这个条款揭示了C++异常处理中最重要的规则之一:析构函数绝不能抛出异常。这是构建异常安全代码的基石,理解这一点对于开发健壮的C++系统至关重要。
思维导图:析构函数异常安全的完整体系
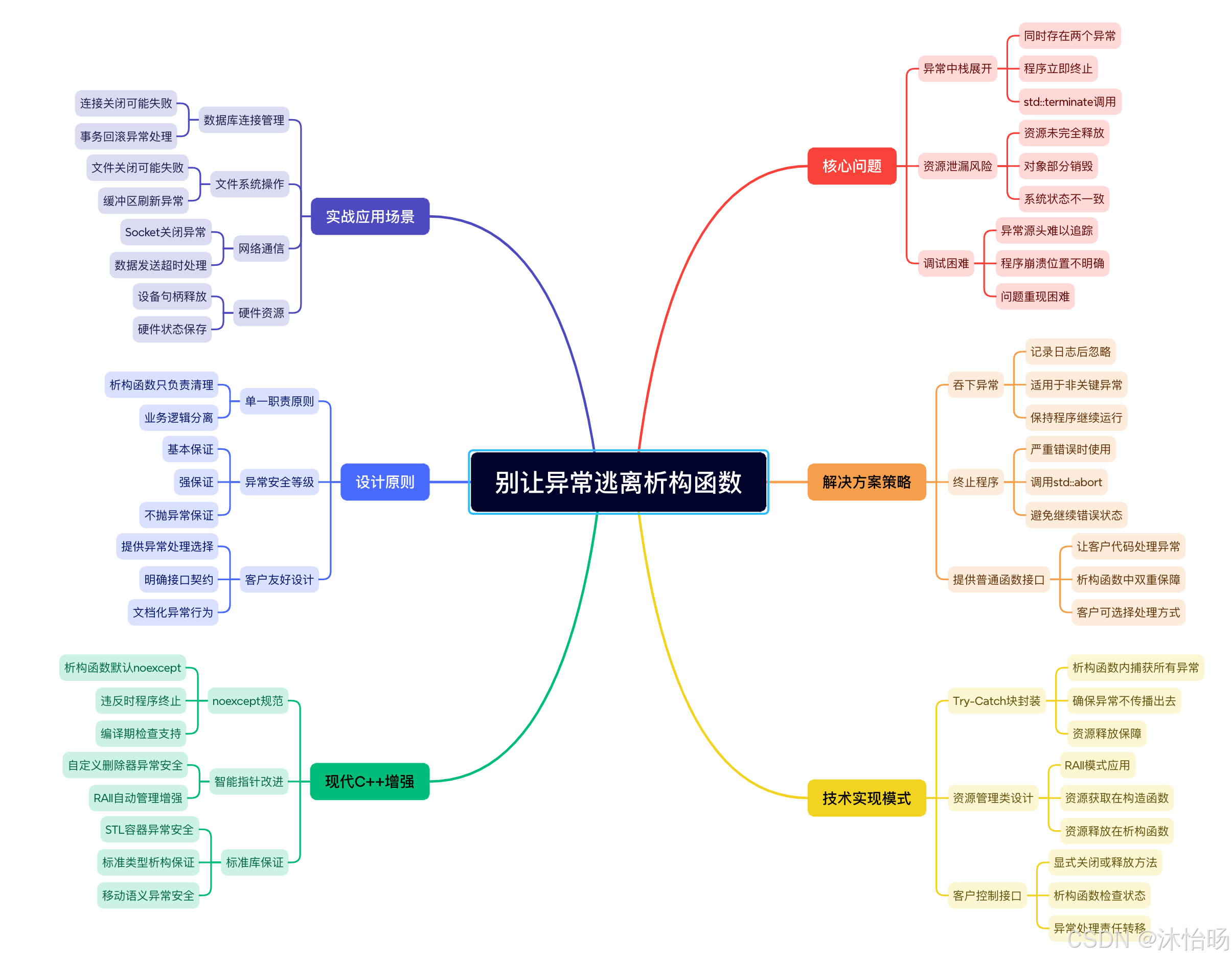
深入解析:析构函数异常的核心危险
1. 双重异常灾难------程序终止的必然性
危险的析构函数设计:
cpp
class DangerousResource {
private:
FILE* file_handle_;
std::vector<int> data_cache_;
public:
DangerousResource(const std::string& filename)
: file_handle_(fopen(filename.c_str(), "w")) {
if (!file_handle_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件");
}
data_cache_.resize(1000); // 分配资源
}
~DangerousResource() {
// 危险!可能抛出异常
if (fclose(file_handle_) != 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("文件关闭失败"); // 异常逃离析构函数!
}
// 更多可能失败的操作
data_cache_.clear(); // 通常不会失败,但理论上可能
}
void writeData(const std::string& data) {
if (fprintf(file_handle_, "%s", data.c_str()) < 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("写入失败");
}
}
};
void demonstrate_catastrophe() {
try {
DangerousResource resource("data.txt");
resource.writeData("重要数据");
// 模拟某些操作可能抛出异常
throw std::logic_error("业务逻辑异常");
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "捕获异常: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// 当resource离开作用域时,析构函数被调用
// 如果析构函数抛出异常,程序会调用std::terminate()!
}
// 程序可能在这里终止!
}C++标准规定: 如果栈展开过程中析构函数抛出异常,且这个异常没有被析构函数自身捕获,程序将调用std::terminate()立即终止。
2. 实际问题重现
cpp
class ProblematicConnection {
private:
network_socket_t socket_;
public:
ProblematicConnection(const char* address) {
socket_ = network_connect(address); // 可能失败
if (!socket_) {
throw std::runtime_error("连接失败");
}
}
~ProblematicConnection() {
// 危险:network_close可能失败并抛出异常
if (network_close(socket_) != 0) {
throw network_exception("关闭连接失败"); // 异常逃离!
}
}
};
void real_world_scenario() {
try {
ProblematicConnection conn("192.168.1.100");
// 业务操作...
process_data(conn);
// 假设这里抛出异常
throw data_processing_error("数据处理失败");
} catch (const data_processing_error& e) {
// 处理业务异常
log_error(e.what());
// 但此时conn的析构函数被调用
// 如果network_close失败,程序立即终止!
}
}解决方案:三种安全策略
1. 策略一:吞下异常(记录并继续)
cpp
class SafeResource_Swallow {
private:
FILE* file_handle_;
std::string resource_name_;
public:
SafeResource_Swallow(const std::string& filename)
: file_handle_(fopen(filename.c_str(), "w")),
resource_name_(filename) {
if (!file_handle_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
}
~SafeResource_Swallow() noexcept { // C++11: 明确声明不抛异常
try {
if (file_handle_) {
if (fclose(file_handle_) != 0) {
// 吞下异常,但记录日志
std::cerr << "警告: 文件关闭失败: " << resource_name_
<< ",错误: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
// 不抛出异常!
}
}
} catch (...) {
// 捕获所有异常,确保没有异常逃离
std::cerr << "严重: 析构函数中发生未知异常,已吞下" << std::endl;
}
}
void writeData(const std::string& data) {
if (fprintf(file_handle_, "%s", data.c_str()) < 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("写入失败");
}
}
// 禁用拷贝
SafeResource_Swallow(const SafeResource_Swallow&) = delete;
SafeResource_Swallow& operator=(const SafeResource_Swallow&) = delete;
};2. 策略二:终止程序(严重错误时)
cpp
class CriticalResource_Abort {
private:
void* system_handle_;
bool resource_critical_;
public:
CriticalResource_Abort()
: system_handle_(acquire_system_resource()),
resource_critical_(true) {
if (!system_handle_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法获取关键系统资源");
}
}
~CriticalResource_Abort() noexcept {
try {
if (resource_critical_ && system_handle_) {
if (release_system_resource(system_handle_) != SUCCESS) {
// 关键资源释放失败,程序状态可能损坏
std::cerr << "致命错误: 关键系统资源释放失败!" << std::endl;
std::abort(); // 立即终止程序
}
resource_critical_ = false;
system_handle_ = nullptr;
}
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "致命错误: 析构函数中发生未知异常" << std::endl;
std::abort();
}
}
void markNonCritical() noexcept {
resource_critical_ = false;
}
};3. 策略三:提供客户控制接口(最佳实践)
cpp
class ClientControlledResource {
private:
FILE* file_handle_;
std::string filename_;
bool is_closed_;
public:
explicit ClientControlledResource(const std::string& filename)
: file_handle_(fopen(filename.c_str(), "w")),
filename_(filename),
is_closed_(false) {
if (!file_handle_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
}
// 客户显式关闭接口,可以处理异常
void close() {
if (is_closed_) return;
if (file_handle_) {
if (fclose(file_handle_) != 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("关闭文件失败: " + filename_);
}
file_handle_ = nullptr;
is_closed_ = true;
}
}
~ClientControlledResource() noexcept {
try {
if (!is_closed_ && file_handle_) {
// 双重保障:如果客户没有关闭,我们尝试关闭
// 但吞下任何异常
if (fclose(file_handle_) != 0) {
std::cerr << "警告: 析构函数中文件关闭失败: "
<< filename_ << std::endl;
}
}
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "警告: 析构函数中文件关闭发生异常: "
<< filename_ << std::endl;
}
}
void writeData(const std::string& data) {
if (is_closed_) {
throw std::logic_error("文件已关闭");
}
if (fprintf(file_handle_, "%s", data.c_str()) < 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("写入失败");
}
}
// 禁用拷贝
ClientControlledResource(const ClientControlledResource&) = delete;
ClientControlledResource& operator=(const ClientControlledResource&) = delete;
};
// 客户使用方式
void client_usage_example() {
ClientControlledResource resource("important_data.txt");
try {
resource.writeData("关键业务数据");
// 业务逻辑...
perform_critical_operation();
// 客户显式关闭,可以处理异常
resource.close(); // 如果失败会抛出异常
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "操作失败: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// resource的析构函数会确保资源释放,但吞下异常
}
}现代C++的增强特性
1. noexcept规范与编译期检查
cpp
class ModernResource {
private:
std::unique_ptr<int[]> data_;
std::atomic<bool> cleanup_done_{false};
public:
ModernResource(size_t size) : data_(std::make_unique<int[]>(size)) {}
// C++11: 明确声明析构函数不抛异常
~ModernResource() noexcept {
// 编译器会检查确保没有异常逃离
perform_cleanup();
}
void perform_cleanup() noexcept {
if (!cleanup_done_.exchange(true)) {
// 所有可能失败的操作都必须处理异常
try {
cleanup_internal();
} catch (...) {
// 必须捕获所有异常
log_cleanup_failure();
}
}
}
private:
void cleanup_internal() {
// 即使这里可能抛出异常...
if (data_) {
data_.reset(); // unique_ptr的reset是noexcept的
}
}
void log_cleanup_failure() const noexcept {
std::cerr << "资源清理失败,但程序继续运行" << std::endl;
}
};
// C++17: 条件性noexcept
template<typename T>
class GenericContainer {
private:
std::vector<T> elements_;
public:
// 析构函数条件性noexcept:只有当T的析构是noexcept时才是noexcept
~GenericContainer() noexcept(std::is_nothrow_destructible_v<T>) {
// 实现...
}
};2. RAII与智能指针的现代应用
cpp
class AdvancedDatabaseTransaction {
private:
struct DatabaseHandle {
void* native_handle;
DatabaseHandle(void* handle) : native_handle(handle) {}
~DatabaseHandle() noexcept {
if (native_handle) {
try {
if (database_release(native_handle) != DB_SUCCESS) {
// 记录但不抛出
log_database_error("数据库句柄释放失败");
}
} catch (...) {
log_database_error("数据库释放过程中发生异常");
}
native_handle = nullptr;
}
}
// 禁用拷贝,允许移动
DatabaseHandle(const DatabaseHandle&) = delete;
DatabaseHandle& operator=(const DatabaseHandle&) = delete;
DatabaseHandle(DatabaseHandle&& other) noexcept
: native_handle(other.native_handle) {
other.native_handle = nullptr;
}
DatabaseHandle& operator=(DatabaseHandle&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
if (native_handle) {
database_release(native_handle);
}
native_handle = other.native_handle;
other.native_handle = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
};
DatabaseHandle db_handle_;
bool transaction_active_;
public:
AdvancedDatabaseTransaction(const std::string& connection_string)
: db_handle_(database_connect(connection_string.c_str())),
transaction_active_(false) {
if (!db_handle_.native_handle) {
throw std::runtime_error("数据库连接失败");
}
}
void beginTransaction() {
if (database_begin_transaction(db_handle_.native_handle) != DB_SUCCESS) {
throw std::runtime_error("事务开始失败");
}
transaction_active_ = true;
}
void commit() {
if (!transaction_active_) return;
if (database_commit(db_handle_.native_handle) != DB_SUCCESS) {
throw std::runtime_error("事务提交失败");
}
transaction_active_ = false;
}
void rollback() noexcept {
if (!transaction_active_) return;
try {
if (database_rollback(db_handle_.native_handle) != DB_SUCCESS) {
log_database_error("事务回滚失败");
}
transaction_active_ = false;
} catch (...) {
log_database_error("事务回滚过程中发生异常");
}
}
~AdvancedDatabaseTransaction() noexcept {
rollback(); // 确保在析构时回滚未完成的事务
}
// 禁用拷贝
AdvancedDatabaseTransaction(const AdvancedDatabaseTransaction&) = delete;
AdvancedDatabaseTransaction& operator=(const AdvancedDatabaseTransaction&) = delete;
};实战案例:复杂系统的异常安全设计
案例1:分布式事务管理器
cpp
class DistributedTransaction {
private:
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<class Participant>> participants_;
bool prepared_{false};
bool committed_{false};
public:
void addParticipant(std::unique_ptr<Participant> participant) {
participants_.push_back(std::move(participant));
}
// 两阶段提交:准备阶段
void prepare() {
for (auto& participant : participants_) {
participant->prepare();
}
prepared_ = true;
}
// 两阶段提交:提交阶段
void commit() {
if (!prepared_) {
throw std::logic_error("事务未准备");
}
try {
for (auto& participant : participants_) {
participant->commit();
}
committed_ = true;
} catch (...) {
// 提交失败,必须回滚
rollback();
throw;
}
}
// 回滚操作 - 必须保证不抛异常
void rollback() noexcept {
try {
for (auto& participant : participants_) {
try {
participant->rollback();
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// 单个参与者回滚失败不影响其他参与者
log_rollback_failure(participant->getId(), e.what());
}
}
} catch (...) {
// 确保没有异常逃离
log_critical_rollback_failure();
}
prepared_ = false;
}
~DistributedTransaction() noexcept {
if (prepared_ && !committed_) {
// 如果准备但未提交,必须回滚
rollback();
}
}
};
class Participant {
public:
virtual ~Participant() = default;
virtual void prepare() = 0; // 可能抛出异常
virtual void commit() = 0; // 可能抛出异常
virtual void rollback() noexcept = 0; // 必须不抛异常!
virtual std::string getId() const = 0;
};案例2:网络连接池
cpp
class ConnectionPool {
private:
struct PooledConnection {
std::unique_ptr<NetworkConnection> connection;
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point last_used;
bool in_use{false};
~PooledConnection() noexcept {
try {
if (connection) {
connection->close(); // 假设close()可能失败
}
} catch (...) {
// 吞下异常,但记录日志
log_connection_cleanup_failure();
}
}
};
std::vector<PooledConnection> connections_;
std::mutex pool_mutex_;
public:
std::unique_ptr<NetworkConnection> acquireConnection() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(pool_mutex_);
for (auto& pooled_conn : connections_) {
if (!pooled_conn.in_use) {
pooled_conn.in_use = true;
pooled_conn.last_used = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// 返回包装器,确保连接正确返回池中
return std::unique_ptr<NetworkConnection>(
pooled_conn.connection.get(),
[this, &pooled_conn](NetworkConnection*) {
releaseConnection(pooled_conn);
}
);
}
}
throw std::runtime_error("无可用连接");
}
private:
void releaseConnection(PooledConnection& pooled_conn) noexcept {
try {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(pool_mutex_);
pooled_conn.in_use = false;
pooled_conn.last_used = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
} catch (...) {
// 互斥锁操作失败是严重错误,但析构函数不能抛出
log_critical_pool_error();
}
}
~ConnectionPool() noexcept {
try {
cleanupIdleConnections();
} catch (...) {
log_pool_cleanup_failure();
}
}
void cleanupIdleConnections() noexcept {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(pool_mutex_);
auto now = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (auto& conn : connections_) {
if (!conn.in_use) {
auto idle_time = now - conn.last_used;
if (idle_time > std::chrono::minutes(30)) {
try {
conn.connection.reset(); // 关闭连接
} catch (...) {
log_connection_cleanup_failure();
}
}
}
}
}
};关键洞见与行动指南
必须遵守的核心规则:
- 析构函数绝对不抛出异常:这是C++异常安全的铁律
- 资源释放操作必须异常安全:确保资源在任何情况下都能正确释放
- 提供客户控制接口:让客户代码有机会处理可能失败的清理操作
- 记录但不传播:在析构函数中记录错误,但继续执行
现代C++开发建议:
- 使用noexcept规范:明确声明析构函数不抛异常
- 智能指针管理资源:利用RAII自动管理生命周期
- try-catch块封装:在析构函数内捕获所有异常
- 单元测试验证:测试析构函数在各种异常场景下的行为
设计原则总结:
- 单一职责:析构函数只负责资源释放,不包含复杂业务逻辑
- 客户友好:提供显式的清理方法,让客户处理异常
- 防御性编程:假设任何操作都可能失败,做好异常处理准备
- 可观测性:即使吞下异常,也要记录足够的调试信息
需要警惕的陷阱:
- 间接异常:调用的函数可能抛出意想不到的异常
- 标准库保证:了解不同STL操作的异常保证级别
- 继承体系:确保所有基类和成员的析构函数都是异常安全的
- 移动语义:移动操作也应该提供基本的异常安全保证
最终建议: 将析构函数视为系统的安全网。培养"异常安全思维"------在编写每个析构函数时都问自己:"如果这里发生异常,系统会怎样?" 这种前瞻性的思考是构建工业级C++系统的关键。
记住:在C++异常处理中,析构函数是最后的防线,绝不能成为问题的源头。 条款8教会我们的不仅是一个技术规则,更是构建健壮软件的系统性思维方式。