前言
本章分析消费者消费:
1)确定消费位点;2)拉取消息;3)提交消费位点;
历史相关文章:
注:本文基于kafka2.6,没有KRaft。
一、回顾Rebalance结果
KafkaConsumer#poll:消费者侧只有一个线程,即用户poll线程。poll方法会完成rebalance+自动提交+拉取消息一系列动作。
java
private ConsumerRecords<K, V> poll(final Timer timer, final boolean includeMetadataInTimeout) {
do {
// 1. rebalance和自动提交
updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded(timer, false);
// 2. 拉取消息
Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records =
pollForFetches(timer);
if (!records.isEmpty()) {
if (fetcher.sendFetches() > 0 ||
client.hasPendingRequests()) {
// 如果2拉取到消息,尝试再次发送FetchRequest
client.transmitSends();
}
// 3. 返回消息
return this.interceptors.onConsume(new ConsumerRecords<>(records));
}
// 4. 用户指定超时时间没超时,继续循环
} while (timer.notExpired());
return ConsumerRecords.empty();
}SubscriptionState 是消费者侧的订阅状态,包含:1-订阅topics(subscription );2-分区分配结果(assignment)。
消费组leader用RangeAssignor分配策略执行分区分配,将assignment通过SyncGroupRequest给到协调者,由协调者通过SyncGroupResponse将assignment下发给所有消费者。
java
public class SubscriptionState {
private enum SubscriptionType {
NONE, AUTO_TOPICS, AUTO_PATTERN, USER_ASSIGNED
}
// 订阅方式
private SubscriptionType subscriptionType;
// AUTO_PATTERN 正则匹配订阅
private Pattern subscribedPattern;
// AUTO_TOPICS 精确匹配订阅
private Set<String> subscription;
// 消费组订阅topics全集
private Set<String> groupSubscription;
// 分配分区-状态
private final PartitionStates<TopicPartitionState> assignment;
// 如果消费组首次创建,初始化消费进度的策略
// auto.offset.reset=latest
private final OffsetResetStrategy defaultResetStrategy;
// 用户subscribe可以提供第二个参数ConsumerRebalanceListener
private ConsumerRebalanceListener rebalanceListener;
// rebalance导致assignment分区改变,assignmentId++
private int assignmentId = 0;
}SubscriptionState#assignFromSubscribed:所有消费者收到SyncGroupResponse得到自身消费分区。初始分区fetch状态TopicPartitionState 为INITIALIZING ,消费位点position为null。
java
public class PartitionStates<S> {
// 分区-分区状态
private final LinkedHashMap<TopicPartition, S> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
private static class TopicPartitionState {
// fetch状态
private FetchState fetchState;
// 消费进度
private FetchPosition position;
TopicPartitionState() {
this.fetchState = FetchStates.INITIALIZING;
this.position = null;
// 其余属性都是null
}
}KafkaConsumer#updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded:消费者完成rebalance后需要确定消费位点updateFetchPositions,才能开始消费。
java
boolean updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded(final Timer timer, final boolean waitForJoinGroup) {
// 1. coordinator.poll,完成rebalance,自动提交
if (coordinator != null && !coordinator.poll(timer, waitForJoinGroup)) {
return false;
}
// 2. 确定消费位点,才能开始发送FetchRequest
return updateFetchPositions(timer);
}分区FetchState有四种状态:
1)INITIALIZING:刚分配到该分区;
2)AWAIT_VALIDATION:消费组曾经消费过,已经获取消费位点;
3)AWAIT_RESET:消费组未曾经消费过,待重置消费位点;
4)FETCHING:消费位点合法,可以开始消费;
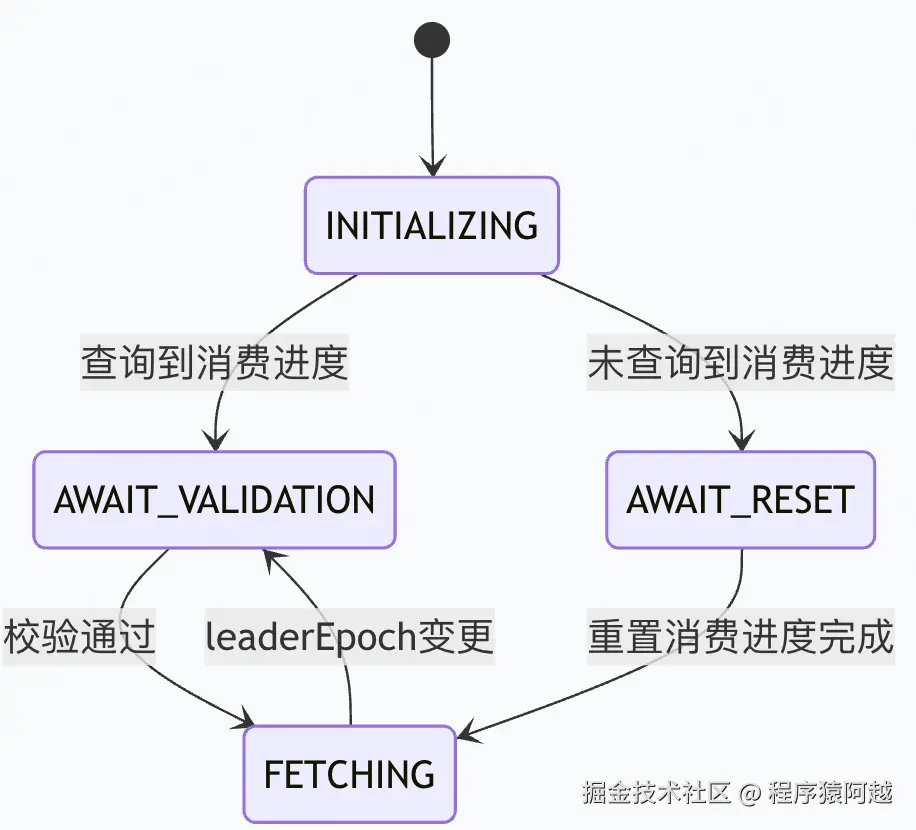
KafkaConsumer#updateFetchPositions:处理四种分区状态,目标是将状态翻转至FETCHING才能拉取消息。
java
private boolean updateFetchPositions(final Timer timer) {
// 1. 【FETCHING】分区leaderEpoch改变【AWAIT_VALIDATION】
// 【AWAIT_VALIDATION】执行leaderEpoch校验【FETCHING】
fetcher.validateOffsetsIfNeeded();
// 2. 所有分区进入【FETCHING】状态,直接返回
cachedSubscriptionHashAllFetchPositions = subscriptions.hasAllFetchPositions();
if (cachedSubscriptionHashAllFetchPositions) return true;
// 3. 【INITIALIZING】获取历史消费进度【AWAIT_VALIDATION】
// refreshCommittedOffsetsIfNeeded=true代表未超时,false代表超时
if (coordinator != null &&
!coordinator.refreshCommittedOffsetsIfNeeded(timer))
return false;
// 4. 【INITIALIZING】获取历史消费进度为空【AWAIT_RESET】,
// 【AWAIT_RESET】使用重置策略【FETCHING】
subscriptions.resetInitializingPositions();
fetcher.resetOffsetsIfNeeded();
return true;
}二、确定消费位点
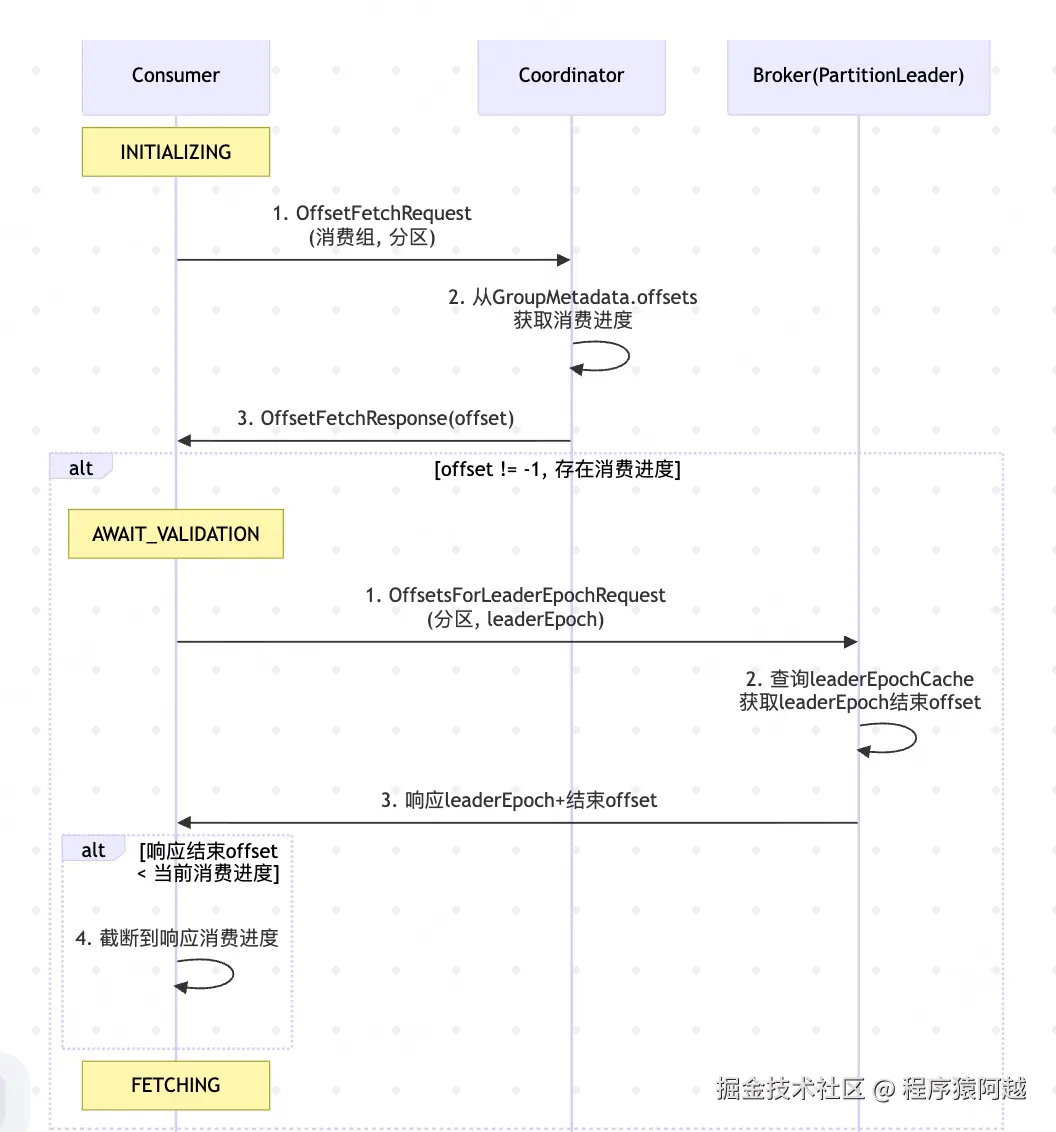
2-1、获取分区消费进度
如果消费组曾经消费过该topic分区,可以从协调者获取消费组该分区消费进度。
2-1-1、consumer发送OffsetFetchRequest
ConsumerCoordinator#refreshCommittedOffsetsIfNeeded:consumer发送OffsetFetchRequest,收到分区进度更新到内存。
java
public boolean refreshCommittedOffsetsIfNeeded(Timer timer) {
// INITIALIZING状态的分区
Set<TopicPartition> initializingPartitions =
subscriptions.initializingPartitions();
// 发送OffsetFetchRequest,获取分区的消费进度
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets =
fetchCommittedOffsets(initializingPartitions, timer);
if (offsets == null) return false; // 超时
// ...处理返回消费进度
return true;
}OffsetFetchRequest请求如下:
java
public class OffsetFetchRequestData implements ApiMessage {
// 消费组id
private String groupId;
// topic和分区
private List<OffsetFetchRequestTopic> topics;
// true
private boolean requireStable;
}
static public class OffsetFetchRequestTopic implements Message {
// topic
private String name;
// 分区id
private List<Integer> partitionIndexes;
}2-1-2、coordinator处理OffsetFetchRequest
GroupMetadataManager#getOffsets:coordinator循环所有分区,获取内存中的消费进度(GroupMetadata#offsets),如果不存在消费进度,返回offset=-1(INVALID_OFFSET)。
coordinator收到消费组的首个成员JoinGroupRequest会创建消费组,一个消费组id对应一个GroupMetadata。
scala
def getOffsets(groupId: String, requireStable: Boolean,
topicPartitionsOpt: Option[Seq[TopicPartition]]):
Map[TopicPartition, PartitionData] = {
val group = groupMetadataCache.get(groupId)
group.inLock {
val topicPartitions =
topicPartitionsOpt.getOrElse(group.allOffsets.keySet)
topicPartitions.map { topicPartition =>
val partitionData = group.offset(topicPartition) match {
case None =>
// 不存在返回offset=-1(INVALID_OFFSET)
new PartitionData(OffsetFetchResponse.INVALID_OFFSET,
Optional.empty(), "", Errors.NONE)
case Some(offsetAndMetadata) =>
new PartitionData(offsetAndMetadata.offset,
offsetAndMetadata.leaderEpoch, offsetAndMetadata.metadata, Errors.NONE)
}
topicPartition -> partitionData
}.toMap
}
}
// GroupMetadata 分区->消费进度
private val offsets = new mutable.HashMap[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]
def offset(topicPartition: TopicPartition): Option[OffsetAndMetadata] = offsets.get(topicPartition).map(_.offsetAndMetadata)OffsetFetchResponse响应如下:
java
public class OffsetFetchResponseData implements ApiMessage {
// topic列表
private List<OffsetFetchResponseTopic> topics;
}
static public class OffsetFetchResponseTopic implements Message {
// topic
private String name;
// 分区offset
private List<OffsetFetchResponsePartition> partitions;
}
static public class OffsetFetchResponsePartition implements Message {
// 分区id
private int partitionIndex;
// 消费进度offset
private long committedOffset;
// 这个offset对应的分区leaderEpoch
private int committedLeaderEpoch;
}2-1-3、consumer处理OffsetFetchResponse
OffsetFetchResponseHandler:offset大于等于0,代表该分区以前被消费组消费过,可以拿到消费进度。
java
private class OffsetFetchResponseHandler {
public void handle(OffsetFetchResponse response,
RequestFuture<Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata>> future) {
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets = new HashMap<>(response.responseData().size());
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData> entry :
response.responseData().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition tp = entry.getKey();
OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData partitionData = entry.getValue();
if (partitionData.offset >= 0) {
// 有消费进度
offsets.put(tp, new OffsetAndMetadata(
partitionData.offset, partitionData.leaderEpoch, partitionData.metadata));
} else {
// 没消费进度
log.info("Found no committed offset for partition {}", tp);
offsets.put(tp, null);
}
}
future.complete(offsets);
}
}ConsumerCoordinator#refreshCommittedOffsetsIfNeeded:分区Fetch状态进入AWAIT_VALIDATION ,将消费位点封装为FetchPosition。
java
public class SubscriptionState {
// 被分配的分区状态
private final PartitionStates<TopicPartitionState> assignment;
}
private static class TopicPartitionState {
// 状态AWAIT_VALIDATION
private FetchState fetchState;
// 消费进度
private FetchPosition position;
}
public static class FetchPosition {
// 消费进度
public final long offset;
// offset消息记录对应的分区leaderEpoch
final Optional<Integer> offsetEpoch;
// 当前的分区leader和epoch
final Metadata.LeaderAndEpoch currentLeader;
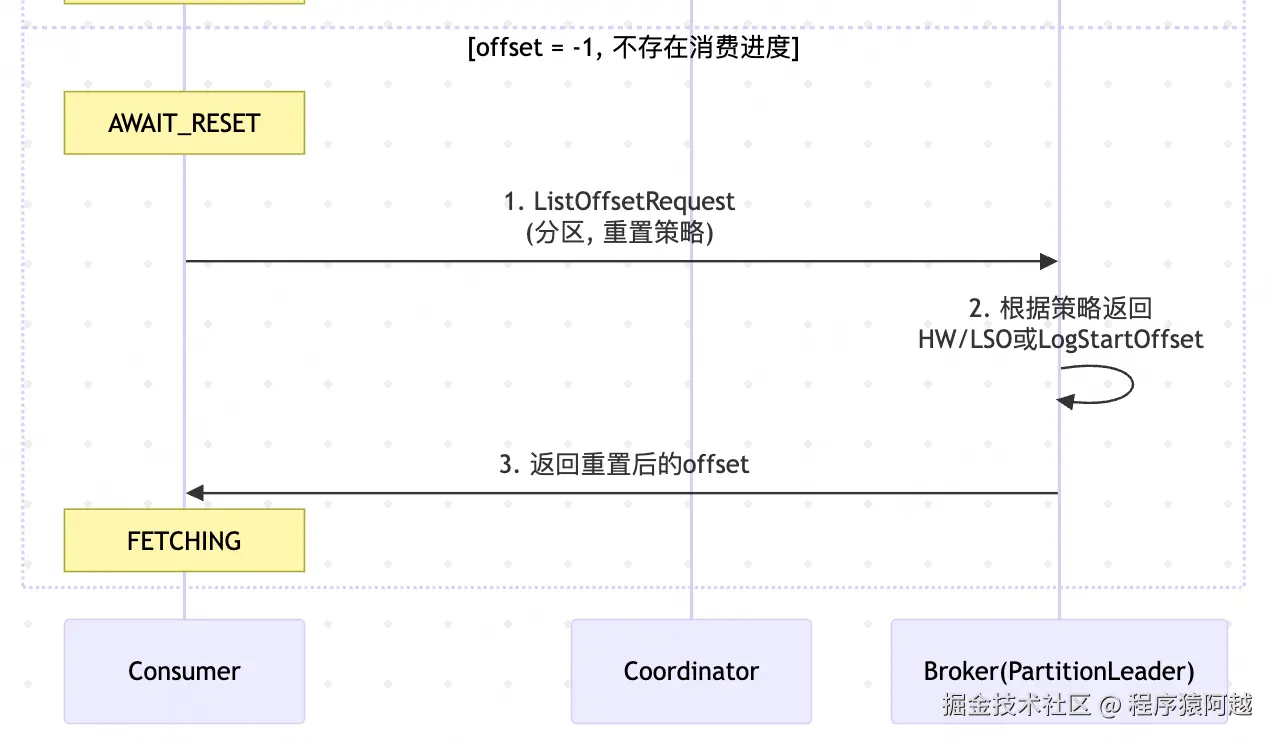
}2-2、重置消费进度
如果上一步分区对应offset返回-1,代表消费组还未消费过该分区 ,使用重置策略 ,从分区leader获取分区offset。
2-2-1、consumer发送ListOffsetRequest
SubscriptionState#resetInitializingPositions:标记所有INITIALIZING 状态分区为AWAIT_RESET。
Fetcher#resetOffsetsIfNeeded:获取分区重置策略,发送ListOffsetRequest。
Fetcher#offsetResetStrategyTimestamp:重置策略有两种,可以通过auto.offset.reset调整:
1)LATEST:默认,重置为分区最新写入进度,传参-1;
2)EARLIEST:重置为分区最早写入进度,传参-2;
java
private Long offsetResetStrategyTimestamp(final TopicPartition partition) {
OffsetResetStrategy strategy = subscriptions.resetStrategy(partition);
if (strategy == OffsetResetStrategy.EARLIEST)
return ListOffsetRequest.EARLIEST_TIMESTAMP; // -2
else if (strategy == OffsetResetStrategy.LATEST) // 默认
return ListOffsetRequest.LATEST_TIMESTAMP; // -1
else
return null;
}Fetcher#resetOffsetsAsync:发送ListOffsetRequest给分区leader broker。
Fetcher和普通broker交互,Coordinator和协调者交互。
java
private void resetOffsetsAsync(
// 分区 - 重置策略(-1、-2)
Map<TopicPartition, Long> partitionResetTimestamps) {
// 分区leader - 分区 - 重置策略(-1、-2)
Map<Node, Map<TopicPartition, ListOffsetRequest.PartitionData>> timestampsToSearchByNode
= groupListOffsetRequests(partitionResetTimestamps, new HashSet<>());
// 循环所有broker发送请求
for (Map.Entry<Node, Map<TopicPartition, ListOffsetRequest.PartitionData>>
entry : timestampsToSearchByNode.entrySet()) {
Node node = entry.getKey();
final Map<TopicPartition, ListOffsetRequest.PartitionData>
resetTimestamps = entry.getValue();
// 发送请求
RequestFuture<ListOffsetResult> future = sendListOffsetRequest(node, resetTimestamps, false);
future.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<ListOffsetResult>() {
//...
});
}
}ListOffsetRequest:
java
public class ListOffsetRequest extends AbstractRequest {
// 副本ID,用于broker间主从复制,普通消费者=-1
private final int replicaId;
// 隔离级别,默认READ_UNCOMMITTED
private final IsolationLevel isolationLevel;
// 分区 - PartitionData
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> partitionTimestamps;
}
public static final class PartitionData {
// -1或-2 重置策略
public final long timestamp;
// 消费者看到的当前分区leaderEpoch
public final Optional<Integer> currentLeaderEpoch;
}2-2-2、分区leader broker处理ListOffsetRequest
回顾一下第四章的几个概念:
1)LEO(LogEndOffset) :写入偏移量 + 1 = 下次写入的offset;
2)HW高水位:min(ISR副本的LEO,与leader同步延迟30s内的副本的LEO);
3)logStartOffset:分区的第一条消息的offset,如果发生过数据清理,则会大于0;
4)leaderEpochCache :分区的 leader任期 和 任期起始offset 缓存。比如:(0,0),(1,222),(2,333),代表:任期0写入offset[0,221]、任期1写入offset[222,332]。这份数据存储在分区log目录下的leader-epoch-checkpoint。
txt
0 // 版本号
3 // 条目数量
0 0 // epoch 起始offset
1 222 // epoch 起始offset
2 333 // epoch 起始offsetPartition#fetchOffsetForTimestamp:
1)基础校验,请求的分区leaderEpoch和自身相等,且自身是leader;
2)如果使用LATEST策略(默认) ,根据隔离级别返回offset 和当前leaderEpoch:
READ_COMMITTED,返回LSO,事务消息相关后续再看;
READ_UNCOMMITTED (默认),返回HW高水位;
scala
def fetchOffsetForTimestamp(timestamp: Long,
isolationLevel: Option[IsolationLevel],
currentLeaderEpoch: Optional[Integer],
fetchOnlyFromLeader: Boolean):
// leaderAndIsr读锁,期间leader和isr不会变
Option[TimestampAndOffset] = inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
// 1. 校验客户端发送的分区leaderEpoch和自己相等
val localLog = localLogWithEpochOrException(currentLeaderEpoch, fetchOnlyFromLeader)
// 最大可拉取的offset
val lastFetchableOffset = isolationLevel match {
// 事务消息相关,消费者设置READ_COMMITTED隔离级别,只能消费LSO
case Some(IsolationLevel.READ_COMMITTED) => localLog.lastStableOffset
// 普通消费者,能消费HW之前的数据,HW高水位=min(ISR副本的写入进度LEO)
case Some(IsolationLevel.READ_UNCOMMITTED) => localLog.highWatermark
case None => localLog.logEndOffset
}
// 根据时间戳查询offset
def getOffsetByTimestamp: Option[TimestampAndOffset] = {
logManager.getLog(topicPartition).flatMap(log => log.fetchOffsetByTimestamp(timestamp))
}
timestamp match {
case ListOffsetRequest.LATEST_TIMESTAMP =>
// 2. 根据隔离级别,返回 offset=HW或LSO,当前leaderEpoch
Some(new TimestampAndOffset(RecordBatch.NO_TIMESTAMP,
lastFetchableOffset,
Optional.of(leaderEpoch)))
case ListOffsetRequest.EARLIEST_TIMESTAMP =>
// 3. 找LogStartOffset
getOffsetByTimestamp
}
}Log#fetchOffsetByTimestamp:EARLIEST 策略,返回logStartOffset 和该offset写入时对应的leaderEpoch。
scala
// 记录了每个leaderEpoch对应的起始offset
// (0,100),(1,222),...
var leaderEpochCache: Option[LeaderEpochFileCache] = None
def fetchOffsetByTimestamp(targetTimestamp: Long):
Option[TimestampAndOffset] = {
if (targetTimestamp == ListOffsetRequest.EARLIEST_TIMESTAMP) {
// 找到第一个任期的leaderEpoch
val earliestEpochEntry = leaderEpochCache.flatMap(_.earliestEntry)
val epochOpt = earliestEpochEntry match {
// 如果logStartOffset在第一个leaderEpoch内,则返回对应leaderEpoch
case Some(entry) if entry.startOffset <= logStartOffset => Optional.of[Integer](entry.epoch)
case _ => Optional.empty[Integer]()
}
return Some(new TimestampAndOffset(RecordBatch.NO_TIMESTAMP, logStartOffset, epochOpt))
}
}ListOffsetResponse:
scala
public class ListOffsetResponse extends AbstractResponse {
// 分区 - 分区数据
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> responseData;
}
public static final class PartitionData {
// 固定-1
public final Long timestamp;
// offset
public final Long offset;
// offset对应分区leader任期
public final Optional<Integer> leaderEpoch;
}2-2-3、consumer处理ListOffsetResponse
SubscriptionState#maybeSeekUnvalidated:重置offset,设置FetchPosition不含leaderEpoch。
java
synchronized void maybeSeekUnvalidated(TopicPartition tp, long offset,
OffsetResetStrategy requestedResetStrategy) {
TopicPartitionState state = assignedStateOrNull(tp);
// ...
log.info("Resetting offset for partition {} to offset {}.", tp, offset);
state.seekUnvalidated(new FetchPosition(offset));
}TopicPartitionState#validatePosition:重置场景下,跳过AWAIT_VALIDATION,直接进入FETCHING。
java
private void validatePosition(FetchPosition position) {
if (position.offsetEpoch.isPresent() && position.currentLeader.epoch.isPresent()) {
// 有leaderEpoch,即非重置情况
transitionState(FetchStates.AWAIT_VALIDATION, () -> {
this.position = position;
this.nextRetryTimeMs = null;
});
} else {
// 没leaderEpoch,直接翻转到FETCHING
transitionState(FetchStates.FETCHING, () -> {
this.position = position;
this.nextRetryTimeMs = null;
});
}
}2-3、校验消费进度
2-3-1、consumer发送OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest
Fetcher#validateOffsetsIfNeeded:每次用户执行poll方法,都会判断分区leaderEpoch是否变更,如果发生变更,fetch状态也会翻转AWAIT_VALIDATION。
java
private boolean maybeValidatePosition(
// 消费者 元数据中的分区leaderEpoch
Metadata.LeaderAndEpoch currentLeaderAndEpoch) {
if (this.fetchState.equals(FetchStates.AWAIT_RESET)) {
return false;
}
if (!currentLeaderAndEpoch.leader.isPresent()) {
return false;
}
if (position != null &&
!position.currentLeader.equals(currentLeaderAndEpoch)) {
// FetchPosition中的leaderEpoch和元数据里的分区leaderEpoch不同
// 翻转分区fetch状态为AWAIT_VALIDATION
FetchPosition newPosition = new FetchPosition(position.offset, position.offsetEpoch, currentLeaderAndEpoch);
validatePosition(newPosition);
preferredReadReplica = null;
}
return this.fetchState.equals(FetchStates.AWAIT_VALIDATION);
}Fetcher#validateOffsetsAsync:对于AWAIT_VALIDATION 状态的分区,发送OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest给分区leader broker。
OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest:
java
public class OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest extends AbstractRequest {
// 分区-分区数据
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> epochsByPartition;
// 普通消费者固定-1
private final int replicaId;
}
public static class PartitionData {
// 当前leaderEpoch---broker需要校验自己epoch和消费者看到的一致
public final Optional<Integer> currentLeaderEpoch;
// offset对应消息的leaderEpoch
public final int leaderEpoch;
}2-3-2、leader broker处理OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest
Partition#lastOffsetForLeaderEpoch:
1)确认自己是leader,且request.currentLeaderEpoch和自己epoch相等;
2)查询request.leaderEpoch任期对应的结束offset;
scala
def lastOffsetForLeaderEpoch(currentLeaderEpoch: Optional[Integer],
leaderEpoch: Int,
fetchOnlyFromLeader: Boolean): EpochEndOffset = {
// leader和isr读锁 期间不变化
inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
// 1. 确认客户端发送的currentLeaderEpoch = 当前leaderEpoch
val localLogOrError = getLocalLog(currentLeaderEpoch, fetchOnlyFromLeader)
localLogOrError match {
case Left(localLog) =>
// 2. 根据客户端传入待校验leaderEpoch,返回leaderEpoch和它的结束offset
localLog.endOffsetForEpoch(leaderEpoch) match {
case Some(epochAndOffset) => new EpochEndOffset(NONE, epochAndOffset.leaderEpoch, epochAndOffset.offset)
case None => new EpochEndOffset(NONE, UNDEFINED_EPOCH, UNDEFINED_EPOCH_OFFSET)
}
case Right(error) =>
new EpochEndOffset(error, UNDEFINED_EPOCH, UNDEFINED_EPOCH_OFFSET)
}
}
}LeaderEpochFileCache#endOffsetFor:根据leaderEpochCache ,返回请求epoch的下一个offset,比如请求epoch=1管理offset范围为[1,10],则返回epoch=1和offset=11。
scala
def endOffsetForEpoch(leaderEpoch: Int): Option[OffsetAndEpoch] = {
leaderEpochCache.flatMap { cache =>
val (foundEpoch, foundOffset) = cache.endOffsetFor(leaderEpoch)
if (foundOffset == EpochEndOffset.UNDEFINED_EPOCH_OFFSET)
None
else
Some(OffsetAndEpoch(foundOffset, foundEpoch))
}
}
def endOffsetFor(requestedEpoch: Int): (Int, Long) = {
inReadLock(lock) {
val epochAndOffset =
if (requestedEpoch == UNDEFINED_EPOCH) {
(UNDEFINED_EPOCH, UNDEFINED_EPOCH_OFFSET)
} else if (latestEpoch.contains(requestedEpoch)) {
// 当前leaderEpoch(latestEpoch) = 请求leaderEpoch,直接返回LEO即可
(requestedEpoch, logEndOffset())
} else {
// subsequentEpochs = 大于请求leaderEpoch的(epoch,startOffset)
// previousEpochs = 小于等于请求leaderEpoch的(epoch,startOffset)
val (subsequentEpochs, previousEpochs) =
epochs.partition { e => e.epoch > requestedEpoch}
if (subsequentEpochs.isEmpty) {
// 没有大于请求epoch的entry,则返回不存在
(UNDEFINED_EPOCH, UNDEFINED_EPOCH_OFFSET)
} else if (previousEpochs.isEmpty) {
// 没有小于等于请求epoch的entry,
// 返回 = 请求epoch + 大于epoch的第一个startOffset
(requestedEpoch, subsequentEpochs.head.startOffset)
} else {
// 有小于等于请求epoch的entry,
// 返回 = 小于等于请求epoch的第一个epoch + 下一个epoch的startOffset
(previousEpochs.last.epoch, subsequentEpochs.head.startOffset)
}
}
epochAndOffset
}
}OffsetsForLeaderEpochResponse:即endOffsetFor的返回
java
public class OffsetsForLeaderEpochResponse extends AbstractResponse {
private final Map<TopicPartition, EpochEndOffset>
epochEndOffsetsByPartition;
}
public class EpochEndOffset {
private int leaderEpoch;
private long endOffset;
}2-3-3、consumer处理OffsetsForLeaderEpochResponse
SubscriptionState#maybeCompleteValidation:如果返回response.endOffset小于当前消费位点,可能是发生新一轮leader选举,数据被截断,消费位点截断至response.endOffset。处理完成,状态翻转到FETCHING可以开始消费。
java
public synchronized Optional<LogTruncation>
maybeCompleteValidation(TopicPartition tp,
FetchPosition requestPosition,
EpochEndOffset epochEndOffset) {
TopicPartitionState state = assignedStateOrNull(tp);
SubscriptionState.FetchPosition currentPosition = state.position;
if (epochEndOffset.endOffset() < currentPosition.offset) {
// 如果返回offset 小于 当前fetch的offset 可能是leader重新选举发生数据截断
// 更新FetchPosition=broker返回的offset
SubscriptionState.FetchPosition newPosition =
new SubscriptionState.FetchPosition(
epochEndOffset.endOffset(),
Optional.of(epochEndOffset.leaderEpoch()),
currentPosition.currentLeader);
// 状态翻转FETCHING
state.seekValidated(newPosition);
} else {
// 状态翻转FETCHING
state.completeValidation();
}
return Optional.empty();
}三、拉取消息
3-1、主流程
KafkaConsumer#pollForFetches:
consumer优先从缓存中获取已经拉到的消息,否则构造FetchRequest从broker拉取消息。
java
private Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>>
pollForFetches (Timer timer) {
long pollTimeout = coordinator == null ? timer.remainingMs() :
// min (下次心跳时间、下次commit时间、用户timer超时时间)
Math.min(coordinator.timeToNextPoll(timer.currentTimeMs()), timer.remainingMs());
// 1. 先从缓存中获取已经拉到的消息
final Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records = fetcher.fetchedRecords();
if (!records.isEmpty()) {
return records;
}
// 2. 构造FetchRequest
fetcher.sendFetches();
// 3. IO
Timer pollTimer = time.timer(pollTimeout);
client.poll(pollTimer, () -> {
return !fetcher.hasAvailableFetches();
});
timer.update(pollTimer.currentTimeMs());
// 4. 返回缓存中获取已经拉到的消息
return fetcher.fetchedRecords();
}3-2、从broker拉取消息
3-2-1、增量FetchRequest介绍
Incremental Fetch在KIP-227中提出,于1.1版本发布。
假设Kafka集群中有上万个分区,如topic0p0到topicNpN。
在主从复制中,Follower每个FetchRequest都携带一个冗长的分区列表,Leader必须为列表中的每一个分区生成元数据(HW高水位等),即使该分区自上次请求后没有新消息。
在分区数量庞大的Kafka集群中,传统的全量枚举式FetchRequest机制导致了显著且不必要的网络带宽和 CPU 资源消耗,这严重制约了集群的可扩展性,并与低延迟的数据同步需求产生了直接冲突。
而KIP-227提出的解决方案正是 "增量FetchRequest" ,它通过建立会话 ,只传输发生变化的分区信息,从而从根本上解决了上述瓶颈。
consumer对每个broker维护一个FetchSessionHandler ,用于维持会话状态。
java
public class Fetcher<K, V> implements Closeable {
// brokerId -> session
private final Map<Integer, FetchSessionHandler> sessionHandlers;
}
public class FetchSessionHandler {
// brokerId
private final int node;
// (sessionId, epoch) 二元组
private FetchMetadata nextMetadata = FetchMetadata.INITIAL;
// 分区 - 分区数据
private LinkedHashMap<TopicPartition, PartitionData> sessionPartitions =
new LinkedHashMap<>(0);
}
// fetch请求数据缓存FetchRequest.PartitionData
public static final class PartitionData {
// 消费位点
public final long fetchOffset;
// logStartOffset
public final long logStartOffset;
// max.partition.fetch.bytes=1mb
// 一次FetchRequest中的单分区最大拉取的字节数
public final int maxBytes;
// 当前leader任期
public final Optional<Integer> currentLeaderEpoch;
}
public class FetchMetadata {
public static final int INVALID_SESSION_ID = 0;
public static final int INITIAL_EPOCH = 0;
// 初始0,0
public static final FetchMetadata INITIAL = new FetchMetadata(INVALID_SESSION_ID, INITIAL_EPOCH);
// 会话id
private final int sessionId;
// epoch
private final int epoch;
}broker通过FetchSessionCache 维护n个会话FetchSession。
FetchSession.partitionMap :每个分区当前的拉取状态CachedPartition,同consumer侧FetchSessionHandler.sessionPartitions类似。
scala
class FetchSessionCache {
// sessionId -> session
private val sessions = new mutable.HashMap[Int, FetchSession]
}
class FetchSession(val id: Int, // sessionId
//...
// 分区-分区数据
val partitionMap: FetchSession.CACHE_MAP,
var epoch: Int) { // sessionEpoch
}
// CACHE_MAP别名,是个map
type CACHE_MAP = ImplicitLinkedHashCollection[CachedPartition]
class CachedPartition(val topic: String,
val partition: Int,
var maxBytes: Int,
var fetchOffset: Long,
var highWatermark: Long,
var leaderEpoch: Optional[Integer],
var fetcherLogStartOffset: Long,
var localLogStartOffset: Long) {}consumer和broker间的FetchRequest通过sessionId维持状态 ,用sessionEpoch保证顺序。
sessionId会话id,首次全量FetchRequest,broker创建返回;
sessionEpoch会话任期,broker每次收到请求+1,consumer每次收到响应+1。
3-2-2、consumer发送FetchRequest
Fetcher#sendFetches:循环每个broker发送FetchRequest。
java
public synchronized int sendFetches() {
// 准备数据
Map<Node, FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData> fetchRequestMap = prepareFetchRequests();
for (Map.Entry<Node, FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData> entry :
fetchRequestMap.entrySet()) {
final Node fetchTarget = entry.getKey();
final FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData data = entry.getValue();
final FetchRequest.Builder request = FetchRequest.Builder
.forConsumer(this.maxWaitMs, this.minBytes, data.toSend())
.isolationLevel(isolationLevel)
.setMaxBytes(this.maxBytes)
.metadata(data.metadata())
.toForget(data.toForget())
.rackId(clientRackId);
RequestFuture<ClientResponse> future = client.send(fetchTarget, request);
this.nodesWithPendingFetchRequests.add(entry.getKey().id());
future.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<ClientResponse>() {
}
}
}Fetcher#prepareFetchRequests:构建每个broker的FetchRequestData。
java
private Map<Node, FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData> prepareFetchRequests() {
Map<Node, FetchSessionHandler.Builder> fetchable = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 检测leaderEpoch是否改变,如果改变,相关分区翻转为AWAIT_VALIDATION
subscriptions.assignedPartitions().forEach(tp ->
subscriptions.maybeValidatePositionForCurrentLeader(apiVersions, tp, metadata.currentLeader(tp))
);
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
// 没有缓存消息 的 FETCHING分区
for (TopicPartition partition : fetchablePartitions()) {
FetchPosition position = this.subscriptions.position(partition);
Optional<Node> leaderOpt = position.currentLeader.leader;
if (!leaderOpt.isPresent()) {
// leader不存在,更新元数据,忽略
metadata.requestUpdate();
continue;
}
// 这里默认只会选择leader节点,#6832在2.4引入可以从follower拉
Node node = selectReadReplica(partition, leaderOpt.get(), currentTimeMs);
if (client.isUnavailable(node)) {
// 节点下线
client.maybeThrowAuthFailure(node);
} else if (this.nodesWithPendingFetchRequests.contains(node.id())) {
// broker有对应fetchrequest未响应,不处理
// log.trace...
} else {
// 正常情况
FetchSessionHandler.Builder builder = fetchable.get(node);
if (builder == null) {
int id = node.id();
// 获取broker对应FetchSessionHandler
FetchSessionHandler handler = sessionHandler(id);
if (handler == null) {
handler = new FetchSessionHandler(logContext, id);
sessionHandlers.put(id, handler);
}
builder = handler.newBuilder();
fetchable.put(node, builder);
}
// 将需要拉消息的分区加入handler.builder
// 包含拉取位点position.offset
builder.add(partition, new FetchRequest.PartitionData(
position.offset, FetchRequest.INVALID_LOG_START_OFFSET,
this.fetchSize, position.currentLeader.epoch));
}
}
// 构建fetchRequest分区数据,注意Builder.build
Map<Node, FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData> reqs = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<Node, FetchSessionHandler.Builder> entry : fetchable.entrySet()) {
reqs.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue().build());
}
return reqs;
}FetchSessionHandler.Builder#add&build:
1)如果session还未建立(nextMetadata.isFull),全量构建所有分区数据;
2)如果session已经建立,和当前sessionPartitions比对,发送变更的分区数据;
java
public class FetchSessionHandler {
// sessionId - epoch 二元组
private FetchMetadata nextMetadata;
// 分区 - 当前fetch数据
private LinkedHashMap<TopicPartition, PartitionData> sessionPartitions;
public class Builder {
// 本轮需要拉取的分区数据
private LinkedHashMap<TopicPartition, PartitionData> next;
public void add(TopicPartition topicPartition, PartitionData data) {
next.put(topicPartition, data);
}
}
}
// Builder#build
public FetchRequestData build() {
// return (this.epoch == INITIAL_EPOCH) || (this.epoch == FINAL_EPOCH);
if (nextMetadata.isFull()) {
// 1. 全量分区
sessionPartitions = next;
next = null;
Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> toSend =
Collections.unmodifiableMap(new LinkedHashMap<>(sessionPartitions));
return new FetchRequestData(toSend, Collections.emptyList(), toSend, nextMetadata);
}
// 2. 增量分区
List<TopicPartition> added = new ArrayList<>();
List<TopicPartition> removed = new ArrayList<>();
List<TopicPartition> altered = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历session中的分区
for (Iterator<Entry<TopicPartition, PartitionData>> iter =
sessionPartitions.entrySet().iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
Entry<TopicPartition, PartitionData> entry = iter.next();
TopicPartition topicPartition = entry.getKey();
PartitionData prevData = entry.getValue();
PartitionData nextData = next.remove(topicPartition);
if (nextData != null) {
// case1 分区变更,比如fetch位点变更,加入altered
if (!prevData.equals(nextData)) {
next.put(topicPartition, nextData);
entry.setValue(nextData);
altered.add(topicPartition);
}
} else {
// case2 分区移除(rebalance),加入removed
iter.remove();
removed.add(topicPartition);
}
}
// case3 分区新增(rebalance)
for (Entry<TopicPartition, PartitionData> entry : next.entrySet()) {
TopicPartition topicPartition = entry.getKey();
PartitionData nextData = entry.getValue();
if (sessionPartitions.containsKey(topicPartition)) {
break;
}
sessionPartitions.put(topicPartition, nextData);
added.add(topicPartition);
}
Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> toSend = Collections.unmodifiableMap(next);
Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> curSessionPartitions =
Collections.unmodifiableMap(new LinkedHashMap<>(sessionPartitions));
next = null;
// toSend=新增或修改分区,toForget=移除分区
return new FetchRequestData(toSend, Collections.unmodifiableList(removed),
curSessionPartitions, nextMetadata);
}返回FetchRequestData包含以下数据:
java
public static class FetchRequestData {
// 本次需要拉取数据的分区 - 分区数据
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> toSend;
// 需要停止消费的分区
private final List<TopicPartition> toForget;
// 所有需要消费的分区 - 分区数据
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> sessionPartitions;
// sessionId,epoch 二元组
private final FetchMetadata metadata;
}
// FetchRequest.PartitionData
public static final class PartitionData {
// 消费进度
public final long fetchOffset;
// 固定-1
public final long logStartOffset;
// max.partition.fetch.bytes=1mb
// 一次FetchRequest中的单分区最大拉取的字节数
public final int maxBytes;
// 当前分区leaderEpoch
public final Optional<Integer> currentLeaderEpoch;
}FetchRequest:注意consumer传入长轮询相关参数:
1)minBytes=fetch.min.bytes,默认1字节。broker只要有消息就直接响应;
2)maxWait=fetch.max.wait.ms,默认500ms。待消费消息不足minBytes,FetchRequest被broker挂起的时长;
java
public class FetchRequest extends AbstractRequest {
// 副本id,消费者固定-1
private final int replicaId;
// fetch.max.wait.ms=500
// 如果消息不足minBytes个字节,FetchRequest在server端被block的时长
private final int maxWait;
// fetch.min.bytes=1
// 如果消息不足minBytes个字节,FetchRequest在server端被block
private final int minBytes;
// fetch.max.bytes=50mb 一次FetchRequest最大拉取的字节数
private final int maxBytes;
// 隔离级别,没事务消息,默认READ_UNCOMMITTED
private final IsolationLevel isolationLevel;
// 需要消费 且 新增或修改的分区 - 分区数据 FetchRequest.PartitionData
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionData> fetchData;
// 需要停止消费的分区
private final List<TopicPartition> toForget;
// sessionId,epoch 二元组
private final FetchMetadata metadata;
// client.rack=null, 忽略
private final String rackId;
}3-2-3、broker处理FetchRequest
3-2-3-1、更新Session
FetchManager#newContext:
1)如果sessionId为空,创建FullFetchContext,新session会在响应阶段创建;
2)否则根据FetchRequest更新Session的分区,session epoch+1;
scala
class FetchManager(private val time: Time,
private val cache: FetchSessionCache) extends Logging {
def newContext(reqMetadata: JFetchMetadata,
fetchData: FetchSession.REQ_MAP,
toForget: util.List[TopicPartition],
isFollower: Boolean): FetchContext = {
val context = if (reqMetadata.isFull) {
val context = if (reqMetadata.epoch == FINAL_EPOCH) {
new SessionlessFetchContext(fetchData)
} else {
// 新session会在响应时创建
new FullFetchContext(time, cache, reqMetadata, fetchData, isFollower)
}
context
} else {
cache.synchronized {
cache.get(reqMetadata.sessionId) match {
case Some(session) => session.synchronized {
// 更新session,比如哪些分区要更新,哪些分区要移除
val (added, updated, removed) = session.update(fetchData, toForget, reqMetadata)
if (session.isEmpty) {
cache.remove(session)
new SessionlessFetchContext(fetchData)
} else {
cache.touch(session, time.milliseconds())
// session epoch +1
session.epoch = JFetchMetadata.nextEpoch(session.epoch)
new IncrementalFetchContext(time, reqMetadata, session)
}
}
}
}
}
context
}
}3-2-3-2、拉消息
回顾第四章。
数据目录下的唯一目录={Topic}-{PartitionId},如Test1-0,存储了每个分区的数据,称为Log。
sql
tree -a
.
├── .kafka_cleanshutdown
├── .lock
├── Test1-0 # topic-partitionId
│ ├── 00000000000000000000.index
│ ├── 00000000000000000000.log
│ ├── 00000000000000000000.timeindex
│ ├── 00000000000000001872.index
│ ├── 00000000000000001872.log
│ ├── 00000000000000001872.timeindex
│ └── leader-epoch-checkpoint
├── cleaner-offset-checkpoint
├── log-start-offset-checkpoint
├── meta.properties
├── recovery-point-offset-checkpoint
└── replication-offset-checkpointLog数据由多个Segment 组成,如0000是第一个segment,1872是第二个segment,文件名是该segment的起始offset(baseOffset) ,如0000存储了offset=[0,1872)共1872条消息。
每个Segment由4个文件构成:
a)log:消息数据文件,追加写,大小超过segment.bytes=1G触发滚动;
b)index:offset索引文件,通过mmap读写,大小=segment.index.bytes=10M;
c)timeindex:时间索引文件;
d)txnindex:中断事务索引文件;
消息以批次格式写入 ,broker每超出4KB大小生成一个索引项。
拉消息需要用到index索引,index索引项包含两部分:
1)key=offset-baseOffset(4byte),是一个批次消息的结束offset ,即该批次的最后一条消息对应的offset;
2)value=消息在log的写入位置(4byte),即一个批次消息的开始物理位置;
KafkaApis#handleFetchRequest:循环所有session中所有分区拉取消息。
scala
def handleFetchRequest(request: RequestChannel.Request): Unit = {
val fetchRequest = request.body[FetchRequest]
// 更新session,创建fetchContext
val fetchContext = fetchManager.newContext(
fetchRequest.metadata, fetchRequest.fetchData,
fetchRequest.toForget, fetchRequest.isFromFollower)
val interesting = mutable.ArrayBuffer[(TopicPartition, FetchRequest.PartitionData)]()
if (fetchRequest.isFromFollower) {
} else {
val partitionMap = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[(TopicPartition, FetchRequest.PartitionData)]
// 循环session中所有分区
fetchContext.foreachPartition { (topicPartition, partitionData) =>
// 分区 -> 分区请求数据
partitionMap += topicPartition -> partitionData
}
partitionMap.foreach { case (topicPartition, data) =>
// 权限...
// 分区 -> 分区请求数据
interesting += (topicPartition -> data)
}
}
if (interesting.isEmpty)
processResponseCallback(Seq.empty)
else {
replicaManager.fetchMessages(
fetchRequest.maxWait.toLong, fetchRequest.replicaId,
fetchMinBytes, fetchMaxBytes,
versionId <= 2, interesting, // session分区 -> 分区数据
replicationQuota(fetchRequest), processResponseCallback,
fetchRequest.isolationLevel, clientMetadata)
}
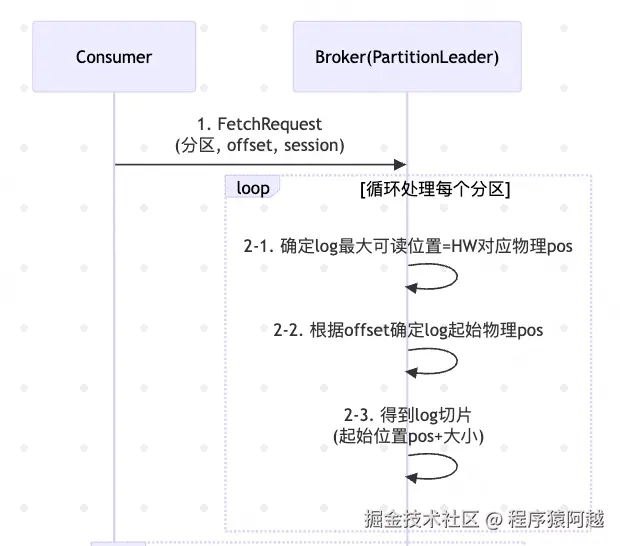
}Log#read:针对某个分区拉取消息。
1)根据隔离级别,确定最大可读offset和对应物理位置;
2)执行Segment#read,传入startOffset=消费进度、maxLength=分区最大可读字节数、maxPosition=最大可读物理位置,返回FetchDataInfo;
scala
def read(startOffset: Long,
maxLength: Int,
isolation: FetchIsolation,
minOneMessage: Boolean): FetchDataInfo = {
val includeAbortedTxns = isolation == FetchTxnCommitted
// LEO(LogEndOffset)当前写进度
val endOffsetMetadata = nextOffsetMetadata
val endOffset = endOffsetMetadata.messageOffset
// 根据 消费位点 找起始segment
var segmentEntry = segments.floorEntry(startOffset)
// 根据隔离级别,决定最大可读offset
val maxOffsetMetadata = isolation match {
// follower拉消息 取LEO
case FetchLogEnd => endOffsetMetadata
// 消费者拉消息 READ_UNCOMMITTED 高水位
case FetchHighWatermark => fetchHighWatermarkMetadata
// 消费者拉消息 事务消息 READ_COMMITTED LastStableOffset(LSO)
case FetchTxnCommitted => fetchLastStableOffsetMetadata
}
if (startOffset == maxOffsetMetadata.messageOffset) {
// 如果 消费位点 和 最大可读offset 一致,说明没消息,直接返回空
return emptyFetchDataInfo(maxOffsetMetadata, includeAbortedTxns)
}
while (segmentEntry != null) {
val segment = segmentEntry.getValue
// segment最大可读物理位置
val maxPosition = {
if (maxOffsetMetadata.segmentBaseOffset == segment.baseOffset) {
// 如果最大可读offset在当前segment,max=比如高水位对应物理位置
maxOffsetMetadata.relativePositionInSegment
} else {
// 如果最大可读offset不在当前segment,max=segment大小
segment.size
}
}
// segment读
val fetchInfo = segment.read(startOffset, maxLength, maxPosition, minOneMessage)
if (fetchInfo == null) {
segmentEntry = segments.higherEntry(segmentEntry.getKey)
} else {
// 返回fetchInfo
return if (includeAbortedTxns)
addAbortedTransactions(startOffset, segmentEntry, fetchInfo)
else
fetchInfo
}
}
FetchDataInfo(nextOffsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY)
}LogSegment#read:【核心方法 】利用 offset索引 定位 log可读数据。
scala
def read(startOffset: Long, // 消费进度
maxSize: Int, // 分区最大返回字节数1mb
maxPosition: Long = size, // 高水位对应物理position
minOneMessage: Boolean = false): FetchDataInfo = {
// 【focus】入参=消费进度,出参=第一个要读取的消息批次(物理位置,大小)
// 读索引和数据的主要逻辑
val startOffsetAndSize = translateOffset(startOffset)
if (startOffsetAndSize == null)
return null
val startPosition = startOffsetAndSize.position
// 消费进度,segment起始offset,读取物理position开始
val offsetMetadata = LogOffsetMetadata(startOffset, this.baseOffset, startPosition)
// minOneMessage=true,本次fetch还未读取到任何一个分区的消息,如果批次大于maxSize也要读
val adjustedMaxSize =
if (minOneMessage) math.max(maxSize, startOffsetAndSize.size)
else maxSize
if (adjustedMaxSize == 0)
return FetchDataInfo(offsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY)
val fetchSize: Int = min((maxPosition - startPosition).toInt, adjustedMaxSize)
// 【focus】log=FileRecords=当前segment的log文件,按照(开始物理位置,最大可读物理位置)切片
FetchDataInfo(offsetMetadata, log.slice(startPosition, fetchSize),
firstEntryIncomplete = adjustedMaxSize < startOffsetAndSize.size)
}关键点:
1)生产者侧,多个消息会合并为一个批次发送;broker侧,以原始批次存储;消费者侧,以批次维度拉取 ,如果fetch请求还未拉取到消息(minOneMessage=true),但是首批消息超过分区消息大小限制(消费者配置max.partition.fetch.bytes=1mb),仍然允许拉取;
2)已知消费进度startOffset ,得到拉取的起始批次的物理位置startOffsetAndSize.position;
3)已知最大拉取字节数maxSize 和拉取物理位置限制maxPosition ,得到最终可拉取log数据大小fetchSize=min(maxSize,maxPosition) ;
4)通过2和3,返回n个消息批次在log文件中的物理位置log.slice;
假设当前消费进度为500,则Segment拉取消息的逻辑如下:
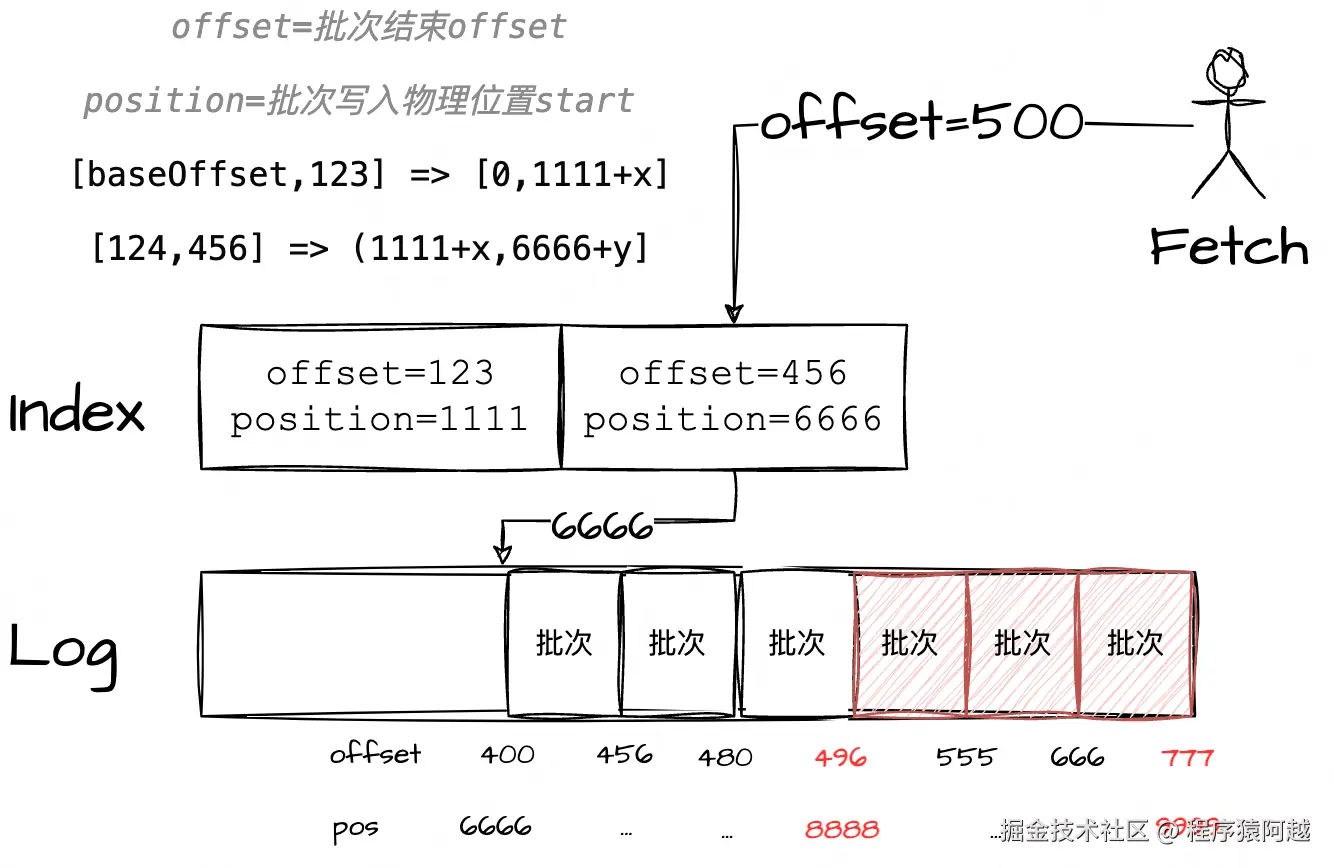
Step1,OffsetIndex#lookup,找到小于等于offset(500)的最大索引项(456,6666);
这里使用二分查找。不过KAFKA-6432做了优化,因为一般拉取的是最新的消息,优先从最新一页的索引项里做二分(8192/10=最后819个索引项),充分利用mmap的pagecache缓存。
Step2,FileRecords#searchForOffsetWithSize,从1返回的物理位置(6666)向后遍历,找到第一个包含请求offset的批次(结束offset=555);
Step3,FileRecords#slice,根据拉取数据大小限制(1mb和高水位),返回Log文件的数据范围(物理位置8888,大小1111),后续可以通过迭代器访问n个消息批次;
java
// 是否为slice=true
private final boolean isSlice;
// 开始物理位置
private final int start;
// 结束物理位置
private final int end;
// 批次迭代器
private final Iterable<FileLogInputStream.FileChannelRecordBatch> batches;
// 数据大小
private final AtomicInteger size;
private final FileChannel channel;
private volatile File file;
public FileRecords slice(int position, int size) throws IOException {
int currentSizeInBytes = sizeInBytes();
int end = this.start + position + size;
if (end < 0 || end > start + currentSizeInBytes)
end = start + currentSizeInBytes;
return new FileRecords(file, channel, this.start + position, end, true);
}
FileRecords(File file, FileChannel channel,
int start, int end, boolean isSlice) throws IOException {
this.file = file;
this.channel = channel;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.isSlice = isSlice;
this.size = new AtomicInteger();
if (isSlice) {
// 大小
size.set(end - start);
} else {
// ...
}
batches = batchesFrom(start);
}
}
public Iterable<FileChannelRecordBatch> batchesFrom(final int start) {
return () -> batchIterator(start);
}
private AbstractIterator<FileChannelRecordBatch> batchIterator(int start) {
final int end;
if (isSlice) // here
end = this.end;
else
end = this.sizeInBytes();
FileLogInputStream inputStream = new FileLogInputStream(this, start, end);
return new RecordBatchIterator<>(inputStream);
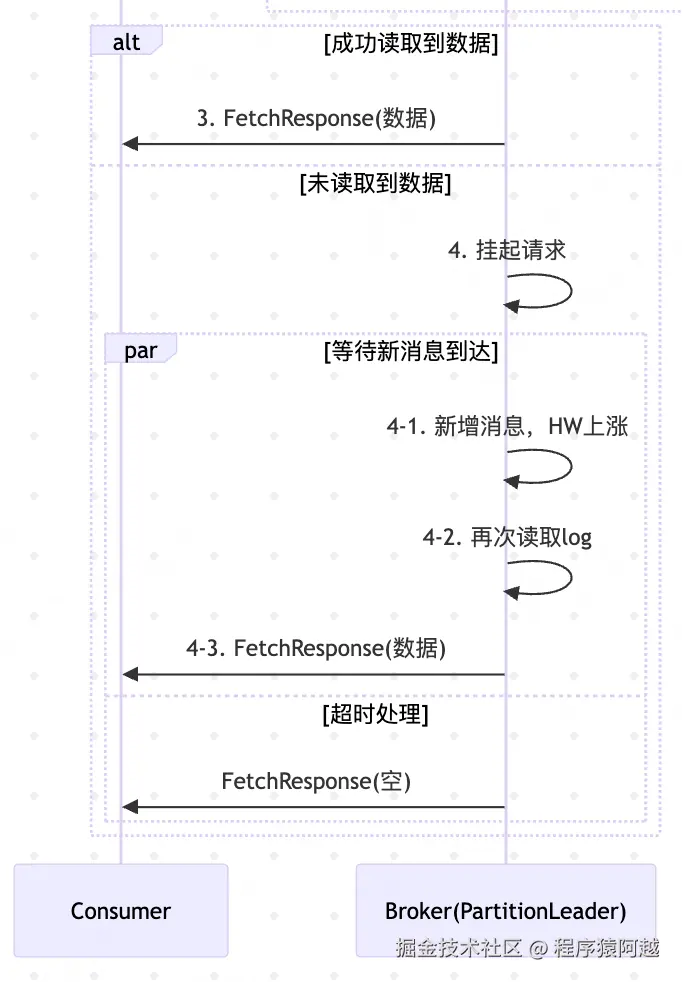
}3-2-3-4、读到消息-回复响应
ReplicaManager#fetchMessages:如果bytesReadable≥fetchMinBytes,默认fetchMinBytes=1字节,只要任意分区读到消息,就回复FetchResponse。
scala
if (timeout <= 0 || fetchInfos.isEmpty || bytesReadable >= fetchMinBytes || errorReadingData) {
val fetchPartitionData = logReadResults.map { case (tp, result) =>
tp -> FetchPartitionData(result.error, result.highWatermark,
result.leaderLogStartOffset,
result.info.records,
result.lastStableOffset, ...)
}
// 回复响应
responseCallback(fetchPartitionData)
} else {
// 没读到消息...
}FullFetchContext#updateAndGenerateResponseData:首次fetch请求创建session,将全量分区拉取情况(updates)加入fetch响应,并缓存到session中。
scala
type RESP_MAP = util.LinkedHashMap[TopicPartition, FetchResponse.PartitionData[Records]]
override def updateAndGenerateResponseData(updates: FetchSession.RESP_MAP): FetchResponse[Records] = {
def createNewSession: FetchSession.CACHE_MAP = {
val cachedPartitions = new FetchSession.CACHE_MAP(updates.size)
// 循环所有分区,加入session
updates.forEach { (part, respData) =>
val reqData = fetchData.get(part)
cachedPartitions.mustAdd(new CachedPartition(part, reqData, respData))
}
cachedPartitions
}
// 创建session并缓存
val responseSessionId = cache.maybeCreateSession(time.milliseconds(), isFromFollower,
updates.size, () => createNewSession)
new FetchResponse(Errors.NONE, updates, 0, responseSessionId)
}
// sessionId生成算法,随机正整数,唯一
def newSessionId(): Int = synchronized {
var id = 0
do {
id = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1, Int.MaxValue)
} while (sessions.contains(id) || id == INVALID_SESSION_ID)
id
}ncrementalFetchContext#updateAndGenerateResponseData:非首次fetch,PartitionInterator过滤分区是否需要响应,当有数据或有异常或HW等offset变更,分区会加入fetch响应。
scala
override def updateAndGenerateResponseData(updates: FetchSession.RESP_MAP): FetchResponse[Records] = {
session.synchronized {
// 用迭代器,判断拉取结果
val partitionIter = new PartitionIterator(updates.entrySet.iterator, true)
while (partitionIter.hasNext) {
partitionIter.next()
}
new FetchResponse(Errors.NONE, updates, 0, session.id)
}
}
// CachedPartition#maybeUpdateResponseData 判断分区是否需要响应
def maybeUpdateResponseData(respData: FetchResponse.PartitionData[Records], updateResponseData: Boolean): Boolean = {
// Check the response data.
var mustRespond = false
if ((respData.records != null) && (respData.records.sizeInBytes > 0)) {
mustRespond = true
}
if (highWatermark != respData.highWatermark) {
mustRespond = true
if (updateResponseData)
highWatermark = respData.highWatermark
}
if (localLogStartOffset != respData.logStartOffset) {
mustRespond = true
if (updateResponseData)
localLogStartOffset = respData.logStartOffset
}
if (respData.preferredReadReplica.isPresent) {
mustRespond = true
}
if (respData.error.code != 0) {
if (updateResponseData)
highWatermark = -1
mustRespond = true
}
mustRespond
}FetchResponse最终如下,注意每个分区的records即为FileRecords(上面拉消息返回的FileRecords#slice)。
java
public class FetchResponse<T extends BaseRecords> extends AbstractResponse {
// sessionId
private final int sessionId;
// 分区-分区数据
private final LinkedHashMap<TopicPartition, PartitionData<T>> responseData;
}
public static final class PartitionData<T extends BaseRecords> {
public final Errors error;
// 分区高水位
public final long highWatermark;
// 分区LSO(事务)
public final long lastStableOffset;
// 分区LogStartOffset
public final long logStartOffset;
public final Optional<Integer> preferredReadReplica;
public final List<AbortedTransaction> abortedTransactions;
// 批次数据记录FileRecords
public final T records;
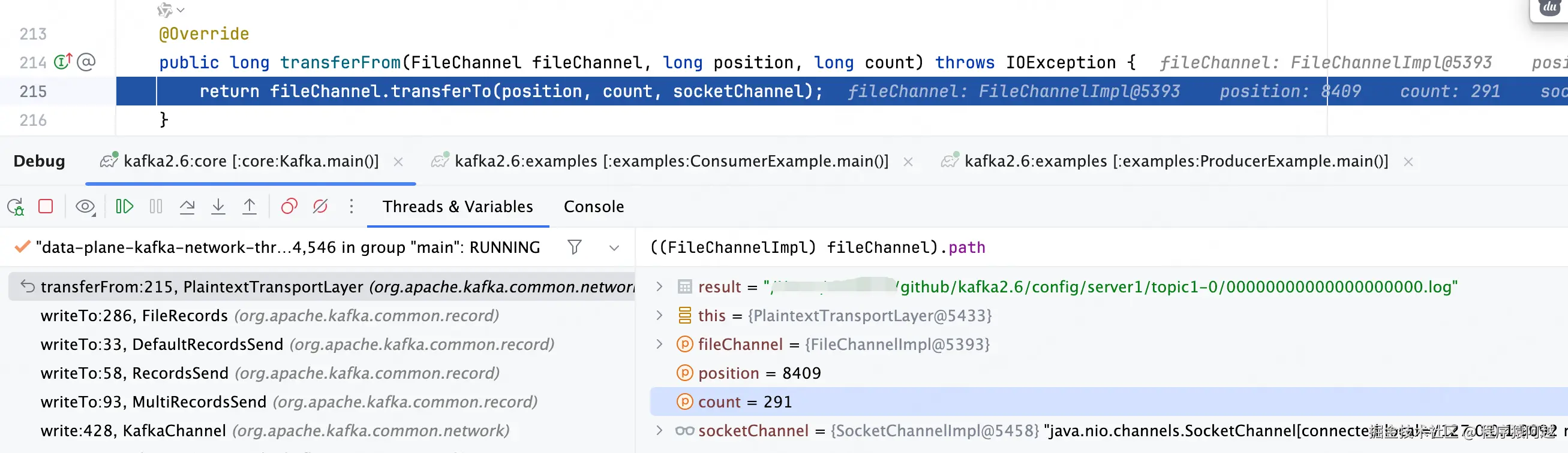
}最终每个分区的FileRecords会通过transferTo零拷贝技术写入通讯channel。
PlaintextTransportLayer#transferFrom:比如下图是0号segment的log,物理偏移量8409,长度291,包含n个批次。
3-2-3-5、未读到消息-挂起请求
ReplicaManager#fetchMessages:如果没读到消息,需要把当前FetchRequest挂起。
scala
if (timeout <= 0 || fetchInfos.isEmpty || bytesReadable >= fetchMinBytes || errorReadingData) {
// 2-2-3-4 读到数据直接响应
} else {
// 分区 -> (本次fetch得到的offset,请求offset)
val fetchPartitionStatus = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[(TopicPartition, FetchPartitionStatus)]
fetchInfos.foreach { case (topicPartition, partitionData) =>
logReadResultMap.get(topicPartition).foreach(logReadResult => {
val logOffsetMetadata = logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata
fetchPartitionStatus += (topicPartition -> FetchPartitionStatus(logOffsetMetadata, partitionData))
})
}
// fetch请求参数 + fetchPartitionStatus
val fetchMetadata: SFetchMetadata = SFetchMetadata(fetchMinBytes, fetchMaxBytes, hardMaxBytesLimit,
fetchOnlyFromLeader, fetchIsolation, isFromFollower, replicaId, fetchPartitionStatus)
val delayedFetch = new DelayedFetch(timeout, fetchMetadata, this, quota, clientMetadata,
responseCallback)
val delayedFetchKeys = fetchPartitionStatus.map { case (tp, _) => TopicPartitionOperationKey(tp) }
// 执行DelayedFetch.tryComplete,失败后提交延迟任务,延迟时长=maxWait=500ms
delayedFetchPurgatory.tryCompleteElseWatch(delayedFetch, delayedFetchKeys)
}DelayedFetch#tryComplete:在挂起fetch请求前,再次获取最大可读位点,如果有新消息到来(fetchMinBytes=fetch.min.bytes默认1byte),onComplete会再次发起读消息,完成响应。
scala
override def tryComplete(): Boolean = {
var accumulatedSize = 0
fetchMetadata.fetchPartitionStatus.foreach {
case (topicPartition, fetchStatus) =>
val fetchOffset = fetchStatus.startOffsetMetadata
val fetchLeaderEpoch = fetchStatus.fetchInfo.currentLeaderEpoch
try {
if (fetchOffset != LogOffsetMetadata.UnknownOffsetMetadata) {
val partition = replicaManager.getPartitionOrException(topicPartition)
// 再次获取 LEO/HW/LSO 等位点
val offsetSnapshot = partition.fetchOffsetSnapshot(fetchLeaderEpoch, fetchMetadata.fetchOnlyLeader)
val endOffset = fetchMetadata.fetchIsolation match {
case FetchLogEnd => offsetSnapshot.logEndOffset
case FetchHighWatermark => offsetSnapshot.highWatermark
case FetchTxnCommitted => offsetSnapshot.lastStableOffset
}
// fetch请求offset < 可读位点,有新数据到来
if (fetchOffset.messageOffset < endOffset.messageOffset) {
val bytesAvailable = math.min(
endOffset.positionDiff(fetchOffset),
fetchStatus.fetchInfo.maxBytes)
// 累加可以读到的字节
accumulatedSize += bytesAvailable
}
}
} catch {
// ...
return forceComplete()
}
}
// 可读数据大小 超过 默认1byte,forceComplete再次读log数据返回
if (accumulatedSize >= fetchMetadata.fetchMinBytes)
forceComplete()
else
false
}
// 满足tryCompelete方法或超时,再次读取后响应
override def onComplete(): Unit = {
val logReadResults = replicaManager.readFromLocalLog(
// ...
// 分区-offset
readPartitionInfo = fetchMetadata.fetchPartitionStatus.map
{ case (tp, status) => tp -> status.fetchInfo })
// 组装结果
val fetchPartitionData = logReadResults.map { case (tp, result) =>
tp -> FetchPartitionData(result.error, result.highWatermark, result.leaderLogStartOffset, result.info.records,
result.lastStableOffset, result.info.abortedTransactions, result.preferredReadReplica,
fetchMetadata.isFromFollower && replicaManager.isAddingReplica(tp, fetchMetadata.replicaId))
}
// 响应
responseCallback(fetchPartitionData)
}如果fetch请求被挂起,当HW发生变化会再次触发DelayedFetch#tryComplete,判断是否满足响应条件,如果满足则执行DelayedFetch#onComplete读数据回复FetchResponse。
Partition#updateFollowerFetchState:比如follower从leader拉消息触发HW高水位增加。
scala
def updateFollowerFetchState(followerId: Int,
followerFetchOffsetMetadata: LogOffsetMetadata,
followerStartOffset: Long,
followerFetchTimeMs: Long,
leaderEndOffset: Long): Boolean = {
getReplica(followerId) match {
case Some(followerReplica) =>
// ...
if (leaderLWIncremented || leaderHWIncremented)
tryCompleteDelayedRequests()
true
}
}
// Partition#tryCompleteDelayedRequests
private def tryCompleteDelayedRequests(): Unit = delayedOperations.checkAndCompleteAll()
// DelayedOperations#checkAndCompleteAll
class DelayedOperations(topicPartition: TopicPartition,
produce: DelayedOperationPurgatory[DelayedProduce],
fetch: DelayedOperationPurgatory[DelayedFetch]) {
def checkAndCompleteAll(): Unit = {
val requestKey = TopicPartitionOperationKey(topicPartition)
// 尝试完成fetch请求
fetch.checkAndComplete(requestKey)
// 尝试完成produce请求
produce.checkAndComplete(requestKey)
deleteRecords.checkAndComplete(requestKey)
}
}如果500ms超时 ,则执行DelayedFetch#onComplete读数据回复FetchResponse。
3-2-4、consumer处理FetchResponse
Fetcher#sendFetches:
1)FetchSessionHandler校验FetchResponse符合要求;
2)将拉取消息结果加入completedFetches队列;
java
private final ConcurrentLinkedQueue<CompletedFetch> completedFetches;
public synchronized int sendFetches() {
// 循环所有broker发送fetch请求
// ...
// 处理每个fetch响应
future.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<ClientResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(ClientResponse resp) {
synchronized (Fetcher.this) {
try {
FetchResponse<Records> response = (FetchResponse<Records>) resp.responseBody();
// 1. session处理
FetchSessionHandler handler = sessionHandler(fetchTarget.id());
if (!handler.handleResponse(response)) {
return;
}
Set<TopicPartition> partitions = new HashSet<>(response.responseData().keySet());
FetchResponseMetricAggregator metricAggregator = new FetchResponseMetricAggregator(sensors, partitions);
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, FetchResponse.PartitionData<Records>> entry : response.responseData().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition partition = entry.getKey();
FetchRequest.PartitionData requestData = data.sessionPartitions().get(partition);
long fetchOffset = requestData.fetchOffset;
FetchResponse.PartitionData<Records> partitionData = entry.getValue();
Iterator<? extends RecordBatch> batches = partitionData.records.batches().iterator();
short responseVersion = resp.requestHeader().apiVersion();
// 2. 加入缓存队列completedFetches
completedFetches.add(new CompletedFetch(partition, partitionData,
metricAggregator, batches, fetchOffset, responseVersion));
}
} finally {
nodesWithPendingFetchRequests.remove(fetchTarget.id());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) {
synchronized (Fetcher.this) {
try {
FetchSessionHandler handler = sessionHandler(fetchTarget.id());
if (handler != null) {
handler.handleError(e);
}
} finally {
nodesWithPendingFetchRequests.remove(fetchTarget.id());
}
}
}
});
return fetchRequestMap.size();
}FetchSessionHandler#handleResponse:
1)返回异常,标记session回到INITIAL_EPOCH,下次会发起全量FetchRequest;
2)新session,校验响应分区=全量session分区,保存response.sessionId,epoch++;
3)已存在session,校验响应分区在session中,epoch++;
java
public boolean handleResponse(FetchResponse<?> response) {
if (response.error() != Errors.NONE) {
log.info("Node {} was unable to process the fetch request with {}: {}.",
node, nextMetadata, response.error());
if (response.error() == Errors.FETCH_SESSION_ID_NOT_FOUND) {
nextMetadata = FetchMetadata.INITIAL;
} else {
// new FetchMetadata(sessionId, INITIAL_EPOCH);
nextMetadata = nextMetadata.nextCloseExisting();
}
return false;
}
if (nextMetadata.isFull()) {
// 新session,校验 响应分区 = 全量session分区
String problem = verifyFullFetchResponsePartitions(response);
if (problem != null) {
nextMetadata = FetchMetadata.INITIAL;
return false;
} else if (response.sessionId() == INVALID_SESSION_ID) {
nextMetadata = FetchMetadata.INITIAL;
return true;
} else {
// sessionId=res.sessionId,epoch++
nextMetadata = FetchMetadata.newIncremental(response.sessionId());
return true;
}
} else {
// 老session,校验 响应分区 包含在 session 中
String problem = verifyIncrementalFetchResponsePartitions(response);
if (problem != null) {
nextMetadata = nextMetadata.nextCloseExisting();
return false;
} else if (response.sessionId() == INVALID_SESSION_ID) {
nextMetadata = FetchMetadata.INITIAL;
return true;
} else {
// epoch++
nextMetadata = nextMetadata.nextIncremental();
return true;
}
}
}
public void handleError(Throwable t) {
log.info("Error sending fetch request {} to node {}:", nextMetadata, node, t);
// new FetchMetadata(sessionId, INITIAL_EPOCH);
nextMetadata = nextMetadata.nextCloseExisting();
}3-3、从缓存拉取消息
从Rebalance来说(HeartbeatThread#run),如果用户处理poll返回的一批消息超过max.poll.interval.ms=5分钟 ,consumer则会在与coordinator的心跳线程中,主动发送LeaveGroup,导致Rebalance。
为了避免这种Rebalance,一方面需要提升消费速度,另一方面可以通过配置max.poll.records(默认500) 来控制每次KafkaConsumer#poll返回的消息数量。
但是从FetchRequest来说:1)按照消息批次完整拉取 ;2)每个分区按照大小限制 拉取max.partition.fetch.bytes=1mb;
Consumer侧,按照实际消费进度 和最大消息数量,拆分消息批次。
Fetcher#fetchedRecords:迭代消息缓存队列completedFetches ,其中每个CompletedFetch元素包含n个消息批次。每次从CompletedFetch拉取后,更新分区消费位点,下次使用新位点发送FetchRequest。
java
// FetchRequest拉来的消息缓存,CompletedFetch包含同一个分区的n个消息批次
private final ConcurrentLinkedQueue<CompletedFetch> completedFetches;
// 正在被消费的CompletedFetch
private CompletedFetch nextInLineFetch = null;
public Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> fetchedRecords() {
// 分区 - 拉取到的消息
Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> fetched = new HashMap<>();
// maxPollRecords=max.poll.records=500
int recordsRemaining = maxPollRecords;
try {
while (recordsRemaining > 0) {
if (nextInLineFetch == null || nextInLineFetch.isConsumed) {
// 1. 从completedFetches获取一个分区的CompletedFetch做初始化
CompletedFetch records = completedFetches.peek();
if (records == null) break;
if (records.notInitialized()) {
// 更新HW等offset到订阅状态,records.notInitialized()=false
nextInLineFetch = initializeCompletedFetch(records);
}
completedFetches.poll();
} else {
// 2. 从当前正在处理的分区中获取数据,数量限制=recordsRemaining
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> records = fetchRecords(nextInLineFetch, recordsRemaining);
if (!records.isEmpty()) {
TopicPartition partition = nextInLineFetch.partition;
fetched.put(partition, records);
recordsRemaining -= records.size();
}
}
}
} catch (KafkaException e) {
if (fetched.isEmpty())
throw e;
}
return fetched;
}
private List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> fetchRecords(CompletedFetch completedFetch, int maxRecords) {
FetchPosition position = subscriptions.position(completedFetch.partition);
// 从CompletedFetch获取消息,移动nextFetchOffset位置
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> partRecords = completedFetch.fetchRecords(maxRecords);
if (completedFetch.nextFetchOffset > position.offset) {
// nextFetchOffset发生改变,更新消费位点
FetchPosition nextPosition = new FetchPosition(
completedFetch.nextFetchOffset,
completedFetch.lastEpoch,
position.currentLeader);
}
return partRecords;
// completedFetch.isConsumed=true,标记completedFetch消费完了
completedFetch.drain();
return emptyList();
}
private List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> fetchRecords(CompletedFetch completedFetch, int maxRecords) {
FetchPosition position = subscriptions.position(completedFetch.partition);
if (completedFetch.nextFetchOffset == position.offset) {
// 从CompletedFetch获取消息,移动nextFetchOffset位置
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> partRecords = completedFetch.fetchRecords(maxRecords);
if (completedFetch.nextFetchOffset > position.offset) {
// nextFetchOffset发生改变,更新消费位点
FetchPosition nextPosition = new FetchPosition(
completedFetch.nextFetchOffset,
completedFetch.lastEpoch,
position.currentLeader);
subscriptions.position(completedFetch.partition, nextPosition);
}
return partRecords;
}
// completedFetch.isConsumed=true,标记completedFetch消费完了
completedFetch.drain();
return emptyList();
}Fetcher.CompletedFetch#fetchRecords:一个CompletedFetch又包含n个批次,需要迭代批次,然后迭代批次里的消息。
java
// 批次的迭代器
private final Iterator<? extends RecordBatch> batches;
// 正在迭代的批次的消息迭代器
private CloseableIterator<Record> records;
// 正在迭代的批次
private RecordBatch currentBatch;
// 已经处理的最后一个消息
private Record lastRecord;
// 当前迭代到的offset
private long nextFetchOffset;
private List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> fetchRecords(int maxRecords) {
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> records = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < maxRecords; i++) {
lastRecord = nextFetchedRecord();
records.add(parseRecord(partition, currentBatch, lastRecord));
nextFetchOffset = lastRecord.offset() + 1;
}
return records;
}
private Record nextFetchedRecord() {
while (true) {
if (records == null || !records.hasNext()) {
// 刚开始迭代 || 当前批次迭代完毕
maybeCloseRecordStream();
// completeFetch
if (!batches.hasNext()) {
drain();
return null;
}
// 迭代消息批次
currentBatch = batches.next();
maybeEnsureValid(currentBatch);
records = currentBatch.streamingIterator(decompressionBufferSupplier);
} else {
// 迭代消息批次里的消息
Record record = records.next();
// 跳过消费进度前的消息,
// 因为消息只能按照批次拉取,所以需要在consumer侧跳过
if (record.offset() >= nextFetchOffset) {
maybeEnsureValid(record);
if (!currentBatch.isControlBatch()) {
return record;
} else {
nextFetchOffset = record.offset() + 1;
}
}
}
}
}DefaultRecordBatch#streamingIterator:迭代消息过程中,完成消息解压,实现端到端压缩。
java
public CloseableIterator<Record> streamingIterator(BufferSupplier bufferSupplier) {
if (isCompressed())
return compressedIterator(bufferSupplier, false);
else
return uncompressedIterator();
}最终返回给用户的ConsumerRecords,实际上是按照分区分组的,通过迭代器按序迭代n个分区的m条消息。
java
public class ConsumerRecords<K, V> implements Iterable<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> {
private final Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records;
public ConsumerRecords(Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records) {
this.records = records;
}
public Iterator<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> iterator() {
return new ConcatenatedIterable<>(records.values()).iterator();
}
}四、提交消费进度
4-1、自动提交消费进度的入口
默认情况下,enable.auto.commit=true,自动提交消费进度。
KafkaConsumer#poll→ConsumerCoordinator#poll:自动提交场景1 ,每次执行poll api都会触发自动提交检测,超过auto.commit.interval.ms=5000ms会触发。
java
public boolean poll(Timer timer, boolean waitForJoinGroup) {
// 尝试更新metadataSnapshot=当前的metadata
maybeUpdateSubscriptionMetadata();
invokeCompletedOffsetCommitCallbacks();
if (subscriptions.hasAutoAssignedPartitions()) {
// case1 精确订阅 / 正则订阅
// 唤醒kafka-coordinator-heartbeat-thread线程
// 更新 Heartbeat 上次 poll 时间
// 维持 max.poll.interval.ms = 5m 避免触发 rebalance
pollHeartbeat(timer.currentTimeMs());
// Step1,发现Coordinator FindCoordinatorRequest 确保Coordinator连接建立
if (coordinatorUnknown() && !ensureCoordinatorReady(timer)) {
return false;
}
// Step2,尝试重新进组
if (rejoinNeededOrPending()) {
// ...
// 消费者进组 JoinGroupRequest + SyncGroupRequest
if (!ensureActiveGroup(waitForJoinGroup ? timer : time.timer(0L))) {
timer.update(time.milliseconds());
return false;
}
}
}
// 自动提交offset
maybeAutoCommitOffsetsAsync(timer.currentTimeMs());
return true;
}
public void maybeAutoCommitOffsetsAsync(long now) {
if (autoCommitEnabled) {
nextAutoCommitTimer.update(now);
// auto.commit.interval.ms=5000
if (nextAutoCommitTimer.isExpired()) {
nextAutoCommitTimer.reset(autoCommitIntervalMs);
doAutoCommitOffsetsAsync();
}
}
}ConsumerCoordinator#onJoinPrepare:自动提交场景2,rebalance前,同步提交消费进度。
java
protected void onJoinPrepare(int generation, String memberId) {
maybeAutoCommitOffsetsSync
(time.timer(rebalanceConfig.rebalanceTimeoutMs));
}ConsumerCoordinator#close:自动提交场景3,消费者关闭。
java
public void close(final Timer timer) {
// ...
maybeAutoCommitOffsetsSync(timer);
}4-2、consumer发送OffsetCommitRequest
SubscriptionState#allConsumed:搜集所有FETCHING状态的分区对应的消费进度,注意此处的消费进度在每次poll返回时就已经移动了,见Fetcher#fetchedRecords。
java
public synchronized Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> allConsumed() {
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> allConsumed = new HashMap<>();
assignment.stream().forEach(state -> {
TopicPartitionState partitionState = state.value();
if (partitionState.hasValidPosition())
allConsumed.put(state.topicPartition(),
new OffsetAndMetadata(partitionState.position.offset,
partitionState.position.offsetEpoch, ""));
});
return allConsumed;
}ConsumerCoordinator#commitOffsetsAsync:确保协调者存活,发送提交请求。
java
public void commitOffsetsAsync(final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, final OffsetCommitCallback callback) {
if (!coordinatorUnknown()) {
// 协调者存活,发送提交offset请求
doCommitOffsetsAsync(offsets, callback);
} else {
// 否则FindCoordinatorRequest,与协调者建立连接后发送提交offset请求
lookupCoordinator().addListener(new RequestFutureListener<Void>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void value) {
doCommitOffsetsAsync(offsets, callback);
client.pollNoWakeup();
}
});
}
client.pollNoWakeup();
}OffsetCommitRequestData:请求参数
java
public class OffsetCommitRequestData implements ApiMessage {
// 消费组id
private String groupId;
// 第几轮Rebalance
private int generationId;
// 成员id 协调者分配的
private String memberId;
// 静态成员id
private String groupInstanceId;
// 提交数据
private List<OffsetCommitRequestTopic> topics;
}
static public class OffsetCommitRequestTopic implements Message {
// topic
private String name;
// 分区
private List<OffsetCommitRequestPartition> partitions;
}
static public class OffsetCommitRequestPartition implements Message {
// 分区id
private int partitionIndex;
// 提交offset
private long committedOffset;
// 提交offset对应的leaderEpoch
private int committedLeaderEpoch;
}4-3、coordinator处理OffsetCommitRequest
GroupMetadataManager#storeOffsets:协调者会将本次提交请求作为一个消息批次,写入topic=__consumer_offsets,partition=分配协调者对应分区。其中每条消息的key=groupId+topic+partition,value=req.offset+req.leaderEpoch+broker收到请求的时间戳
scala
def storeOffsets(group: GroupMetadata,
consumerId: String,
offsetMetadata: immutable.Map[TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata],
responseCallback: immutable.Map[TopicPartition, Errors] => Unit,
producerId: Long = RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_ID,
producerEpoch: Short = RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_EPOCH): Unit = {
val filteredOffsetMetadata = offsetMetadata.filter { case (_, offsetAndMetadata) =>
validateOffsetMetadataLength(offsetAndMetadata.metadata)
}
val isTxnOffsetCommit = producerId != RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_ID
if (filteredOffsetMetadata.isEmpty) {
val commitStatus = offsetMetadata.map { case (k, _) => k -> Errors.OFFSET_METADATA_TOO_LARGE }
responseCallback(commitStatus)
None
} else {
getMagic(partitionFor(group.groupId)) match {
case Some(magicValue) =>
val timestampType = TimestampType.CREATE_TIME
val timestamp = time.milliseconds()
// 每个分区一条消息
val records = filteredOffsetMetadata.map { case (topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata) =>
// key = groupId + topic + partition
val key = GroupMetadataManager.offsetCommitKey(group.groupId, topicPartition)
// value = offset + leaderEpoch + 创建时间戳
val value = GroupMetadataManager.offsetCommitValue(offsetAndMetadata, interBrokerProtocolVersion)
new SimpleRecord(timestamp, key, value)
}
// topic=__consumer_offsets partition=分配协调者对应分区
val offsetTopicPartition = new TopicPartition(Topic.GROUP_METADATA_TOPIC_NAME, partitionFor(group.groupId))
// 这些消息作为一个消息批次写入
val buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytes(magicValue, compressionType, records.asJava))
val builder = MemoryRecords.builder(buffer, magicValue, compressionType, timestampType, 0L, time.milliseconds(),
producerId, producerEpoch, 0, isTxnOffsetCommit, RecordBatch.NO_PARTITION_LEADER_EPOCH)
records.foreach(builder.append)
val entries = Map(offsetTopicPartition -> builder.build())
// 写消息
appendForGroup(group, entries, putCacheCallback)
}
}
}GroupMetadataManager#appendForGroup:作为正常消息写入,acks默认为-1,需要等待所有isr写入成功。
scala
private def appendForGroup(group: GroupMetadata,
records: Map[TopicPartition, MemoryRecords],
callback: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse] => Unit): Unit = {
replicaManager.appendRecords(
// offsets.commit.timeout.ms=5000
timeout = config.offsetCommitTimeoutMs.toLong,
// offsets.commit.required.acks=-1 --- 等待所有isr写入
requiredAcks = config.offsetCommitRequiredAcks,
internalTopicsAllowed = true,
origin = AppendOrigin.Coordinator,
entriesPerPartition = records,
delayedProduceLock = Some(group.lock),
responseCallback = callback)
}GroupMetadata#onOffsetCommitAppend:写消息完成,将消费进度更新到消费组元数据内存GroupMetadata#offsets,后续可以从内存中快速读取消费组的消费进度。
scala
private val offsets =
new mutable.HashMap[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]
def onOffsetCommitAppend(topicPartition: TopicPartition,
offsetWithCommitRecordMetadata: CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset): Unit = {
if (!offsets.contains(topicPartition)
|| offsets(topicPartition).olderThan(offsetWithCommitRecordMetadata))
// 提交进度大于当前进度,则更新消费进度
offsets.put(topicPartition, offsetWithCommitRecordMetadata)
}OffsetCommitResponseData:响应数据包含每个分区提交是否异常。
java
public class OffsetCommitResponseData implements ApiMessage {
private int throttleTimeMs;
private List<OffsetCommitResponseTopic> topics;
}
static public class OffsetCommitResponseTopic implements Message {
private String name;
private List<OffsetCommitResponsePartition> partitions;
}
static public class OffsetCommitResponsePartition implements Message {
private int partitionIndex;
private short errorCode;
}ConsumerCoordinator#doAutoCommitOffsetsAsync:消费者对此不会做额外处理,仅打印日志:
java
private void doAutoCommitOffsetsAsync() {
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> allConsumedOffsets = subscriptions.allConsumed();
commitOffsetsAsync(allConsumedOffsets, (offsets, exception) -> {
if (exception != null) {
log.warn("Asynchronous auto-commit of offsets {} failed: {}", offsets, exception.getMessage());
}
}
});
}4-4、coordinator加载消费组消费进度
回顾第五章,协调者节点=leaderOf(hash(groupId) %__consumer_offsets的分区数),默认__consumer_offsets的分区数为50个。
onLeadershipChange:当broker收到controller下发的LeaderAndIsrRequest,发现自己成为__consumer_offsets的某个分区leader,触发消费组加载。
scala
def onLeadershipChange(updatedLeaders: Iterable[Partition], updatedFollowers: Iterable[Partition]): Unit = {
updatedLeaders.foreach { partition =>
// topic==__consumer_offsets
if (partition.topic == GROUP_METADATA_TOPIC_NAME)
groupCoordinator.onElection(partition.partitionId)
}
}GroupMetadataManager#doLoadGroupsAndOffsets:读分区log,回放所有记录,加载消费组和消费进度到内存。
注意消费组元数据 和消费组消费进度都在这个topic,通过key区分。
scala
private def doLoadGroupsAndOffsets(topicPartition: TopicPartition, onGroupLoaded: GroupMetadata => Unit): Unit = {
def logEndOffset: Long = replicaManager.getLogEndOffset(topicPartition).getOrElse(-1L)
replicaManager.getLog(topicPartition) match {
case Some(log) =>
// 被加载的消费进度
val loadedOffsets = mutable.Map[GroupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]()
val pendingOffsets = mutable.Map[Long, mutable.Map[GroupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]]()
val loadedGroups = mutable.Map[String, GroupMetadata]()
val removedGroups = mutable.Set[String]()
var buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(0)
var currOffset = log.logStartOffset
var readAtLeastOneRecord = true
// 从头读到尾
while (currOffset < logEndOffset && readAtLeastOneRecord && !shuttingDown.get()) {
// 5mb一次读消息
val fetchDataInfo = log.read(currOffset,
// offsets.load.buffer.size=5mb
maxLength = config.loadBufferSize,
isolation = FetchLogEnd,
minOneMessage = true)
readAtLeastOneRecord = fetchDataInfo.records.sizeInBytes > 0
// 转换为MemoryRecords
val memRecords = fetchDataInfo.records match {
case records: MemoryRecords => records
case fileRecords: FileRecords =>
val sizeInBytes = fileRecords.sizeInBytes
val bytesNeeded = Math.max(config.loadBufferSize, sizeInBytes)
if (buffer.capacity < bytesNeeded) {
buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytesNeeded)
} else {
buffer.clear()
}
fileRecords.readInto(buffer, 0)
MemoryRecords.readableRecords(buffer)
}
// 迭代批次
memRecords.batches.forEach { batch =>
val isTxnOffsetCommit = batch.isTransactional
if (batch.isControlBatch) {
// ...
} else {
var batchBaseOffset: Option[Long] = None
// 迭代消息
for (record <- batch.asScala) {
if (batchBaseOffset.isEmpty)
batchBaseOffset = Some(record.offset)
GroupMetadataManager.readMessageKey(record.key) match {
case offsetKey: OffsetKey =>
// 消费进度
// ... 忽略事务消息
val groupTopicPartition = offsetKey.key
val offsetAndMetadata = GroupMetadataManager.readOffsetMessageValue(record.value)
loadedOffsets.put(groupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset(batchBaseOffset, offsetAndMetadata))
case groupMetadataKey: GroupMetadataKey =>
// 消费组
val groupId = groupMetadataKey.key
val groupMetadata = GroupMetadataManager.readGroupMessageValue(groupId, record.value, time)
loadedGroups.put(groupId, groupMetadata)
}
}
}
currOffset = batch.nextOffset
}
}
// 非空组的offset,空组的offset(所有成员下线)
val (groupOffsets, emptyGroupOffsets) = loadedOffsets
.groupBy(_._1.group)
.map { case (k, v) =>
k -> v.map { case (groupTopicPartition, offset) => (groupTopicPartition.topicPartition, offset) }
}.partition { case (group, _) => loadedGroups.contains(group) }
loadedGroups.values.foreach { group =>
val offsets = groupOffsets.getOrElse(group.groupId, Map.empty[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset])
val pendingOffsets = pendingGroupOffsets.getOrElse(group.groupId, Map.empty[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]])
// 加载
loadGroup(group, offsets, pendingOffsets)
onGroupLoaded(group)
}
}
}
private def loadGroup(group: GroupMetadata, offsets: Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset],
pendingTransactionalOffsets: Map[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]]): Unit = {
group.initializeOffsets(offsets, pendingTransactionalOffsets.toMap)
val currentGroup = addGroup(group)
}
// GroupMetadata#initializeOffsets
private val offsets = new mutable.HashMap[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]
def initializeOffsets(offsets: collection.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset],
pendingTxnOffsets: Map[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]]): Unit = {
this.offsets ++= offsets
this.pendingTransactionalOffsetCommits ++= pendingTxnOffsets
}总结
获取消费位点
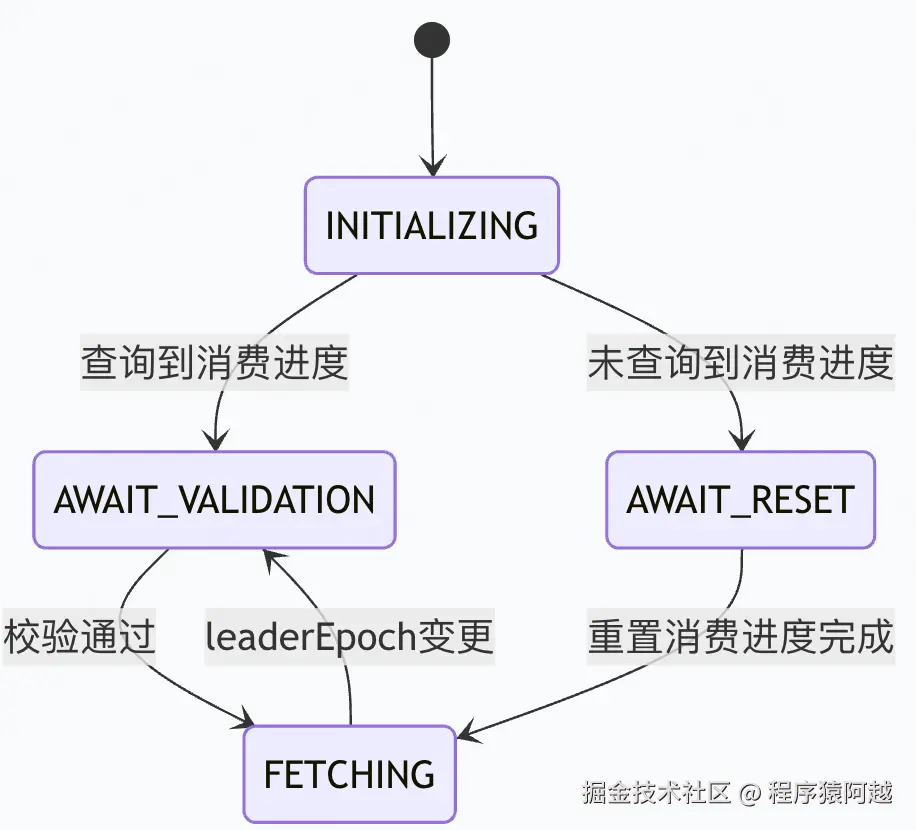
在Consumer侧,分区FetchState有四种状态:
1)INITIALIZING:刚分配到该分区;
2)AWAIT_VALIDATION:消费组曾经消费过,已经获取消费位点;
3)AWAIT_RESET:消费组未曾经消费过,待重置消费位点;
4)FETCHING:消费位点合法,可以开始消费;
如果分区有消费进度:
1)INITIALIZING→AWAIT_VALIDATION:consumer发送OffsetFetchRequest,coordinator返回内存中的消费进度GroupMetadata#offsets;
2)AWAIT_VALIDATION→FETCHING:consumer发送OffsetForLeaderEpochRequest(offset对应的leaderEpoch)给对应分区Leader;分区leader通过leaderEpoch记录(每个分区都有多个leaderEpoch-startOffset的二元组,记录每个leader任期内的offset区间)得到leaderEpoch的结束offset,如果返回offset<当前offset,代表发生数据截断,消费位点=leaderEpoch的结束offset;
如果分区无消费进度,使用重置策略获取重置消费位点。
INITIALIZING→AWAIT_RESET:OffsetFetchRequest返回offset=-1,分区无消费进度。
AWAIT_RESET→FETCHING :auto.offset.reset重置策略有两种:
1)LATEST :默认策略,根据隔离级别重置为分区最新写入进度,READ_COMMITTED ,返回LSO,事务消息相关;READ_UNCOMMITTED (默认),返回HW高水位;
2)EARLIEST :重置为分区最早写入进度,返回分区LogStartOffset起始写入位点;
后续消费过程中(执行poll方法),会检测缓存元数据的分区leaderEpoch与Fetch状态中的leaderEpoch是否一致,如果发生改变,Fetch状态再次进入AWAIT_VALIDATION。
拉取消息
拉取消息分为几步:
1)Consumer发起FetchRequest传入FETCHING分区消费进度;
2)Broker收到FetchRequest,读取消息,如果有消息(默认fetch.min.bytes=1byte)立即响应FetchResponse;否则挂起等待高水位上涨,再次读数据响应FetchResponse;
3)Consumer将消息批次记录缓存在队列中,依次消费;
KIP-227提出增量FetchRequest ,通过建立会话 ,只传输发生变化的分区信息,避免consumer和broker间(主要是follower和leader间)全量传输分区信息,即使没有任何变更。
首次Fetch :Request包含全量分区 和消费位点,Broker生成sessionId响应Response包含全量分区;增量Fetch :Request包含发生变化分区和消费位点,Broker生成sessionEpoch+1响应Response仅包含变化分区(有消息或各种offset变更)。
Step1,Consumer发送FetchRequest中包含3个配置参数:
1)minBytes=fetch.min.bytes,默认1字节;
2)maxWait=fetch.max.wait.ms,默认500ms。待消费消息不足minBytes,FetchRequest被broker挂起的时长;
3)max.partition.fetch.bytes,默认1mb。每个分区最大拉取的消息大小;

Step2,Broker侧拉取消息:
1)循环所有分区,以批次维度拉取;
2)已知隔离级别READ_UNCOMMITTED (默认),得到结束位置 =HW高水位=(offset=778,pos=9999);
3)已知消费进度offset=500,二分查找index,得到小于等于offset的最大索引项(offset=456,pos=6666);
4)从3对应物理位置(6666),向后遍历log,找包含offset(500)的批次 (结束offset=555,pos=8888)作为起始位置;
5)根据2和4定位数据块位置(pos=8888,size=9999-8888);
6)利用FileChannel.transferTo零拷贝技术将消息数据写入通讯channel;
Step3,Consumer消费消息:
1)将FetchResponse返回数据缓存在completedFetches队列中;
2)从completedFetches 拉取消息,按照实际消费进度(因为broker以批次返回需要consumer自行按照消费进度跳过一些offset) 和最大消息数量( 每次KafkaConsumer#poll最多返回max.poll.records=默认500 条消息),拆分消息批次,迭代过程中完成内存消费位点更新;
提交消费进度
默认情况下,enable.auto.commit =true,自动提交消费进度。KafkaConsumer#poll每超过auto.commit.interval.ms=5000ms触发一次自动提交。
Consumer发送OffsetCommitRequest,包含所有FETCHING状态分区当前的消费位点(在上面消费拉取消息的时候已经更新);
Coordinator处理OffsetCommitRequest,将本次请求中所有分区的消费进度作为一批消息写入topic=__consumer_offsets,partition=消费组的协调者对应分区=hash(groupId) %__consumer_offsets的分区数。其中每条消息的key=groupId+topic+partition,value=req.offset+req.leaderEpoch+broker收到请求的时间戳。默认offsets.commit.required.acks=-1,需要等待所有ISR副本写入后响应成功,将消费进度更新到内存GroupMetadata#offsets。
如果__consumer_offsets的分区重新发生leader选举(比如broker重启),会触发该分区对应的消费组加载。此时会全量读取分区中的消息,重新更新消费进度到内存GroupMetadata#offsets。