一、背景
在开发鸿蒙应用时,性能优化是极其重要的,特此整理下常见的性能问题及解决方案,后续工作中能有效避免类似问题出现
二、常见问题
2.1、问题1:优化组件绘制
2.1.1、避免在定义组件生命周期内执行高耗时操作
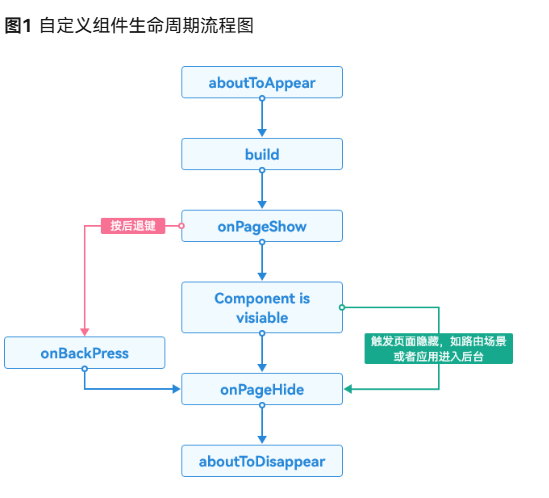
自定义组件创建完成之后,在build函数执行之前,将先执行aboutToAppear()生命周期回调函数。此时若在该函数中执行耗时操作,将阻塞UI渲染,增加UI主线程负担。因此,应尽量避免在自定义组件的生命周期内执行高耗时操作。
场景1:使用异步执行耗时操作
问题:在aboutToAppear生命周期函数中,运行了业务数据解析和处理等耗时操作,影响了上一页面点击跳转该页面的时延。
解决:可以把耗时操作的执行从同步执行改为异步或者延后执行,比如使用setTimeOut执行耗时操作
TypeScript
aboutToAppear(): void {
//在生命周期中,使用异步处理数据,延时大小视情况确定
setTimeout(() => {
this.workoutResult()
}, 1000)
}
workoutResult(): string[] {
//处理需要展示的业务数据
let data: Data[] = []
for (let i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
result += data[i]
}
return result
}2.2、问题2:控制渲染范围
2.2.1、合理控制元素显示与隐藏
控制元素显示与隐藏是一种常见的场景,频繁现在组件显示与隐藏的界面使用Visibility.None或Visibility.Visible、if条件判断控制的是组件的创建、布局阶段
TypeScript
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State isVisible: boolean = true
build() {
Column() {
Button('Switch visible and hidden').onClick(() => {
this.isVisible = !(this.isVisible)
})
Stack() {
Scroll() {
Column() {
Image($r('app.media.startIcon'))
}
}.visibility(this.isVisible ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.None)
}
}
}
}2.2.2、懒加载
懒加载LazyForEach是一种延迟加载的技术,它是在需要的时候才加载数据或资源,并在每次迭代过程中创建相应的组件,而不是一次性将所有内容都加载出来
TypeScript
// 数据源实现
class MyDataSource implements IDataSource {
private dataArray: string[] = ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3', 'Item 4', 'Item 5', 'Item 6', 'Item 7', 'Item 8', 'Item 9', 'Item 10']
private listeners: DataChangeListener[] = []
totalCount(): number {
return this.dataArray.length
}
getData(index: number): string {
return this.dataArray[index]
}
registerDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {
this.listeners.push(listener)
}
unregisterDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {
let index = this.listeners.indexOf(listener)
if (index >= 0) {
this.listeners.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct LazyForEachExample {
private data: MyDataSource = new MyDataSource()
build() {
List({ space: 10 }) {
// 使用 LazyForEach 实现懒加载
LazyForEach(this.data,
(item: string) => {
ListItem() {
// 每个列表项在需要显示时才创建
LazyItemComponent({ content: item })
}
},
(item: string) => item // key 生成器
)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(0xF1F3F5)
}
}
// 列表项组件 - 只在需要显示时创建
@Component
struct LazyItemComponent {
@Prop content: string
build() {
Row() {
Text(this.content)
.fontSize(18)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Text('(懒加载组件)')
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
}
.width('100%')
.height(100)
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor(Color.White)
.borderRadius(8)
.shadow(ShadowStyle.OUTER_DEFAULT_SM)
}
}2.2.3、组件复用
可复用组件从组件树上移除时,会进入到一个回收缓存区。后续创建新组件节点时,会复用缓存区中的节点,节约组件重新创建的时间。使用组件复用可以大幅度降低了因频繁创建与销毁组件带来的性能损耗
TypeScript
// 可复用的列表项组件
@Component
struct ReusableListItem {
@Prop itemText: string
@Prop itemIndex: number
@State isActive: boolean = false
aboutToAppear() {
console.log(`创建组件: ${this.itemText}`)
}
aboutToDisappear() {
console.log(`组件进入回收区: ${this.itemText}`)
}
build() {
Row() {
Text(`${this.itemIndex + 1}. ${this.itemText}`)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(this.isActive ? FontWeight.Bold : FontWeight.Normal)
.fontColor(this.isActive ? Color.Blue : Color.Black)
Blank()
Text(this.isActive ? '已激活' : '未激活')
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
}
.width('100%')
.height(50)
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor(this.isActive ? 0xECF5FF : Color.White)
.border({ width: 1, color: this.isActive ? Color.Blue : Color.Transparent })
.onClick(() => {
this.isActive = !this.isActive
})
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentReuseExample {
@State itemList: string[] = [
'项目 A', '项目 B', '项目 C', '项目 D', '项目 E',
'项目 F', '项目 G', '项目 H', '项目 I', '项目 J'
]
build() {
Column() {
Text('组件复用演示')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 10 })
Text('滚动列表观察组件复用情况')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 操作按钮
Row() {
Button('添加项目')
.onClick(() => {
this.itemList.push(`新项目 ${this.itemList.length + 1}`)
this.itemList = [...this.itemList] // 触发更新
})
Button('删除首个')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.itemList.length > 0) {
this.itemList.splice(0, 1)
this.itemList = [...this.itemList] // 触发更新
}
})
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 列表显示 - 系统会自动复用组件
List({ space: 5 }) {
ForEach(this.itemList, (item: string, index?: number) => {
ListItem() {
// 当列表项滚动出屏幕时,组件进入回收区
// 当新项需要显示时,复用回收区中的组件
ReusableListItem({
itemText: item,
itemIndex: index
})
}
}, (item: string) => item)
}
.width('100%')
.layoutWeight(1)
.backgroundColor(0xF8F9FA)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(10)
}
}2.3、问题3:减少布局节点
2.3.1、优先使用@Builder方法代替自定义组件
由于@Builder不涉及生命周期,在自定义组件大量嵌套的场景中,更加轻量级的@Builder在性能方面更加出色。所以不涉及到状态变量和自定义生命周期时,优先使用@Builder替换自定义组件
TypeScript
//反例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
num: number = 20
build() {
Column() {
NewComponent({ num: this.num })
}
}
}
@Component
struct NewComponent {
num?: number
build() {
Column() {
Text(`${this.num}`)
}
}
}
//⭐正例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
num: number = 29
build() {
Column() {
this.NewComponent()
}
}
@Builder
NewComponent(){
Text(`${this.num}`)
}
}2.3.2、移除冗余节点
对于常出现冗余的情况,例如可能会在Row容器包含一个同样也是Row容器的子级。这种嵌套实际是多余的,并且会给布局层次结构造成不必要的开销。
TypeScript
//反例代码
Row() {
Row(){
Image()
Text()
}
Image()
}
//⭐正例代码
//由于其中Row容器父子布局方向相同,所以可以去掉Image和Text外层的Row来减少层级,
//如果视图更加复杂,布局在渲染时,会产生没有必要的计算。
Row() {
Image()
Text()
Image()
}2.3.3、使用扁平化布局减少节点数
使用Column/Row替代Flex构建线性布局
这是由于Flex本身带来的二次布局的影响,Flex的性能明显低于Column和Row容器
TypeScript
//反例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column }) {
Flex().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
Flex().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
Flex().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Gray)
}
}
}
//⭐正例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Column() {
Row().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
Row().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
Row().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Gray)
}
}
}2.4、问题4:合理管理状态变量
2.4.1、精准控制组件的更新范围
在复杂页面开发的场景下,精准控制组件的范围对提高应用运行性能尤为重要。应该避免状态变量的滥用引起容器组件的刷新,进而影响帧率
使用Stack包裹条件渲染组件,减少更新范围
TypeScript
//反例代码
import { Data, dataInfo } from '../viewmodel/data'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State isVisible: boolean = false
@State realData: Data[] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(dataInfo))
build() {
Column() {
if (this.isVisible) {
Text()
}
ForEach(this.realData, (item: Data) => {
Text(item.lable)
})
}
}
}
//⭐正例代码
import { Data, dataInfo } from '../viewmodel/data'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State isVisible: boolean = false
@State realData: Data[] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(dataInfo))
build() {
Column() {
Stack() {
if (this.isVisible) {
Text()
}
ForEach(this.realData, (item: Data) => {
Text(item.lable)
})
}
}
}
}2.4.2、避免不必要的状态变量使用
场景1:删除冗余的状态变量@State
状态变量的管理有一定的开销,应在合理场景使用,普通的变量用状态变量标记可能会导致性能劣化
TypeScript
//反例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State bgColor: string | Color = '#ffffff'
@State selectColor: string | Color = '#007DFF'
build() {
}
}
//⭐正例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
bgColor: string | Color = '#ffffff'
selectColor: string | Color = '#007DFF'
build() {
}
}场景2:正确使用@Prop
@Prop 一般用来接父组件主动传的动态数据,若传递的数据固定不变那不用使用该装饰器,这样可以减少不必要的监听开销,提示性能
TypeScript
//反例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
num: number = 20
build() {
Column() {
NewComponent({ num: this.num })
}
}
}
@Component
struct NewComponent {
@Prop num?: number // ❌ 不必要的响应式监听
build() {
Text(`${this.num}`)
}
}
//⭐正例代码
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
num: number = 20 // 普通成员变量,不会触发响应式更新
build() {
Column() {
NewComponent({ num: this.num }) // 一次性传递,不会建立响应式连接
}
}
}
@Component
struct NewComponent {
num?: number // 普通参数,不会监听变化
build() {
Text(`${this.num}`) // 始终显示初始值 20
}
}2.5、内存管理优化
2.5.1 及时取消订阅
作用:避免组件销毁后仍监听事件,导致事件总线持续持有组件引用,同时防止后续事件触发时执行已销毁组件的回调逻辑(可能引发错误或内存泄漏)
TypeScript
@Component
struct SubscriptionExample {
private eventController: EventController = new EventController()
aboutToAppear() {
// 注册事件监听
this.eventController.on('customEvent', this.handleEvent)
}
aboutToDisappear() {
// 及时取消监听,防止内存泄漏
this.eventController.off('customEvent', this.handleEvent)
}
private handleEvent = (): void => {
// 处理事件
}
}2.5.2、大数据集分页加载
TypeScript
@Component
struct PaginationExample {
@State currentPage: number = 1
@State pageSize: number = 20
@State data: string[] = []
build() {
List() {
ForEach(this.data, (item: string) => {
ListItem() {
Text(item)
}
})
}
.onReachEnd(() => {
// 滚动到底部加载更多
this.loadMoreData()
})
}
private loadMoreData(): void {
// 分页加载数据,避免一次性加载过多
this.currentPage++
// 模拟加载数据
const newData = this.fetchData(this.currentPage, this.pageSize)
this.data = this.data.concat(newData)
}
}2.6、图片优化处理
如用 TinyPNG 这类工具压缩图片,或者把图片转成 WebP 格式,能在保证画质的同时减小文件大小