项目链接
http://github.com/microsoft/magentic-ui
planning
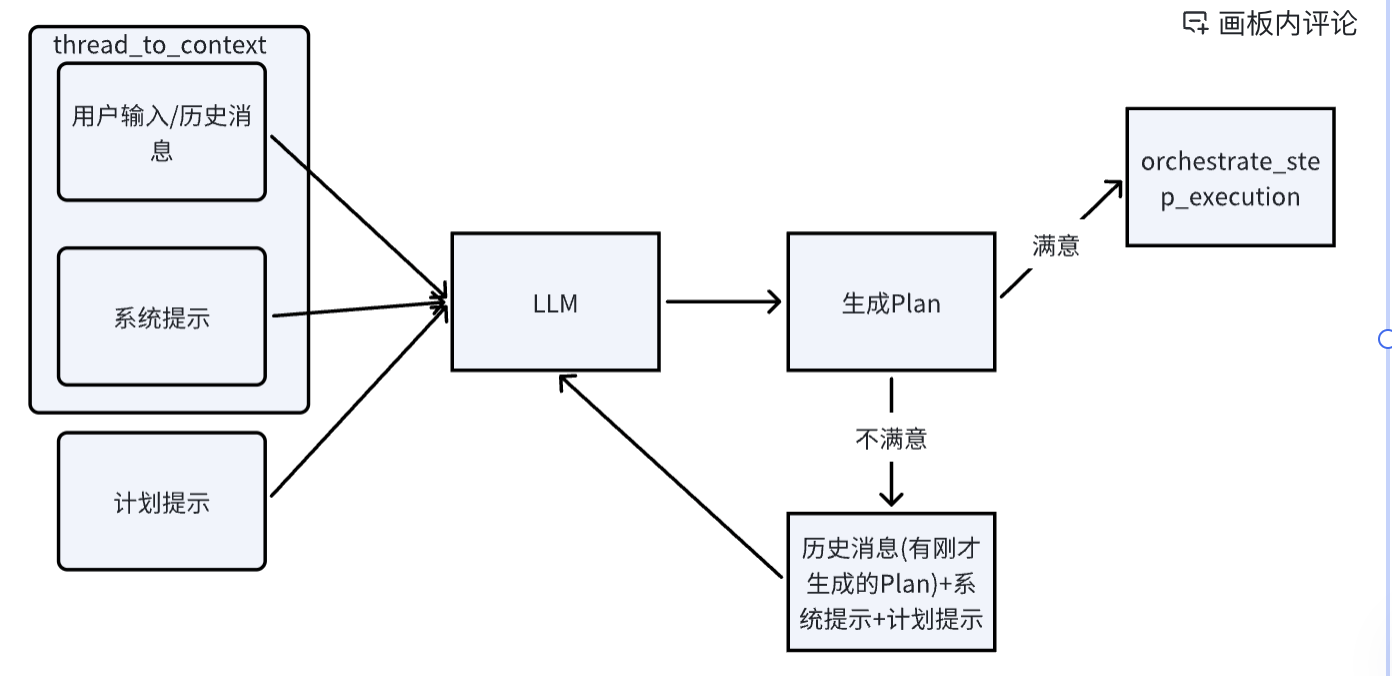
编排器的orchestrate_step_planning这个方法就是依据用户的输入,和用户进行多轮对话,产生一个计划的方法。首先是将聊天消息ChatMessage转变为LLMMessage,这个过程发生在thread_to_context中,这个方法首先是添加一个系统提示,在计划行为中这个系统提示的作用是判断是否需要计划以及生成结构清晰的计划。这个提示词需要 AI 判断用户的请求是否缺少信息,以及用户的问题是否可以从对话历史中回答,如果是这样的话,那么就提供答案,以及将need_plan设置为false,否则的话就应该制定一个计划。对于制定计划而言,那么就是对标题和详细步骤的要求。计划提示则是要求返回的JSON格式。
{{
"response": "a complete response to the user request for Case 1.",
"task": "a complete description of the task requested by the user",
"plan_summary": "a complete summary of the plan if a plan is needed, otherwise an empty string",
"needs_plan": boolean,
"steps":
[
{{
"title": "title of step 1",
"details": "recap the title in one short sentence \\n remaining details of step 1",
"agent_name": "the name of the agent that should complete the step"
}},
{{
"title": "title of step 2",
"details": "recap the title in one short sentence \\n remaining details of step 2",
"agent_name": "the name of the agent that should complete the step"
}},
...
]
}}在生成Plan的JSON格式后,将它保存到ChatMessage中,注意,系统提示和计划提示不会进行保留到ChatMessage中。用户满意,那么进入orchestrate_step_exectution中开始执行,否则的话,用户可以修改步骤,然后重复前面的步骤,再次生成一个新的计划,直到用户满意开始执行
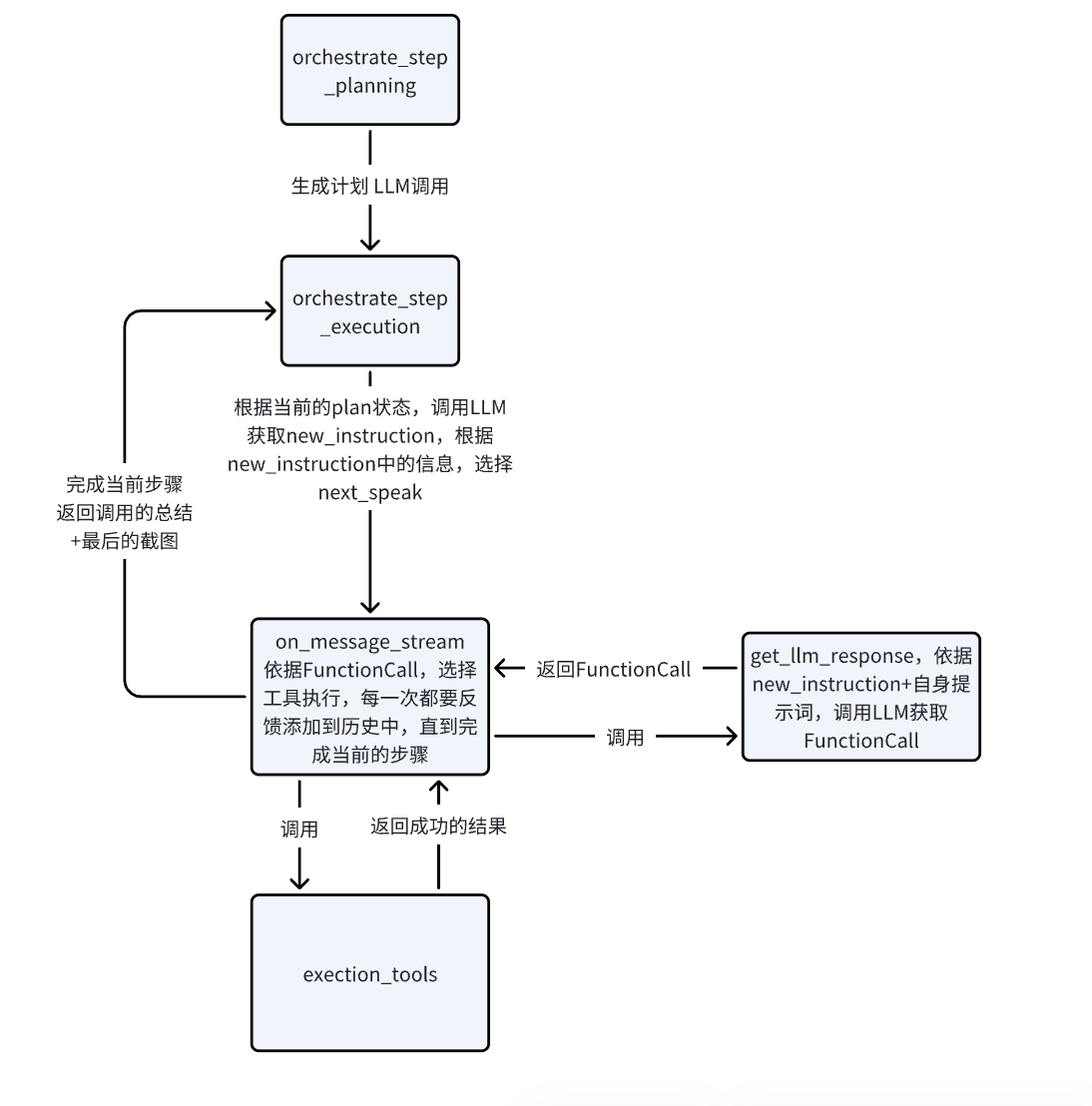
execution
plan_str
Task: 用户的任务
索引号. 代理名称:任务标题
任务细节
索引号. 代理名称:任务标题
任务细节
...在确定要进入execution后,在planning方法中,先把plan转化为plan_str,保存到state.plan中。在execution中使用get_task_ledger_full_prompt,将plan_str转化为提示词添加到历史消息。
还是使用thread_to_content,将历史消息转化为LLMMessage。之后添加一个提示词get_progress_ledger_prompt,这个提示词收集当前的任务task,完整的计划plan_str,当前的步骤index,当前步骤的详情(title,details,agent_name),可用的代理名称,然后依据这些让LLM返回一个JSON结构
{{
"is_current_step_complete": {{
"reason": string,
"answer": boolean
}},
"need_to_replan": {{
"reason": string,
"answer": boolean
}},
"instruction_or_question": {{
"answer": string,
"agent_name": string (the name of the agent that should complete the step from {names})
}},
"progress_summary": "a summary of the progress made so far"
}}调用LLM获取到相应的json结构progress_ledger,当前步骤完成,那么步骤+1,去执行下一个步骤。此时调用get_agent_instruction这个prompt,它是让下一个agent知道自己在任务的第几步(step_index),任务标题详细内容以及从progress_ledger中获取的answer 和 agent_name,answer 就是一个指令,代理可以依据这个指令进行行动,把这些包成new_instruction 。然后把new_instruction通过notify_all发送给代理,在通过next_speak通知某某代理,使其进行执行。代理实际收到的内容就是new_instruction。
new_instruction形式
step_index
step_title
step_details
agent_name. (agent_name)
instruction (answer)execute_tools
这个方法依据传进来的单个FunctionCall,依据name选择工具,返回工具的执行结果(例如,点击了某个元素)
get_llm_response
系统提示:告诉AI每次决策的时候,收到可交互元素的列表以及当前页面的截图(此时这个暂不启用),列出当前的定义好的工具,以及使用这些工具的规则。简单来说,根据这个提示词,AI可以根据页面上的元素选择正确的工具。
直接构建LLMMessage,不需要获取ChatMessage,在此时,LLMMessage中仅仅有这个系统提示。然后获取当前页面的聚焦元素(focused_hint)以及可交互元素的列表(visible_targets+other_targets),然后构建提示词。这个提示词让AI知道指令(last_outside_message),多标签页状态(tabs_info_str),当前页纯文本(webpage_text),截图说明(consider_screenshot+url),可交互元素的说明(最后的三个)
rust
let text_prompt = format!(
r#" The last request received was: {}
Note that attached images may be relevant to the request.
{}
The webpage has the following text:
{}
Attached is a screenshot of the current page:
{} which is open to the page '{}'. In this screenshot, interactive elements are outlined in bounding boxes in red. Each bounding box has a numeric ID label in red. Additional information about each visible label is listed below:
{}{}{}"#,
last_outside_message,
tabs_info_str,
webpage_text,
consider_screenshot,
url,
visible_targets,
other_targets_str,
focused_hint,
).trim().to_string();构建好这个prompt后,加入LLMMessage中,然后将LLMMessage和tool交给LLM,返回的是一个或者一系列的FunctionCall,当不执行工具的时候,返回的是纯文本的内容。注意,这个FunctionCall就是整个这一步全部的FunctionCall
on_message_stream
获取最后一条历史消息,实际上就是new_instruction,这里重新命名为last_outside_message。这里的last_outside_message就是要交给get_llm_response去进行使用的。从get_llm_response出来后,那么获取了当前步骤所有的FunctionCall。
对于on_message_stream中的处理纯文本的情况,将get_llm_response记录在emited_response中包装成ChatMessage返回给用户。(第一次返回)
对于on_message_stream中处理FunctionCall的情况,在即将执行某某工具时,将执行动作包装成ChatMessage返回给用户。(第二次返回,例如在搜索框输入github)
真正开始调用工具进行执行,将工具的执行结果和执行完毕的截图包装成ChatMessage返回给用户。(第三次返回,输入操作成功,截图:xxx)
然后将操作的结果以及页面的文本加入对话的历史中,循环第二次和第三次,直到选择到了stop_action,这一次返回的结果是本步骤完成后的最终结果,仅仅包含文本,返回给用户(第四次返回)
最终,构造all_response,将以上所有的操作和结果进行汇总(文本),加上一次截图,包装成ChatMessage返回给execution(第五次返回)
这里,返回给了编排器中的orchestrate_step_execution,然后orchestrate_step_execution调用thread_to_content,将历史消息转化为LLMMessage。循环继续
审批机制
requires_approval:判断当前的动作是否需要进行审批。先提取审批动作的描述(从对话的历史中),然后构造LLM判断提示词,系统消息(判断的标准)和用户消息(动作的描述)结合,只接受yes 和 no,否则其他视为yes(需要审批)。
get_approval:向用户展示当前要执行的操作(动作描述),并询问用户是否同意(get_input),根据用户的输出结果返回true/false。
它并不是每一个动作都是需要审批的,在工具的定义当中,有个元数据参数metadate,它包含着"requires_approval": "never"或者"requires_approval": "maybe",在on_message_stream中确定好要使用的FunctionCall后,依据FunctionCall内部的name从ToolSchema获取ToolSchema中的"maybe","nerver"(统称为baseline_needs_approval),然后把baseline_needs_approval和chat_message注入到requires_approval中,对于nerver的情况直接放行,对于maybe的情况,构造系统消息和用户消息(chat_message)传入的让LLM进行判断。如果需要进行审批,那么让用户进行审批,如果不需要进行审批,那么就直接使用工具。