Spring提供了一些内置功能,也可以在Bean的生命周期阶段提供一些额外功能。内置功能主要有Aware回调接口以及InitializingBean接口。
1.BeanNameAware
实现该接口可以设置bean的名字,这是一个回调接口。
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
public interface BeanNameAware extends Aware {
void setBeanName(String var1);
}2.ApplicationContextAware
实现该接口可以设置ApplicationContext容器。
java
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.context;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware;
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}3.InitializingBean
实现这个这个接口在Bean的初始化前可以做一些额外处理。
java
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}4.测试类
java
package com.example.demo2.b04;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**
* @author zhou
* @version 1.0
* @description TODO
* @date 2025/10/11 20:42
*/
public class Mybean implements BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(b04Application.class);
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
log.info("当前bean "+this+"名字叫:"+name);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
log.info("当前bean "+this+"容器是:"+applicationContext);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.info("当前bean "+this+"初始化");
}
}
java
package com.example.demo2.b04;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
/**
* @author zhou
* @version 1.0
* @description TODO
* @date 2025/10/11 20:41
*/
public class b04Application {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(b04Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("myBean", Mybean.class);
context.refresh();
context.close();
}
}结果:
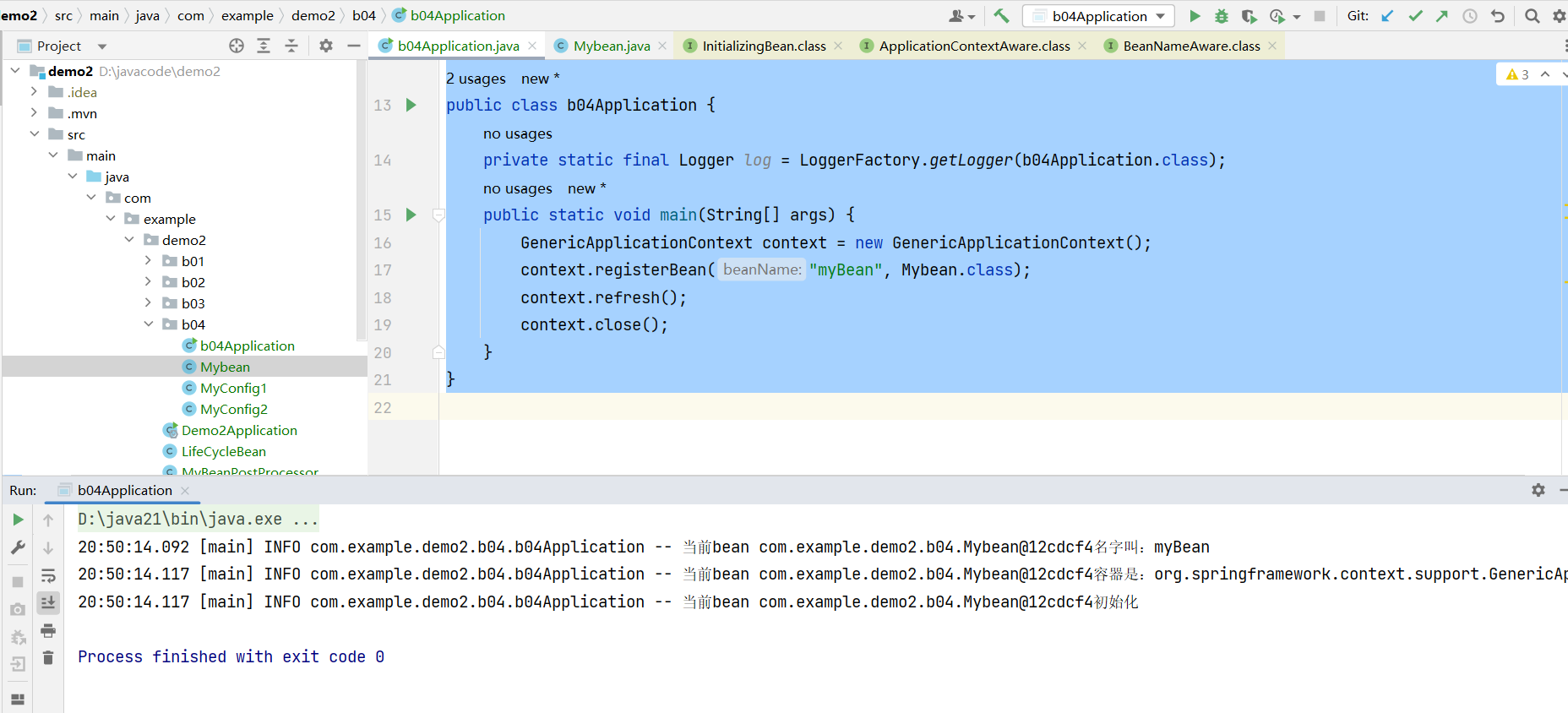
上面三个接口的方法都实现了,Aware接口先生效,后面才是InitializingBean接口。
5.对比@Autowired实现
@Autowired也能实现上面的Spring的内置功能,下面举一个例子。
java
@Autowired
public void test(ApplicationContext applicationContext){
log.info("当前bean "+this+"容器是"+applicationContext);
}结果如下:
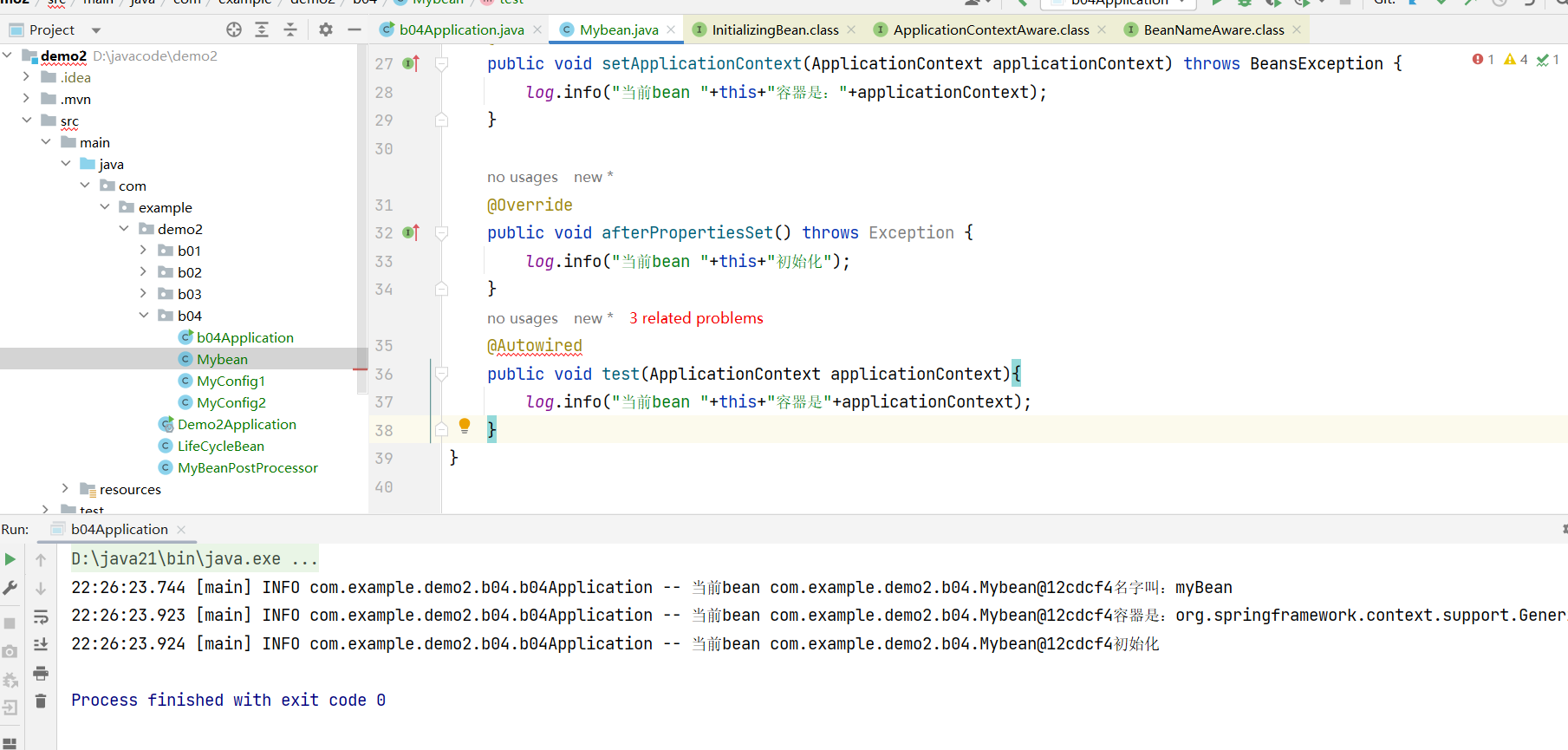
由于没有注册Bean的后处理器所以没生效,添加解析@Autowired的后处理器。
java
package com.example.demo2.b04;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
/**
* @author zhou
* @version 1.0
* @description TODO
* @date 2025/10/11 20:41
*/
public class b04Application {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(b04Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("myBean", Mybean.class);
context.registerBean(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
context.refresh();
context.close();
}
}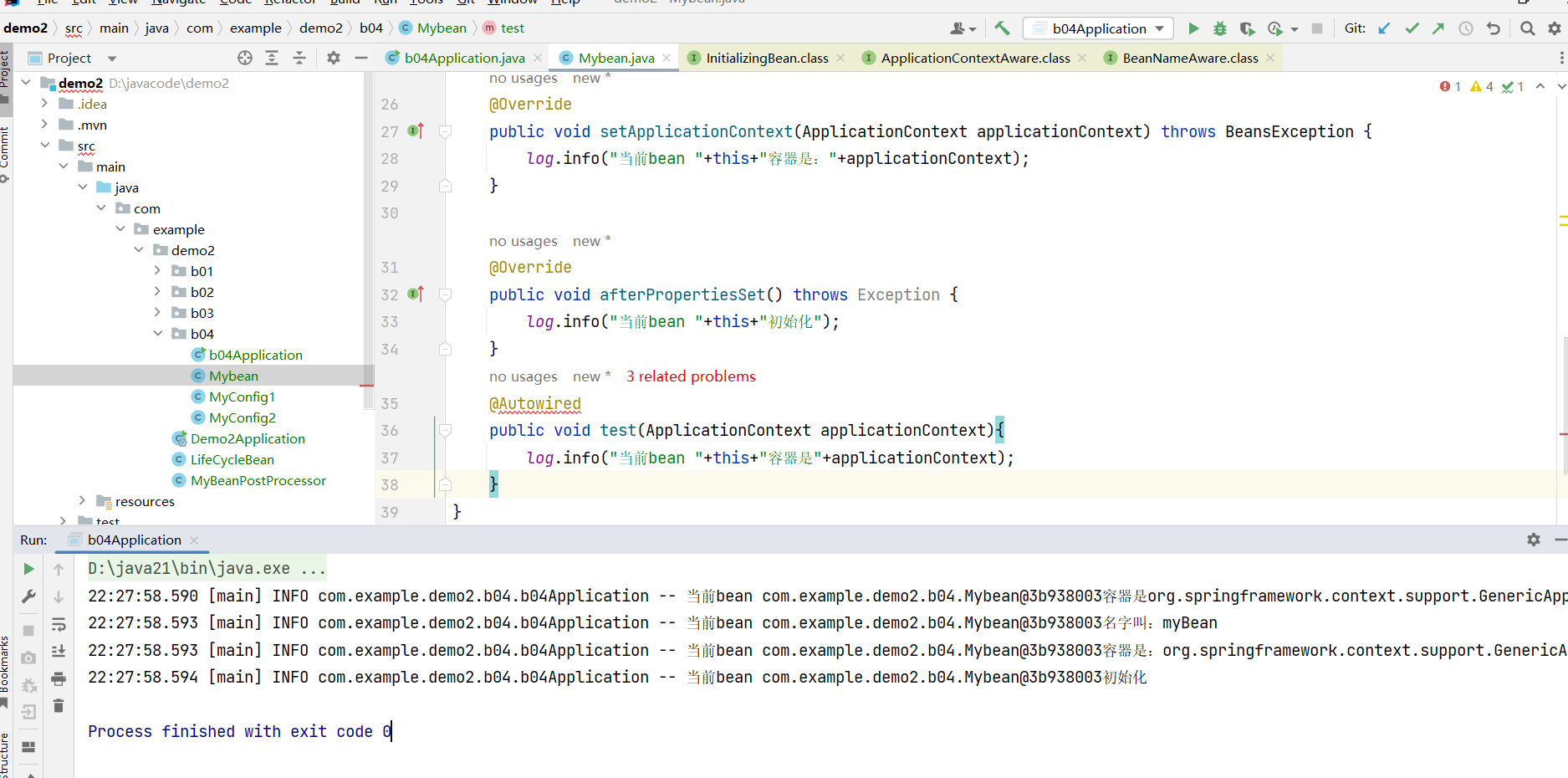
相比于前面的内置功能,@Autowired的实现方式是一种拓展功能,它需要加对应的Bean后处理器才能生效,而且有时可能会失效,没有内置功能稳定。