一、智能体实现关键技术
CoT思维链
作用
让Ai能想人一样可以思考,帮助AI在解决复杂的问题时,可以按照步骤一次思考执行。
实现方法
主要针对propmt去做优化,当用户输入完成后,开发者可以在用户输入后拼接提示词(让我们一步一步思考这个问题),可以让模型逐步的去生成答案。
OpenManus prompt参考:
latex
You are an assistant focused on Chain of Thought reasoning. For each question, please follow these steps:
1. Break down the problem: Divide complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts
2. Think step by step: Think through each part in detail, showing your reasoning process
3. Synthesize conclusions: Integrate the thinking from each part into a complete solution
4. Provide an answer: Give a final concise answer
Your response should follow this format:
Thinking: [Detailed thought process, including problem decomposition, reasoning for each step, and analysis]
Answer: [Final answer based on the thought process, clear and concise]
Remember, the thinking process is more important than the final answer, as it demonstrates how you reached your conclusion.
latex
翻译:
你是一名专注于思维链推理的助手。对于每个问题,请按照以下步骤操作:
1.分解问题:将复杂问题分解为更小、更易于管理的部分
2.逐步思考:仔细思考每个部分,展示你的推理过程
3.综合结论:将每个部分的思维整合成一个完整的解决方案
4.提供答案:给出一个简洁的最终答案
您的回复应遵循以下格式:
思考:[详细的思考过程,包括问题分解、每一步推理和分析]
答案:[基于思维过程的最终答案,清晰简洁]
记住,思考过程比最终答案更重要,因为它展示了你是如何得出结论的。
Agent Loop
Agent Loop是智能体的核心工作机制
作用
在用户没有输入的情况下,可以让智能体自主重复的进行思考推理和工具调用
实现
我们可以定义可以执行的最大步骤数量,如果在目标数量内并没有得到需要的结果就一直执行。
java
public String agentLoop(){
List<String> results = new ArrayList();
int maxStep= 10;
int currentStep=0;
while(currentStep<=maxStep){
currentStep++;
// 工具调用并返回结果
String result = resultMessage();
results.add("工具调用次数为:" + currentstop+"结果为:"+result);
}
if(currentStep>maxStep){
results.add("达到最大步骤了"+maxStep):
}
return Stirong.join("\n",results);
}ReAct模式
ReAct模式是一种结合推理和行动的智能体架构
作用
模仿人类"思考--行动--观察"的循环
核心:
java
推理(Reason):将原始问题拆分为多步骤任务,明确当前要执行的步骤,比如 "第一步需要打开网站"。
行动(Act):调用外部工具执行动作,比如调用搜索引擎、打开浏览器访问网页等。
观察(Observe):获取工具返回的结果,反馈给智能体进行下一步决策。比如将打开的网页代码输入给 AI。
循环迭代:不断重复上述 3 个过程,直到任务完成或达到终止条件。实现
java
void executeReAct(String task) {
String state = "开始";
while (!state.equals("完成")) {
String thought = "思考下一步行动";
System.out.println("推理: " + thought);
String action = "执行具体操作";
System.out.println("行动: " + action);
String observation = "观察执行结果";
System.out.println("观察: " + observation);
state = "完成";
}
}二、分析OpenManus源码
项目整体结构
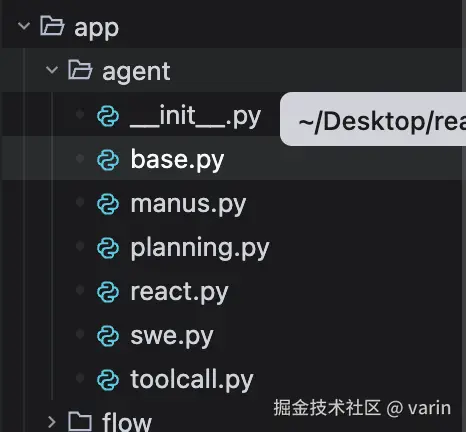
base.py
最为核心的基类,主要提供了状态管理 和执行循环
在这个类文件中,分别定义了四种状态来判断大模型是否需要下一步操作。
通过run方法来进行循环控制
python
class AgentState(str, Enum):
"""Agent execution states"""
IDLE = "IDLE" # 空闲
RUNNING = "RUNNING" # 运行
FINISHED = "FINISHED" # 完成
ERROR = "ERROR" # 错误
python
async def run(self, request: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
"""Execute the agent's main loop asynchronously.
Args:
request: Optional initial user request to process.
Returns:
A string summarizing the execution results.
Raises:
RuntimeError: If the agent is not in IDLE state at start.
"""
if self.state != AgentState.IDLE:
# 判断是否空闲
raise RuntimeError(f"Cannot run agent from state: {self.state}")
if request:
self.update_memory("user", request) # 配置对象
results: List[str] = []
async with self.state_context(AgentState.RUNNING):
while (
# 判断条件,是否到最大步骤数和状态是否为完成
self.current_step < self.max_steps and self.state != AgentState.FINISHED
):
self.current_step += 1
logger.info(f"Executing step {self.current_step}/{self.max_steps}")
step_result = await self.step() # 执行步骤并返回结果
# Check for stuck state
if self.is_stuck():
self.handle_stuck_state()
results.append(f"Step {self.current_step}: {step_result}") # 添加结果到集合中
# # 循环结束,判断步数,并重制参数,
if self.current_step >= self.max_steps:
self.current_step = 0
self.state = AgentState.IDLE
results.append(f"Terminated: Reached max steps ({self.max_steps})")
# 集合转为字符串
return "\n".join(results) if results else "No steps executed"
python
#base类还定义了一个抽象方法给子类去具体实现,
@abstractmethod
async def step(self) -> str:
"""Execute a single step in the agent's workflow.
Must be implemented by subclasses to define specific behavior.
"""react.py
作用:继承base,并实现ReAct模式,具有思考和行动两个步骤
python
class ReActAgent(BaseAgent, ABC):
// 思考
@abstractmethod
async def think(self) -> bool:
"""Process current state and decide next action"""
# 行动
@abstractmethod
async def act(self) -> str:
"""Execute decided actions"""
#步骤:先进行思考,如果思考后没有结果直接返回(可能程序结束,也有可以会重新思考),有结果就执行行动。
async def step(self) -> str:
"""Execute a single step: think and act."""
should_act = await self.think()
if not should_act:
return "Thinking complete - no action needed"
return await self.act()toolcall.py
作用:继承react类,并重写think和act方法,实现具体的工具调用。
在该类中定义了_handle_special_tool方法,用于判断某个工具的名称是否在工具列表中,这样我们就可以通过定义一个终止工具来让程序停止。
python
async def _handle_special_tool(self, name: str, result: Any, **kwargs):
"""Handle special tool execution and state changes"""
if not self._is_special_tool(name):
return
if self._should_finish_execution(name=name, result=result, **kwargs):
# Set agent state to finished
logger.info(f"🏁 Special tool '{name}' has completed the task!")
self.state = AgentState.FINISHED
python
@staticmethod
def _should_finish_execution(**kwargs) -> bool:
"""Determine if tool execution should finish the agent"""
return True
def _is_special_tool(self, name: str) -> bool:
"""Check if tool name is in special tools list"""
return name.lower() in [n.lower() for n in self.special_tool_names]manus.py
核心智能体实例,集成了各种工具和能力,
继承Toolcall类
python
class Manus(ToolCallAgent):
"""
A versatile general-purpose agent that uses planning to solve various tasks.
This agent extends PlanningAgent with a comprehensive set of tools and capabilities,
including Python execution, web browsing, file operations, and information retrieval
to handle a wide range of user requests.
"""
name: str = "Manus"
description: str = (
"A versatile agent that can solve various tasks using multiple tools"
)
system_prompt: str = SYSTEM_PROMPT
next_step_prompt: str = NEXT_STEP_PROMPT
max_observe: int = 2000
max_steps: int = 20
# 添加工具
available_tools: ToolCollection = Field(
default_factory=lambda: ToolCollection(
PythonExecute(), GoogleSearch(), BrowserUseTool(), FileSaver(), Terminate()
)
)
# 特殊工具处理
async def _handle_special_tool(self, name: str, result: Any, **kwargs):
await self.available_tools.get_tool(BrowserUseTool().name).cleanup()
await super()._handle_special_tool(name, result, **kwargs)关键实现细节
工具系统设计
Toolbase
让所有的工具类都继承把Toolbase类,提供统一的接口和行为
python
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from typing import Any, Dict, Optional
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class BaseTool(ABC, BaseModel):
name: str
description: str
parameters: Optional[dict] = None
class Config:
arbitrary_types_allowed = True
# 调用工具
async def __call__(self, **kwargs) -> Any:
"""Execute the tool with given parameters."""
return await self.execute(**kwargs)
@abstractmethod
async def execute(self, **kwargs) -> Any:
"""Execute the tool with given parameters."""
def to_param(self) -> Dict:
"""Convert tool to function call format."""
return {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": self.name,
"description": self.description,
"parameters": self.parameters,
},
}
class ToolResult(BaseModel):
"""Represents the result of a tool execution."""
output: Any = Field(default=None)
error: Optional[str] = Field(default=None)
system: Optional[str] = Field(default=None)
class Config:
arbitrary_types_allowed = True
def __bool__(self):
return any(getattr(self, field) for field in self.__fields__)
def __add__(self, other: "ToolResult"):
def combine_fields(
field: Optional[str], other_field: Optional[str], concatenate: bool = True
):
if field and other_field:
if concatenate:
return field + other_field
raise ValueError("Cannot combine tool results")
return field or other_field
return ToolResult(
output=combine_fields(self.output, other.output),
error=combine_fields(self.error, other.error),
system=combine_fields(self.system, other.system),
)
def __str__(self):
return f"Error: {self.error}" if self.error else self.output
def replace(self, **kwargs):
"""Returns a new ToolResult with the given fields replaced."""
# return self.copy(update=kwargs)
return type(self)(**{**self.dict(), **kwargs})
class CLIResult(ToolResult):
"""A ToolResult that can be rendered as a CLI output."""
class ToolFailure(ToolResult):
"""A ToolResult that represents a failure."""
class AgentAwareTool:
agent: Optional = None终止工具 Terminate
允许智能体通过 AI 大模型自主决定何时结束任务,避免无限循环或者过早结束。
python
from app.tool.base import BaseTool
_TERMINATE_DESCRIPTION = """Terminate the interaction when the request is met OR if the assistant cannot proceed further with the task.
When you have finished all the tasks, call this tool to end the work."""
class Terminate(BaseTool):
name: str = "terminate"
description: str = _TERMINATE_DESCRIPTION
parameters: dict = {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"status": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The finish status of the interaction.",
"enum": ["success", "failure"],
}
},
"required": ["status"],
}
async def execute(self, status: str) -> str:
"""Finish the current execution"""
return f"The interaction has been completed with status: {status}"三、自主实现Manus智能体
AgentState
定义智能体状态
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.agent;
/**
* Agent execution states
* 空闲
* 运行
* 完成
* 错误
*/
public enum AgentState {
IDLE ,
RUNNING ,
FINISHED,
ERROR
}BaseAgent类
定义智能体基本属性并通过run方法实现智能体自主思考执行
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.agent;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.security.SecurityScheme;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.messages.Message;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.messages.UserMessage;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.Prompt;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Data
@Slf4j
public abstract class BaseAgent {
private String name;
private AgentState agentState=AgentState.IDLE;
private String SystemPrompt;
private String nextStepPrompt;
private Integer maxStep=10;
private Integer currentStep=0;
private ChatClient chatClient;
// 存储提示词的
private List<Message> contextMessageList= new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 步骤
* @return
*/
public abstract String step();
public String run(String userPrompt ){
System.out.println(currentStep);
//1. 判断状态是否为空闲
if (this.agentState!= AgentState.IDLE) {
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot run agent from state: " + this.agentState);
}
//2.判断用户是否输入提示词
if (StringUtils.isBlank(userPrompt)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot run agent with empty user prompt");
}
// 2.修改状态为运行
this.agentState =AgentState.RUNNING;
// 添加上下文
this.contextMessageList.add(new UserMessage(userPrompt));
List<String > results = new ArrayList<>();
try {
//3. 循环
while (this.agentState!= AgentState.FINISHED && this.currentStep<=this.maxStep) {
this.currentStep++;
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
result.append("step " +this.currentStep+":");
String step = step();
result.append(step);
results.add(result.toString());
}
if (this.currentStep>this.maxStep) {
this.agentState =AgentState.FINISHED;
results.add("终止:已达到最大步数("+this.maxStep+"+")");
}
return String.join("\n",results);
}catch (Exception e){
this.agentState =AgentState.ERROR;
return "程序执行错误:"+e.getMessage();
}finally {
// 清除资源
this.clearup();
}
}
public void clearup(){
}
}ReActAgent类
实现ReAct模式
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.agent;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
public abstract class ReActAgent extends BaseAgent {
/**
* 思考
* @return
*/
public abstract Boolean think();
/**
* 行动
* @return
*/
public abstract String act();
@Override
public String step() {
try {
Boolean thinkStatus = think();
if (!thinkStatus) { //
return "思考完成,无需行动";
}
return act();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return "reAct执行失败:"+e.getMessage();
}
}
}终止工具定义
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
public class TerminateTool {
@Tool(description = """
Terminate the interaction when the request is met OR if the assistant cannot proceed further with the task.
"When you have finished all the tasks, call this tool to end the work.
""")
public String doTerminate() {
return "任务结束";
}
}ToolCallAgent类
具体思考和工具调用实现
实现ToolCallAgent三种方式:
- 因为 Spring AI 完全托管了工具调用,我们可以直接把所有工具调用的代码作为 think 方法,而 act 方法不定义任何动作。
- 基于 Spring AI 的工具调用能力,手动控制工具执行。关闭SpringAi自主调用工具,通过创建ToolCallingManager类,手动实现工具调用
- 自己写 Prompt,引导 AI 回复想要调用的工具列表和调用参数,然后再执行工具并将结果返送给 AI 再次执行。
本文选择方式二
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.agent;
import cn.hutool.core.collection.CollUtil;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.dashscope.agent.DashScopeAgentOptions;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.dashscope.chat.DashScopeChatOptions;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.messages.AssistantMessage;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.messages.Message;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.messages.ToolResponseMessage;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.messages.UserMessage;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatResponse;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.ChatOptions;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.Prompt;
import org.springframework.ai.model.tool.ToolCallingManager;
import org.springframework.ai.model.tool.ToolExecutionResult;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallback;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Data
@Slf4j
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
public class ToolCallAgent extends ReActAgent{
// 可用用具
private ToolCallback[] userableTools;
// 每次模型回答的响应
private ChatResponse tollCallchatResponse;
// 工具管理
private final ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager;
//自定义模型参数
private final ChatOptions chatOptions;
public ToolCallAgent(ToolCallback[] userableTools) {
super();
this.userableTools = userableTools;
this.toolCallingManager= ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
this.chatOptions = DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
// 关闭模型托管工具功能,现在需要我们自主实现
.withProxyToolCalls(true)
.build();
}
@Override
public Boolean think() {
// 判断下一步骤的提示词是否不为空
if (getNextStepPrompt() !=null && StringUtils.isNotBlank(getNextStepPrompt())) {
// 有值的话添加到上下文
getContextMessageList().add(new UserMessage(getNextStepPrompt()));
}
List<Message> contextMessageList = getContextMessageList();
// 构建prompt
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(contextMessageList, this.chatOptions);
try {
// 开始交互
ChatResponse chatResponse = getChatClient().prompt(prompt)
.system(getSystemPrompt())
.tools(this.userableTools)
.call()
.chatResponse();
this.tollCallchatResponse = chatResponse;
// 得到响应流
AssistantMessage assistantMessage = chatResponse.getResult().getOutput();
// 得到思考内容
String result = assistantMessage.getText();
//获取模型调用了哪些工具
List<AssistantMessage.ToolCall> toolCalls = assistantMessage.getToolCalls();
// 打印日志
log.info(getName()+"的思考内容为:"+result);
log.info(getName() + "选择了 " + toolCalls.size() + " 个工具来使用");
String toolCallInfo = toolCalls.stream()
.map(toolCall -> String.format("工具名称:%s,参数:%s",
toolCall.name(),
toolCall.arguments())
)
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
log.info(toolCallInfo);
if (toolCalls.isEmpty()) {
//没有工具调用
getContextMessageList().add(assistantMessage);
return false;
}else {
return true;
}
}catch (Exception e){
log.error(getName() + "的思考过程遇到了问题: " + e.getMessage());
getContextMessageList().add(
new AssistantMessage("处理时遇到错误: " + e.getMessage()));
return false;
}
}
@Override
public String act() {
// 1 判断ai思考时模型是否需要工具
if (!this.getTollCallchatResponse().hasToolCalls()) {
return "没有工具调用";
}
// 2. 构建提示词
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(getContextMessageList(), this.chatOptions);
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(prompt, this.getTollCallchatResponse());
// 因为ToolExecutionResult.conversationHistory中存储了所有的上下文信息,所以我们替换下,保持一致
setContextMessageList(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory());
//获取最后一条信息
ToolResponseMessage toolResponseMessage = (ToolResponseMessage) CollUtil.getLast(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory());
String results = toolResponseMessage.getResponses().stream()
.map(response -> "工具 " + response.name() + " 完成了它的任务!结果: " + response.responseData())
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
log.info(results);
// 判断是否调用了终止工具
boolean doTerminateisExec = toolResponseMessage.getResponses().stream()
.anyMatch(response -> "doTerminate".equals(response.name()));
// 如果调用了直接结束
if (doTerminateisExec) {
setAgentState(AgentState.FINISHED);
}
return results;
}
}Manus智能体实现
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.agent;
import cn.varin.varaiagent.advisors.MyLogAdvisor;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatModel;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.ChatOptions;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallback;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class VarinManus extends ToolCallAgent{
public VarinManus(ToolCallback[] toolCallbacks, ChatModel dashscopeChatModel) {
super(toolCallbacks);
this.setName("VarinManus");
String SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
You are YuManus, an all-capable AI assistant, aimed at solving any task presented by the user.
You have various tools at your disposal that you can call upon to efficiently complete complex requests.
""";
this.setSystemPrompt(SYSTEM_PROMPT);
String NEXT_STEP_PROMPT = """
Based on user needs, proactively select the most appropriate tool or combination of tools.
For complex tasks, you can break down the problem and use different tools step by step to solve it.
After using each tool, clearly explain the execution results and suggest the next steps.
If you want to stop the interaction at any point, use the `terminate` tool/function call.
""";
this.setNextStepPrompt(NEXT_STEP_PROMPT);
this.setMaxStep(20);
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(dashscopeChatModel).defaultAdvisors(new MyLogAdvisor()).build();
this.setChatClient(chatClient);
}
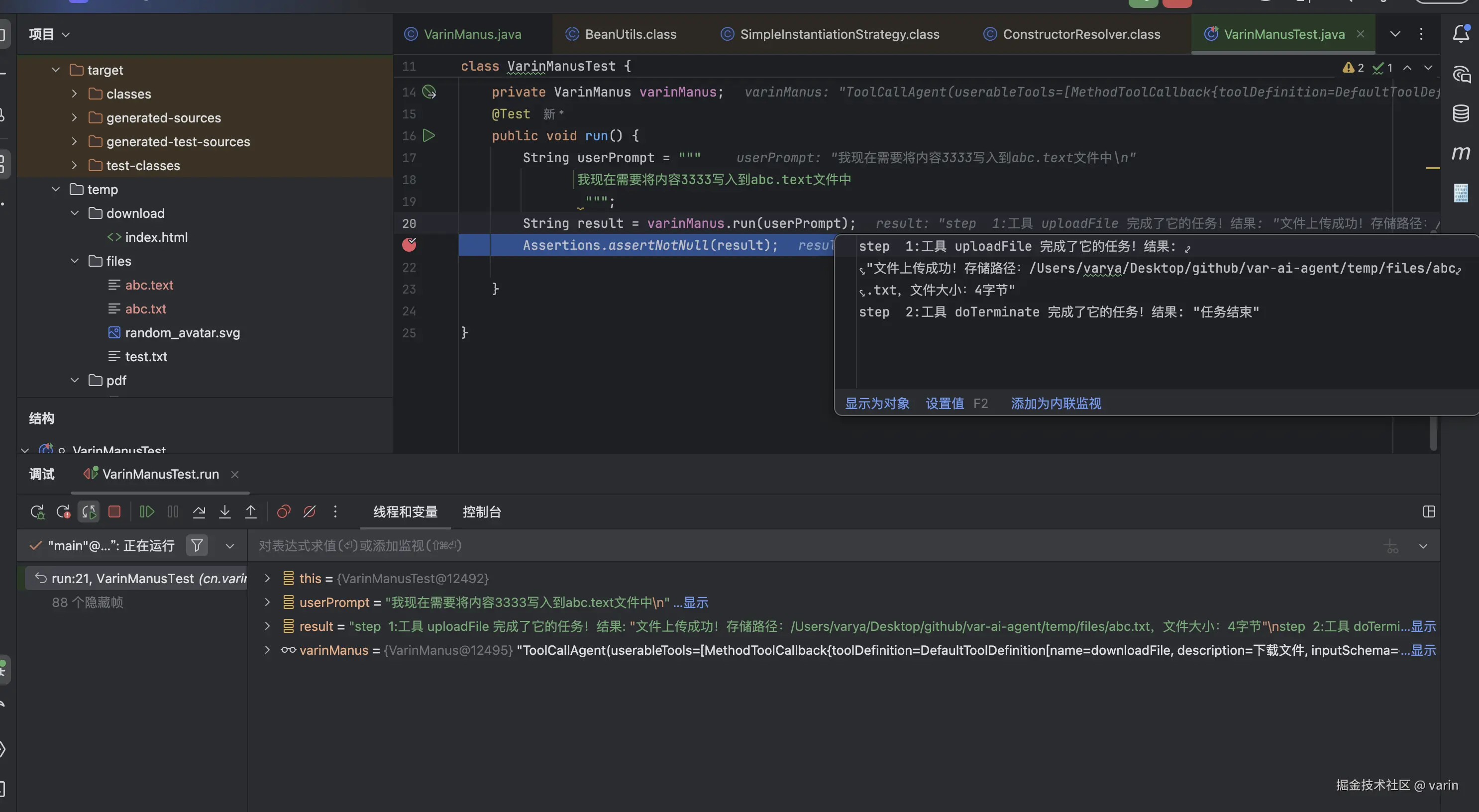
}测试
java
package cn.varin.varaiagent.agent;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
class VarinManusTest {
@Resource
private VarinManus varinManus;
@Test
public void run() {
String userPrompt = """
我现在需要将内容3333写入到abc.text文件中
""";
String result = varinManus.run(userPrompt);
Assertions.assertNotNull(result);
}
}实现效果