MarkDown格式文档的结构化提取
前言
在做RAG工作中,数据处理的好坏往往决定着RAG效果的好坏。经过实际的测试,MarkDown格式的文本相较docx、pdf等格式无疑是最合适的,本篇将详细介绍MarkDown格式文档的结构化提取的全流程。
样例格式
为了兼顾更加全面的场景,本篇采用的文章格式为:文章标题-编-章-节-条-内容。由于不同文章的格式并不一定完全一致,为了兼容由docx或pdf转换而来的markdown(很难完全正确提取出二级标题、三级标题),全流程只有文章标题直接使用了markdown中一级标题的格式,其余标题均使用正则表达式以及内容匹配的方式实现。
由于由docx与pdf转换来的markdown格式并不完全一致,所以本篇代码并不能直接兼容所有格式,但针对相关的函数中正则表达式稍加修改仍然可以流畅使用。
处理的实际内容不便展示,所以用AI生成了类似结构的markdown文档,示例如下:

生成时用到的提示词如下:
bash
写一个AI的介绍,要求满足以下格式:文章标题-编-章-节-条,具体格式类似于:第一编、第一章、第一节、第一条提取文章标题结构
导入依赖包
python
import os
import re判断是否为文章标题
这个函数看起有些复杂,但实质上的判断逻辑是
- 以#开头
- 排除掉处理的文字为:编、章、节、条的可能性
python
def is_title(line):
# 判断是否为问题标题
head = (len(line.strip()) > 0) and (line[0] == "#")
is_preface = "序言" in line.strip().replace("#", "").replace(" ", "") # 序言应该排除在外
is_general_outline = "总纲" in line.strip().replace("#", "").replace(" ", "") # 总纲应该排除在外
is_supplementary_provisions = "附则" in line.strip().replace("#", "").replace(" ", "") # 附则排除
volume_pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+编'
is_normal_volume = bool(re.search(volume_pattern, line))
chapter_pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+章'
is_normal_chapter = bool(re.search(chapter_pattern, line)) # 第一章、第二章之类的常规章应该排除在外
attachment_pattern = r'附件[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+'
is_normal_attachment = bool(re.search(attachment_pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", ""))) # 附件归为章
section_pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+节'
is_normal_section = bool(re.search(section_pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", ""))) # 第一节、第二节之类的常规节应该排除在外
article_pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+条'
is_article_head = bool(re.search(article_pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", "")))
item_pattern = r"[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+、"
is_item = bool(re.search(item_pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", "")))
number_start_pattern = r'[0-9].+' # 数字开始排除
is_number_start = bool(re.search(number_start_pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", "")))
return head and not (is_general_outline or is_normal_chapter or is_normal_section or is_article_head or is_item or is_normal_volume or is_preface or is_supplementary_provisions or is_normal_attachment or is_number_start)判断第几编
使用正则表达式判断是否为编
python
def is_volume(line):
# 判断编
head = (len(line.strip()) > 0) and (line[0] == "#")
volume_pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+编'
is_normal_volume = bool(re.search(volume_pattern, line))
return head and is_normal_volume判断第几章
判断章的逻辑如下:
- 以"第X章"开头
- 以"附件"开头
- "总纲"、"序言"、"附则"也归为章
python
def is_chapter(line):
# 判断是否为章
head = (len(line.strip()) > 0) and (line[0] == "#")
pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+章'
is_normal_chapter = bool(re.search(pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", ""))) # 判断 第一章、第二章之类的常规章
attachment_pattern = r'附件[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+'
is_normal_attachment = bool(re.search(attachment_pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", ""))) # 附件归为章
is_general_outline = "总纲" in line.strip().replace("#", "").replace(" ", "") # 总纲也算作章这一类里
is_preface = "序言" in line.strip().replace("#", "").replace(" ", "") # 序言应该算进来
is_supplementary_provisions = "附则" in line.strip().replace("#", "").replace(" ", "") # 附则算入
return head and (is_normal_chapter or is_general_outline or is_preface or is_supplementary_provisions or is_normal_attachment)判断第几节
以"第X节"开头的认为是节
python
def is_section(line):
# 判断是否为节
head = (len(line.strip()) > 0) and (line[0] == "#")
pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+节'
is_normal_section = bool(re.search(pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", ""))) # 判断 第一节、第二节之类的常规节
return head and is_normal_section判断条的开头
以"第X条"开头的要归为条
python
def is_article(line):
# 判断是否为条的开头
pattern = r'第[\u4e00-\u9fa50-9]+条'
is_article_head = bool(re.search(pattern, line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", "")))
return is_article_head划分函数
主体的思路就是读取每一行,然后判断每一行属于章节还是内容,并构建字典,如果文章中不存在某个结构,字典的键应该为"未分章"、"未分节"这种样式。
需要注意的是,如果一行文字,不属于标题、编、章、节,也没有以"第X条"开头,说明他是"第X条"的一部分,应该与上面的条信息拼合
python
blank_list = ["目录"]
def split_title(path):
file_dict = dict()
with open(path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
pre_title = ""
pre = ""
title_line = ""
volume_line = ""
chapter_line = ""
section_line = ""
article_line = ""
for line in f.readlines():
if len(line.strip()) > 0:
striped_line = line.replace("#", "").replace(" ", "").strip()
if is_title(line) and striped_line not in blank_list:
# 判断文章标题
volume_line = ""
chapter_line = ""
section_line = ""
article_line = ""
if pre_title == "title":
del file_dict[pre]
title_line = pre + striped_line
else:
title_line = striped_line
file_dict[title_line] = {}
pre_title = "title"
elif is_volume(line):
# 编
volume_line = striped_line
chapter_line = ""
section_line = ""
article_line = ""
pre_title = "volume"
if len(file_dict) > 0:
file_dict[title_line][volume_line] = {}
pre_title = "volume"
elif is_chapter(line):
# 章
chapter_line = striped_line
section_line = ""
article_line = ""
pre_title = "chapter"
if len(file_dict) > 0:
tmp_volume = volume_line if volume_line != "" else "未分编"
if tmp_volume not in file_dict[title_line].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume] = {}
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][chapter_line] = {}
pre_title = "chapter"
elif is_section(line):
# 节
section_line = striped_line
article_line = ""
tmp_volume = volume_line if volume_line != "" else "未分编"
tmp_chapter = chapter_line if chapter_line != "" else "未分章"
if tmp_volume not in file_dict[title_line].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume] = {}
if tmp_chapter not in file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter] = {}
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][striped_line] = []
pre_title = "section"
elif is_article(line):
# 条
article_line = striped_line
tmp_volume = volume_line if volume_line != "" else "未分编"
tmp_chapter = chapter_line if chapter_line != "" else "未分章"
tmp_section = section_line if section_line != "" else "未分节"
if tmp_volume not in file_dict[title_line].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume] = {}
if tmp_chapter not in file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter] = {}
if tmp_section not in file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section] = []
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section].append(article_line)
pre_title = "article"
else:
# 普通
tmp_volume = volume_line if volume_line != "" else "未分编"
tmp_chapter = chapter_line if chapter_line != "" else "未分章"
tmp_section = section_line if section_line != "" else "未分节"
if tmp_volume not in file_dict[title_line].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume] = {}
if tmp_chapter not in file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter] = {}
if tmp_section not in file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter].keys():
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section] = []
if len(file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section]) > 0:
# print("tmp_section:", file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section][-1] )
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section][-1] += striped_line
else:
# print("normal:", striped_line)
file_dict[title_line][tmp_volume][tmp_chapter][tmp_section].append(striped_line)
pre_title = ""
pre = striped_line
# for title in file_dict:
# print(title.keys())
with open(path.replace(".md", ".json"), "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(file_dict, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
split_title("./md_file/人工智能(AI)全景介绍.md")提取到的信息满足以下结构
bash
{
"标题"{
"编":{
"章":{
"节":[
"第一条",
"第二条",
etc...
],
etc...
},
etc...
},
etc...
},
etc...
}提取后的效果如下:
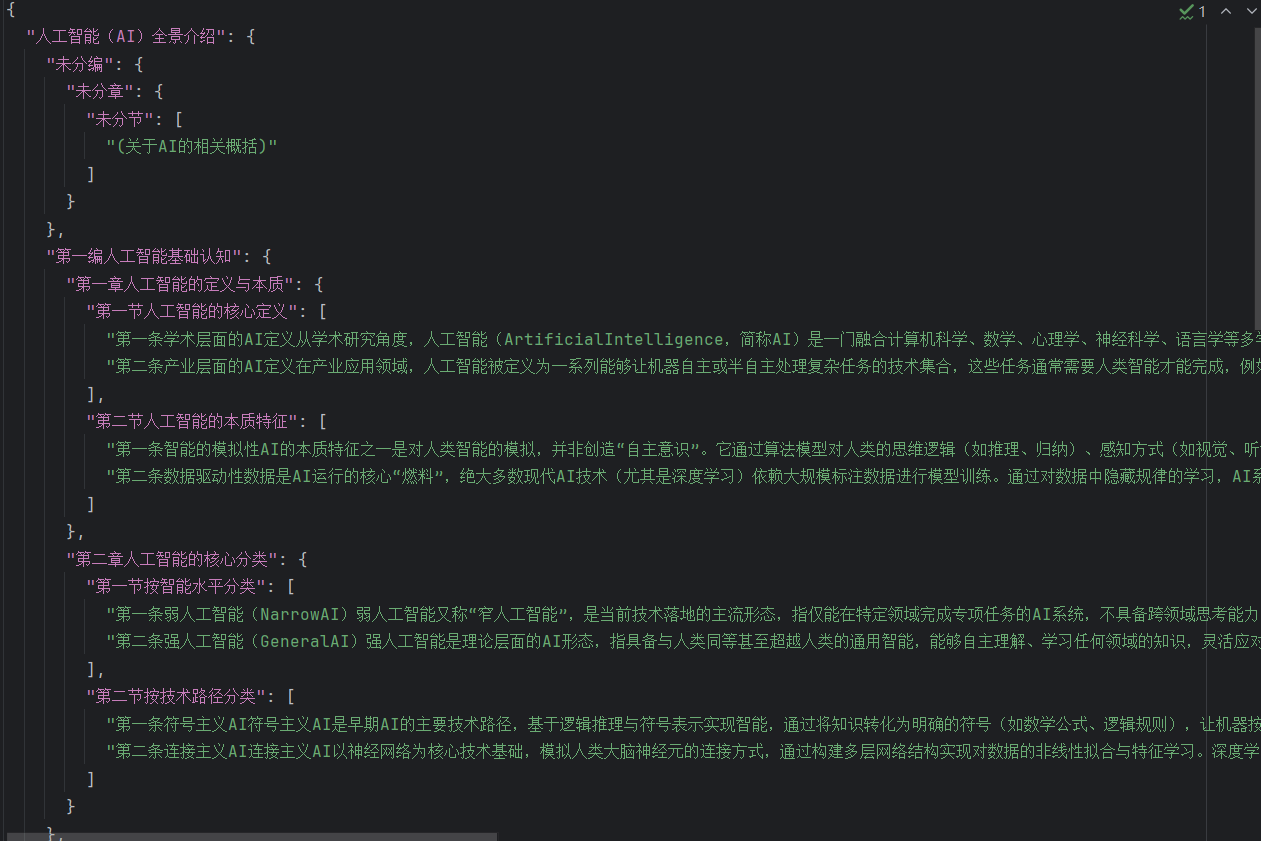
从结构化信息中分离标题和内容
上面得到的结构化的数据并不能够直接用于RAG,并且有时内容过长需要进行切割。为了尽可能保证信息的完整性,切割时要完整保存文章标题-编-章-节-条的信息,仅对内容信息进行切割。为了实现这一功能,首先要把标题和内容区分开
提取条开头
由于我们前面已经得到结构化的标题-编-章-节数据了,所以接下来只需要提取条就可以了
python
def extract_by_prefixes(text):
"""
提取文本中以"第XXX条"或"【任意字符】"为开头的内容
参数:
text: 待处理的文本
include_content: 是否包含该条目的后续内容(直到下一个前缀出现或文本结束)
返回:
包含匹配结果的列表,每个元素为字典,包含前缀信息和内容(如启用)
"""
# 正则模式:匹配两种前缀
# 1. 第XXX条:支持数字、汉字数字(一至十、百、千等)
# 2. 【任意字符】:匹配以【开头、】结尾的任意内容(非贪婪匹配)
pattern = r'(第[零一二三四五六七八九十百千万\d]+条|【.*?】)'
results = []
# 找到所有匹配的前缀及其位置
match = re.match(pattern, text) # re.DOTALL让.匹配换行符
if match:
prefix = match.group() # 完整前缀(如"第3条"或"【注意事项】")
start_pos = match.end() # 前缀结束的位置(内容开始处)
result = {"prefix": prefix, "content": text[start_pos:]}
results.append(result)
return results分离标题和内容
分离的过程十分简单,遍历字典,并且提取出条开头,然后合并标题信息即可。
python
def split_prefix(path):
with open(path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.loads(f.read())
prefix2data = []
for title in data.keys():
for volume in data[title]:
for chapter in data[title][volume]:
for section in data[title][volume][chapter]:
for article in data[title][volume][chapter][section]:
cur_title = title
if volume != "未分编":
cur_title += volume
if chapter != "未分章":
cur_title += chapter
if section != "未分节":
cur_title += section
full_results = extract_by_prefixes(article)
if len(full_results) > 0:
for item in full_results:
prefix2data.append({"prefix": cur_title + item["prefix"], "data": item['content']})
else:
prefix2data.append({"prefix": cur_title, "data": article})
for data in prefix2data:
print(data)
with open(path.replace(".json", "-prefix.json"), "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(prefix2data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
split_prefix(path="./md_file/人工智能(AI)全景介绍.json")提取到的信息的结构如下:
python
[
{
"prefix": "标题",
"data": "信息"
},
etc...
]提取后的效果如下:
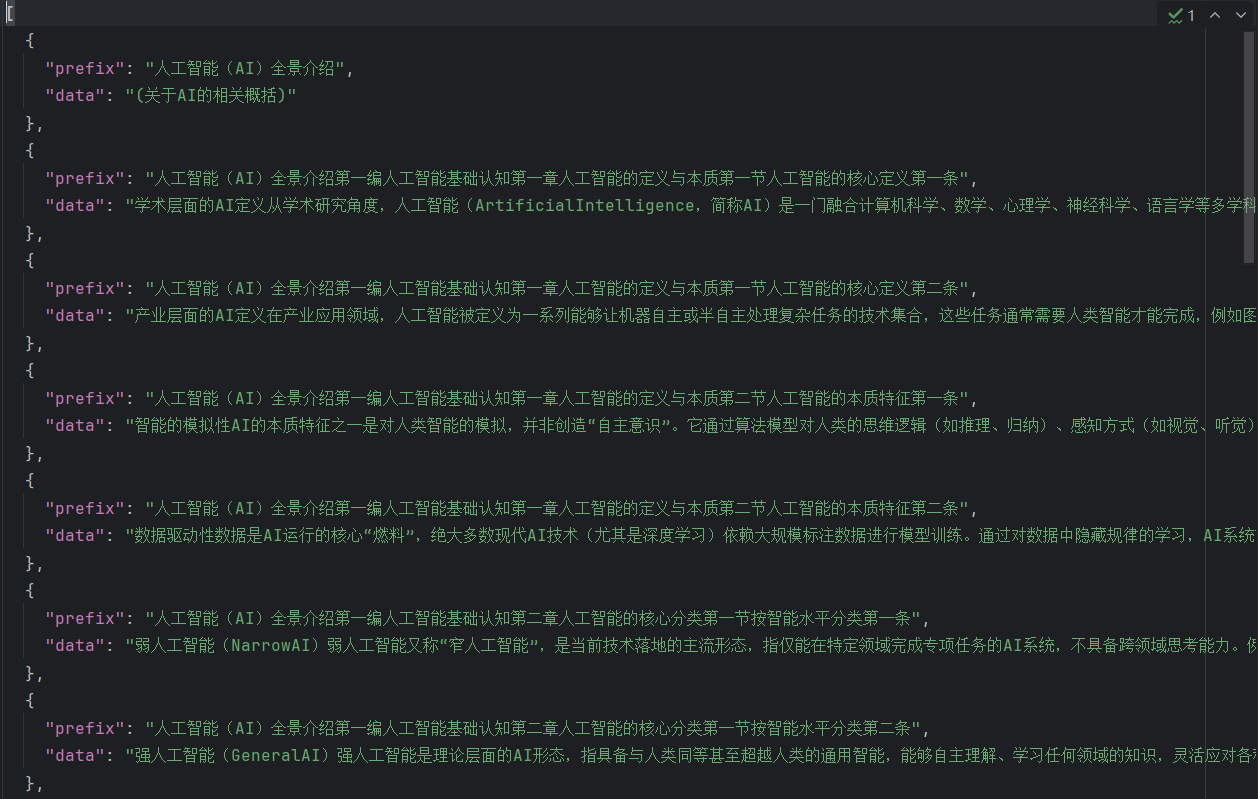
信息入库前的切分
切分的原因主要考虑两方面
- 大模型上下文的限制
- embedding模型的限制
句子末尾坐标提取
为了保证句子的完整性,最好是按照句子分割,第一步就是要找到结尾符号的坐标,同样的也是用到了正则表达式。
python
def find_sentence_endings(text):
"""
查找字符串中所有句尾符号(中英文句号、问号、叹号)及其位置
参数:
text: 待查询的字符串
返回:
包含元组的列表,每个元组格式为(符号, 位置索引)
"""
# 定义需要查找的句尾符号(中英文)
end_symbols = {'.', '。', '?', '?', '!', '!', ';'}
# 存储结果的列表
results = []
# 遍历字符串,检查每个字符
for index, char in enumerate(text):
if char in end_symbols:
results.append((char, index))
return results结合坐标和间隔分割字符串
python
def split_string_by_coords_and_interval(text, coords, interval_limit, overlap):
"""
结合坐标和间隔分割字符串
参数:
text: 待分割的原始字符串
coords: 含有部分字符串位置的坐标列表(需已排序)
interval_limit: 间隔限定(最大段长度)
overlap_ratio: 重叠度(0-1之间,例如0.2表示20%重叠)
返回:
分割后的字符串列表
"""
if not text:
return []
# 确保坐标在有效范围内且已排序
valid_coords = sorted([c for c in coords if 0 <= c <= len(text)])
# 添加首尾位置确保完整分割
all_points = [0] + valid_coords + [len(text)]
segments = []
i = 0
while i < len(all_points) - 1:
start = all_points[i]
end = all_points[i + 1]
segment_length = end - start
if len(segments) > 0 and segment_length + len(segments[-1]) < interval_limit:
# 当上文再加上这一句仍然没有超过长度限制时
segments[-1] = segments[-1] + text[start:end]
elif segment_length < interval_limit:
# 当上文超过限制,但是这一句没超过限制时
segments.append(text[start: end])
else:
# 按照重叠字符和长度限制切割
for idx in range(0, segment_length, int(interval_limit - overlap)):
segments.append(text[start:end][idx:idx+interval_limit])
if segments[-1] in text[start:end][-interval_limit:]:
segments[-1] = text[start:end][-interval_limit:]
i += 1
return segments调用并切分
python
def data_cut_for_vector(path, max_token=200):
with open(path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.loads(f.read())
with open(path.replace(".json", "-cuted.txt"), "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for d in data:
prefix = d["prefix"]
file = d["data"]
diff = max_token - len(prefix)
endings = find_sentence_endings(file)
pos_lst = [pos + 1 for symbol, pos in endings]
overlap = 40 # 重叠度40
segments = split_string_by_coords_and_interval(file, coords=pos_lst, interval_limit=diff, overlap=40)
for line in segments:
if line != "":
f.write(prefix + " " + line + "\n")
data_cut_for_vector(path="./md_file/人工智能(AI)全景介绍-prefix.json")切割后结果如下:
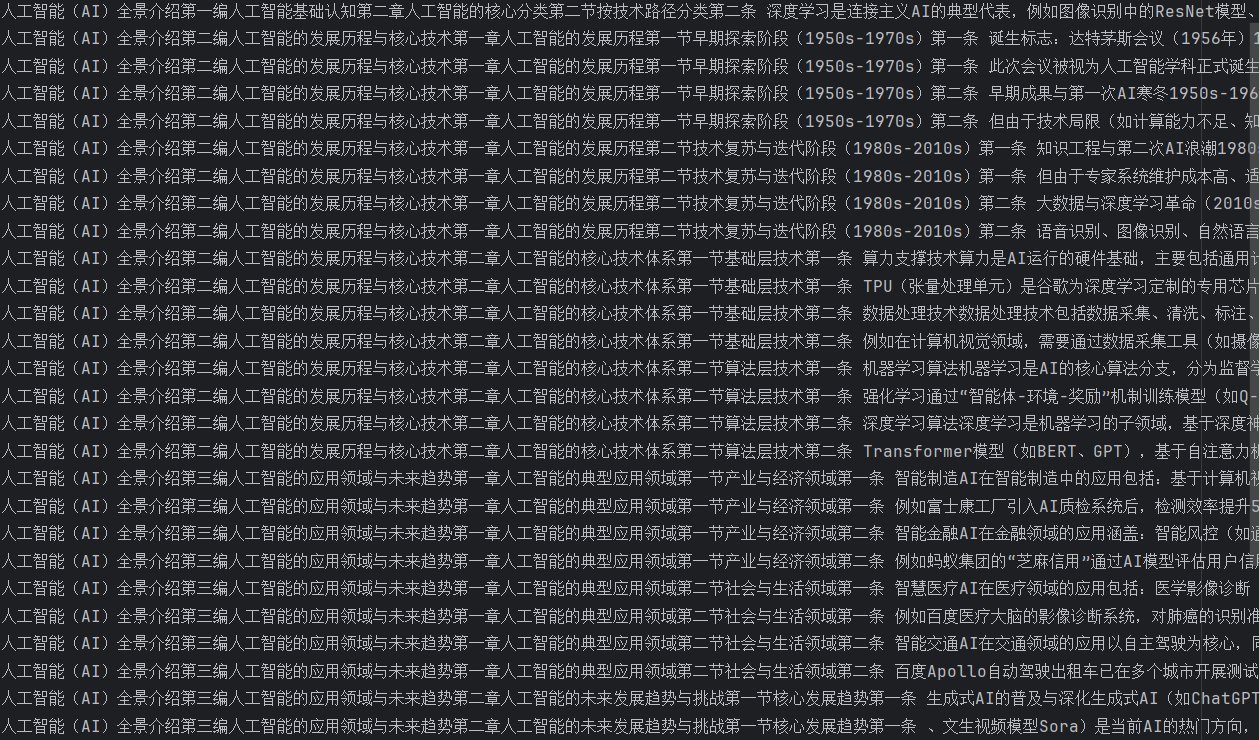
左侧是标题,右侧是切好的内容,以空格分割