AnimationState() }
// 多个动画基于复合状态
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (animationState.isExpanded) 1.5f else 1f
)
val alpha by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (animationState.isHighlighted) 1f else 0.7f
)
}3. 动画组合与编排
并行动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun ParallelAnimations() {
var trigger by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// 多个动画同时进行
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (trigger) 1.5f else 1f,
animationSpec = spring(stiffness = Spring.StiffnessLow)
)
val rotation by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (trigger) 360f else 0f,
animationSpec = tween(1000)
)
val color by animateColorAsState(
targetValue = if (trigger) Color.Red else Color.Blue,
animationSpec = tween(500)
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.scale(scale)
.rotate(rotation)
.background(color, CircleShape)
.clickable { trigger = !trigger }
)
}序列动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun SequentialAnimations() {
var phase by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope()
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = when (phase) {
0 -> 1f
1 -> 1.5f
2 -> 0.8f
else -> 1f
},
finishedListener = {
// 动画完成后自动进入下一阶段
if (phase < 3) {
coroutineScope.launch {
delay(200)
phase++
}
}
}
)
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
// 启动动画序列
phase = 1
}
}交错动画
kotlin
@Composable
fun StaggeredAnimations() {
var startAnimation by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
val items = remember { (1..5).toList() }
Column {
items.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
val delay = index * 100 // 交错延迟
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (startAnimation) 1f else 0f,
animationSpec = tween(
durationMillis = 300,
delayMillis = delay
)
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(50.dp)
.scale(scale)
.background(Color.Blue, CircleShape)
)
}
Button(onClick = { startAnimation = !startAnimation }) {
Text("开始交错动画")
}
}
}性能优化与最佳实践
1. 避免不必要的重组
问题代码
kotlin
@Composable
fun BadPerformanceExample() {
var count by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
// ❌ 每次count变化都会重新计算expensive操作
val expensiveValue = expensiveCalculation(count)
val animatedValue by animateFloatAsState(count.toFloat())
Column {
Text("Count: $count")
Text("Expensive: $expensiveValue")
Text("Animated: $animatedValue")
}
}优化代码
kotlin
@Composable
fun GoodPerformanceExample() {
var count by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
// ✅ 使用remember缓存expensive操作
val expensiveValue by remember(count) {
derivedStateOf { expensiveCalculation(count) }
}
// ✅ 使用derivedStateOf避免不必要的动画更新
val animatedValue by animateFloatAsState(count.toFloat())
Column {
Text("Count: $count")
Text("Expensive: ${expensiveValue.value}")
Text("Animated: $animatedValue")
}
}2. 合理使用LaunchedEffect
问题代码
kotlin
@Composable
fun BadLaunchedEffectExample(clickCount: Int) {
var animations by remember { mutableStateOf<List<Animation>>(emptyList()) }
// ❌ 每次重组都会启动新的协程
LaunchedEffect(true) {
while (true) {
// 无限循环动画
delay(16)
animations = updateAnimations(animations)
}
}
}优化代码
kotlin
@Composable
fun GoodLaunchedEffectExample(clickCount: Int) {
var animations by remember { mutableStateOf<List<Animation>>(emptyList()) }
// ✅ 使用正确的key,避免重复启动
LaunchedEffect(clickCount) {
if (clickCount > 0) {
// 只在clickCount变化时启动新动画
val newAnimation = createAnimation(clickCount)
animations = animations + newAnimation
// 动画完成后清理
delay(2000)
animations = animations.filter { it.id != clickCount }
}
}
}3. 内存管理
限制动画数量
kotlin
@Composable
fun MemoryEfficientAnimations() {
var activeAnimations by remember { mutableStateOf<List<AnimationData>>(emptyList()) }
val maxAnimations = 10 // 限制最大数量
fun addAnimation(newAnimation: AnimationData) {
activeAnimations = (activeAnimations + newAnimation)
.takeLast(maxAnimations) // 只保留最新的N个动画
}
fun removeAnimation(animationId: Int) {
activeAnimations = activeAnimations.filter { it.id != animationId }
}
}及时清理资源
kotlin
@Composable
fun ResourceManagement() {
val animatables = remember { mutableMapOf<Int, Animatable<Float, AnimationVector1D>>() }
DisposableEffect(Unit) {
onDispose {
// 组件销毁时清理所有动画
animatables.values.forEach { animatable ->
animatable.stop()
}
animatables.clear()
}
}
}4. 动画性能监控
性能监控工具
kotlin
@Composable
fun AnimationPerformanceMonitor() {
var frameCount by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
var lastTime by remember { mutableLongStateOf(System.currentTimeMillis()) }
var fps by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(0f) }
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
while (true) {
delay(16) // 60fps
frameCount++
val currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
if (currentTime - lastTime >= 1000) {
fps = frameCount * 1000f / (currentTime - lastTime)
frameCount = 0
lastTime = currentTime
}
}
}
Text(
text = "FPS: ${fps.toInt()}",
modifier = Modifier
.background(Color.Black.copy(alpha = 0.7f))
.padding(8.dp),
color = Color.White
)
}5. 最佳实践总结
推荐做法
kotlin
// 1. 使用状态驱动动画
val scale by animateFloatAsState(targetValue = if (isExpanded) 1.5f else 1f)
// 2. 合理使用remember缓存
val expensiveData = remember(key) { computeExpensiveData(key) }
// 3. 使用derivedStateOf避免不必要计算
val computedValue by remember { derivedStateOf { expensiveComputation() } }
// 4. 限制动画数量
val animations = animations.takeLast(MAX_ANIMATIONS)
// 5. 及时清理资源
DisposableEffect(key) {
onDispose { cleanup() }
}避免的做法
kotlin
// 1. 避免在Composable中直接创建动画对象
val animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(...) // ❌
// 2. 避免无限制的动画创建
repeat(1000) { createAnimation() } // ❌
// 3. 避免在动画中进行expensive操作
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
while (true) {
expensiveOperation() // ❌
delay(16)
}
}
// 4. 避免不必要的状态更新
var state by mutableStateOf(initialValue)
state = state.copy() // 如果值没变化,避免这样做 ❌KMM跨平台动画实现
KMM跨平台效果展示

图:同样的动画效果在iOS设备上的运行表现 - 一套KMM代码,双平台运行
Kotlin Multiplatform项目结构
bash
项目结构
├── shared/
│ └── src/
│ ├── commonMain/kotlin/ # 共享动画代码
│ │ ├── ui/
│ │ │ ├── effects/ # 动画效果
│ │ │ ├── components/ # UI组件
│ │ │ └── models/ # 数据模型
│ │ └── SharedAnimationDemo.kt
│ ├── androidMain/kotlin/ # Android特定代码
│ └── iosMain/kotlin/ # iOS特定代码
├── app/ (Android)
└── iosApp/ (iOS)共享动画代码
共享的动画组件
kotlin
// shared/src/commonMain/kotlin/ui/SharedAnimationDemo.kt
@Composable
fun SharedAnimationDemo() {
// 这个组件可以在Android和iOS上运行
LikeAnimationDemo()
}
// 共享的动画效果
@Composable
fun CrossPlatformFireworkEffect(clickCount: Int) {
// 使用Compose Multiplatform的共享API
var activeFireworks by remember { mutableStateOf<List<Int>>(emptyList()) }
LaunchedEffect(clickCount) {
if (clickCount > 0) {
activeFireworks = activeFireworks + clickCount
}
}
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
activeFireworks.forEach { fireworkId ->
CrossPlatformSingleFirework(
fireworkId = fireworkId,
onComplete = {
activeFireworks = activeFireworks.filter { it != fireworkId }
}
)
}
}
}平台特定的实现
kotlin
// shared/src/commonMain/kotlin/Platform.kt
expect fun getPlatformName(): String
expect fun getScreenDensity(): Float
// shared/src/androidMain/kotlin/Platform.android.kt
actual fun getPlatformName(): String = "Android"
actual fun getScreenDensity(): Float {
return Resources.getSystem().displayMetrics.density
}
// shared/src/iosMain/kotlin/Platform.ios.kt
actual fun getPlatformName(): String = "iOS"
actual fun getScreenDensity(): Float {
return UIScreen.mainScreen.scale.toFloat()
}Android集成
Android应用入口
kotlin
// app/src/main/java/MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
MyAppTheme {
// 使用共享的动画组件
SharedAnimationDemo()
}
}
}
}iOS集成
iOS SwiftUI集成
swift
// iosApp/iosApp/ContentView.swift
import SwiftUI
import Shared
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
ComposeView()
.ignoresSafeArea(.keyboard)
}
}
struct ComposeView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIViewController {
MainViewControllerKt.MainViewController()
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIViewController, context: Context) {}
}iOS Kotlin入口
kotlin
// shared/src/iosMain/kotlin/MainViewController.kt
import androidx.compose.ui.window.ComposeUIViewController
fun MainViewController() = ComposeUIViewController {
SharedAnimationDemo()
}跨平台动画差异处理
平台适配
kotlin
@Composable
fun PlatformAdaptiveAnimation() {
val platformName = remember { getPlatformName() }
val density = remember { getScreenDensity() }
// 根据平台调整动画参数
val animationDuration = when (platformName) {
"iOS" -> 300 // iOS用户习惯更快的动画
"Android" -> 400 // Android标准动画时长
else -> 350
}
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = if (isExpanded) 1.5f else 1f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = animationDuration)
)
// 根据屏幕密度调整大小
val adjustedSize = (100 * density).dp
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(adjustedSize)
.scale(scale)
)
}性能优化差异
kotlin
@Composable
fun PlatformOptimizedAnimation() {
val platformName = getPlatformName()
// iOS设备通常性能更好,可以支持更多并发动画
val maxAnimations = when (platformName) {
"iOS" -> 15
"Android" -> 10
else -> 8
}
var activeAnimations by remember { mutableStateOf<List<Animation>>(emptyList()) }
fun addAnimation(animation: Animation) {
activeAnimations = (activeAnimations + animation).takeLast(maxAnimations)
}
}总结与展望
技术总结
Compose动画 + KMM的优势
- 声明式编程:代码更简洁、可读性更强
- 状态驱动:动画自动响应状态变化,减少手动管理
- 类型安全:编译时检查,减少运行时错误
- 性能优化:智能重组机制,只更新必要部分
- 跨平台支持:一套KMM代码,Android和iOS双平台运行
- 开发效率:减少重复开发,统一维护成本
- 一致性体验:确保不同平台的动画效果完全一致
项目实战收获
- 渐进式学习:从简单波纹到复杂烟花效果
- 性能优化:独立动画状态、内存管理、条件渲染
- 代码复用:组件化设计,便于维护和扩展
- KMM跨平台实现:Android和iOS共享动画逻辑,一套代码双平台运行
- 开发效率提升:减少50%的重复开发工作
- 维护成本降低:统一的代码库,统一的bug修复
最佳实践总结
开发建议
kotlin
// 1. 优先使用高级API
AnimatedVisibility(visible = isVisible) { /* content */ }
// 2. 状态驱动动画
val scale by animateFloatAsState(targetValue = if (isExpanded) 1.5f else 1f)
// 3. 合理使用remember
val expensiveData = remember(key) { computeExpensiveData(key) }
// 4. 性能监控
val fps = remember { PerformanceMonitor() }
// 5. 及时清理资源
DisposableEffect(key) {
onDispose { cleanup() }
}性能优化清单
- 使用
derivedStateOf避免不必要计算 - 限制并发动画数量
- 条件渲染,只显示可见元素
- 使用
remember缓存expensive操作 - 及时清理动画资源
- 监控FPS和内存使用
未来发展方向
技术演进
- 更丰富的动画API:Google持续完善Compose动画生态
- 更好的性能:编译器优化、运行时优化
- 更强的跨平台能力:Compose Multiplatform的完善
- AI辅助动画:智能动画生成和优化
应用场景扩展
- 游戏开发:Compose for Games
- 桌面应用:Compose for Desktop
- Web应用:Compose for Web
- 嵌入式设备:Compose for Embedded
团队技能提升
- 学习路径:从基础API到高级技巧
- 实践项目:通过实际项目积累经验
- 社区参与:贡献开源项目,分享经验
- 持续学习:关注最新技术动态
推荐学习资源
官方文档
开源项目
社区资源
结语
Compose动画为我们带来了全新的动画开发体验,通过声明式的API设计和强大的性能优化机制,让复杂的动画实现变得简单而高效。
通过本文的实战案例分析,我们看到了从基础波纹效果到复杂烟花动画的完整实现过程,以及如何通过性能优化技巧让动画在各种设备上都能流畅运行。
跨平台动画的实现更是展示了Compose Multiplatform的强大能力,让我们能够用一套代码为Android和iOS用户提供一致的动画体验。
希望这些经验和技巧能够帮助你在项目中更好地运用Compose动画技术,创造出更加优秀的用户体验!
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏和分享!有任何问题或建议,也欢迎在评论区交流讨论。
标签: #Compose #KMM #Android #iOS #动画 #跨平台 #性能优化 #KotlinMultiplatform