目录
[一、A题 小彩找数](#一、A题 小彩找数)
[二、B题 小彩的好字符串](#二、B题 小彩的好字符串)
[三、C题 小彩的字符串交换](#三、C题 小彩的字符串交换)
[四、D题 小彩的数组选数](#四、D题 小彩的数组选数)
[五、E题 小彩的数组构造](#五、E题 小彩的数组构造)
[六、F题 小彩的好数构](#六、F题 小彩的好数构)
一、A题 小彩找数
枚举 ,可能写的有点复杂
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
static IoScanner sc = new IoScanner();
// static final int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7);
static int n;
static int arr[];
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void solve() throws IOException {
// todo
int arr[]=new int[4];
int a=sc.nextInt();
if(a==1){
arr[1]=1;
}else if(a==2){
arr[2]=1;
}else if(a==3){
arr[3]=1;
}
int b=sc.nextInt();
if(b==1){
arr[1]=2;
}else if(b==2){
arr[2]=2;
}else if(b==3){
arr[3]=2;
}
int c=sc.nextInt();
if(c==1){
arr[1]=3;
}else if(c==2){
arr[2]=3;
}else if(c==3){
arr[3]=3;
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int t = 1;
// t = sc.nextInt();
while (t-- > 0) {
solve();
}
}
}
/**
* IoScanner类
*
* @author Dduo
* @version 1.0
* @description 通过IO流操作缓冲区减少了与底层输入输出设备的交互次数,旨在简化 Java 中的标准输入读取操作。
*/
class IoScanner {
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public IoScanner() {
bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException {
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}二、B题 小彩的好字符串
暴力,判断 3 的倍数的长度的 子串 即可
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
static IoScanner sc = new IoScanner();
// static final int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7);
static int n;
static int arr[];
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void solve() throws IOException {
int n=sc.nextInt();
String str=sc.next();
long cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i+2;j<n;j++){
String substring = str.substring(i, j + 1);
if(substring.length()%3!=0){
continue;
}
int cnt1=0;
int cnt2=0;
int cnt3=0;
for(int k=0;k<substring.length();k++){
if(substring.charAt(k)=='1'){
cnt1++;
}else if(substring.charAt(k)=='2'){
cnt2++;
}else if(substring.charAt(k)=='3'){
cnt3++;
}
}
if(cnt1==cnt2 && cnt2==cnt3){
cnt++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int t = 1;
// t = sc.nextInt();
while (t-- > 0) {
solve();
}
}
}
/**
* IoScanner类
*
* @author Dduo
* @version 1.0
* @description 通过IO流操作缓冲区减少了与底层输入输出设备的交互次数,旨在简化 Java 中的标准输入读取操作。
*/
class IoScanner {
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public IoScanner() {
bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException {
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}三、C题 小彩的字符串交换
因为最多只需要操作 1 次
所以其实也就三种答案 -1 0 1
先检查 如果没有 1 2 3 这三个数 结果是 -1
再检查直接存在 123 靠一起的情况 结果是 0
剩下的结果都是 1
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
static IoScanner sc = new IoScanner();
// static final int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7);
static int n;
static int arr[];
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void solve() throws IOException {
// todo
int n=sc.nextInt();
String str=sc.next();
if(count(str)==false){
System.out.println("-1");
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<n-3;i++){
String substring = str.substring(i, i + 3);
if(count(substring)==true){
System.out.println("0");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("1");
}
static boolean count(String str){
int cnt1=0;
int cnt2=0;
int cnt3=0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c=str.charAt(i);
if(c=='1'){
cnt1++;
}else if(c=='2'){
cnt2++;
}else if(c=='3'){
cnt3++;
}
}
// System.out.println(cnt1+" "+cnt2+" "+cnt3);
if(cnt1!=0&&cnt2!=0&&cnt3!=0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int t = 1;
t = sc.nextInt();
while (t-- > 0) {
solve();
}
}
}
/**
* IoScanner类
*
* @author Dduo
* @version 1.0
* @description 通过IO流操作缓冲区减少了与底层输入输出设备的交互次数,旨在简化 Java 中的标准输入读取操作。
*/
class IoScanner {
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public IoScanner() {
bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException {
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}四、D题 小彩的数组选数
动态规划
dp[] 数组的值为当前最大贪心值
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
static IoScanner sc = new IoScanner();
// static final int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7);
static int n;
static int arr[];
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void solve() throws IOException {
// todo
int n=sc.nextInt();
long arr[]=new long[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextLong();
}
// dp[i]表示到第i个元素的最大贪心值
long dp[]=new long[n+1];
// long max=0;
dp[1]=arr[0];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
// 不操作
long num1 = dp[i - 1];
// 操作
long num2 = dp[i - 2] + arr[i - 1];
dp[i] = Math.max(num1, num2);
}
System.out.println(dp[n]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int t = 1;
// t = sc.nextInt();
while (t-- > 0) {
solve();
}
}
}
/**
* IoScanner类
*
* @author Dduo
* @version 1.0
* @description 通过IO流操作缓冲区减少了与底层输入输出设备的交互次数,旨在简化 Java 中的标准输入读取操作。
*/
class IoScanner {
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public IoScanner() {
bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException {
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}五、E题 小彩的数组构造
因为每个子数组肯定都是 1 的倍数
所以由 a 可知 n
即构造数组的长度为 a+2
我们可以一位一位的构造 这样就能每次构造出一个子数组
我们的目的是一步步消耗 b 和 c 的值
构造和为 2 的倍数的子数组但不是 3 的倍数的数的话 b--
构造和为 3 的倍数的子数组但不是 2 的倍数的数的话 c--
构造和为 6 的倍数的子数组的话 b-- c--
构造和为 5 的倍数的子数组 不变
最后要使 b 和 c 得为 0
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
static IoScanner sc = new IoScanner();
// static final int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7);
static int n;
static int arr[];
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void solve() throws IOException {
// todo
long a=sc.nextInt();
long b=sc.nextInt();
long c=sc.nextInt();
if(b>a||c>a){
System.out.println("-1");
return;
}
long n=a+2;
long arr[]=new long[(int)n];
arr[0]=2;
arr[1]=3;
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
if(a==b+c){
// 构造和为2的倍数的子数组但不是3的倍数的数
if (b != 0) {
long sumPrev = arr[i - 1] + arr[i - 2];
long total = sumPrev;
// 找到第一个是2的倍数且不是3的倍数的total
do {
total++;
} while (total % 2 != 0 || total % 3 == 0);
arr[i] = total - sumPrev;
a--;
b--;
}
// 构造和为3的倍数的子数组但不是2的倍数的数
else if (c != 0) {
long sumPrev = arr[i - 1] + arr[i - 2];
long base = (sumPrev / 3 + 1) * 3;
long ans = (base % 2 == 0) ? base + 3 : base;
arr[i] = ans - sumPrev;
a--;
c--;
}
}else if(a<b+c){
// 构造和为6的子数组
long ans = (((arr[i-1]+arr[i-2])/6)+1)*6;
arr[i]=ans-arr[i-1]-arr[i-2];
a--;
b--;
c--;
}
else if (a > b + c) {
// 构造和为5的倍数,但不是2或3的倍数的子数组
long sumPrev = arr[i - 1] + arr[i - 2];
long base = ((sumPrev / 5) + 1) * 5;
while (base % 2 == 0 || base % 3 == 0) {
base += 5;
}
arr[i] = (int) (base - sumPrev);
a--;
}
}
System.out.println(n);
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
for (long i : arr) {
sb.append(i).append(" ");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int t = 1;
// t = sc.nextInt();
while (t-- > 0) {
solve();
}
}
}
/**
* IoScanner类
*
* @author Dduo
* @version 1.0
* @description 通过IO流操作缓冲区减少了与底层输入输出设备的交互次数,旨在简化 Java 中的标准输入读取操作。
*/
class IoScanner {
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public IoScanner() {
bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException {
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}六、F题 小彩的好数构
构造题
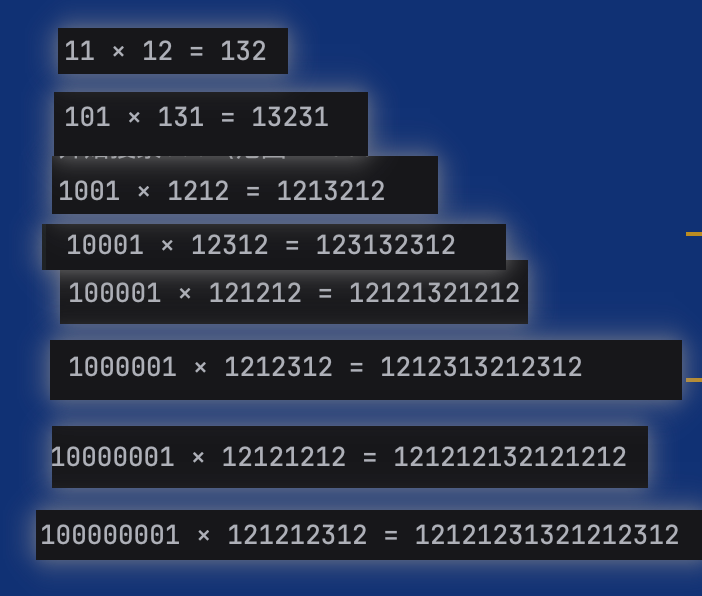
我是打表打出来的
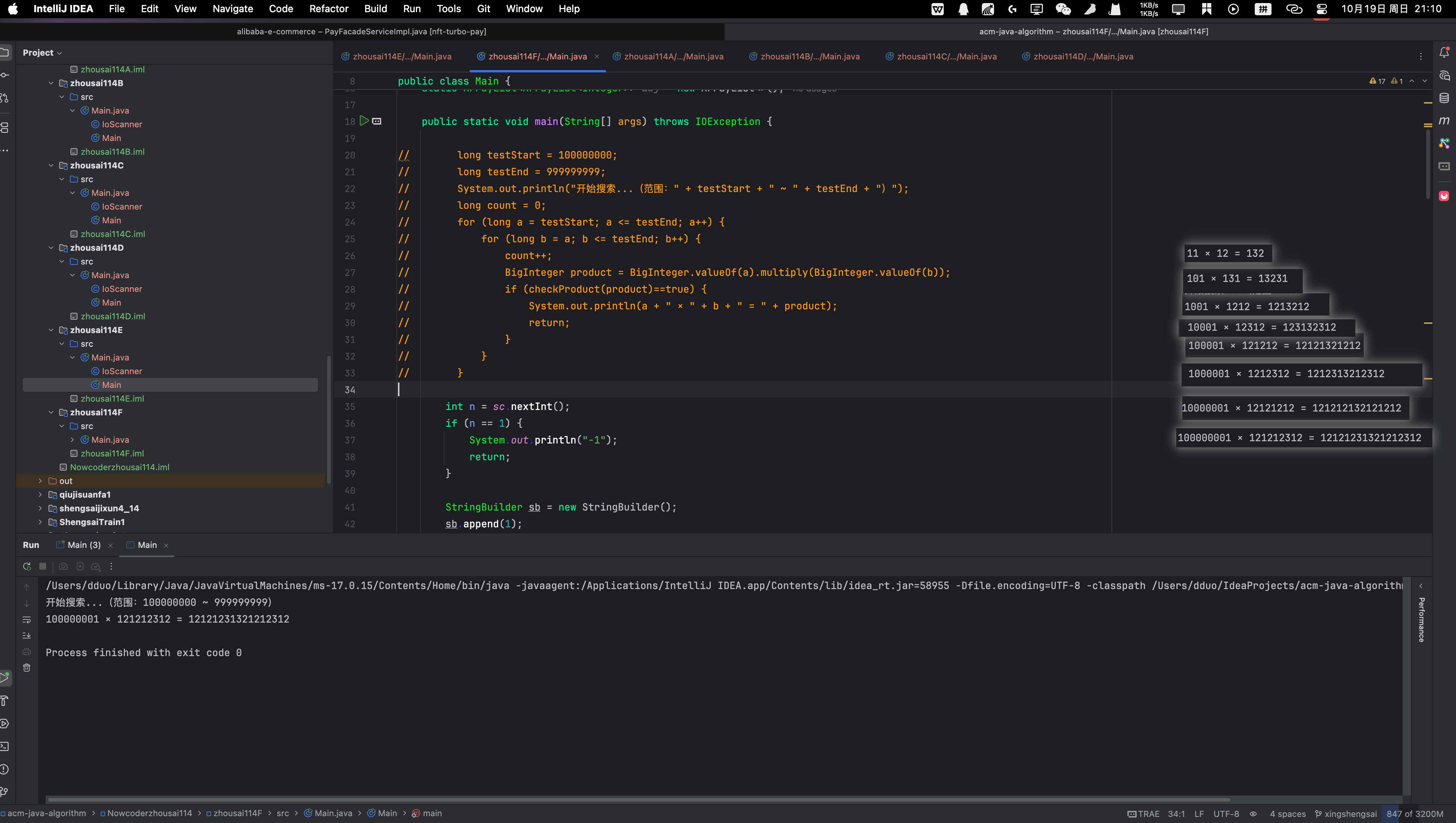
这是结果
如果 n 是偶数
构造如下 1000000001 1212121212
如果 n 是奇数
构造如下 10000000001 12121212312
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
static IoScanner sc = new IoScanner();
// static final int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7);
static int n;
static int arr[];
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// long testStart = 100000000;
// long testEnd = 999999999;
// System.out.println("开始搜索...(范围:" + testStart + " ~ " + testEnd + ")");
// long count = 0;
// for (long a = testStart; a <= testEnd; a++) {
// for (long b = a; b <= testEnd; b++) {
// count++;
// BigInteger product = BigInteger.valueOf(a).multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(b));
// if (checkProduct(product)==true) {
// System.out.println(a + " × " + b + " = " + product);
// return;
// }
// }
// }
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("-1");
return;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(1);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++) {
sb.append(0);
}
sb.append(1);
String num1=sb.toString();
if(n%2==0){
sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i+=2) {
sb.append("12");
}
String num2 = sb.toString();
System.out.println(num1+" "+num2);
}else {
if(n==3){
System.out.println(num1+" 131");
}else{
sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n-3; i+=2) {
sb.append("12");
}
sb.append("312");
String num2 = sb.toString();
System.out.println(num1+" "+num2);
}
}
}
// 检查乘积是否符合条件(仅含1、2、3,无连续相同字符,且同时存在1、2、3)
private static boolean checkProduct(BigInteger product) {
String numStr = product.toString();
boolean has1 = false;
boolean has2 = false;
boolean has3 = false;
for (char c : numStr.toCharArray()) {
if (c < '1' || c > '3') {
return false;
}
if (c == '1') {
has1 = true;
} else if (c == '2') {
has2 = true;
} else if (c == '3') {
has3 = true;
}
}
if (!has1 || !has2 || !has3) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < numStr.length() - 1; i++) {
if (numStr.charAt(i) == numStr.charAt(i + 1)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* IoScanner类
*
* @author Dduo
* @version 1.0
* @description 通过IO流操作缓冲区减少了与底层输入输出设备的交互次数,旨在简化 Java 中的标准输入读取操作。
*/
class IoScanner {
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public IoScanner() {
bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException {
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}