背景
AI Agent(智能体)是基于 LLM(大语言模型)构建的智能系统,能够自主理解人类的自然语言指令,感知环境状态,决策并采取行动。
智能体的核心要素包括:记忆、工具、知识与规划。
更多关于智能体原理的内容,可参考 GitHub 笔记:github.com/BaqiF2/ydc_...
本文主要围绕智能体要素之一的工具,从以下三个方向展开说明:
- Function Calling(框架调用):使用 OpenAI 提供的 Function Calling 格式进行工具调用
- 原理层(提示词):使用 JSON Schema 与 XML 实现工具调用,适用于调用准确率较低时的优化场景
- MCP(Model Context Protocol):通过 MCP Server 封装多个工具,结合 MCP 平台实现工具调用
Function calling(框架调用)
概述
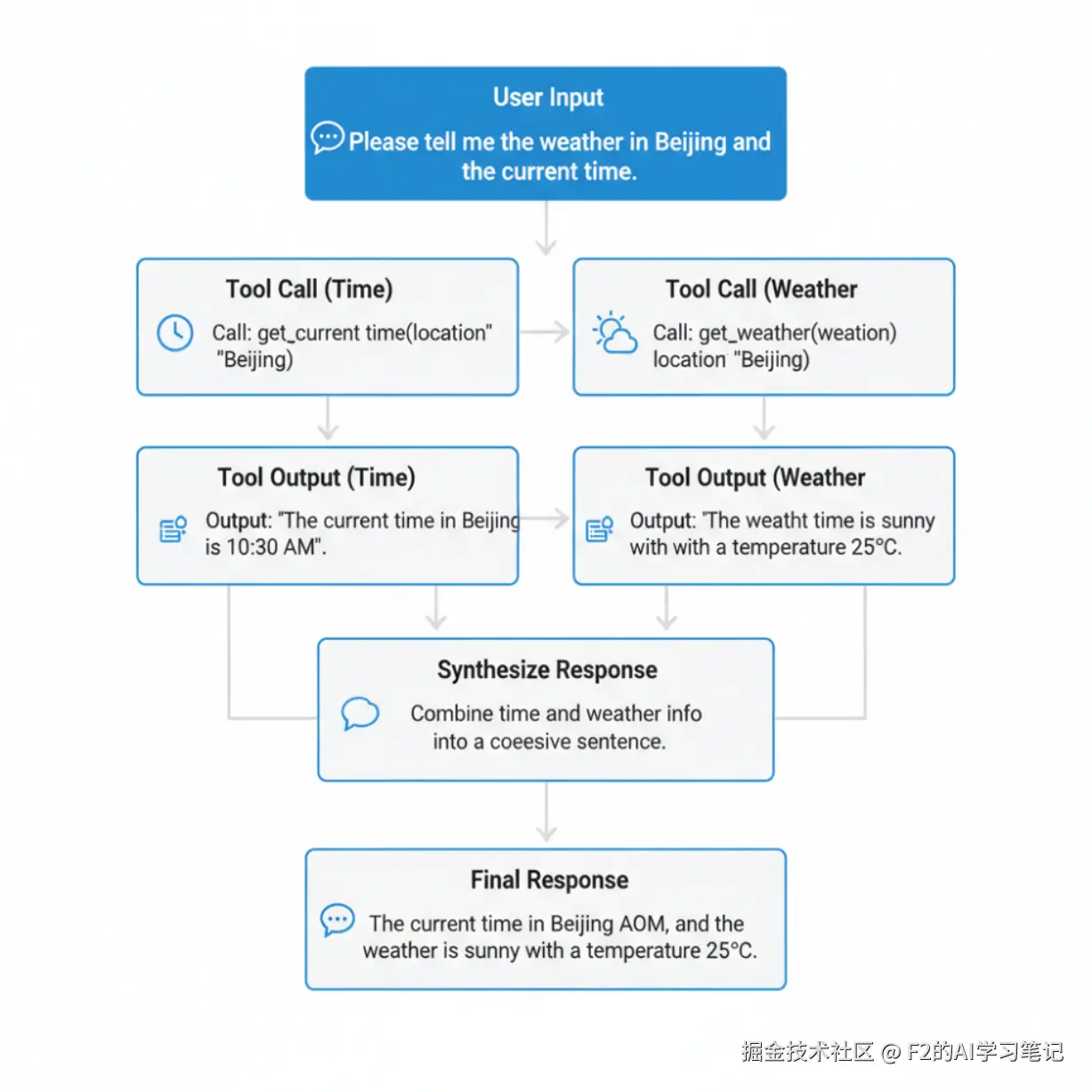
Function Calling 是 AI 模型的关键能力,使大语言模型能够根据用户请求,智能识别并调用外部工具或 API 接口。它如同模型的"手",将语言理解转化为实际行动------无论是查询天气、计算数据,还是操作软件,都能通过结构化输出实现与真实世界的交互。这一技术极大拓展了 AI 的应用边界,让智能助手真正成为高效的数字生产力伙伴。
交互流程说明
使用 SDK 调用 OpenAI 模型并希望模型调用工具时,通常遵循以下流程:
"北京天气怎么样?" C->>S: chat.completions.create(
messages, tools) S->>A: HTTP POST /chat/completions
{model, messages, tools} Note over A: 构造完整提示词
整合:系统指令 + 工具定义 + 用户消息 A->>M: 发送构造后的提示词 M->>M: 分析用户意图
匹配可用工具
生成工具调用参数 M->>A: 返回工具调用决策 A->>S: 返回JSON响应
{tool_calls, finish_reason} S->>C: 返回结构化对象
包含tool_calls列表 C->>C: 解析tool_calls
提取function name和arguments Note over U, T: 第二轮:执行工具并返回结果 C->>T: 调用外部工具
get_weather("北京") T->>C: 返回工具执行结果
{"temp": 25, "condition": "晴朗"} Note over U, T: 第三轮:最终回复生成 C->>S: chat.completions.create(
包含工具结果的新消息) S->>A: HTTP POST /chat/completions
{
messages: [
原始用户消息,
工具调用消息,
工具执行结果消息
]
} A->>M: 发送包含工具结果的完整上下文 M->>M: 整合工具结果
生成最终自然语言回复 M->>A: 返回最终回复 A->>S: 返回JSON响应
{content: "北京今天天气晴朗..."} S->>C: 返回结构化回复对象 C->>U: 显示最终答案
"北京今天天气晴朗,气温25℃..."
注:此处的"客户端"是相对于模型提供商而言,并非指应用本身的客户端/服务端结构。
第一阶段:工具调用决策
- 用户输入(客户端) → 客户端接收消息
- SDK 封装(客户端) → 将 tools 参数格式化为 API 请求
- API 层提示词构造(服务商) → 自动整合工具描述到系统上下文中
- 模型推理(服务商) → 分析用户意图,决定调用工具并生成参数
第二阶段:工具执行
- 客户端解析(客户端) → 提取工具名称和参数
- 调用外部工具(客户端) → 执行实际的业务逻辑(如查询天气 API)
- 获取工具结果(客户端) → 接收工具返回的数据
json
{
"model": "gpt-4",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "北京天气怎么样?"}],
"tools": [{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"parameters": {"location": "string"}
}
}]
}
json
{
"tool_calls": [{
"id": "call_123",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\": \"北京\"}"
}
}]
}第三阶段:结果整合
- 传递工具结果(客户端) → 将执行结果以
tool角色消息传回 - 模型最终推理(服务商) → 基于工具结果生成自然语言回复
- 返回最终答案(服务商) → 用户获得包含工具数据的智能回复
json
{
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "北京天气怎么样?"},
{"role": "assistant", "tool_calls": [...]},
{"role": "assistant", "tool_call_id": "call_123", "content": "北京今天天气晴朗,气温25℃..."}
]
}
python
{
"messages": [
{"role": "assistant", "tool_call_id": "call_123", "content": "北京今天天气晴朗,气温25℃..."}
]
}代码实践
python
llm = ChatOpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
model="qwen3-max")
@tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""获取指定城市的天气信息"""
return f"{city}的天气是晴天,温度为25度。"
@tool
def get_time() -> str:
"""获取当前时间"""
from datetime import datetime
return datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# 绑定多个工具到LLM
tool_llm = llm.bind_tools(tools=[get_weather, get_time])
message_history = [{"role":"user", "content":"请告诉我北京天气和当前时间"}]
print("\n=== 测试多个工具调用 ===")
multi_response = tool_llm.invoke(message_history)
print(f'内容: {multi_response.content}')
print(f'工具调用: {multi_response.tool_calls}')
python
print("\n=== 工具调用结果处理 ===")
if multi_response.tool_calls:
for tool_call in multi_response.tool_calls:
print(f"工具名称: {tool_call['name']}")
print(f"参数: {tool_call['args']}")
# 实际项目中这里会执行工具函数
if tool_call['name'] == 'get_weather':
# 调用基础函数
result = get_weather.invoke(tool_call['args']['city'])
print(f"执行结果: {result}")
message_history.append({"role": "tool", "content": result, "tool_call_id": tool_call['id']})
elif tool_call['name'] == 'get_time':
# 调用基础函数
result = get_time.invoke(None)
print(f"执行结果: {result}")
message_history.append({"role": "tool", "content": result, "tool_call_id": tool_call['id']})
final_result = tool_llm.invoke(message_history)
print(f"最终结果: {final_result.content}")输出示例:
python
=== 测试多个工具调用 ===
内容:
工具调用: [{'name': 'get_weather', 'args': {'city': '北京'}, 'id': 'call_2f7397098f7648f18bf3ff95', 'type': 'tool_call'}, {'name': 'get_time', 'args': {}, 'id': 'call_c49f888c34814863928c1506', 'type': 'tool_call'}]
=== LangChain 1.0新特性 - content_blocks ===
内容块: [{'type': 'tool_call', 'name': 'get_weather', 'args': {'city': '北京'}, 'id': 'call_2f7397098f7648f18bf3ff95'}, {'type': 'tool_call', 'name': 'get_time', 'args': {}, 'id': 'call_c49f888c34814863928c1506'}]
=== 工具调用结果处理 ===
工具名称: get_weather
参数: {'city': '北京'}
执行结果: 北京的天气是晴天,温度为25度。
工具名称: get_time
参数: {}
执行结果: 2025-10-30 21:28:42
最终结果: 北京当前天气是晴天,温度为25度。当前时间为2025年10月30日21点28分42秒。总结
本示例完整展示了工具调用的流程:借助框架封装的 SDK 调用 LLM,LLM 返回需调用的工具及其参数;客户端执行工具后获得结果,并将历史上下文再次发送给 LLM,最终由 LLM 生成包含工具执行结果的回复。
备注:本示例还使用了 LangChain 1.0 的新特性 content_blocks 来输出文本块内容。
json schema + xml(提示词+原理)
概述
通过 JSON Schema 或 XML 定义工具的参数规范,结合提示词描述任务目标与调用逻辑,可精准引导 LLM 进行工具调用。其原理是:JSON Schema/XML 提供结构化的任务上下文,确保输出标准化,LLM 据此生成符合要求的参数,最终通过解析器执行外部工具调用。该方法显著提升了工具调用的准确性与可控性。
交互流程说明
定义tools字典
包含JSON Schema定义 Chat->>Chat: 定义tools(包含schema) else XML实现 Note right of Chat: XML方式:
构造XML格式system prompt
包含工具调用示例 Chat->>Chat: 构造XML格式system prompt end Note over Chat: 第一次API调用 Chat->>API: POST /api/v1/services/aigc/text-generation/generation alt JSON Schema实现 Note right of API: 请求包含:
- model: qwen3-max
- messages: [system, user]
- tools: JSON Schema定义 else XML实现 Note right of API: 请求包含:
- model: qwen3-max
- messages: [system, user]
- 不传递tools参数 end API-->>Chat: 返回响应 Note over Chat: 解析响应 alt JSON Schema实现 Note right of Chat: 使用JSON解析:
json.loads(content)
提取tool_calls数组 Chat->>Parse: JSON解析响应内容 Parse->>Parse: 提取tool_calls数组 Parse-->>Chat: 返回JSON解析结果 else XML实现 Note right of Chat: 使用正则表达式:
匹配
匹配
assistant消息包含tool_calls字段
tool消息包含执行结果 Chat->>Chat: 添加assistant消息(tool_calls字段) Chat->>Chat: 添加tool消息(执行结果) else XML实现 Note right of Chat: 添加XML格式消息:
重建XML格式的tool_calls文本
作为assistant消息content Chat->>Chat: 重建XML格式的tool_calls文本 Chat->>Chat: 添加assistant消息(XML格式) Chat->>Chat: 添加user消息(工具结果) end Chat->>API: 第二次API调用(包含完整对话历史) API-->>Chat: 返回最终回答 Chat-->>Main: 返回最终回答 else 无工具调用 Chat-->>Main: 直接返回回答内容 end Main->>User: 输出最终回答
第一阶段: 初始化阶段
- 用户提问: 触发整个工具调用流程
- 系统提示词: 定义AI角色、可用工具和调用格式
- 工具定义: 使用JSON Schema描述工具接口
第二阶段: 第一次API调用 (决策阶段)
- 请求构造: 包含消息历史和工具定义
- LLM分析: 判断是否需要调用工具以及调用哪些工具
- 返回决策: 以JSON格式返回工具调用计划
第三阶段:工具解析与执行阶段
- 双重解析: 优先JSON解析,降级到原生tool_calls
- 并发执行: 依次或并发执行多个工具调用
- 结果收集: 存储每个工具的执行结果和ID
第四阶段: 消息历史构建
- 格式标准化: 按照OpenAI格式构建多轮消息
- 角色分配: assistant(工具调用) + tool(执行结果)
- ID关联: 通过tool_call_id关联调用和结果
第五阶段. 第二次API调用 (生成阶段)
- 完整上下文: 包含原始问题、工具调用、工具结果
- 最终推理: LLM基于所有信息生成最终回答
- 答案返回: 综合工具结果的完整回答
代码实践
python
# 构造提示词
system_prompt = f"""
你是一个专业的人工智能助手,你会根据用户的问题来解答。你可以借助工具来辅助你生成答案。
工具定义:
1. get_weather: 获取指定城市的天气信息,参数:city (string, required) - 城市名称
2. get_time: 获取当前时间,无需参数
请根据用户的问题,选择合适的工具来调用。如果你需要调用工具,请按照以下JSON格式返回:
{{
"tool_calls": [
{{
"name": "工具名称",
"arguments": {{"参数名": "参数值"}}
}}
]
}}
如果不需要调用工具,请直接回答用户问题。
"""
# ....
# 请求模型厂商
def call_qwen_api(messages: list, tools: dict = None) -> dict:
"""调用通义千问API"""
# ...省略
# 如果有工具定义,添加到请求中
if tools:
data["input"]["tools"] = [{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool_name,
"description": tool_desc,
"parameters": tool_schema
}
} for tool_name, (tool_desc, tool_schema) in tools.items()]
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
# ...省略
# 解析json, 调用工具
try:
message = response["output"]["choices"][0]["message"]
content = message.get("content", "")
try:
content_dict = json.loads(content)
tool_calls = content_dict.get("tool_calls", [])
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f"解析响应失败: {content}")
tool_calls = message.get("tool_calls", [])
print(f"第一次返回调用结果: {content}")
# 如果有工具调用
if tool_calls:
print("\n=== 工具调用 ===")
# 省略工具调用和再次发起....
python
# 构造XML格式的提示词
system_prompt = """
你是一个专业的人工智能助手,你会根据用户的问题来解答。你可以借助工具来辅助你生成答案。
工具定义:
1. get_weather: 获取指定城市的天气信息,参数:city (string, required) - 城市名称
2. get_time: 获取当前时间,无需参数
请根据用户的问题,选择合适的工具来调用。如果你需要调用工具,请按照以下XML格式返回:
<tool_calls>
<invoke name="工具名称">
<parameter name="参数名">参数值</parameter>
<parameter name="参数名">参数值</parameter>
</invoke>
<invoke name="另一个工具名称">
<parameter name="参数名">参数值</parameter>
</invoke>
</tool_calls>
如果不需要调用工具,请直接回答用户问题。
"""
# 省略...
def call_qwen_api(messages: list) -> dict:
"""调用通义千问API"""
api_key = os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY")
url = "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1/services/aigc/text-generation/generation"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# 构建请求数据
data = {
"model": "qwen3-max",
"input": {
"messages": messages
},
"parameters": {
"result_format": "message",
"temperature": 0.7
}
}
try:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
# ...省略
# 解析xml, 调用工具
def parse_xml_tool_calls(content: str) -> list:
"""解析XML格式的工具调用"""
tool_calls = []
# 使用正则表达式解析XML
# 匹配 <tool_calls> 标签内的内容
tool_calls_match = re.search(r'<tool_calls>(.*?)</tool_calls>', content, re.DOTALL)
if not tool_calls_match:
return tool_calls
tool_calls_content = tool_calls_match.group(1)
# 匹配所有 <invoke> 标签
invoke_pattern = r'<invoke name="([^"]+)">(.*?)</invoke>'
invoke_matches = re.findall(invoke_pattern, tool_calls_content, re.DOTALL)
for tool_name, params_content in invoke_matches:
# 解析参数
param_pattern = r'<parameter name="([^"]+)">([^<]*)</parameter>'
param_matches = re.findall(param_pattern, params_content, re.DOTALL)
arguments = {}
for param_name, param_value in param_matches:
arguments[param_name] = param_value.strip()
tool_calls.append({
"name": tool_name,
"arguments": arguments
})
return tool_calls总结
JSON Schema 与 XML 两种方式均可实现大模型的工具调用。值得注意的是,XML 方式并未按照 API 要求传递 tools 参数,但仍能正确调用。这是因为许多模型在训练中强化了对 XML Tags 格式的理解,同时 XML 本身具有结构简洁、易于闭合、出错率低等优势。
因此,在编写系统提示词时,可将关键部分改写为 XML Tags 形式,以增强智能体遵循指令的能力。
MCP
概述
MCP(Model Context Protocol)是由Anthropic推出的开放协议,旨在标准化LLM与外部数据源及工具的安全连接。它通过定义清晰的通信规范,使模型能无缝、安全地调用多种"资源"(如数据库、API),有效扩展AI能力边界,同时保障可控性与互操作性,是开发生态应用的重要桥梁。
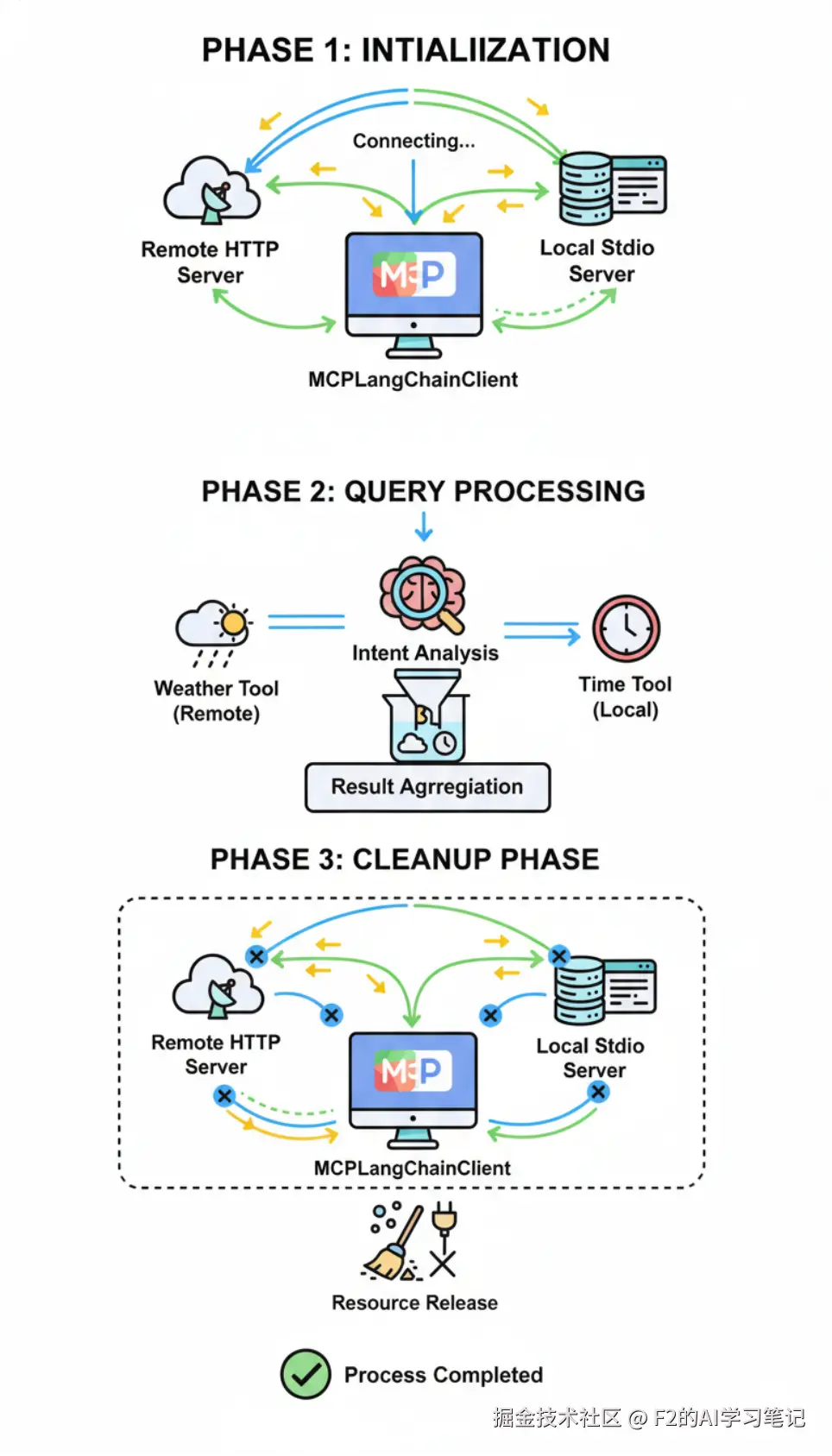
交互流程说明
(mcp_server.py) participant RemoteServer as 百炼MCP服务器
(墨迹天气API) Note over User,RemoteServer: === 初始化阶段 === User->>Client: 启动程序 (asyncio.run(main())) Client->>Client: MCPLangChainClient() Client->>Client: initialize() Note over Client: 创建MultiServerMCPClient Client->>MultiClient: MultiServerMCPClient(server_config) Note over MultiClient: 并行连接MCP服务器 par 本地stdio连接 MultiClient->>LocalServer: 启动进程 (python mcp_server.py) LocalServer->>LocalServer: FastMCP初始化并注册时间工具 LocalServer-->>MultiClient: 连接建立 and 远程HTTP连接 MultiClient->>RemoteServer: HTTP请求 (Bearer认证) RemoteServer-->>MultiClient: 服务发现响应 end MultiClient->>MultiClient: get_tools() Note over MultiClient: 获取工具列表 par 本地工具 MultiClient->>LocalServer: 列出工具请求 LocalServer-->>MultiClient: 返回时间工具
(get_current_time等) and 远程工具 MultiClient->>RemoteServer: 列出工具请求 RemoteServer-->>MultiClient: 返回天气工具 end MultiClient-->>Client: 返回合并工具列表 Client->>Client: create_agent(llm, tools) Client-->>User: 初始化完成 Note over User,RemoteServer: === 查询处理阶段 === User->>Client: chat("请告诉我北京天气和当前时间") Client->>Agent: agent.ainvoke({messages}) Note over Agent: ReAct推理循环 Agent->>Agent: 分析用户意图,选择工具 Note over MultiClient: 并行调用工具 par 天气查询 Agent->>MultiClient: 调用天气工具 MultiClient->>RemoteServer: HTTP POST请求
Authorization: Bearer {API_KEY} RemoteServer->>RemoteServer: 查询墨迹天气API RemoteServer-->>MultiClient: 返回天气数据 MultiClient-->>Agent: 天气查询结果 and 时间查询 Agent->>MultiClient: 调用时间工具 MultiClient->>LocalServer: stdio消息
get_current_time("Asia/Shanghai") LocalServer->>LocalServer: 获取北京时间 LocalServer-->>MultiClient: 返回时间字符串 MultiClient-->>Agent: 时间查询结果 end Agent->>Agent: 处理工具结果,生成最终回复 Agent-->>Client: 返回完整回复 Client-->>User: 显示结果(天气+时间) Note over User,RemoteServer: === 清理阶段 === User->>Client: 程序结束 Client->>Client: cleanup() MultiClient->>LocalServer: 关闭stdio进程 MultiClient->>MultiClient: 清理HTTP连接
第一阶段: 初始化阶段
- 启动客户端: 创建MCPLangChainClient实例
- 连接服务器: 并行连接本地stdio服务器和远程HTTP服务器
- 工具发现: 获取所有MCP服务器提供的工具列表
- 创建Agent: 使用LLM和工具列表创建ReAct Agent
第二阶段:查询处理阶段
- 用户提问: 用户提出查询请求
- 意图分析: Agent分析问题,确定需要的工具
- 并行调用: 同时调用天气工具(远程)和时间工具(本地)
- 结果整合: 合并多个工具的结果生成最终回复
第三阶段: 清理阶段
- 连接关闭: 优雅关闭所有MCP服务器连接
- 资源释放: 清理进程和HTTP连接池
代码实践
python
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# 创建FastMCP服务器实例
mcp = FastMCP("Time Service")
@mcp.tool()
def get_current_time(
timezone: str = "UTC",
format: Literal["iso", "readable", "timestamp"] = "iso"
) -> str:
"""
获取当前时间
Args:
timezone: 时区,例如 'UTC', 'Asia/Shanghai', 'America/New_York'
format: 返回格式
- iso: ISO 8601格式 (默认)
- readable: 可读格式
- timestamp: Unix时间戳
Returns:
格式化的当前时间字符串
"""
try:
# 获取指定时区
tz = pytz.timezone(timezone)
now = datetime.now(tz)
# 根据格式返回不同的时间表示
if format == "iso":
return now.isoformat()
elif format == "readable":
return now.strftime("%Y年%m月%d日 %H:%M:%S %Z")
elif format == "timestamp":
return str(int(now.timestamp()))
else:
return now.isoformat()
except Exception as e:
return f"错误: {str(e)}"
# 省略
# 启动mcp
def main():
"""
MCP服务器入口函数
支持命令行参数配置传输方式和端口
"""
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Time Service MCP Server")
parser.add_argument(
"--transport",
choices=["stdio", "streamable-http"],
default="stdio",
help="传输方式:stdio(默认,用于AI客户端)或 streamable-http(用于Web)"
)
parser.add_argument(
"--port",
type=int,
default=8000,
help="HTTP服务端口(仅在streamable-http模式下有效),默认8000"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
# 打印启动信息
print(f"Time Service MCP Server 启动中...")
print(f"传输方式: {args.transport}")
if args.transport == "streamable-http":
print(f"访问地址: http://localhost:{args.port}/mcp")
# 运行服务器
if args.transport == "streamable-http":
mcp.run(transport="streamable-http", port=args.port)
else:
# stdio模式下不打印到stdout,避免干扰MCP协议通信
mcp.run()
python
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ LangGraph Agent (ReAct模式) │
│ • 自动工具选择和调用 │
│ • 多轮对话和推理 │
└───────────┬──────────────────────┬──────────────────────┘
│ │
┌───────▼────────┐ ┌───────▼────────┐
│ 本地MCP (stdio) │ │ 百炼MCP (HTTP) │
│ mcp_server.py │ │ 墨迹天气API │
│ • 时间查询工具 │ │ • 天气查询工具 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
# 配置MCP
async def initialize(self):
"""
初始化MCP客户端和Agent
"""
print("初始化MCP客户端...")
# 配置多个MCP服务器
server_config = {
# 本地时间服务(stdio传输)
"time-service": {
"command": "python",
"args": ["mcp_server.py"],
"transport": "stdio",
"env": {},
},
# 百炼墨迹天气服务(HTTP传输)
"weather-service": {
"url": "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1/mcps/market-cmapi013828/mcp",
"transport": "streamable_http",
"headers": {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {os.getenv('MOJI_API_KEY')}"
}
}
}
# 创建MultiServerMCPClient
self.client = MultiServerMCPClient(server_config)
# 获取所有MCP服务器的工具
self.tools = await self.client.get_tools()stdio与SSE/HTTP 区别
在 MCP 中,stdio(标准输入/输出) 和 SSE/HTTP(基于 HTTP 的服务器发送事件) 是两种不同的传输方式,决定了客户端与服务器(或 MCP 服务器与资源)之间的通信信道。
核心区别:
- 架构与通信模式:
- stdio: 采用一对一、紧密耦合的进程间通信。客户端直接启动并连接到一个本地 MCP 服务器进程,通过标准输入输出流进行双向、同步的请求-响应通信。
- SSE/HTTP: 采用客户端-服务器模型,通常通过网络进行通信。客户端通过 HTTP 向一个远程的、独立运行的 MCP 服务器发起请求。服务器使用 SSE 流式地返回响应,更适合异步和长时间运行的任务。
- 部署与位置:
- stdio: 通信双方必须在同一台机器上。适用于本地工具和资源的集成。
- SSE/HTTP: 客户端和服务器可以部署在不同的机器上。适用于远程服务、云资源或需要跨网络访问的场景。
- 连接生命周期:
- stdio: 连接与 MCP 服务器进程的生命周期绑定。客户端启动服务器,会话开始;客户端断开,服务器进程通常终止。
- SSE/HTTP: 连接是无状态的 HTTP 请求。MCP 服务器是长期运行的,可以同时服务多个客户端连接。
总结
MCP Server 提供了 MCP 发布的示例代码(未加入鉴权),可在局域网环境中供内部应用调用。
MCP Client 提供了调用百炼平台及局域网环境下客户端的示例,能够管理多个平台的 MCP 工具,并根据任务需求选择合适的工具进行调用。
更多文档****
访问 Github:github.com/BaqiF2/ydc_...