【 声明:版权所有,欢迎转载,请勿用于商业用途。 联系信箱:feixiaoxing @163.com】
图形旋转是一种常见的处理方式。有的时候是游戏本身需要旋转,有的时候是仿真需要旋转,至于哪一种就看具体情况。比如说,现在数字孪生比较火,说白了就是拿到传感器和工厂的数据,仿制出一模一样的3d场景。这种情况下,就势必会涉及到旋转了。
1、围绕某个点的旋转
这种旋转比较好理解,就好像地球绕着太阳转一样,只要我们算好了旋转中心,和旋转点之间的距离,这样就可以处理好旋转的步骤了。
while (true)
{
cleardevice();
#if 0
angle += 2; // update angle
if (angle == 360)
{
angle = 0;
}
#else
if (angle == 0)
{
angle = 360;
}
angle -= 2;
#endif
setfillcolor(RED);
fillcircle(320, 240, 30);
setfillcolor(BLUE);
fillcircle(320 + (int)(160.0 * cos(angle *6.28 / 360.0)), 240 + (int)(160.0 * sin(angle*6.28 / 360.0)), 15);
FlushBatchDraw();
Sleep(50);
}如果是图像效果的话,应该是这样的,
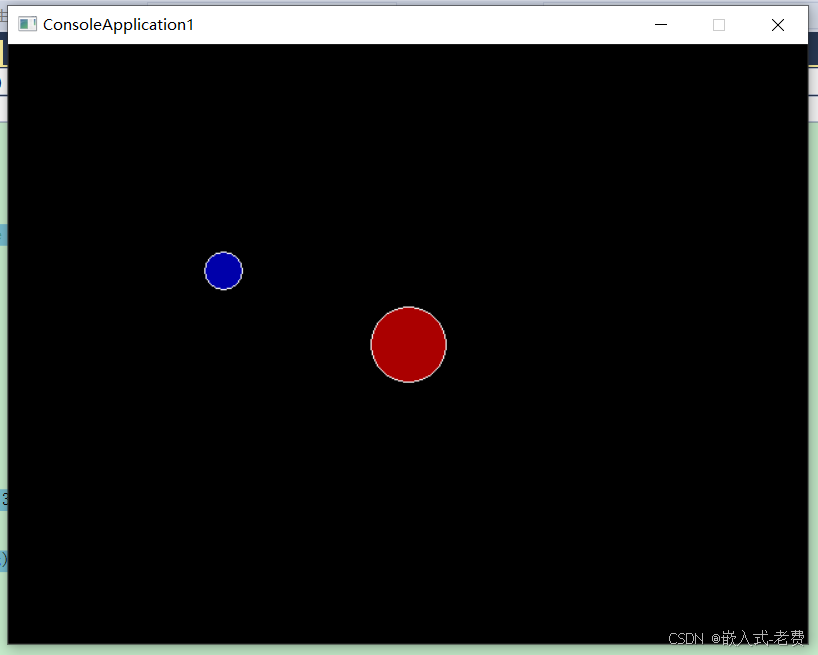
2、围绕自身中心的旋转
这种旋转比较见于圆形物体。大家能够经常看到的圆形旋转,比如扫地机器人,这就是明显的围绕自身中心的旋转。这种旋转一般不太好画,我们通常会在上面再添加一个小圆,这样观察起来就容易多了。写代码的时候,一般是这样,
while (true)
{
cleardevice();
angle += 2;
if (angle == 360)
{
angle = 0;
}
setfillcolor(RED);
fillcircle(320, 240, 50);
setfillcolor(BLUE);
fillcircle(320 + (int)(30.0 * cos(angle *6.28 / 360.0)), 240 + (int)(30.0 * sin(angle*6.28 / 360.0)), 10);
FlushBatchDraw();
Sleep(20);
}如下面场景所示,虽然画的是里面的小圆,实际我们的感受却是,外面的大圆动了,所以里面的小圆才一起动,
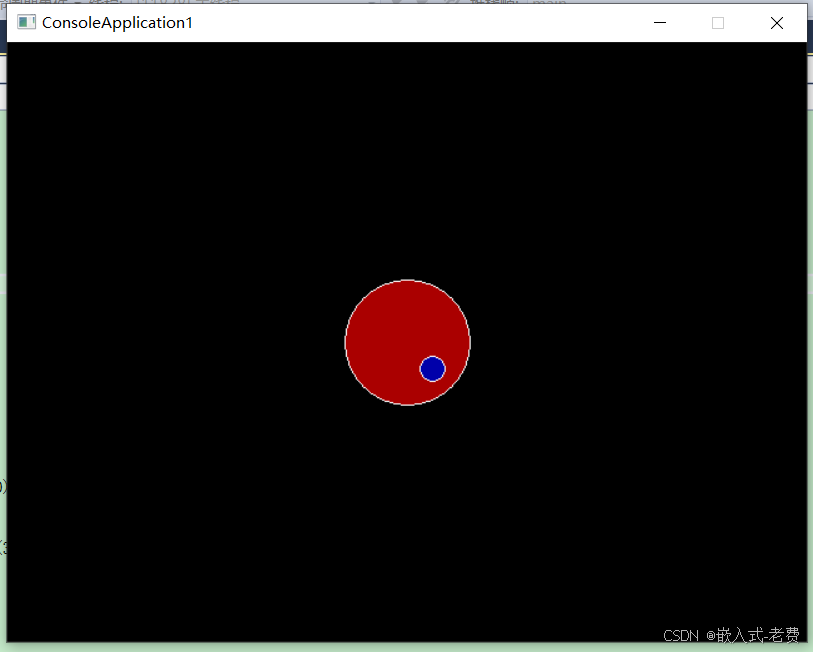
3、非规则图形的旋转
上面的图形旋转相对不是很难,还有一种非规则图形的旋转。**这种旋转一般也是先切分成不同的点,算出每一个点的旋转结果。**再用直线把这些结果link在一起,这样就能得到我们想要的结果了。也就是用fillpoly函数来实现。
setlinecolor(RED);
setfillcolor(RED);
fillpoly(4, new int[8]{ x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 });如果是效果的话,就是这样的,
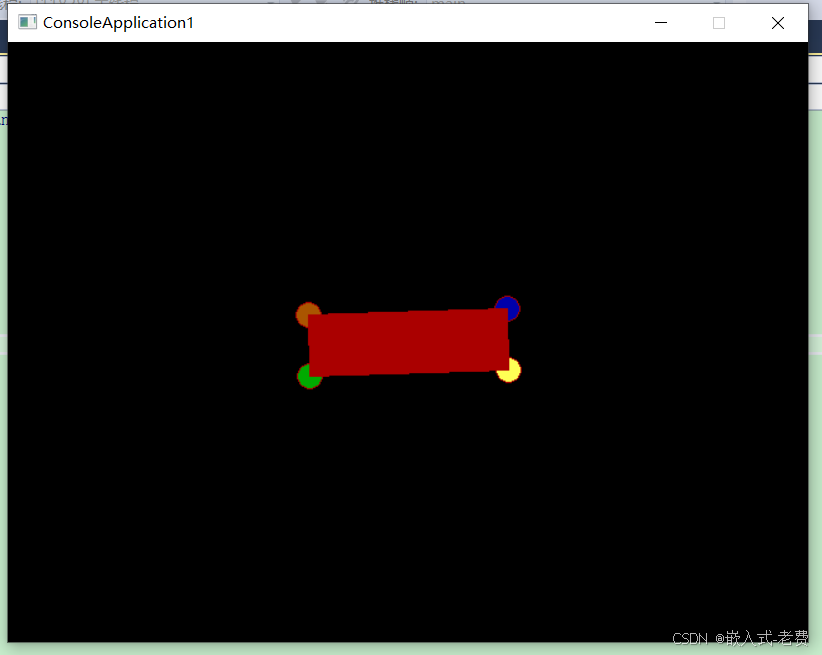
四周画了四个圆形,主要也是为了演示一下旋转的效果。
4、总结
旋转本身是非常务实的一个需求,大家可以好好实现一下。更重要的是,要把它用在自己的项目中,这样才会有更深的感受,明白自己的所学所看是可以有大用处的。最后给出代码,权当抛砖引玉,对大家有所帮助。
#include <graphics.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <cmath>
int main() // rotate to some point
{
int angle = 0;
//int angle = 90;
//int angle = 180;
//int angle = 270;
initgraph(640, 480);
BeginBatchDraw();
while (true)
{
cleardevice();
#if 0
angle += 2; // update angle
if (angle == 360)
{
angle = 0;
}
#else
if (angle == 0)
{
angle = 360;
}
angle -= 2;
#endif
setfillcolor(RED);
fillcircle(320, 240, 30);
setfillcolor(BLUE);
fillcircle(320 + (int)(160.0 * cos(angle *6.28 / 360.0)), 240 + (int)(160.0 * sin(angle*6.28 / 360.0)), 15);
FlushBatchDraw();
Sleep(50);
}
_getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
int main2() // rotate to itself
{
const int WIDTH = 640;
const int HEIGHT = 480;
int angle = 90;
//int angle = 0;
//int angle = 0;
//int angle = 0;
initgraph(WIDTH, HEIGHT);
BeginBatchDraw();
while (true)
{
cleardevice();
angle += 2;
if (angle == 360)
{
angle = 0;
}
setfillcolor(RED);
fillcircle(320, 240, 50);
setfillcolor(BLUE);
fillcircle(320 + (int)(30.0 * cos(angle *6.28 / 360.0)), 240 + (int)(30.0 * sin(angle*6.28 / 360.0)), 10);
FlushBatchDraw();
Sleep(20);
}
EndBatchDraw();
closegraph();
}
int main3() // not regular shape rotate
{
const int WIDTH = 640;
const int HEIGHT = 480;
int rect_width = 160;
int rect_height = 50;
int center_x = WIDTH / 2;
int center_y = HEIGHT / 2;
int angle = 0;
initgraph(WIDTH, HEIGHT);
BeginBatchDraw();
while (true)
{
cleardevice();
int x1 = center_x - rect_width / 2; // get position of each point
int y1 = center_y - rect_height / 2;
int x2 = center_x + rect_width / 2;
int y2 = center_y - rect_height / 2;
int x3 = center_x + rect_width / 2;
int y3 = center_y + rect_height / 2;
int x4 = center_x - rect_width / 2;
int y4 = center_y + rect_height / 2;
int temp_x;
int temp_y;
float radians = (float)(angle * 3.14159 / 180); // translate to theta
// rotate each point
temp_x = x1;
temp_y = y1;
x1 = center_x + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * cos(radians) - (temp_y - center_y) * sin(radians));
y1 = center_y + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * sin(radians) + (temp_y - center_y) * cos(radians));
setfillcolor(BROWN);
fillcircle(x1, y1, 10);
temp_x = x2;
temp_y = y2;
x2 = center_x + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * cos(radians) - (temp_y - center_y) * sin(radians));
y2 = center_y + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * sin(radians) + (temp_y - center_y) * cos(radians));
setfillcolor(BLUE);
fillcircle(x2, y2, 10);
temp_x = x3;
temp_y = y3;
x3 = center_x + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * cos(radians) - (temp_y - center_y) * sin(radians));
y3 = center_y + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * sin(radians) + (temp_y - center_y) * cos(radians));
setfillcolor(YELLOW);
fillcircle(x3, y3, 10);
temp_x = x4;
temp_y = y4;
x4 = center_x + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * cos(radians) - (temp_y - center_y) * sin(radians));
y4 = center_y + (int)((temp_x - center_x) * sin(radians) + (temp_y - center_y) * cos(radians));
setfillcolor(GREEN);
fillcircle(x4, y4, 10);
setlinecolor(RED);
setfillcolor(RED);
fillpoly(4, new int[8]{ x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 });
angle += 2;
if (angle >= 360)
{
angle = 0;
}
FlushBatchDraw();
Sleep(20);
}
EndBatchDraw();
closegraph();
return 0;
}