Advanced layout concepts - MAD Skills
Compose 提供各种开箱即用型解决方案,可帮助您快速轻松地从头开始构建界面。但是,如果您需要更进一步,以实现完全自定义的界面,该怎么办?详细了解高级布局概念,以便自行构建自定义布局,让您的设计实现更上一层楼。
1. Advanced Layout Concepts
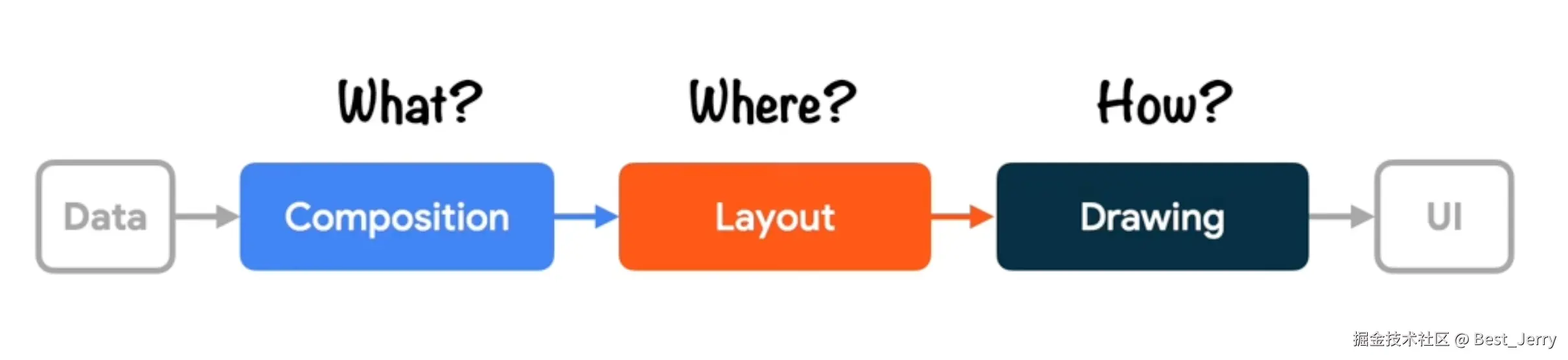
Layout 这一术语在 Compose 中有多种含义:
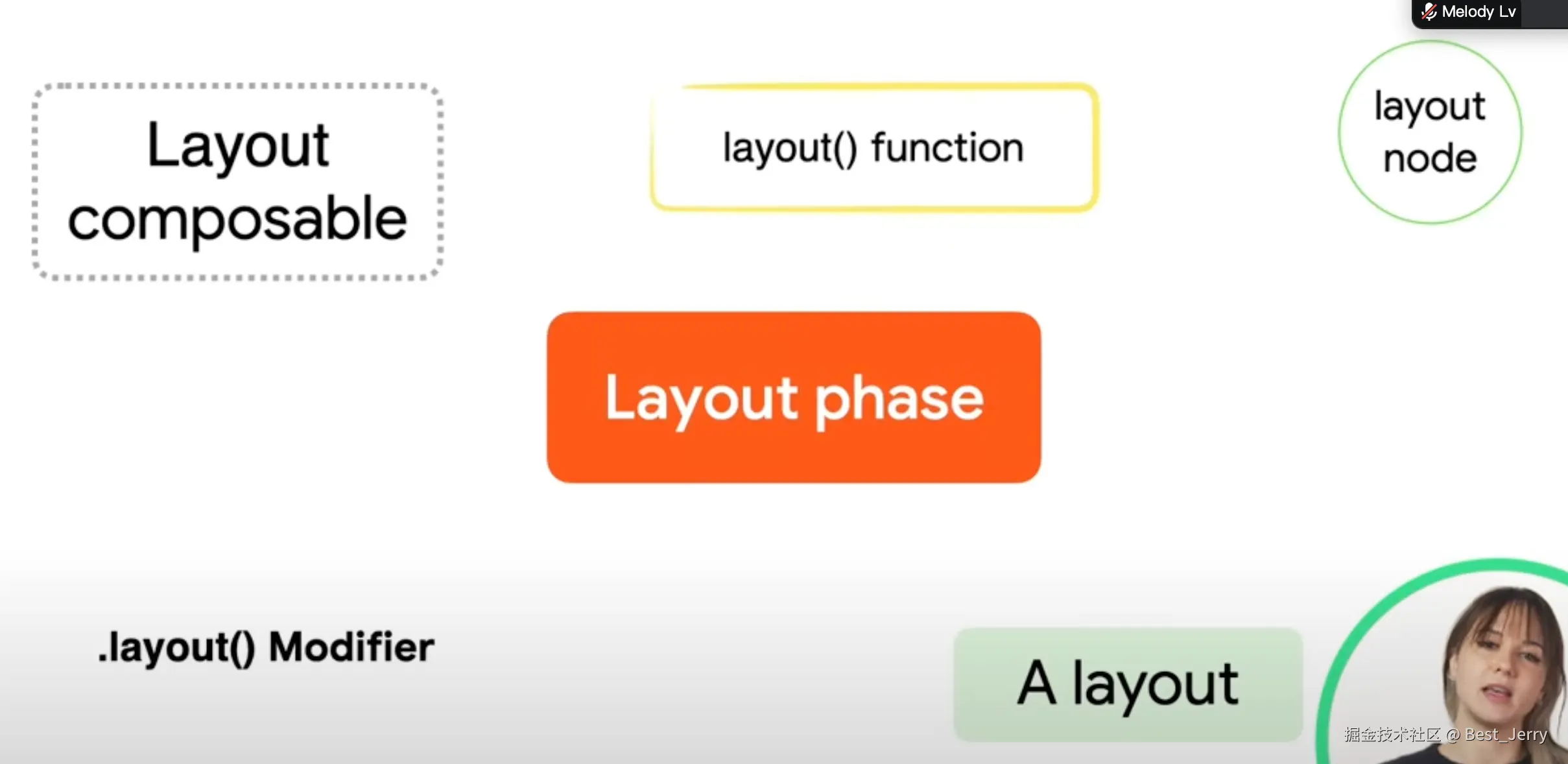
以下是每种含义的相关解释:


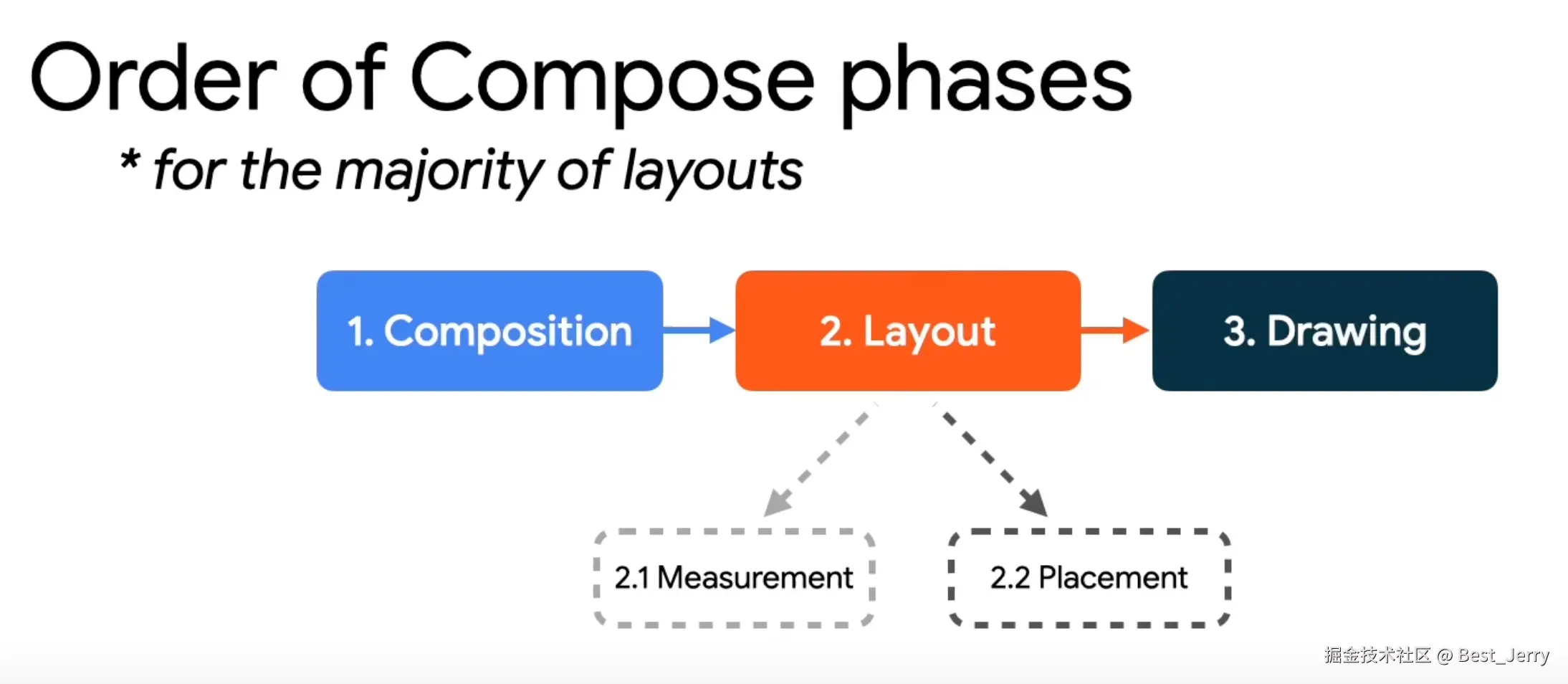
2. Layout phase and constraints
for building custom layouts
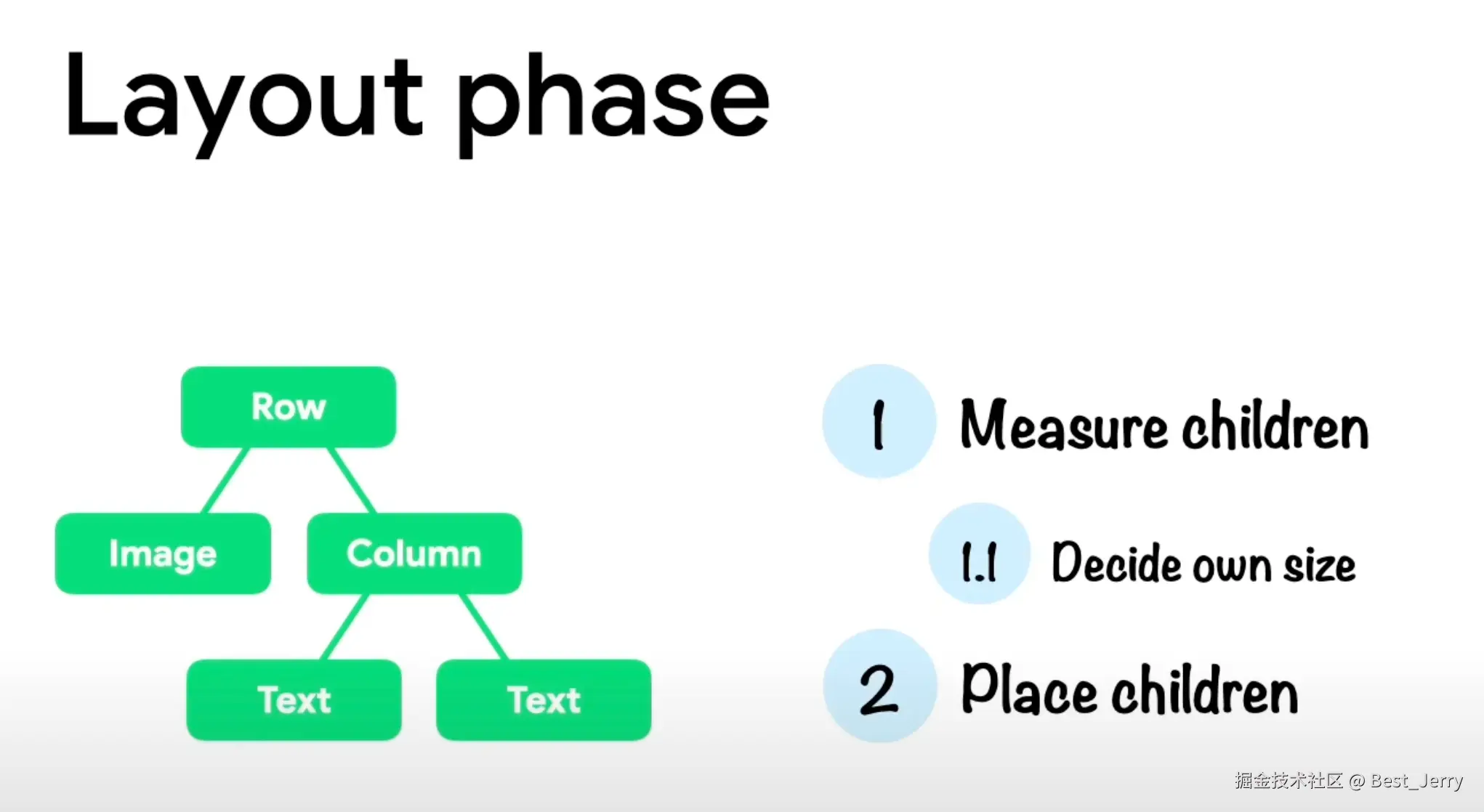

How to enter it
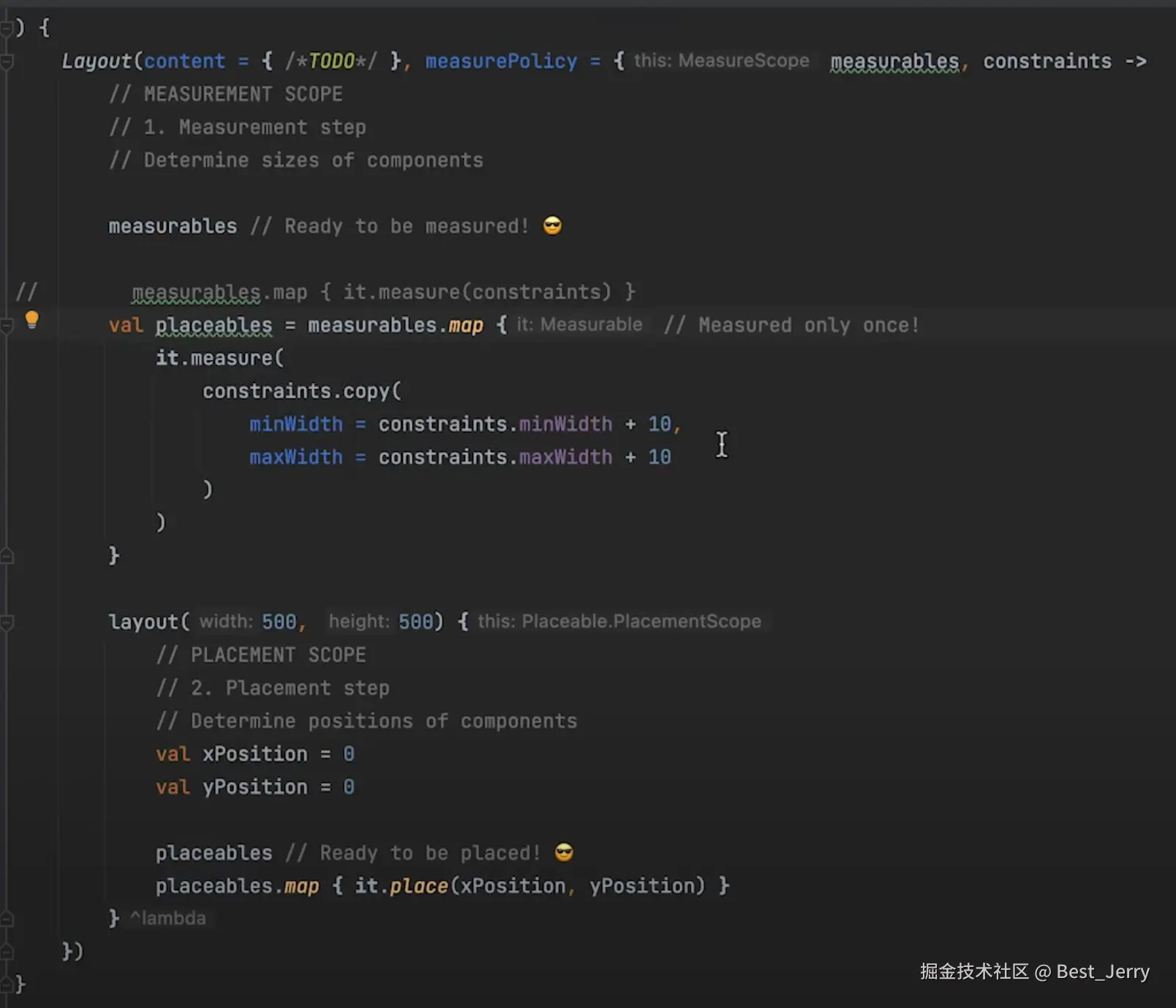
Layout()
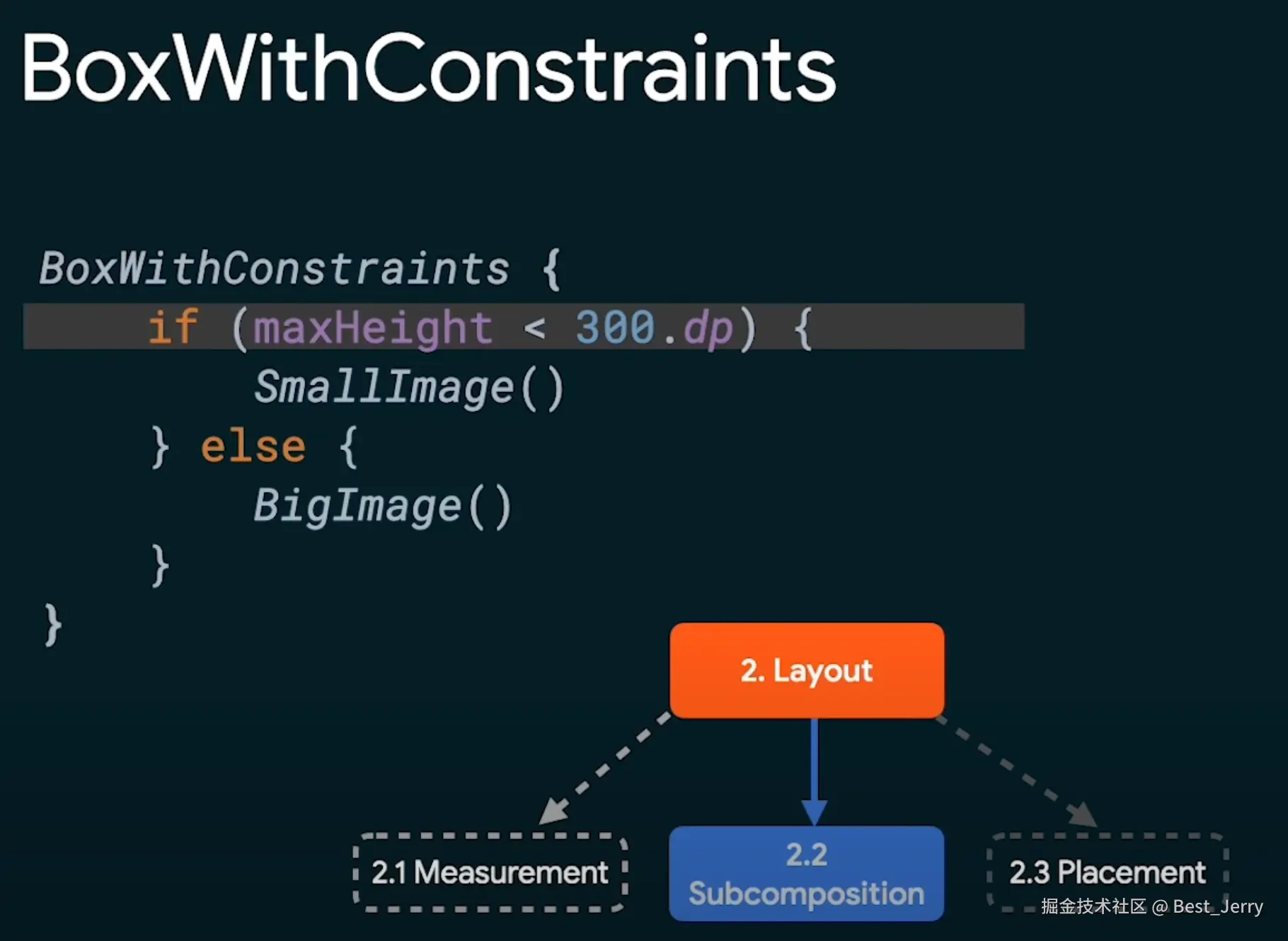
调用 Layout() 可组合项是布局阶段和构建自定义布局的起点。
Layout() 目前有三个重载方法:
kotlin
@Suppress("ComposableLambdaParameterPosition")
@UiComposable
@Composable
inline fun Layout(
content: @Composable @UiComposable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
measurePolicy: MeasurePolicy
) {
...
}
@Suppress("NOTHING_TO_INLINE")
@Composable
@UiComposable
inline fun Layout(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
measurePolicy: MeasurePolicy
) {
...
}
@Suppress("ComposableLambdaParameterPosition", "NOTHING_TO_INLINE")
@UiComposable
@Composable
inline fun Layout(
contents: List<@Composable @UiComposable () -> Unit>,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
measurePolicy: MultiContentMeasurePolicy
) {
...
}Measurement and placement for building custom layouts
自定义布局示例
Modifier.layout()
如果只想对某一个 Composable 自定义布局,使用 Modifier.layout() 更为方便。
kotlin
fun Modifier.layout(
measure: MeasureScope.(Measurable, Constraints) -> MeasureResult
) = this then LayoutElement(measure)
private data class LayoutElement(
val measure: MeasureScope.(Measurable, Constraints) -> MeasureResult
) : ModifierNodeElement<LayoutModifierImpl>() {
override fun create() = LayoutModifierImpl(measure)
override fun update(node: LayoutModifierImpl) {
node.measureBlock = measure
}
override fun InspectorInfo.inspectableProperties() {
name = "layout"
properties["measure"] = measure
}
}Modifier.layout()示例:
kotlin
Box(
Modifier.background(Color.Gray)
.layout { measurable, constraints ->
// an example modifier that adds 50 pixels of vertical padding.
val padding = 50
val placeable = measurable.measure(constraints.offset(vertical = -padding))
layout(placeable.width, placeable.height + padding) {
placeable.placeRelative(0, padding)
}
}
) {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize().background(Color.DarkGray))
}Modifier.requiredWidth 源码:
kotlin
@Stable
fun Modifier.requiredWidth(width: Dp) = this.then(
SizeElement(
minWidth = width,
maxWidth = width,
enforceIncoming = false,
inspectorInfo = debugInspectorInfo {
name = "requiredWidth"
value = width
}
)
)Modifier.requiredWidth示例:
kotlin
// The result is a 50.dp x 50.dp magenta box centered in a 100.dp x 100.dp space.
// Note that although a previous modifier asked it to be 100.dp width, this
// will not be respected. They would be respected if width was used instead of requiredWidth.
Box(
Modifier
.requiredWidth(100.dp)
.requiredWidth(50.dp)
.aspectRatio(1f)
.background(Color.Magenta)
)
3. Subcompose layout
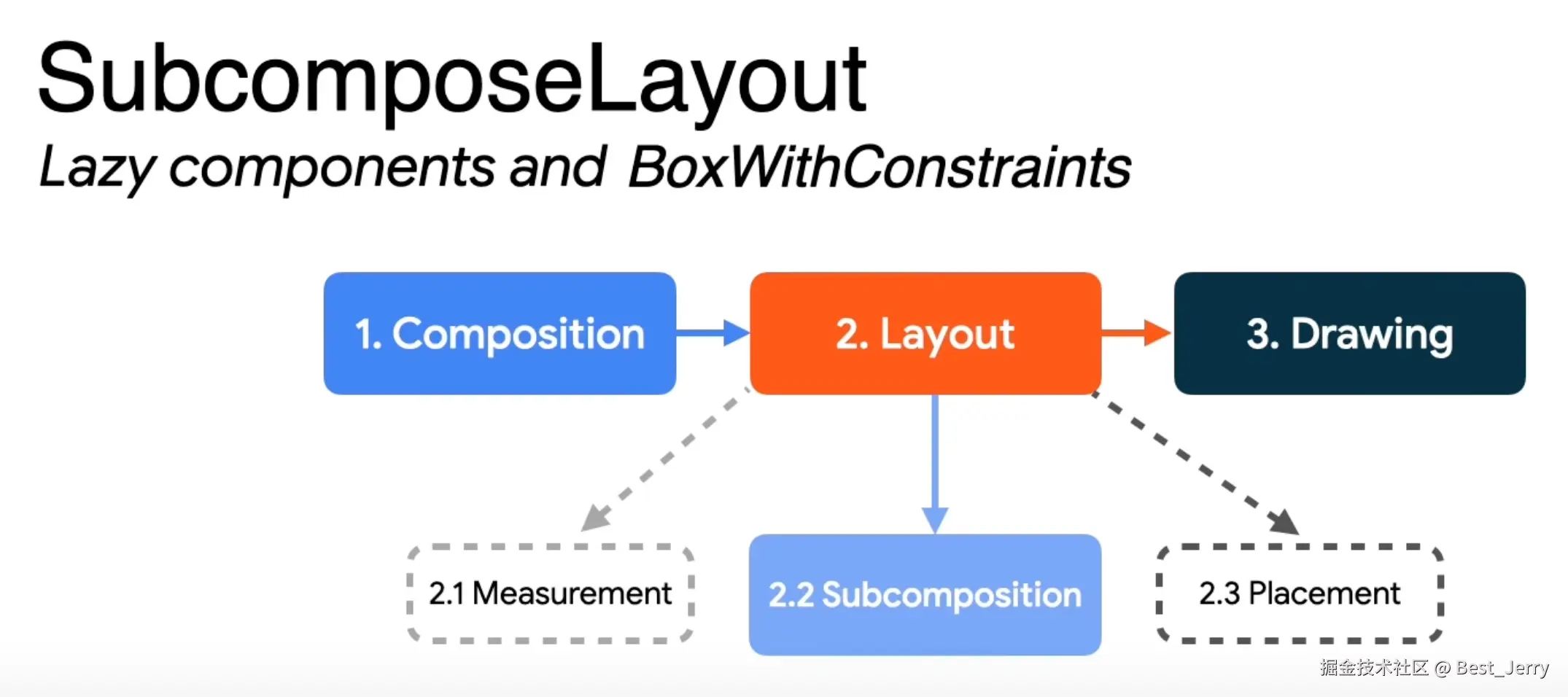
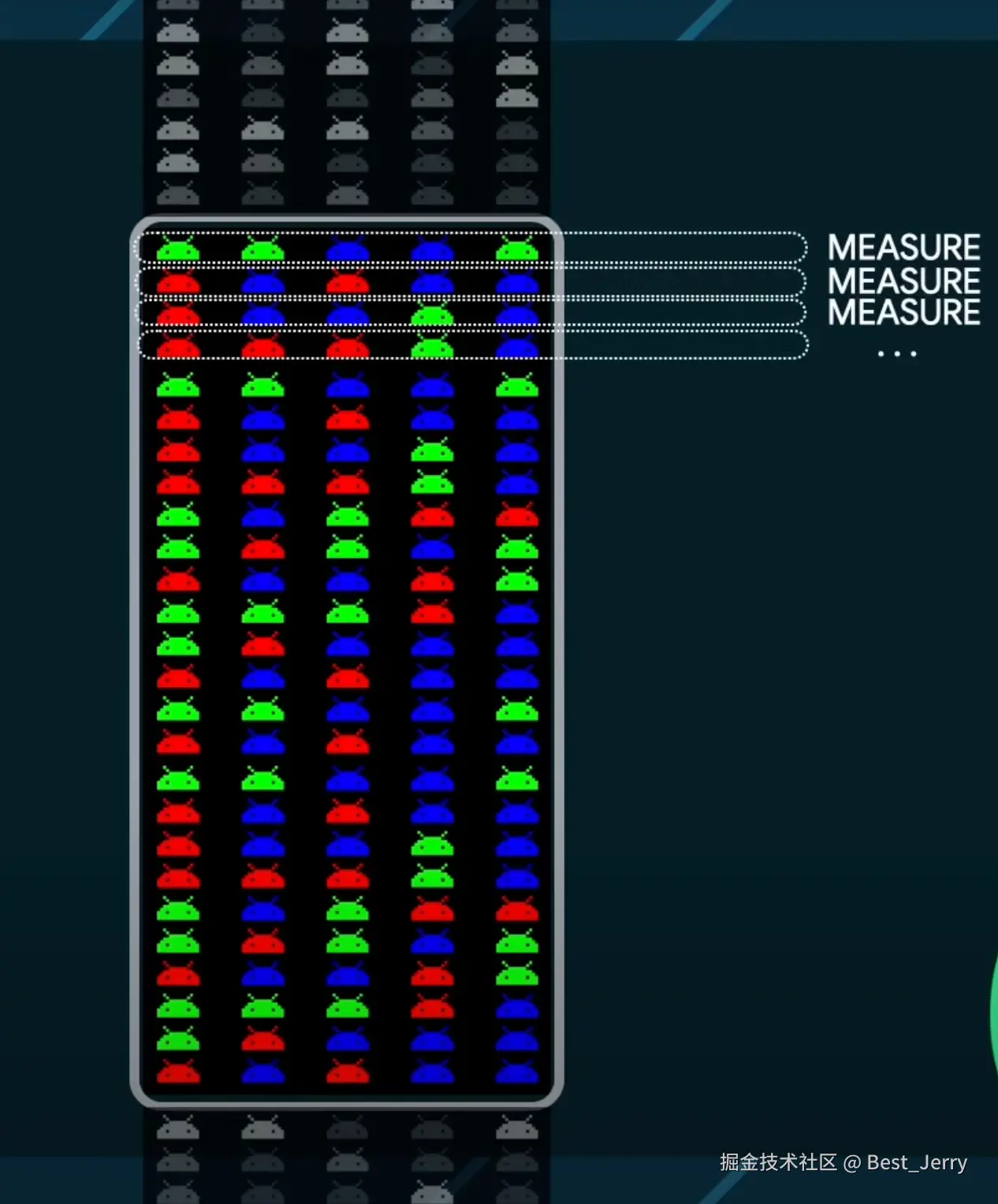
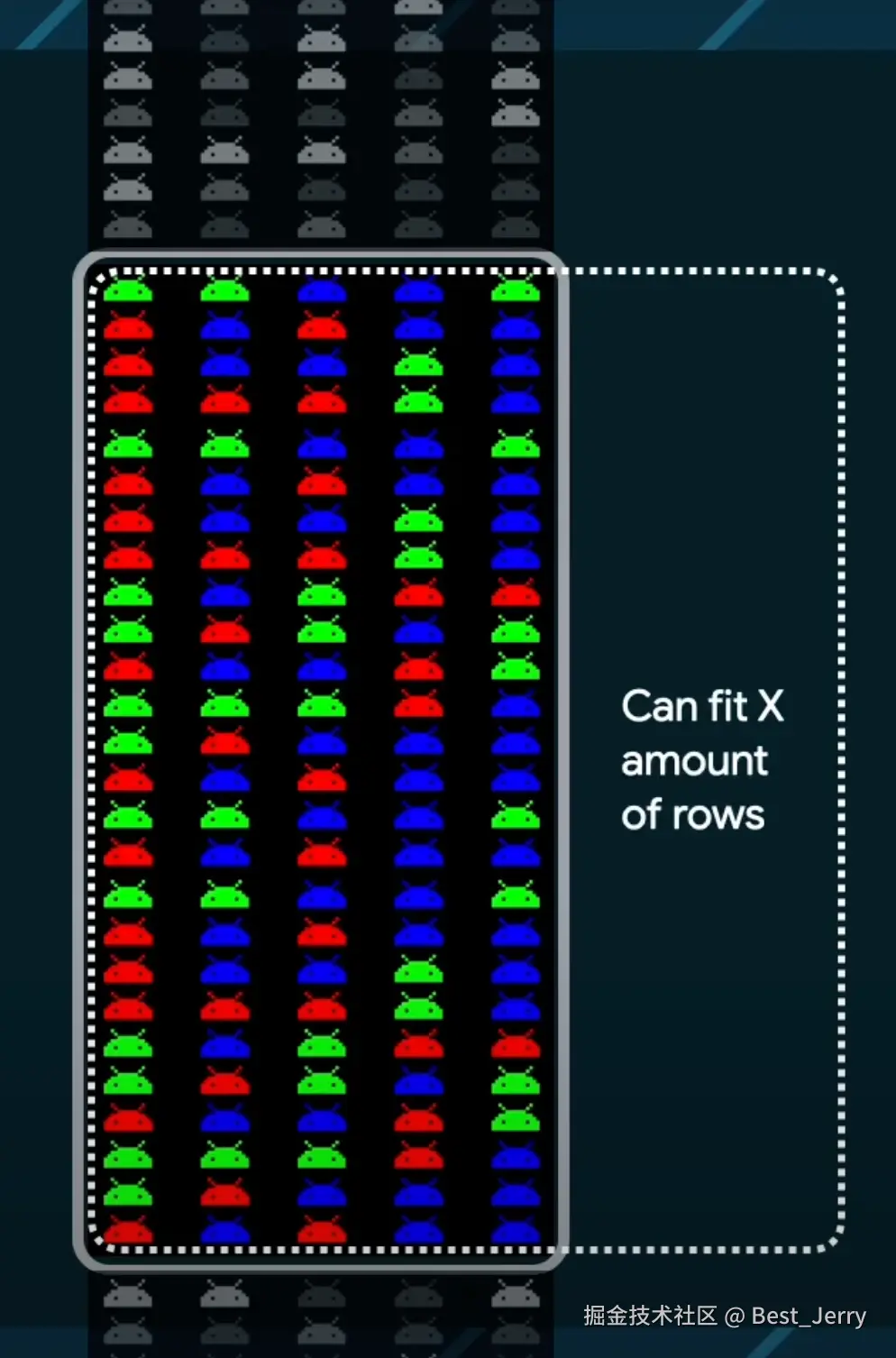

BoxWithConstraints
kotlin
@Composable
@UiComposable
fun BoxWithConstraints(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
contentAlignment: Alignment = Alignment.TopStart,
propagateMinConstraints: Boolean = false,
content:
@Composable @UiComposable BoxWithConstraintsScope.() -> Unit
) {
val measurePolicy = maybeCachedBoxMeasurePolicy(contentAlignment, propagateMinConstraints)
SubcomposeLayout(modifier) { constraints ->
val scope = BoxWithConstraintsScopeImpl(this, constraints)
val measurables = subcompose(Unit) { scope.content() }
with(measurePolicy) { measure(measurables, constraints) }
}
}

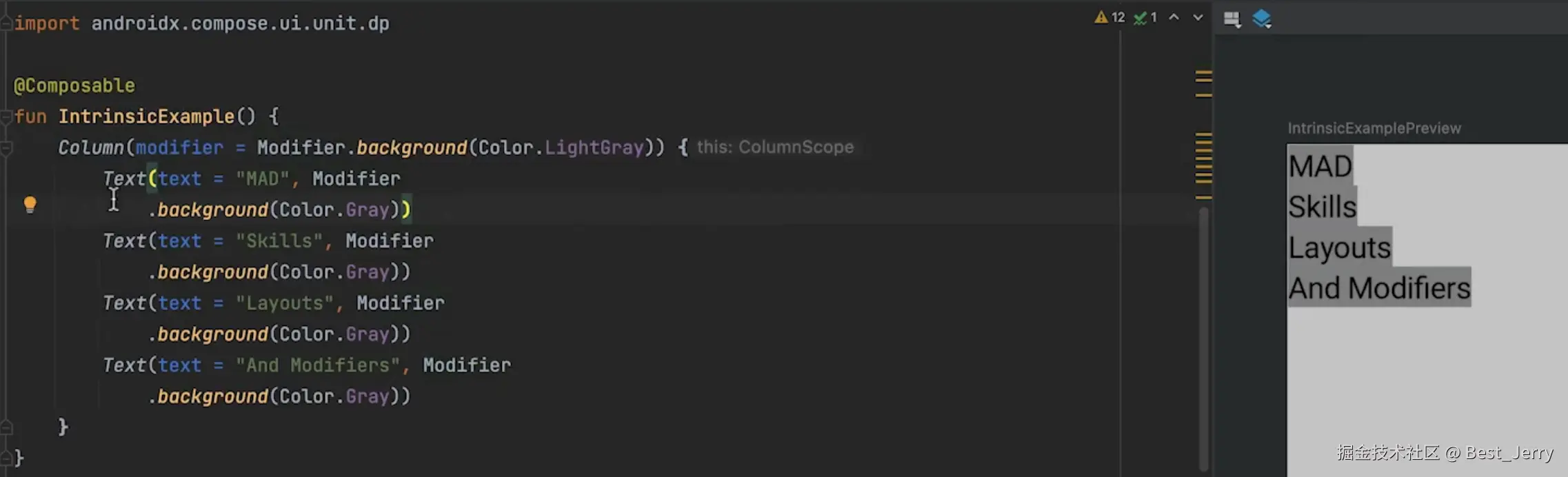
4. Intrinsic measurements
Intrinsic measurements 并不会测量两次。

如何使用 Intrinsic measurements


kotlin
@Stable
fun Modifier.width(intrinsicSize: IntrinsicSize) = this then IntrinsicWidthElement(
width = intrinsicSize,
enforceIncoming = true,
inspectorInfo = debugInspectorInfo {
name = "width"
properties["intrinsicSize"] = intrinsicSize
}
)
/**
* Intrinsic size used in [width] or [height] which can refer to width or height.
*/
enum class IntrinsicSize { Min, Max }
private class IntrinsicWidthElement(
val width: IntrinsicSize,
val enforceIncoming: Boolean,
val inspectorInfo: InspectorInfo.() -> Unit
) : ModifierNodeElement<IntrinsicWidthNode>() {
override fun create() = IntrinsicWidthNode(width, enforceIncoming)
override fun update(node: IntrinsicWidthNode) {
node.width = width
node.enforceIncoming = enforceIncoming
}
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
val otherModifierElement = other as? IntrinsicWidthElement ?: return false
return width == otherModifierElement.width &&
enforceIncoming == otherModifierElement.enforceIncoming
}
override fun hashCode() = 31 * width.hashCode() + enforceIncoming.hashCode()
override fun InspectorInfo.inspectableProperties() {
inspectorInfo()
}
}
private class IntrinsicWidthNode(
var width: IntrinsicSize,
override var enforceIncoming: Boolean
) : IntrinsicSizeModifier() {
override fun MeasureScope.calculateContentConstraints(
measurable: Measurable,
constraints: Constraints
): Constraints {
var measuredWidth = if (width == IntrinsicSize.Min) {
measurable.minIntrinsicWidth(constraints.maxHeight)
} else {
measurable.maxIntrinsicWidth(constraints.maxHeight)
}
if (measuredWidth < 0) { measuredWidth = 0 }
return Constraints.fixedWidth(measuredWidth)
}
override fun IntrinsicMeasureScope.minIntrinsicWidth(
measurable: IntrinsicMeasurable,
height: Int
) = if (width == IntrinsicSize.Min) measurable.minIntrinsicWidth(height) else
measurable.maxIntrinsicWidth(height)
override fun IntrinsicMeasureScope.maxIntrinsicWidth(
measurable: IntrinsicMeasurable,
height: Int
) = if (width == IntrinsicSize.Min) measurable.minIntrinsicWidth(height) else
measurable.maxIntrinsicWidth(height)
}SameWidthBoxes
kotlin
// Builds a layout containing three Box having the same width as the widest one.
//
// Here width min intrinsic is adding a width premeasurement pass for the
// Column, whose minimum intrinsic width will correspond to the preferred width of the largest
// Box. Then width min intrinsic will measure the Column with tight width, the
// same as the premeasured minimum intrinsic width, which due to fillMaxWidth will force
// the Box's to use the same width.
Box {
Column(Modifier.width(IntrinsicSize.Min).fillMaxHeight()) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
.size(20.dp, 10.dp)
.background(Color.Gray)
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
.size(30.dp, 10.dp)
.background(Color.Blue)
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
.size(10.dp, 10.dp)
.background(Color.Magenta)
)
}
}SameWidthTextBoxes
kotlin
// Builds a layout containing three Text boxes having the same width as the widest one.
//
// Here width max intrinsic is adding a width premeasurement pass for the Column,
// whose maximum intrinsic width will correspond to the preferred width of the largest
// Box. Then width max intrinsic will measure the Column with tight width, the
// same as the premeasured maximum intrinsic width, which due to fillMaxWidth modifiers will
// force the Boxs to use the same width.
Box {
Column(Modifier.width(IntrinsicSize.Max).fillMaxHeight()) {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().background(Color.Gray)) {
Text("Short text")
}
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().background(Color.Blue)) {
Text("Extremely long text giving the width of its siblings")
}
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().background(Color.Magenta)) {
Text("Medium length text")
}
}
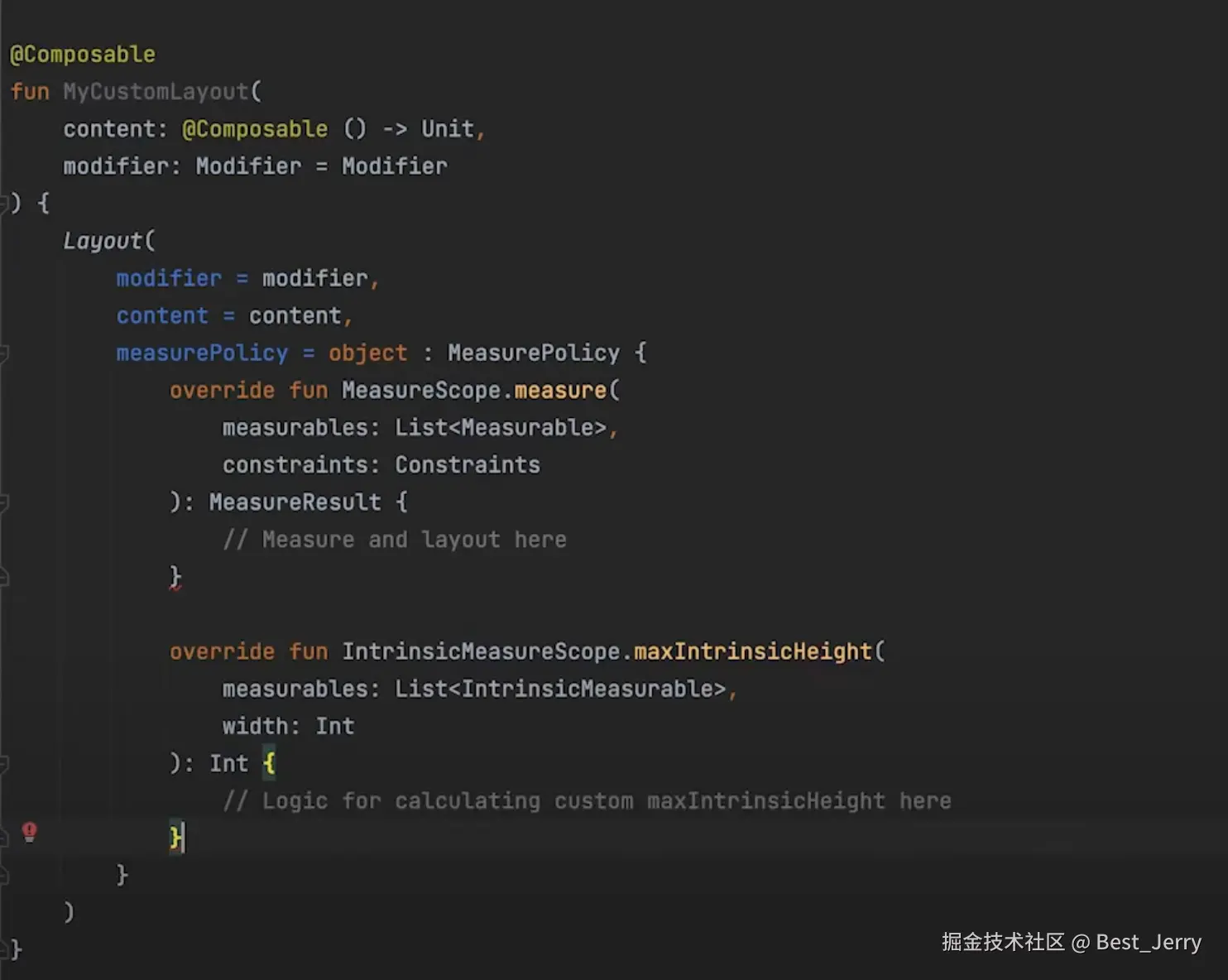
}自定义 Intrinsic measurements
5. Rules in Compose
-
Order of Compose phases
-
Single pass measurement