什么是GKE
GKE(Google Kubernetes Engine)是 Google Cloud 提供的容器管理服务,它基于 Kubernetes 构建,可以帮助您轻松部署、管理和扩展容器化的应用程序。您可以把它想象成一个强大的"容器编排大师",让您的应用在云端高效、稳定地运行。GKE 简化了 Kubernetes 的复杂性,让您专注于应用开发,而无需花费大量精力在底层基础设施的管理上。它提供了自动伸缩、自动修复、滚动更新等功能,确保您的应用始终可用并保持最佳性能。简单来说,GKE 就是一个托管的 Kubernetes 服务。
一句话就是Google 在GCP上装好了k8s 让你使用
为什么选择GKE
既然是k8s, 那么不自己在gcp上的vm自己搭建? GKE到底提供了什么inhouse build k8s 没有的功能?
- 不再需要搭建k8s 平台软件(安装过的都知道有多烦)而无需手动配置和管理底层基础设施。包括后续的版本升级
- 强大的可伸缩性和弹性:
自动伸缩: GKE 可以根据应用程序的负载自动调整集群的大小,确保应用程序始终具有足够的资源。
自动修复: GKE 会自动检测并修复集群中的故障,确保应用程序的持续可用性。
区域集群: GKE 支持区域集群,可以将集群部署在多个可用区中,从而提高应用程序的可用性和容错能力。
3.与 Google Cloud Platform 的深度集成:
集成的身份验证和授权: GKE 与 Google Cloud IAM 集成,可以轻松管理集群的访问权限。
集成的日志记录和监控: GKE 与 Google Cloud Logging 和 Monitoring 集成,可以集中收集和分析集群的日志和指标。
集成的网络: GKE 与 Google Cloud VPC 集成,可以轻松创建安全的网络环境。
至于使用方法与inhouse build k8s一样, 用kubectl 可轻松管理。
而且gcp 提供一个基本的cluster /pod 管理ui
什么是GKE private cluster
GKE Private Cluster(私有集群)
GKE Private Cluster 是一种 Kubernetes 集群,它与公共互联网隔离。这意味着集群中的节点没有公共 IP 地址,并且只能通过内部网络访问。
总的来说,GKE Private Cluster 通过限制对公共互联网的访问来增强安全性,但同时也增加了配置和管理的复杂性
一些区别:
| item | master | nodes vm |
|---|---|---|
| normal cluster | 具有public ip endpoint | 每个node 都有public ip |
| private cluster | 两种都支持, 是否具有public endpoint 基于用户配置 | 没有public ip, 外部不能直接访问node vm |
由于public cluster 每个node 都是创建在gce里的, 都分配public ip的话 需要一笔额外的cost, 本文 不考虑这个方案
至于 private cluster 也有两种:
一种是master 节点也没有public endpoint, 这样整个集群都在内网, 一般需要设置堡垒机才能访问master, 本文也不考虑这个方案
另一种是master 节点具有public endpiont, nodes是没有的, 本文关注的是这个方案
创建一个空的github terrform 项目
https://github.com/nvd11/terraform-gke-private-cluster2
之后准备好backend.tf 和provider.tf 两个关键配置
python
terraform {
backend "gcs" {
bucket = "jason-hsbc"
prefix = "terraform/my-cluster2/state"
}
}
python
terraform {
required_providers {
google = {
source = "hashicorp/google"
version = "~> 7.0.0"
}
}
}
provider "google" {
project = var.project_id
region = var.region_id
zone = var.zone_id
}
python
variable "project_id" {
description = "The ID of the project"
default = "jason-hsbc"
type = string
}
variable "region_id" {
description = "The region of the project"
default = "europe-west2"
type = string
}
variable "zone_id" {
description = "The zone id of the project"
default = "europe-west2-c"
type = string
}
//https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/service-agents
variable "gcs_sa" {
description = "built-in service acount of GCS"
default = "service-912156613264@gs-project-accounts.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
type = string
}
//https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/service-agents
variable "sts_sa" {
description = "built-in service acount of Storage Transer service"
default = "project-912156613264@storage-transfer-service.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
type = string
}
variable "vpc0" {
description = "The name of the VPC network"
default = "tf-vpc0"
type = string
}到这里就可以测试 terraform init 和 terraform plan了
创建1个vpc network 和vpc subnet
其中vpc network 我沿用之前创建的tf-vpc0, 这里不再重复创建
vpc network的tf 配置参考:
Google cloud 的VPC Network 虚拟局域网 介绍
但我这里会创建一个新的subnet 来for 这个cluster
vpc0-subnet3。tf
python
# create a subnet
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/google/latest/docs/resources/compute_subnetwork
resource "google_compute_subnetwork" "tf-vpc0-subnet3" {
project = var.project_id
name = "tf-vpc0-subnet3"
ip_cidr_range = "192.168.5.0/24" # 192.168.4.1 ~ 192.168.04.255
region = var.region_id
# only PRIVATE could allow vm creation, the PRIVATE item is displayed as "None" in GCP console subnet creation page
# but we cannot set purpose to "None", if we did , the subnet will still created as purpose = PRIVATE , and next terraform plan/apply will try to recreate the subnet!
# as it detect changes for "PRIVATE" -> "NONE"
# gcloud compute networks subnets describe tf-vpc0-subnet3 --region=europe-west2
purpose = "PRIVATE"
role = "ACTIVE"
private_ip_google_access = "true" # to eanble the vm to access gcp products via internal network but not internet, faster and less cost!
network = "tf-vpc0"
# Although the secondary\_ip\_range is not within the subnet's IP address range,
# they still belong to the same VPC network. GKE uses routing and firewall rules to ensure communication between Pods, Services, and VMs."
secondary_ip_range {
range_name = "pods-range" # 用于 Pods
ip_cidr_range = "192.171.16.0/20" # 选择一个不冲突的范围
}
secondary_ip_range {
range_name = "services-range" # 用于 Services
ip_cidr_range = "192.172.16.0/20" # 选择一个不冲突的范围
}
}值得注意的是pod-range 和 seervices-range 的ip 都不能在这个subnet 本身的ip范围, 而且不能与任何vpc-network内定义过的subnet(or 其secondary ip range) 冲突。
也就是讲, 通常只有gfe 的node 节点会under 这个subnet本身定义的ip range内(192.168. 5.2~192.168.5.255)
创建cluster
python
resource "google_container_cluster" "my-cluster2" {
project = var.project_id
name = "my-cluster2"
location = var.region_id
# use custom node pool but not default node pool
remove_default_node_pool = true
# initial_node_count - (Optional) The number of nodes to create in this cluster's default node pool.
# In regional or multi-zonal clusters, this is the number of nodes per zone. Must be set if node_pool is not set.
# If you're using google_container_node_pool objects with no default node pool,
# you'll need to set this to a value of at least 1, alongside setting remove_default_node_pool to true.
initial_node_count = 1
deletion_protection = false
# Gke master will has his own managed vpc
#but gke will create nodes and svcs under below vpc and subnet
# they will use vpc peering to connect each other
network = var.vpc0
subnetwork = google_compute_subnetwork.tf-vpc0-subnet3.name
# the desired configuration options for master authorized networks.
#Omit the nested cidr_blocks attribute to disallow external access (except the cluster node IPs, which GKE automatically whitelists)
# we could just remove the whole block to allow all access
#master_authorized_networks_config {
#}
ip_allocation_policy {
# tell where pods could get the ip
cluster_secondary_range_name = "pods-range" # need pre-defined in tf-vpc0-SUbnet0
#tell where svcs could get the ip
services_secondary_range_name = "services-range"
}
private_cluster_config {
enable_private_nodes = true # nodes do not have public ip
enable_private_endpoint = false # master have public ip, we need to set it to false , or we need to configure master_authorized_networks_config to allow our ip
master_global_access_config {
enabled = true
}
}
fleet {
#Can't configure a value for "fleet.0.membership": its value will be decided automatically based on the result of applying this configuration.
#membership = "projects/${var.project_id}/locations/global/memberships/${var.cluster_name}"
project = var.project_id
}
}几个points:
什么是gke 的fleet
Fleet 配置在 GKE 集群中用于将集群注册到 Google Cloud Fleet Management。 Fleet Management 允许您将多个集群(无论它们位于何处,例如 Google Cloud、其他云提供商或本地)组织成一个逻辑单元,以便进行统一管理和策略应用。
fleet 在gcp 项目创建时就会自动创建, 通常不需要特别关注
private_cluster_config
这里就是private cluster 的核心配置
enable_private_endpoint = true 则代表master 没有任何public endpoint ,需要额外通过master_authorized_networks_config 来配置一些白名单(例如堡垒机)从集群外部访问Master。
这里配置enable_private_endpoint= false
python master_global_access_config { enabled = true }
这个配置则允许master 能从外网访问
创建node pool
由于我在 cluster 配置了不是用default node pool
则需要配置一个custom的
python
resource "google_container_node_pool" "my-cluster2-node-pool1" {
count =1
name ="node-pool1"
#│ Because google_container_cluster.my-cluster1 has "count" set, its attributes must be accessed on
# specific instances.
cluster = google_container_cluster.my-cluster2.name
location = google_container_cluster.my-cluster2.location
#The number of nodes per instance group. This field can be used to update the number of nodes per instance group but should not be used alongsid
node_count =1
node_config {
machine_type = "n2d-highmem-4"
image_type = "COS_CONTAINERD"
#grants the nodes in "my-node-pool1" full access to all Google Cloud Platform services.
oauth_scopes = ["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform"]
service_account = "vm-common@jason-hsbc.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
}注意的是node_count , gke 会在当前选择的region( europe-west2) 中的每个zone(europe-west2-a,europe-west2-b,europe-west2-c) 中分别创建1个instance group
这个node_count 是配置每个mig内 有多少个node(gce-vm)
如果配置1, 就代表有3个nodes, 够用了
terraform apply
没什么好说的, 等个5分钟左右就创建好了
检查node pool 配置
首先是mig
bash
gateman@MoreFine-S500: terraform-gke-private-cluster2$ gcloud compute instance-groups managed list
NAME LOCATION SCOPE BASE_INSTANCE_NAME SIZE TARGET_SIZE INSTANCE_TEMPLATE AUTOSCALED
gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-5cad8c5c-grp europe-west2-a zone gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-5cad8c5c 2 2 gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-11210656 no
gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-01eff82c-grp europe-west2-a zone gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-01eff82c 1 1 gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-01eff82c no
gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-f7d2eb2b-grp europe-west2-b zone gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-f7d2eb2b 2 2 gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-13492c03 no
gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-6a83612b-grp europe-west2-b zone gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-6a83612b 1 1 gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-6a83612b no
gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-8902d932-grp europe-west2-c zone gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-8902d932 2 2 gke-my-cluster1-my-node-pool1-ccef768c no
gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-8bb426f2-grp europe-west2-c zone gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-8bb426f2 1 1 gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-8bb426f2 no可见创建出来了3个 mig 分别在不同的zone
然后再看gce vm
bash
gateman@MoreFine-S500: terraform-gke-private-cluster2$ gcloud compute instances list| grep -i my-cluster2
gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-01eff82c-1r5b europe-west2-a n2d-highmem-4 192.168.5.18 RUNNING
gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-6a83612b-mj40 europe-west2-b n2d-highmem-4 192.168.5.16 RUNNING
gke-my-cluster2-node-pool1-8bb426f2-3nqn europe-west2-c n2d-highmem-4 192.168.5.17 RUNNING注意3个node 都没有分配外网ip 而且内网ip都在tf-vpc0-subnet3 内
使用kubectl 连接集群
虽然nodes是内网的, 但是我们已经配置了让master 可以从外网访问, 所以可以很方便地从cloudshell连接
用下面命令enable kubectl 配置
bash
gcloud container clusters get-credentials my-cluster2 --region europe-west2 --project jason-hsbc接下来就可以使用kubectl管理集群了
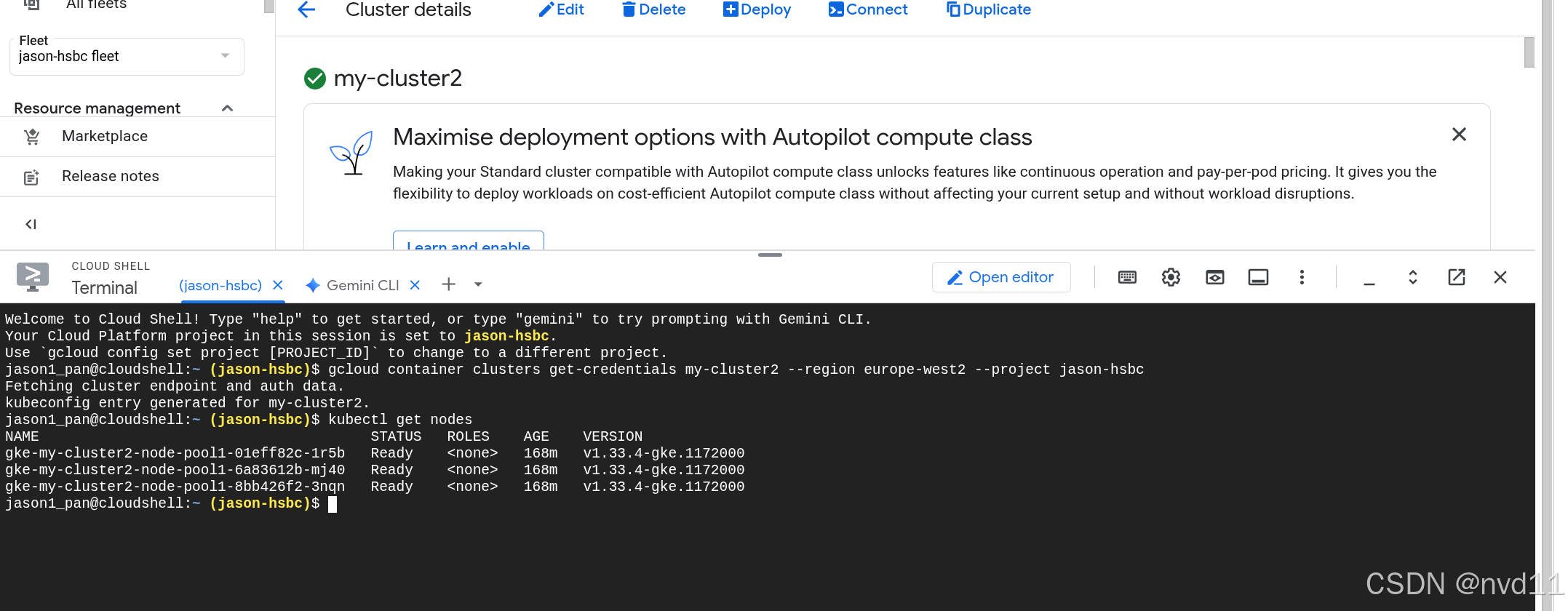
如何查看master 节点信息, master 到底部署在哪
其实上从gce vm 的list 里是找不到master node的。
我们先查看 cluster的相信信息
bash
gateman@MoreFine-S500: envoy-config$ gcloud container clusters describe my-cluster2 --region=europe-west2
addonsConfig:
gcePersistentDiskCsiDriverConfig:
enabled: true
kubernetesDashboard:
disabled: true
networkPolicyConfig:
disabled: true
anonymousAuthenticationConfig:
mode: ENABLED
autopilot: {}
autoscaling:
autoscalingProfile: BALANCED
binaryAuthorization: {}
clusterIpv4Cidr: 192.171.16.0/20
controlPlaneEndpointsConfig:
dnsEndpointConfig:
allowExternalTraffic: false
endpoint: gke-059344205081454eb228f72a1d7a92706645-912156613264.europe-west2.gke.goog
ipEndpointsConfig:
authorizedNetworksConfig:
privateEndpointEnforcementEnabled: true
enablePublicEndpoint: true
enabled: true
globalAccess: true
privateEndpoint: 192.168.5.9
publicEndpoint: 34.147.241.202
createTime: '2025-10-02T15:57:21+00:00'
currentMasterVersion: 1.33.4-gke.1172000
currentNodeCount: 3
currentNodeVersion: 1.33.4-gke.1172000
...信息很长, 我们看重点
ipEndpointsConfig:
authorizedNetworksConfig:
privateEndpointEnforcementEnabled: true
enablePublicEndpoint: true
enabled: true
globalAccess: true
privateEndpoint: 192.168.5.9
publicEndpoint: 34.147.241.202
这里就是master 的外网ip和内网ip
至于master 装在哪? 其实gke 是把master纳入control plane管理, 并没有显示部署master节点