
python
import math
import numpy as np
from pyautocad import Autocad, APoint
def get_selection_or_model_space(acad, doc):
"""获取用户选择的对象"""
print("请选择对象")
try:
import time
unique_name = f"Temp_Selection_Set_{int(time.time() * 1000) % 10000}"
selection_set = doc.SelectionSets.Add(unique_name)
selection_set.SelectOnScreen()
if selection_set.Count > 0:
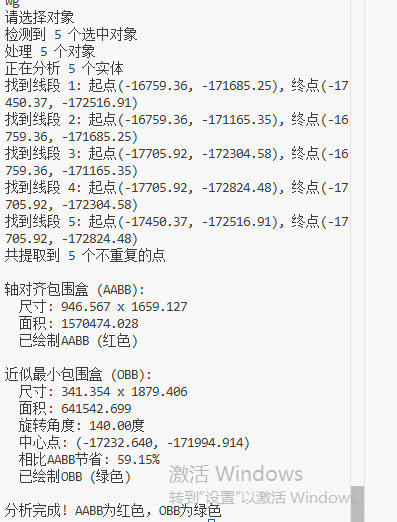
print(f"检测到 {selection_set.Count} 个选中对象")
selection = []
for i in range(selection_set.Count):
try:
entity = selection_set.Item(i)
selection.append(entity)
except Exception as e:
print(f"无法访问选中对象 {i}: {e}")
selection_set.Delete()
return selection
else:
selection_set.Delete()
return []
except Exception as e:
print(f"无法获取选择集: {e}")
return None
def get_points_from_entities(entities):
"""从AutoCAD实体中提取线段的端点"""
points = []
for i, entity in enumerate(entities):
try:
if entity.ObjectName == "AcDbLine":
start = entity.StartPoint[:2]
end = entity.EndPoint[:2]
points.append(tuple(start))
points.append(tuple(end))
print(f"找到线段 {len(points)//2}: 起点({start[0]:.2f}, {start[1]:.2f}), 终点({end[0]:.2f}, {end[1]:.2f})")
else:
print(f"跳过非线段对象 {i+1}: {entity.ObjectName}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理对象 {i+1} 时出错: {e}")
continue
points = list(set(points))
print(f"共提取到 {len(points)} 个不重复的点")
return points
def get_aabb_bounding_box(points):
"""获取轴对齐的最小包围矩形"""
if len(points) < 1:
return None
x_coords = [p[0] for p in points]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in points]
min_x, max_x = min(x_coords), max(x_coords)
min_y, max_y = min(y_coords), max(y_coords)
width = max_x - min_x
height = max_y - min_y
# 计算四个角点
corners = [
(min_x, min_y),
(max_x, min_y),
(max_x, max_y),
(min_x, max_y)
]
return {
'type': 'AABB',
'corners': corners,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'area': width * height,
'angle': 0,
'center': ((min_x + max_x) / 2, (min_y + max_y) / 2)
}
def rotate_point(point, angle, center=(0, 0)):
"""绕指定中心点旋转点"""
x, y = point
cx, cy = center
x -= cx
y -= cy
rad = math.radians(angle)
cos_rad, sin_rad = math.cos(rad), math.sin(rad)
new_x = x * cos_rad - y * sin_rad
new_y = x * sin_rad + y * cos_rad
new_x += cx
new_y += cy
return (new_x, new_y)
def get_oriented_bounding_box_approx(points):
"""获取近似最小面积包围矩形"""
if len(points) < 2:
return None
min_area = float('inf')
best_box = None
angles_to_check = []
for i in range(0, 180, 5):
angles_to_check.append(i)
max_dist = 0
farthest_pair = None
for i in range(len(points)):
for j in range(i+1, len(points)):
dist = math.sqrt((points[i][0]-points[j][0])**2 + (points[i][1]-points[j][1])**2)
if dist > max_dist:
max_dist = dist
farthest_pair = (points[i], points[j])
if farthest_pair:
p1, p2 = farthest_pair
angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(p2[1] - p1[1], p2[0] - p1[0]))
angles_to_check.extend([angle, angle + 90])
angles_to_check = list(set([a % 180 for a in angles_to_check]))
for angle in angles_to_check:
rotated_points = [rotate_point(p, -angle) for p in points]
x_coords = [p[0] for p in rotated_points]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in rotated_points]
min_x, max_x = min(x_coords), max(x_coords)
min_y, max_y = min(y_coords), max(y_coords)
width = max_x - min_x
height = max_y - min_y
area = width * height
if area < min_area:
min_area = area
# 计算旋转后的四个角点
rotated_corners = [
(min_x, min_y),
(max_x, min_y),
(max_x, max_y),
(min_x, max_y)
]
# 将角点旋转回原始坐标系
corners = [rotate_point(p, angle) for p in rotated_corners]
center_x = (min_x + max_x) / 2
center_y = (min_y + max_y) / 2
center_original = rotate_point((center_x, center_y), angle)
best_box = {
'type': 'OBB',
'corners': corners,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'area': area,
'angle': angle,
'center': center_original
}
return best_box
def draw_bounding_box(acad, box, color_index):
"""在AutoCAD中绘制包围框
:param acad: Autocad实例
:param box: 包围框字典,包含corners列表
:param color_index: AutoCAD颜色索引 (1=红色, 3=绿色, 5=蓝色等)
"""
if not box or 'corners' not in box:
return None
corners = box['corners']
model = acad.model
# 绘制四条边,形成闭合矩形
lines = []
for i in range(4):
p1 = APoint(corners[i][0], corners[i][1], 0)
p2 = APoint(corners[(i+1)%4][0], corners[(i+1)%4][1], 0)
line = model.AddLine(p1, p2)
line.Color = color_index
lines.append(line)
return lines
def analyze_and_draw_bounding_boxes(acad, entities):
"""分析实体并绘制包围框"""
print(f"正在分析 {len(entities)} 个实体")
points = get_points_from_entities(entities)
if len(points) < 1:
print("未找到有效点")
return None
# 计算AABB
aabb = get_aabb_bounding_box(points)
if aabb:
print("\n轴对齐包围盒 (AABB):")
print(f" 尺寸: {aabb['width']:.3f} x {aabb['height']:.3f}")
print(f" 面积: {aabb['area']:.3f}")
# 绘制AABB (红色)
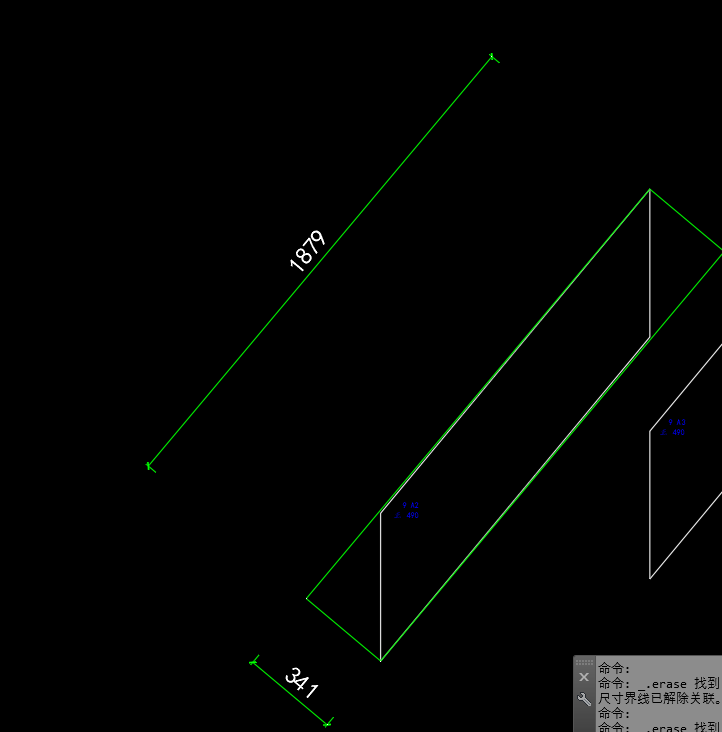
draw_bounding_box(acad, aabb, 1)
print(" 已绘制AABB (红色)")
# 计算OBB
obb = get_oriented_bounding_box_approx(points)
if obb:
print("\n近似最小包围盒 (OBB):")
print(f" 尺寸: {obb['width']:.3f} x {obb['height']:.3f}")
print(f" 面积: {obb['area']:.3f}")
print(f" 旋转角度: {obb['angle']:.2f}度")
print(f" 中心点: ({obb['center'][0]:.3f}, {obb['center'][1]:.3f})")
if aabb:
saving = (1 - obb['area'] / aabb['area']) * 100
print(f" 相比AABB节省: {saving:.2f}%")
# 绘制OBB (绿色)
draw_bounding_box(acad, obb, 3)
print(" 已绘制OBB (绿色)")
return {
'points': points,
'aabb': aabb,
'obb': obb
}
def main():
"""主函数"""
try:
acad = Autocad(create_if_not_exists=True)
doc = acad.doc
print(f"成功连接到 AutoCAD 文档: {doc.Name}")
except Exception as e:
print("无法连接到 AutoCAD:", e)
return
try:
entities = get_selection_or_model_space(acad, doc)
if entities is None:
print("获取对象过程中发生错误,程序退出")
return
if not entities:
print("没有找到任何对象,程序退出")
return
print(f"处理 {len(entities)} 个对象")
result = analyze_and_draw_bounding_boxes(acad, entities)
if result:
print("\n分析完成! AABB为红色,OBB为绿色")
else:
print("分析失败")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理对象时出错: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()二分搜索
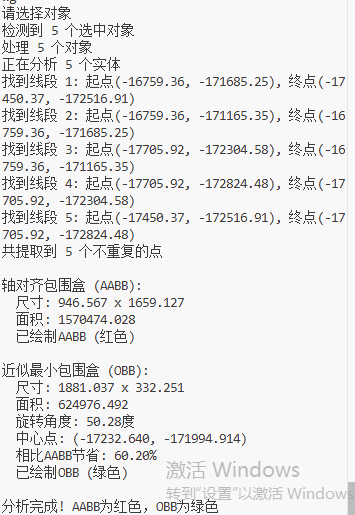
可以看到二分搜索更准确
主要改进点:
-
使用三分搜索算法:
- 实现了
ternary_search_min_area函数,使用三分法来搜索最小面积角度 - 三分法比二分法更适合单峰函数的极值搜索
- 实现了
-
更精确的角度搜索:
- 先用粗略搜索找到大致最优角度
- 再在该角度附近用三分法进行精细搜索
- 搜索精度可以通过
eps参数控制
-
处理角度边界情况:
- 当搜索区间跨越0度时,分别在两个区间进行搜索
- 确保能找到全局最优解
-
提高搜索效率:
- 三分法的收敛速度比逐步搜索快得多
- 可以在保证精度的同时大幅减少计算量
这种实现方式比原来的固定步长搜索更加高效和精确,能够在较少的迭代次数内找到接近最优的解。
二分法的特点:
- 适用场景:适用于单调函数或寻找特定值(如零点)
- 工作原理:每次将搜索区间分成两部分,根据中间点的函数值决定保留哪一半
- 前提条件:需要函数具有单调性或者能通过函数值判断目标在左半区还是右半区
三分法的特点:
- 适用场景:适用于单峰函数的极值搜索
- 工作原理:每次将搜索区间分成三部分,通过比较两个内点的函数值来缩小搜索范围
- 前提条件:函数必须是单峰的(只有一个最大值或最小值)
为什么包围矩形面积适合用三分法?
在我们的场景中,包围矩形面积随着旋转角度的变化呈现单峰特性:
python
# 示例示意:面积随角度变化的单峰特性 # 角度: 0° 10° 20° 30° 40° 50° 60° # 面积: 100 80 60 50 60 80 100 # ↓ 最小值在这里
当我们将点集旋转不同角度并计算轴对齐包围盒时,面积函数通常是单峰的------存在一个最小值点。
三分法的工作原理图解:
初始区间 [left, right] 计算两个内点: mid1 = left + (right-left)/3 mid2 = right - (right-left)/3 情况1: f(mid1) < f(mid2) 最小值在左半部分 新区间: [left, mid2] 情况2: f(mid1) > f(mid2) 最小值在右半部分 新区间: [mid1, right] 情况3: f(mid1) ≈ f(mid2) 最小值在中间 可以任选一种策略
关键优势对比:
| 方法 | 收敛速度 | 适用函数类型 | 实现复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 二分法 | 快速 | 单调函数 | 简单 |
| 三分法 | 较快 | 单峰函数 | 中等 |
python
import math
import numpy as np
from pyautocad import Autocad, APoint
import pyperclip
def get_selection_or_model_space(acad, doc):
"""获取用户选择的对象"""
print("请选择对象")
try:
import time
unique_name = f"Temp_Selection_Set_{int(time.time() * 1000) % 10000}"
selection_set = doc.SelectionSets.Add(unique_name)
selection_set.SelectOnScreen()
if selection_set.Count > 0:
print(f"检测到 {selection_set.Count} 个选中对象")
selection = []
for i in range(selection_set.Count):
try:
entity = selection_set.Item(i)
selection.append(entity)
except Exception as e:
print(f"无法访问选中对象 {i}: {e}")
selection_set.Delete()
return selection
else:
selection_set.Delete()
return []
except Exception as e:
print(f"无法获取选择集: {e}")
return None
def get_points_from_entities(entities):
"""从AutoCAD实体中提取线段的端点"""
points = []
for i, entity in enumerate(entities):
try:
if entity.ObjectName == "AcDbLine":
start = entity.StartPoint[:2]
end = entity.EndPoint[:2]
points.append(tuple(start))
points.append(tuple(end))
print(f"找到线段 {len(points)//2}: 起点({start[0]:.2f}, {start[1]:.2f}), 终点({end[0]:.2f}, {end[1]:.2f})")
else:
print(f"跳过非线段对象 {i+1}: {entity.ObjectName}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理对象 {i+1} 时出错: {e}")
continue
points = list(set(points))
print(f"共提取到 {len(points)} 个不重复的点")
return points
def get_aabb_bounding_box(points):
"""获取轴对齐的最小包围矩形"""
if len(points) < 1:
return None
x_coords = [p[0] for p in points]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in points]
min_x, max_x = min(x_coords), max(x_coords)
min_y, max_y = min(y_coords), max(y_coords)
width = max_x - min_x
height = max_y - min_y
# 计算四个角点
corners = [
(min_x, min_y),
(max_x, min_y),
(max_x, max_y),
(min_x, max_y)
]
return {
'type': 'AABB',
'corners': corners,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'area': width * height,
'angle': 0,
'center': ((min_x + max_x) / 2, (min_y + max_y) / 2)
}
def rotate_point(point, angle, center=(0, 0)):
"""绕指定中心点旋转点"""
x, y = point
cx, cy = center
x -= cx
y -= cy
rad = math.radians(angle)
cos_rad, sin_rad = math.cos(rad), math.sin(rad)
new_x = x * cos_rad - y * sin_rad
new_y = x * sin_rad + y * cos_rad
new_x += cx
new_y += cy
return (new_x, new_y)
def get_bounding_box_area(points, angle):
"""计算给定角度下的包围盒面积和边界信息"""
rotated_points = [rotate_point(p, -angle) for p in points]
x_coords = [p[0] for p in rotated_points]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in rotated_points]
min_x, max_x = min(x_coords), max(x_coords)
min_y, max_y = min(y_coords), max(y_coords)
width = max_x - min_x
height = max_y - min_y
area = width * height
return area, (min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y)
def ternary_search_min_area(points, left, right, eps=1e-6):
"""使用三分法搜索最小面积角度"""
while right - left > eps:
mid1 = left + (right - left) / 3
mid2 = right - (right - left) / 3
area1, _ = get_bounding_box_area(points, mid1)
area2, _ = get_bounding_box_area(points, mid2)
if area1 < area2:
right = mid2
else:
left = mid1
optimal_angle = (left + right) / 2
min_area, bounds = get_bounding_box_area(points, optimal_angle)
return optimal_angle, min_area, bounds
def get_oriented_bounding_box_approx(points):
"""使用三分搜索获取最小面积包围矩形"""
if len(points) < 2:
return None
# 首先找到一个较好的初始角度范围
angles_to_check = []
# 使用较小步长进行初步搜索
for i in range(0, 180, 2):
angles_to_check.append(i)
# 找到距离最远的点对
max_dist = 0
farthest_pair = None
for i in range(len(points)):
for j in range(i+1, len(points)):
dist = math.sqrt((points[i][0]-points[j][0])**2 + (points[i][1]-points[j][1])**2)
if dist > max_dist:
max_dist = dist
farthest_pair = (points[i], points[j])
if farthest_pair:
p1, p2 = farthest_pair
angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(p2[1] - p1[1], p2[0] - p1[0]))
angles_to_check.extend([angle, angle + 90])
angles_to_check = list(set([a % 180 for a in angles_to_check]))
# 找到初步的最小面积角度
min_area = float('inf')
best_angle = 0
best_bounds = None
for angle in angles_to_check:
area, bounds = get_bounding_box_area(points, angle)
if area < min_area:
min_area = area
best_angle = angle
best_bounds = bounds
# 在最优角度附近使用三分法进行精细搜索
search_range = 5 # 搜索范围±5度
left_angle = (best_angle - search_range) % 180
right_angle = (best_angle + search_range) % 180
# 处理跨越0度的情况
if left_angle > right_angle:
# 在[0, right_angle]和[left_angle, 180]两个区间分别搜索
optimal_angle1, min_area1, bounds1 = ternary_search_min_area(points, 0, right_angle)
optimal_angle2, min_area2, bounds2 = ternary_search_min_area(points, left_angle, 180)
if min_area1 < min_area2:
optimal_angle = optimal_angle1
min_area = min_area1
best_bounds = bounds1
else:
optimal_angle = optimal_angle2
min_area = min_area2
best_bounds = bounds2
else:
optimal_angle, min_area, best_bounds = ternary_search_min_area(points, left_angle, right_angle)
# 构造最终的包围盒
min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y = best_bounds
width = max_x - min_x
height = max_y - min_y
# 计算旋转后的四个角点
rotated_corners = [
(min_x, min_y),
(max_x, min_y),
(max_x, max_y),
(min_x, max_y)
]
# 将角点旋转回原始坐标系
corners = [rotate_point(p, optimal_angle) for p in rotated_corners]
center_x = (min_x + max_x) / 2
center_y = (min_y + max_y) / 2
center_original = rotate_point((center_x, center_y), optimal_angle)
return {
'type': 'OBB',
'corners': corners,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'area': min_area,
'angle': optimal_angle,
'center': center_original
}
def draw_bounding_box(acad, box, color_index):
"""在AutoCAD中绘制包围框
:param acad: Autocad实例
:param box: 包围框字典,包含corners列表
:param color_index: AutoCAD颜色索引 (1=红色, 3=绿色, 5=蓝色等)
"""
if not box or 'corners' not in box:
return None
corners = box['corners']
model = acad.model
# 绘制四条边,形成闭合矩形
lines = []
for i in range(4):
p1 = APoint(corners[i][0], corners[i][1], 0)
p2 = APoint(corners[(i+1)%4][0], corners[(i+1)%4][1], 0)
line = model.AddLine(p1, p2)
line.Color = color_index
lines.append(line)
return lines
def analyze_and_draw_bounding_boxes(acad, entities, draw_boxes=True):
"""分析实体并绘制包围框
:param acad: Autocad实例
:param entities: 实体列表
:param draw_boxes: 是否绘制边界框,默认为True
"""
print(f"正在分析 {len(entities)} 个实体")
points = get_points_from_entities(entities)
if len(points) < 1:
print("未找到有效点")
return None
# 计算AABB
aabb = get_aabb_bounding_box(points)
if aabb:
print("\n轴对齐包围盒 (AABB):")
print(f" 尺寸: {aabb['width']:.3f} x {aabb['height']:.3f}")
print(f" 面积: {aabb['area']:.3f}")
# 绘制AABB (红色)
if draw_boxes:
draw_bounding_box(acad, aabb, 1)
print(" 已绘制AABB (红色)")
# 计算OBB
obb = get_oriented_bounding_box_approx(points)
if obb:
print("\n近似最小包围盒 (OBB):")
print(f" 尺寸: {obb['width']:.3f} x {obb['height']:.3f}")
print(f" 面积: {obb['area']:.3f}")
print(f" 旋转角度: {obb['angle']:.2f}度")
print(f" 中心点: ({obb['center'][0]:.3f}, {obb['center'][1]:.3f})")
# 将OBB尺寸复制到剪贴板(去掉空格)
obb_dimensions = f"{obb['width']:.0f}x{obb['height']:.0f}"
pyperclip.copy(obb_dimensions)
print(f" OBB尺寸已复制到剪贴板: {obb_dimensions}")
if aabb:
saving = (1 - obb['area'] / aabb['area']) * 100
print(f" 相比AABB节省: {saving:.2f}%")
# 绘制OBB (绿色)
if draw_boxes:
draw_bounding_box(acad, obb, 3)
print(" 已绘制OBB (绿色)")
return {
'points': points,
'aabb': aabb,
'obb': obb
}
def main():
"""主函数"""
try:
acad = Autocad(create_if_not_exists=True)
doc = acad.doc
print(f"成功连接到 AutoCAD 文档: {doc.Name}")
except Exception as e:
print("无法连接到 AutoCAD:", e)
return
try:
entities = get_selection_or_model_space(acad, doc)
if entities is None:
print("获取对象过程中发生错误,程序退出")
return
if not entities:
print("没有找到任何对象,程序退出")
return
print(f"处理 {len(entities)} 个对象")
# 控制是否绘制边界框的变量
DRAW_BOUNDING_BOXES = True
result = analyze_and_draw_bounding_boxes(acad, entities, DRAW_BOUNDING_BOXES)
if result:
if DRAW_BOUNDING_BOXES:
print("\n分析完成! AABB为红色,OBB为绿色")
else:
print("\n分析完成! 边界框未绘制")
else:
print("分析失败")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理对象时出错: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()