想象一下,你开了一家非常智能的咖啡馆。顾客点餐、制作咖啡、展示菜单,一切都井井有条。MVVM就像这个咖啡馆的幕后英雄,让每个环节都高效且独立地运作。
MVVM 代表:
-
M (Model) :菜单和食材库。它存储着所有咖啡的种类、价格、配料(数据),以及制作咖啡的规则(业务逻辑)。它不会直接和顾客打交道。
-
V (View) :智能点餐触摸屏。顾客直接看到和操作的部分。它展示咖啡信息,接收顾客的点单,但它不知道咖啡是怎么做出来的,也不直接去拿食材。它只管显示和把顾客的操作传达出去。
-
VM (ViewModel) :点餐系统的大脑/咖啡师助手。这是最核心的部分!它像是连接触摸屏(View)和菜单/食材库(Model)的智能中介。
- 它从菜单库(Model)那里获取咖啡信息,然后智能地整理好,告诉触摸屏(View)应该显示什么。
- 它接收触摸屏(View)传来的顾客点单请求,然后根据这些请求,去指挥菜单库(Model)怎么操作(比如"给我一份拿铁的配方")。
- 最厉害的是,它记住了当前的点单状态。即使触摸屏(View)暂时黑屏重启了(比如手机旋转导致Activity重建),它也能立刻恢复之前的点单信息,不会让顾客重新点一遍!
-
LiveData :透明的咖啡制作进度牌。当咖啡师助手(ViewModel)告诉厨房(Model)去做咖啡时,厨房会把制作进度实时更新到这个进度牌上。触摸屏(View)只要盯着这个进度牌,一有更新就立即显示给顾客看,而不需要一直去问厨房"做好了没?"
为什么要用MVVM?
在没有MVVM之前,我们的"点餐系统"可能是这样的:服务员(View)直接跑到厨房(Model)去拿菜单,然后回来告诉顾客。顾客点了单,服务员又直接跑去厨房说"做一杯拿铁"。这样会导致:
- 服务员太累了:既要面对顾客,又要懂厨房的各种配方和制作流程,职责太多。
- 效率低下:服务员频繁往返于顾客和厨房之间,而且一旦服务员换班,新来的服务员可能要重新熟悉厨房。
- 难以扩展:如果厨房新增了咖啡种类,服务员也要重新学习。
MVVM的出现,就像引入了"点餐系统的大脑/咖啡师助手",让各司其职,大大提升了效率和可维护性。
MVVM在Android中的代码实现(简化版咖啡馆示例)
我们来做一个简单的Android应用,显示咖啡信息并可以更新。
1. Model (菜单和食材库)
这里我们用Repository模式来代表Model层,它负责数据的获取和管理。
Coffee.kt (实体类 - 具体的一杯咖啡)
kotlin
// src/main/java/com/example/mvvmcoffeebar/model/Coffee.kt
package com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.model
data class Coffee(
val id: String,
val name: String,
val description: String,
val price: Double
)CoffeeRepository.kt (数据仓库 - 模拟数据源)
kotlin
// src/main/java/com/example/mvvmcoffeebar/model/CoffeeRepository.kt
package com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.model
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
// 菜单和食材库,负责提供咖啡数据
class CoffeeRepository {
private var currentCoffee = Coffee("latte_001", "拿铁", "香醇牛奶与浓缩咖啡的完美融合", 25.0)
// 模拟从数据库或网络获取咖啡信息
suspend fun getCoffeeById(id: String): Coffee {
delay(1000) // 模拟网络延迟
return currentCoffee // 简化处理,每次都返回当前咖啡
}
// 模拟更新咖啡信息
suspend fun updateCoffeeDescription(id: String, newDescription: String): Coffee {
delay(500) // 模拟网络延迟
if (currentCoffee.id == id) {
currentCoffee = currentCoffee.copy(description = newDescription)
}
return currentCoffee
}
}2. ViewModel (点餐系统的大脑/咖啡师助手)
它持有LiveData,并与Repository交互。
kotlin
// src/main/java/com/example/mvvmcoffeebar/viewmodel/CoffeeViewModel.kt
package com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.viewmodel
import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.model.Coffee
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.model.CoffeeRepository
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
// 咖啡师助手,连接 View 和 Model,管理UI状态
class CoffeeViewModel(private val repository: CoffeeRepository) : ViewModel() {
// MutableLiveData 是可变的,供 ViewModel 内部修改
private val _coffee = MutableLiveData<Coffee>()
// LiveData 是不可变的,供 View 观察,保证数据只能由 ViewModel 修改
val coffee: LiveData<Coffee> get() = _coffee
private val _isLoading = MutableLiveData<Boolean>()
val isLoading: LiveData<Boolean> get() = _isLoading
private val _errorMessage = MutableLiveData<String>()
val errorMessage: LiveData<String> get() = _errorMessage
init {
loadCoffeeDetails("latte_001") // 初始加载拿铁信息
}
// 从 Model 获取咖啡详情
fun loadCoffeeDetails(coffeeId: String) {
viewModelScope.launch {
_isLoading.value = true // 显示加载状态
_errorMessage.value = null // 清除错误信息
try {
val coffeeData = repository.getCoffeeById(coffeeId)
_coffee.value = coffeeData // 更新 LiveData,View 会自动收到通知
} catch (e: Exception) {
_errorMessage.value = "加载咖啡信息失败: ${e.message}"
} finally {
_isLoading.value = false // 隐藏加载状态
}
}
}
// 更新咖啡描述(通过用户输入)
fun updateCoffeeDescription(newDescription: String) {
_coffee.value?.let { currentCoffee ->
viewModelScope.launch {
_isLoading.value = true
_errorMessage.value = null
try {
val updatedCoffee = repository.updateCoffeeDescription(currentCoffee.id, newDescription)
_coffee.value = updatedCoffee // 更新 LiveData
} catch (e: Exception) {
_errorMessage.value = "更新描述失败: ${e.message}"
} finally {
_isLoading.value = false
}
}
}
}
}CoffeeViewModelFactory.kt (ViewModel的工厂类,用于构造ViewModel)
kotlin
// src/main/java/com/example/mvvmcoffeebar/viewmodel/CoffeeViewModelFactory.kt
package com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.viewmodel
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.model.CoffeeRepository
// 用于创建带有参数的 ViewModel 实例
class CoffeeViewModelFactory(private val repository: CoffeeRepository) : ViewModelProvider.Factory {
override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T {
if (modelClass.isAssignableFrom(CoffeeViewModel::class.java)) {
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
return CoffeeViewModel(repository) as T
}
throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown ViewModel class")
}
}3. View (智能点餐触摸屏)
Activity或Fragment,负责显示数据和处理用户交互。我们使用 Data Binding 来让 View 和 ViewModel 之间的连接更简洁。
activity_main.xml (布局文件)
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<!-- 声明一个 ViewModel 变量,用于在布局中直接访问 ViewModel 的数据和方法 -->
<data>
<variable
name="viewModel"
type="com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.viewmodel.CoffeeViewModel" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp"
tools:context=".view.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_coffee_name_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="咖啡名称:"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_coffee_name"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:text="@{viewModel.coffee.name}"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/tv_coffee_name_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@id/tv_coffee_name_label"
tools:text="拿铁" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_coffee_desc_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:text="描述:"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/tv_coffee_name" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_coffee_description"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:text="@{viewModel.coffee.description}"
android:textSize="16sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/tv_coffee_desc_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@id/tv_coffee_desc_label"
tools:text="香醇牛奶与浓缩咖啡的完美融合" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_coffee_price_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:text="价格:"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/tv_coffee_description" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_coffee_price"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(viewModel.coffee.price)}"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/tv_coffee_price_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@id/tv_coffee_price_label"
tools:text="25.0" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_new_description"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
android:hint="输入新的咖啡描述"
android:minHeight="48dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/tv_coffee_price" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_update_description"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:onClick="@{() -> viewModel.updateCoffeeDescription(etNewDescription.getText().toString())}"
android:text="更新描述"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/et_new_description" />
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="@{viewModel.isLoading ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_error_message"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textColor="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:text="@{viewModel.errorMessage}"
android:visibility="@{viewModel.errorMessage != null ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/btn_update_description"
tools:text="加载失败" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>MainActivity.kt (Activity)
kotlin
// src/main/java/com/example/mvvmcoffeebar/view/MainActivity.kt
package com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.view
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.viewModels
import androidx.databinding.DataBindingUtil
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.R
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.model.CoffeeRepository
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.viewmodel.CoffeeViewModel
import com.example.mvvmcoffeebar.viewmodel.CoffeeViewModelFactory
// 智能点餐触摸屏,只负责显示和接收用户操作
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
private val coffeeViewModel: CoffeeViewModel by viewModels {
CoffeeViewModelFactory(CoffeeRepository()) // 使用工厂创建 ViewModel 实例
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 初始化 Data Binding
binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main)
// 将 ViewModel 绑定到布局,这样布局可以直接访问 ViewModel 的数据和方法
binding.viewModel = coffeeViewModel
// 将 Activity 的生命周期所有者设置为 Data Binding,
// 这样 LiveData 的观察者就能正确地跟随 Activity 的生命周期
binding.lifecycleOwner = this
// 如果不使用 Data Binding,你需要手动观察 LiveData 变化并更新 UI
// coffeeViewModel.coffee.observe(this) { coffee ->
// binding.tvCoffeeName.text = coffee.name
// binding.tvCoffeeDescription.text = coffee.description
// binding.tvCoffeePrice.text = coffee.price.toString()
// }
//
// coffeeViewModel.isLoading.observe(this) { isLoading ->
// binding.progressBar.visibility = if (isLoading) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE
// }
//
// coffeeViewModel.errorMessage.observe(this) { message ->
// binding.tvErrorMessage.text = message
// binding.tvErrorMessage.visibility = if (message != null) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE
// }
}
}必要的 build.gradle 配置
在 app/build.gradle 中添加以下依赖和配置:
gradle
android {
...
buildFeatures {
dataBinding true // 启用 Data Binding
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = '1.8'
}
}
dependencies {
// ViewModel 和 LiveData
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.6.2"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-livedata-ktx:2.6.2"
// Kotlin Coroutines 支持 ViewModel
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.6.2"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.7.1"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.7.1"
// Activity KTX (用于 by viewModels() 委托)
implementation "androidx.activity:activity-ktx:1.8.0"
// 其他默认依赖
implementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.12.0'
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.6.1'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.9.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.1.4'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.13.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.5'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.5.1'
}整个调用过程时序图
让我们用时序图来描述这个智能咖啡馆点餐系统的整个流程:
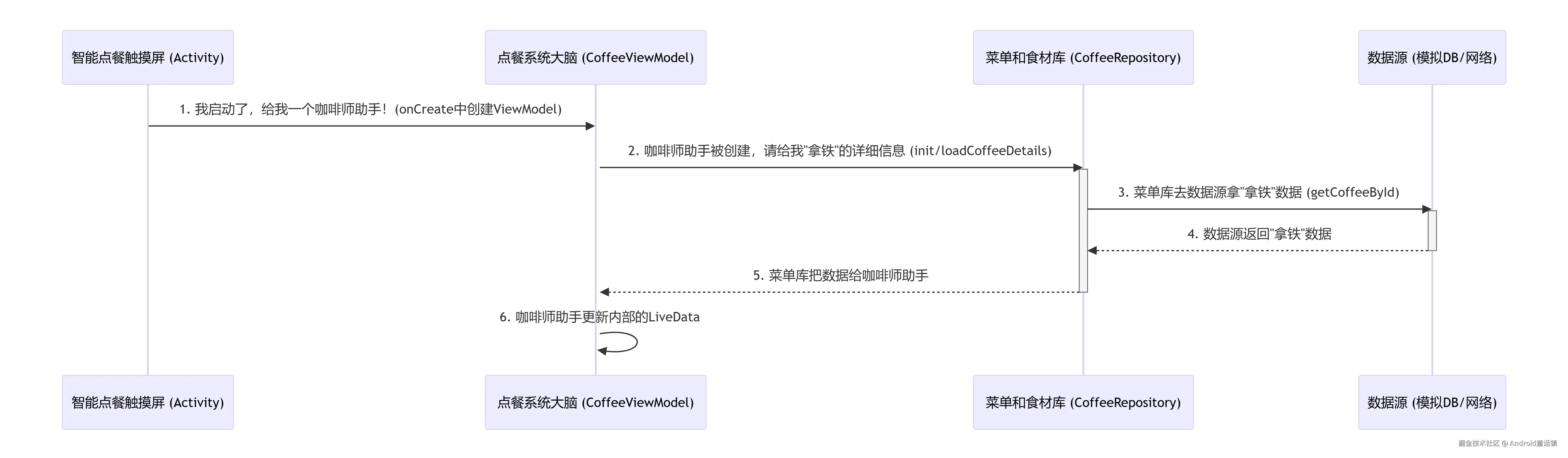
总结
MVVM模式通过View、ViewModel和Model三者的清晰职责划分,以及LiveData(或StateFlow等)这种响应式的数据流,大大提高了Android应用的:
- 职责分离:View 只负责 UI 渲染和事件传递,ViewModel 负责 UI 逻辑和状态管理,Model 负责业务逻辑和数据。
- 可测试性:ViewModel 不依赖 Android 框架,可以独立进行单元测试。
- 生命周期感知 :
LiveData和ViewModel能感知Activity/Fragment的生命周期,自动管理数据更新,避免内存泄漏。ViewModel还能在配置变化(如屏幕旋转)时存活,保存UI状态。 - 可维护性和可扩展性:各模块独立,修改一处不易影响其他部分。
就像我们的智能咖啡馆,每个角色都只做自己最擅长的事情,从而提供更稳定、高效、易于管理的点餐体验!希望这个故事和代码示例能让你对MVVM有一个深刻且有趣的理解!