应用层协议HTTP
- (http是一个应用层协议,底层用的tcp)
一.HTTP补充知识:
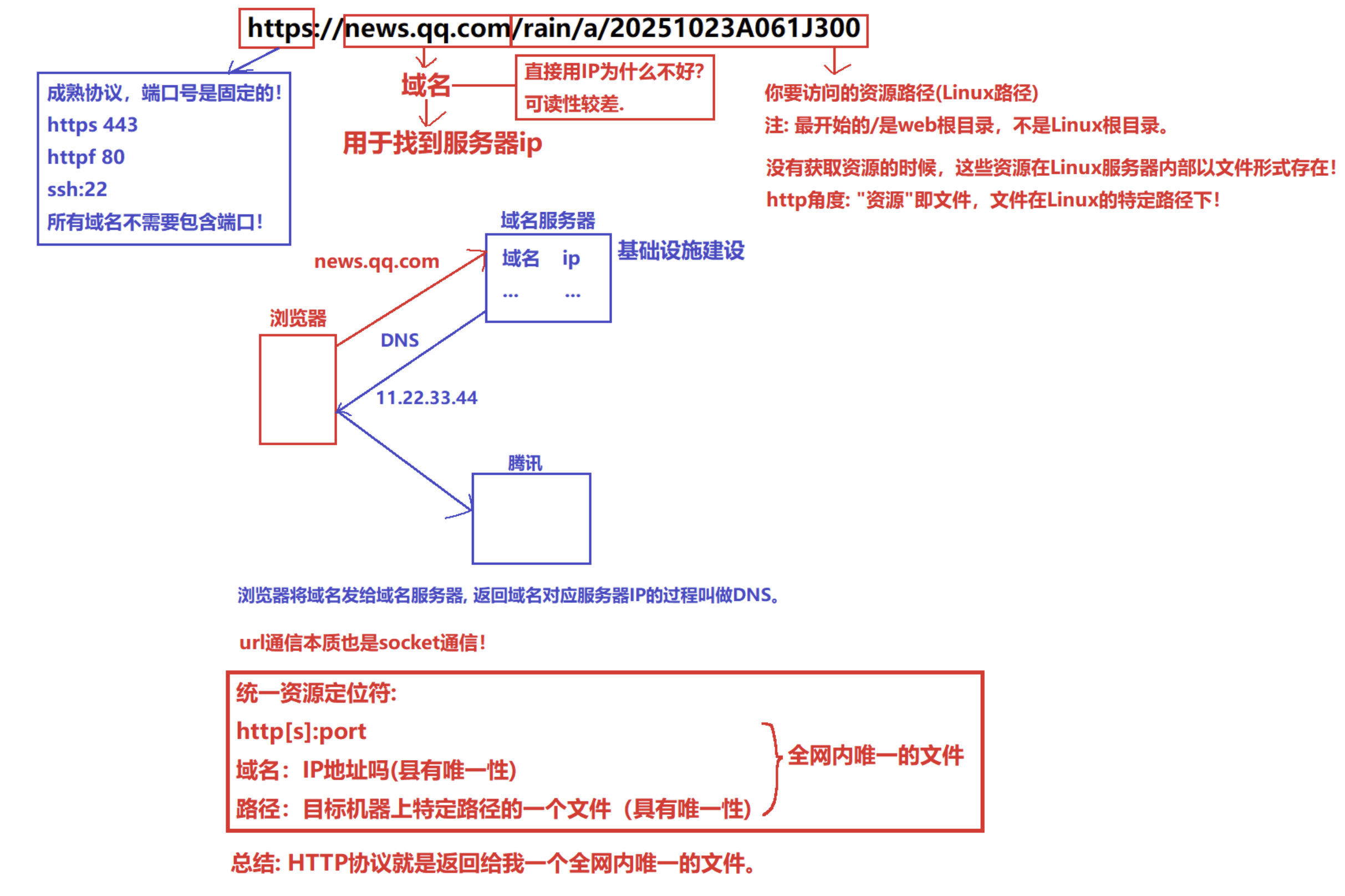
域名和IP之间的关系
二.HTTP协议
虽然我们说, 应用层协议是我们程序猿自己定的. 但实际上, 已经有大佬们定义了一些现成的, 又非常好用的应用层协议 , 供我们直接参考使用. HTTP(超文本传输协议)就是其中之一。
在互联网世界中,HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol,超文本传输协议)是一个至关重要的协议。
它定义了客户端(如浏览器)与服务器之间如何通信,以交换或传输超文本(如HTML文档)。
HTTP协议是客户端与服务器之间通信的基础。客户端通过HTTP协议向服务器发送请求,服务器收到请求后处理并返回响应。HTTP协议是一个无连接、无状态的协议,即每次请求都需要建立新的连接,且服务器不会保存客户端的状态信息。
三.认识URL
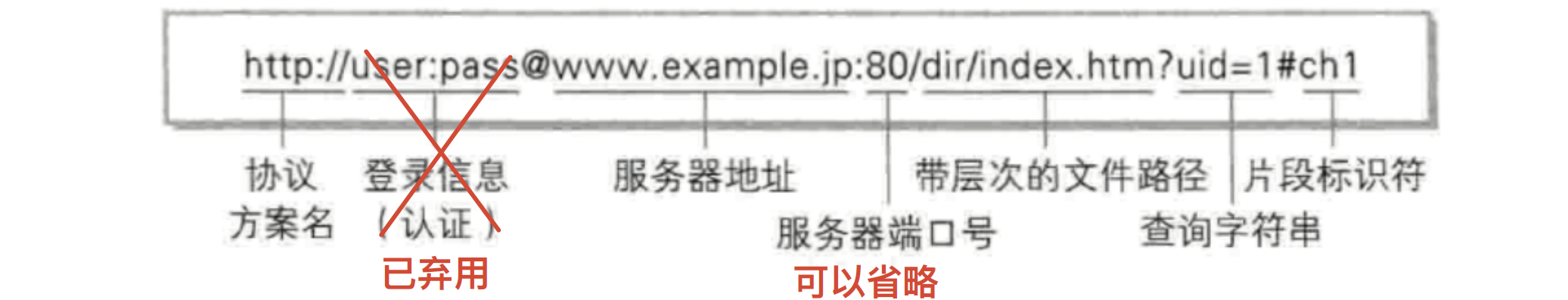
平时我们俗称的 "网址" 其实就是说的 URL(统一资源定位符)也就是超链接
四.urlencode和urldecode(了解)
像 / ? : 等这样的字符, 已经被url 当做特殊意义理解了. 因此这些字符不能随意出现.
比如, 某个参数中需要带有这些特殊字符, 就必须先对特殊字符进行转义.
转义的规则如下:
将需要转码的字符转为16进制,然后从右到左,取4位(不足4位直接处理),每2位做一位,前面加上%,编码成%XY格式
例如:
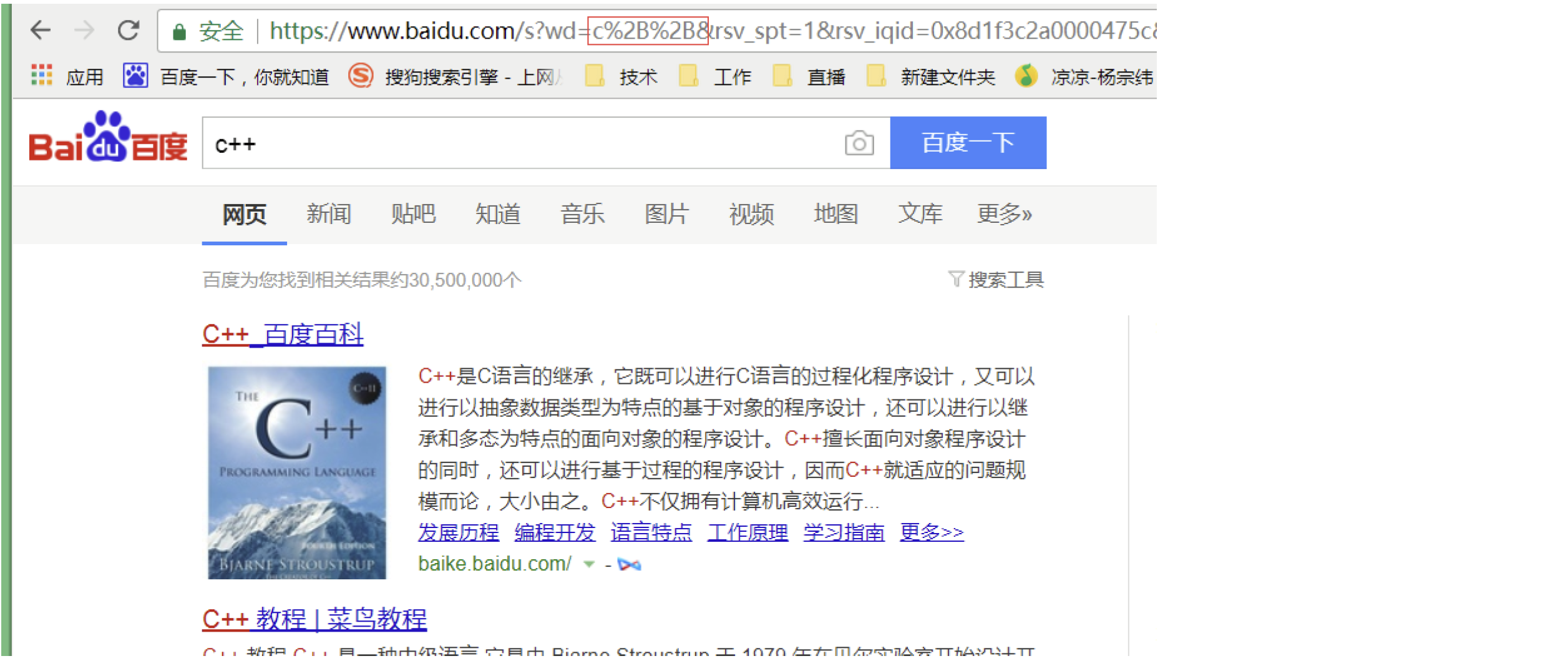
"+" 被转义成了 "%2B"
urldecode就是urlencode的逆过程;
浏览器urlencode;服务器urldecode;-- 这种模式叫作B/S模式
五.HTTP协议请求与响应格式
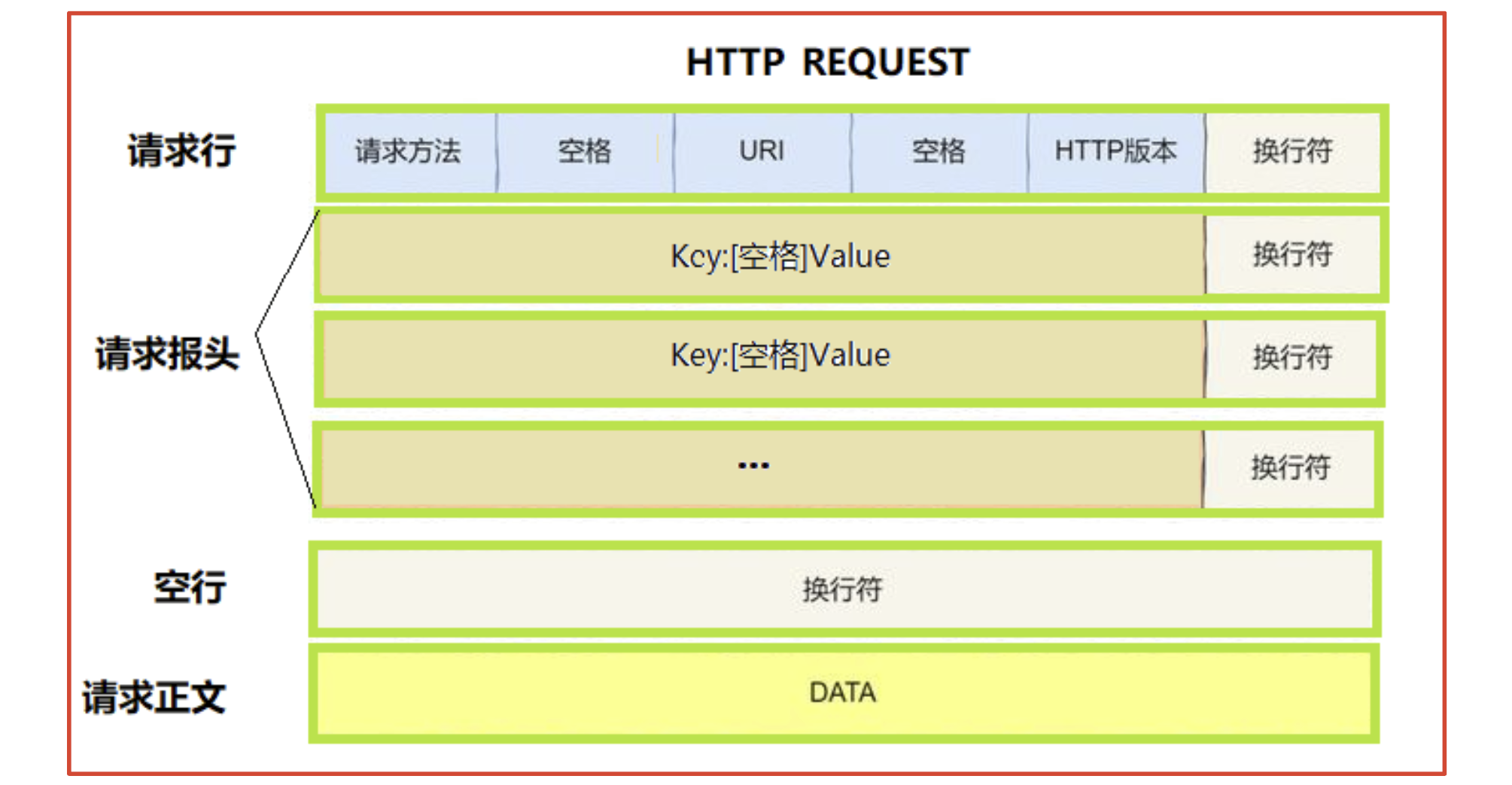
1. HTTP请求
- http协议,序列和反序列化用的是特殊字符(空格或换行符)进行子串拼接,且不依赖任何第三方库
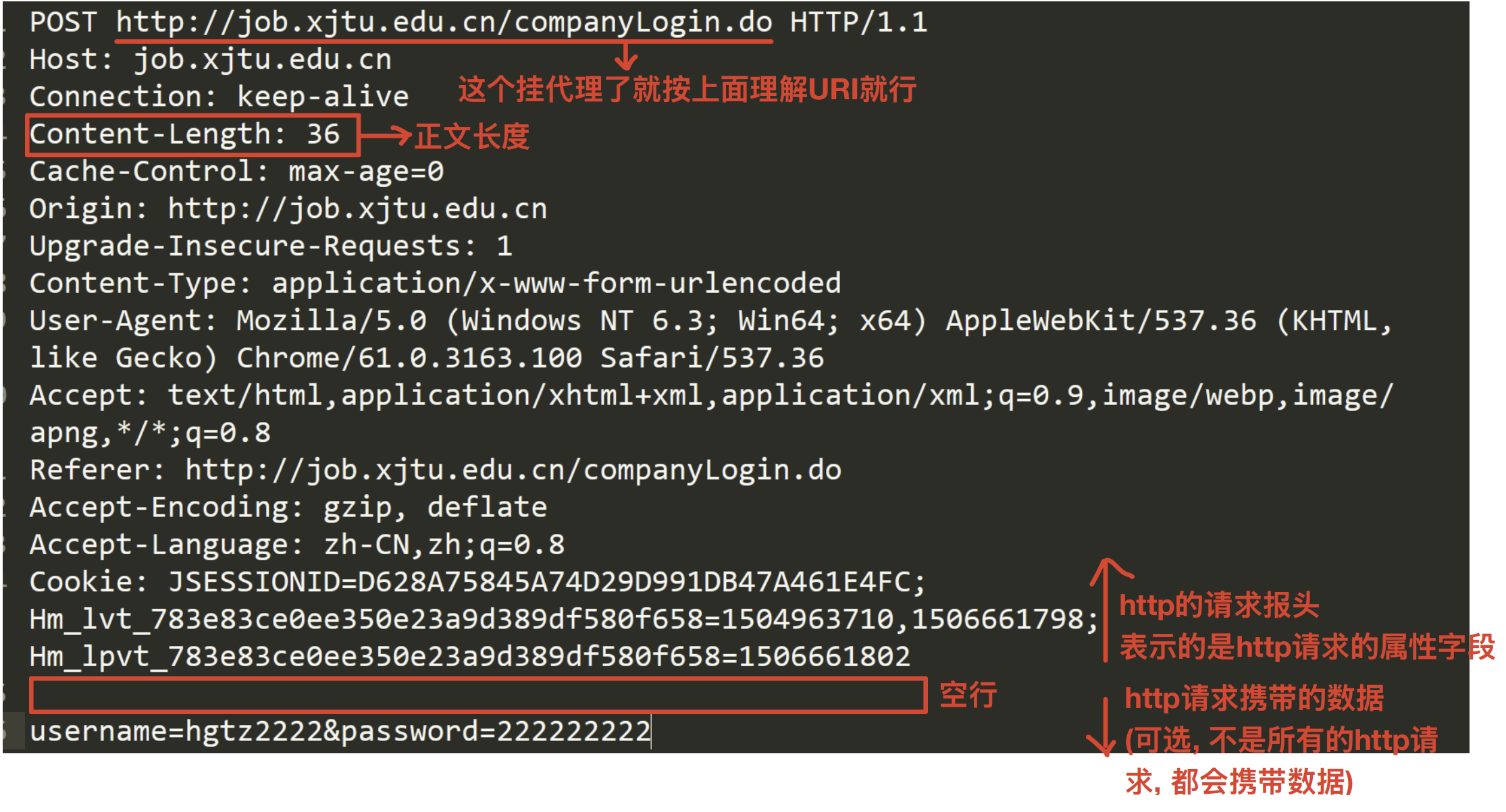
- 首行: [方法] + [url] + [版本]
- Header: 请求的属性, 冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用
\r\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束 - Body: 空行后面的内容都是Body. Body允许为空字符串. 如果Body存在, 则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度;
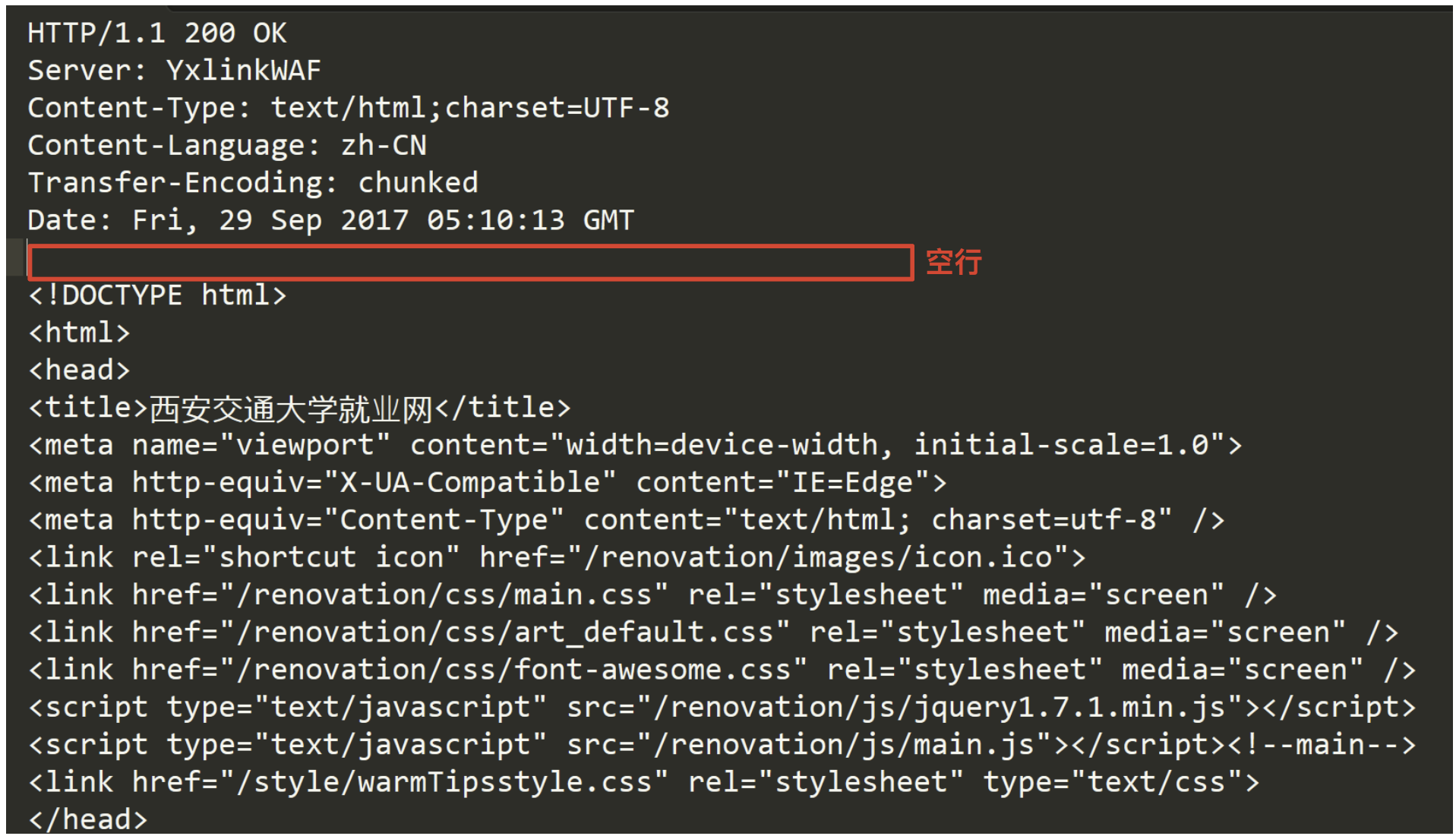
2. HTTP响应
完整请求获取方法:没法直接确定读到原完整报文,但是我有方法读到当前请求的完整报头!
- 读取到完整的请求报头[空行];
- 对报头进行反序列化,提取一个属性:Content-Length:有效载荷的长度;
- 在从剩余的字符串内容中,提取content-length个字符。
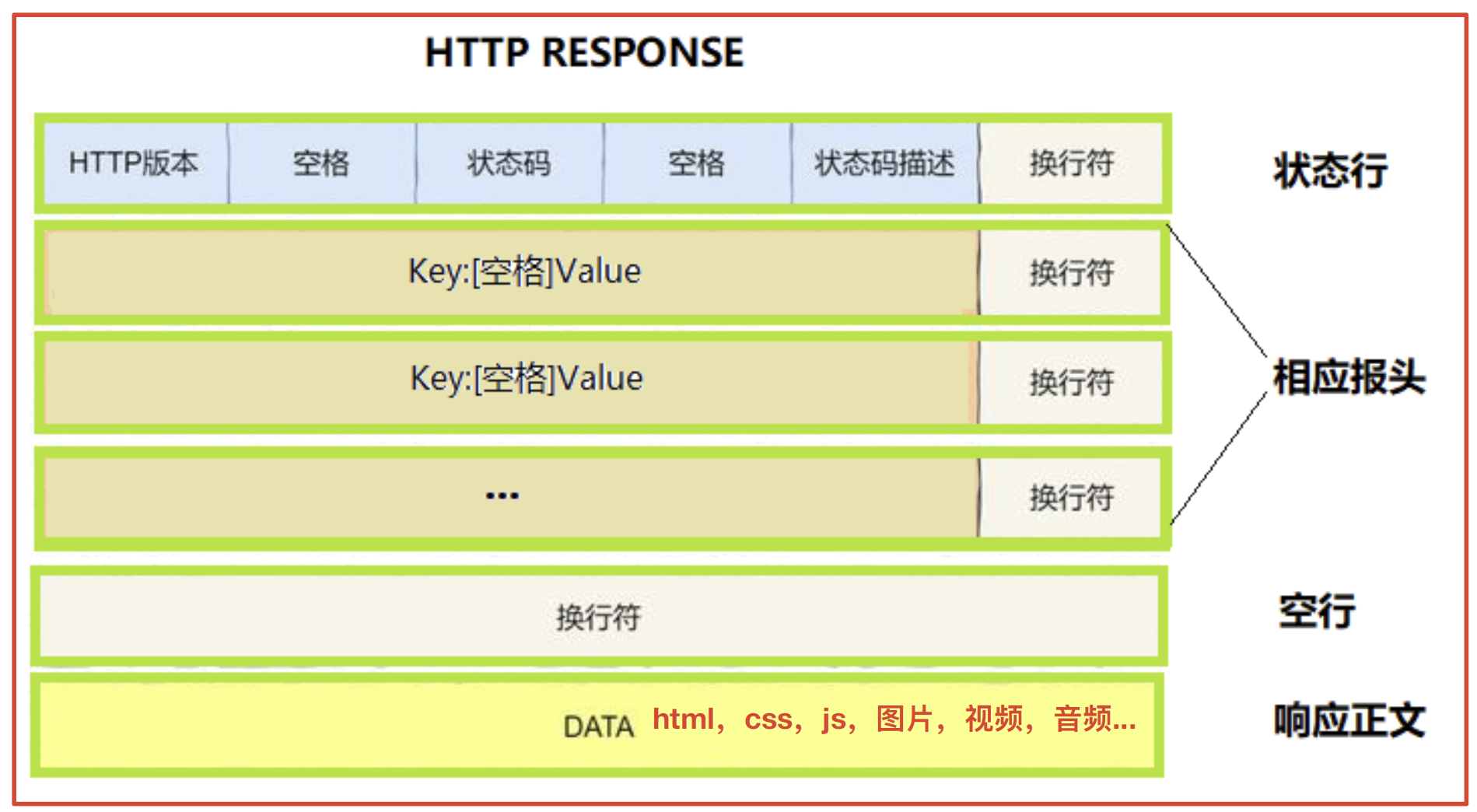
- 首行: [版本号] + [状态码] + [状态码解释]
- Header: 请求的属性, 冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用\r\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束
- Body: 空行后面的内容都是Body. Body允许为空字符串. 如果Body存在, 则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度; 如果服务器返回了一个html页面, 那么html页面内容就是在body中.
基本的应答格式
六.HTTP的方法
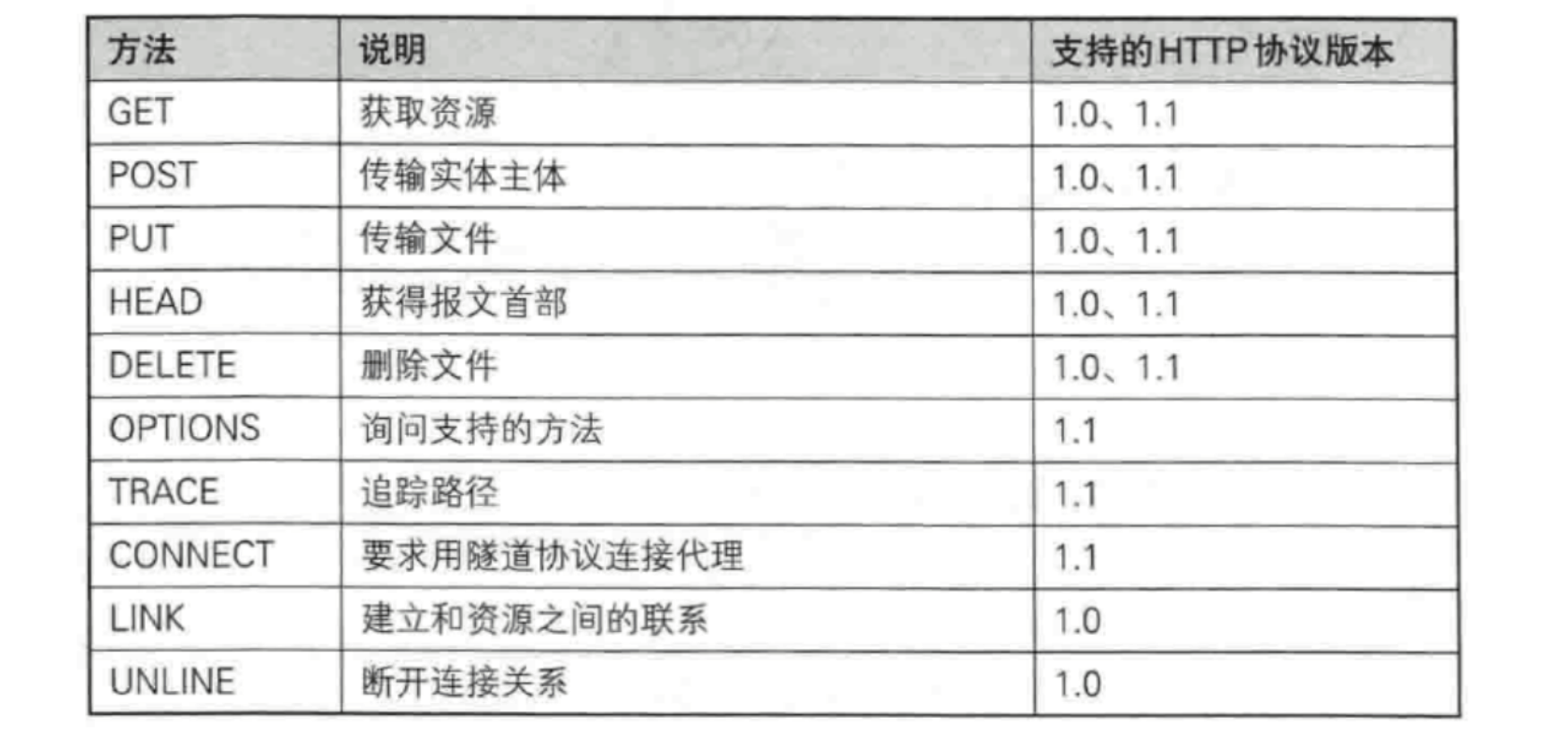
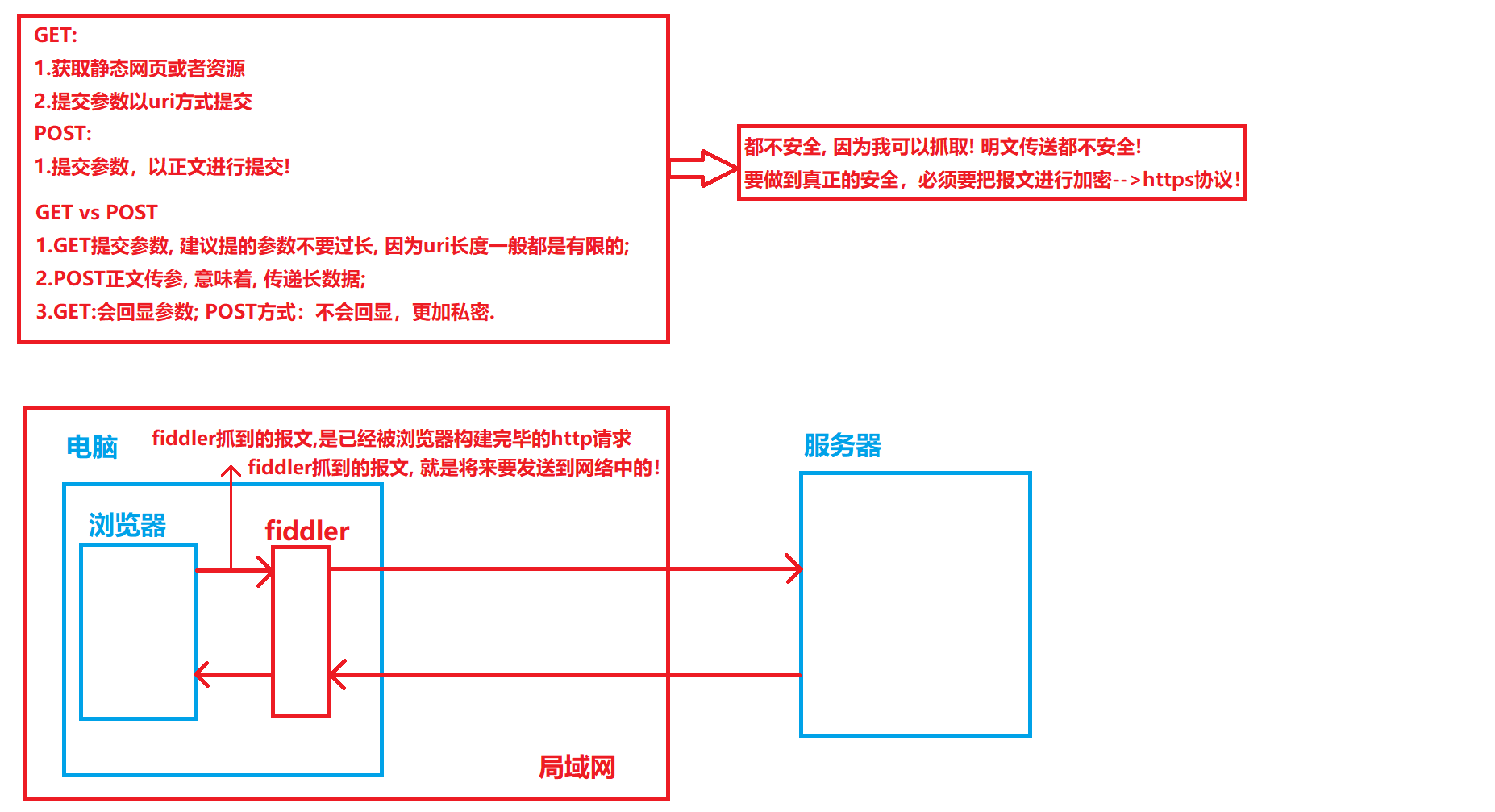
其中最常用的就是GET方法和POST方法.
请求是怎么表示自己要请求什么?资源服务端,资源在哪里?
资源位置用URI表示;资源都放在web(http)根目录下;
如果是GET/服务器要自动拼接首页(/index.html或/index.htm);
网页内容,必须是在服务器特定路径下的文件(图片,视频...,CSS,jS...).
1. HTTP常见方法
(1).GET方法(重点)
(GET: 获取资源)
用途:用于请求URL指定的资源。
示例: GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
特性:指定资源经服务器端解析后返回响应内容。
form表单:https://www.runoob.com/html/html-forms.html
cpp
std::string GetFileContentHelper(const std::string &path)
{
// 一份简单的读取二进制文件的代码
std::ifstream in(path, std::ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open())
return "";
in.seekg(0, in.end);
int filesize = in.tellg();
in.seekg(0, in.beg);
std::string content;
content.resize(filesize);
in.read((char *)content.c_str(), filesize);
// std::vector<char> content(filesize);
// in.read(content.data(), filesize);
in.close();
return content;
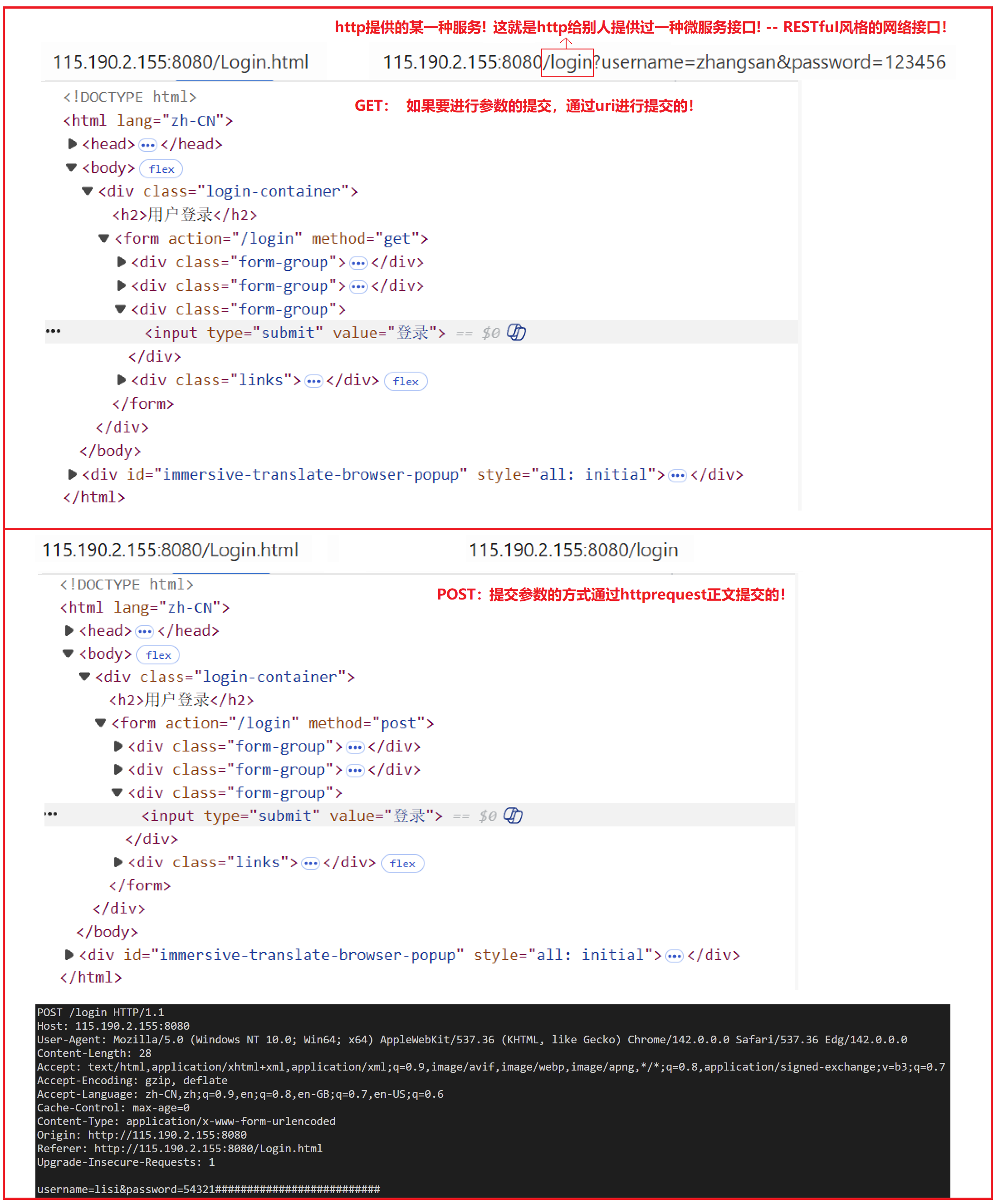
}(2).POST方法(重点)
用途:用于传输实体的主体,通常用于提交表单数据。
示例: POST /submit.cgi HTTP/1.1
特性:可以发送大量的数据给服务器,并且数据包含在请求体中。
form表单:https://www.runoob.com/html/html-forms.html
(3).PUT方法(不常用)
防止用户给服务器乱上传东西,大多数浏览器都把这个方法禁掉了,
用途:用于传输文件,将请求报文主体中的文件保存到请求URL指定的位置。
示例: PUT /example.html HTTP/1.1
特性:不太常用,但在某些情况下,如RESTful API中,用于更新资源。
(4).HEAD方法
用途:与GET方法类似,但不返回报文主体部分,仅返回响应头。
示例: HEAD /index.html HTTP/1.1
特性:用于确认URL的有效性及资源更新的日期时间等。
shell
// curl -i 显示
$ curl -i www.baidu.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Cache-Control: private, no-cache, no-store, proxy-revalidate, no-transform
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 2381
Content-Type: text/html
Date: Sun, 16 Jun 2024 08:38:04 GMT
Etag: "588604dc-94d"
Last-Modified: Mon, 23 Jan 2017 13:27:56 GMT
Pragma: no-cache
Server: bfe/1.0.8.18
Set-Cookie: BDORZ=27315; max-age=86400; domain=.baidu.com; path=/
<!DOCTYPE html>
...
// 使用head方法,只会返回响应头
$ curl --head www.baidu.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Cache-Control: private, no-cache, no-store, proxy-revalidate, no-transform
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 277
Content-Type: text/html
Date: Sun, 16 Jun 2024 08:43:38 GMT
Etag: "575e1f71-115"
Last-Modified: Mon, 13 Jun 2016 02:50:25 GMT
Pragma: no-cache
Server: bfe/1.0.8.18(5).DELETE方法(不常用)
用途:用于删除文件,是PUT的相反方法。
示例: DELETE /example.html HTTP/1.1
特性:按请求URL删除指定的资源。
(6).OPTIONS方法
用途:用于查询针对请求URL指定的资源支持的方法。
示例: OPTIONS * HTTP/1.1
特性:返回允许的方法,如GET、POST等。
不支持的效果
shell
// 搭建一个nginx用来测试
// sudo apt install nginx
// sudo nginx -- 开启
// ps ajx | grep nginx -- 查看
// sudo nginx -s stop -- 停止服务
$ sudo nginx -s stop
$ ps ajx | grep nginx
2944845 2945390 2945389 2944845 pts/1 2945389 S+ 1002 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
$ sudo nginx
$ ps axj | grep nginx
1 2945393 2945393 2945393 ? -1 Ss 0 0:00 nginx: master process nginx
2945393 2945394 2945393 2945393 ? -1 S 33 0:00 nginx: worker process
2945393 2945395 2945393 2945393 ? -1 S 33 0:00 nginx: worker process
2944845 2945397 2945396 2944845 pts/1 2945396 S+ 1002 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
// -X(大x) 指明方法
$ curl -X OPTIONS -i http://127.0.0.1/
HTTP/1.1 405 Not Allowed
Server: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Sun, 16 Jun 2024 08:48:22 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 166
Connection: keep-alive
<html>
<head><title>405 Not Allowed</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>405 Not Allowed</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)</center>
</body>
</html>支持的效果
shell
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Allow: GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 0
Server: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Sun, 16 Jun 2024 09:04:44 GMT
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, OPTIONS
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Authorization
// 注意:这里没有响应体,因为Content-Length为0七.HTTP的状态码
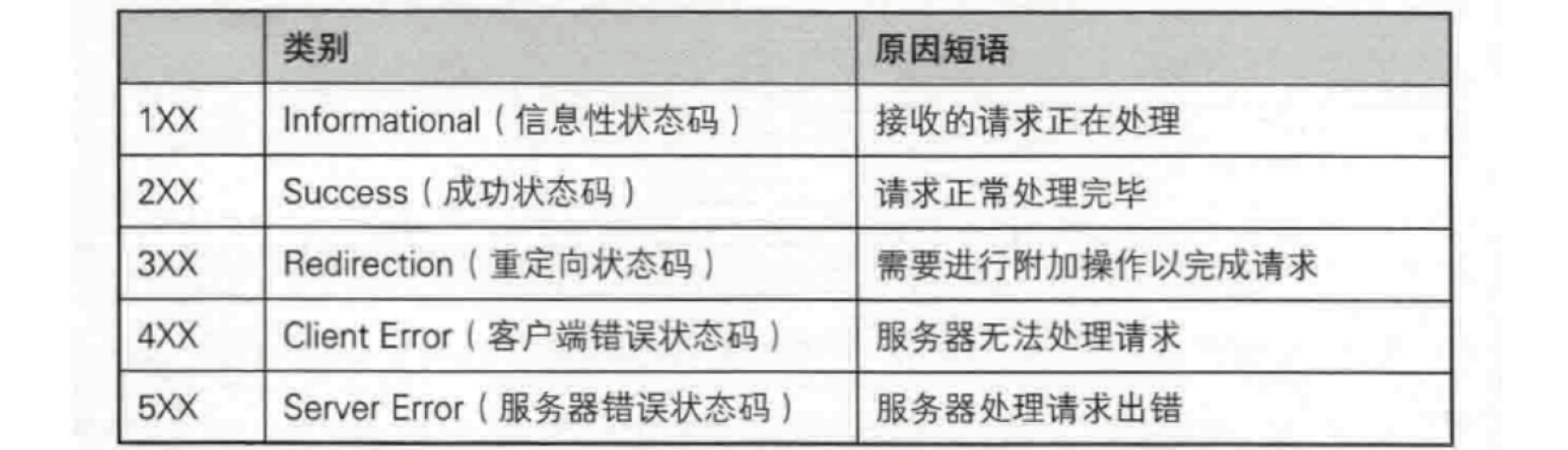
最常见的状态码, 比如 200(OK), 404(Not Found), 403(Forbidden), 302(Redirect, 重定向), 504(Bad Gateway)
| 状态码 | 含义 | 应用样例 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | Continue | 上传大文件时,服务器告诉客户端可以继续上传 |
| 200 | OK | 访问网站首页,服务器返回网页内容 |
| 201 | Created | 发布新文章,服务器返回文章创建成功的信息 |
| 204 | No Content | 删除文章后,服务器返回"无内容"表示操作成功 |
| 301 | Moved Permanently 永久式重定向 | 网站换域名后,自动跳转到新域名;搜索引擎更新网站链接时使用 |
| 302 | Found / See Other 临时重定向 | 用户登录成功后,重定向到用户首页 |
| 304 | Not Modified | 浏览器缓存机制,对未修改的资源返回304状态码 |
| 400 | Bad Request | 填写表单时,格式不正确导致提交失败 |
| 401 | Unauthorized | 访问需要登录的页面时,未登录或认证失败 |
| 403 | Forbidden | 尝试访问你没有权限查看的页面 |
| 404 | Not Found | 访问不存在的网页链接 |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | 服务器崩溃或数据库错误导致页面无法加载 |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | 代理服务器无法从上游服务器获取有效响应 |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | 服务器维护或过载,暂时无法处理请求 |
以下是仅包含重定向相关状态码的表格:
| 状态码 | 含义 | 是否为临时重定向 | 应用样例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 301 | Moved Permanently | 否(永久重定向) | 网站换域名后,自动跳转到新域名; 搜索引擎更新网站链接时使用(最大意义) |
| 302 | Found 或 See Other | 是(临时重定向) | 用户登录成功后,重定向到用户首页 |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | 是(临时重定向) | 临时重定向资源到新的位置(较少使用) |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | 否(永久重定向) | 永久重定向资源到新的位置(较少使用) |
重定向的htp的请求,至少是三部分:状态行,报头,空行;正文常常没有.

关于重定向的验证,以301为代表
**HTTP状态码301(永久重定向)和302(临时重定向)都依赖Location选项。**以下是关于两者依赖Location选项的详细说明:
- HTTP状态码301(永久重定向)
- 网站更换域名,或者更换网址
- 当服务器返回HTTP 301状态码时,表示请求的资源已经被永久移动到新的位置。
- 在这种情况下,服务器会在响应中添加一个Location头部,用于指定资源的新位置。这个Location头部包含了新的URL地址,浏览器会自动重定向到该地址。
- 例如,在HTTP响应中,可能会看到类似于以下的头部信息:
shell
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently\r\n
Location: https://www.new-url.com\r\n- HTTP状态码302(临时重定向)
-
临时重定向--不改变任何信息; 多用于登录跳转, 页面跳转之类的工作。
-
当服务器返回HTTP 302状态码时,表示请求的资源临时被移动到新的位置。
-
同样地,服务器也会在响应中添加一个Location头部来指定资源的新位置。浏览器会暂时使用新的URL进行后续的请求,但不会缓存这个重定向。
-
例如,在HTTP响应中,可能会看到类似于以下的头部信息:
shell
HTTP/1.1 302 Found\r\n
Location: https://www.new-url.com\r\n总结:无论是HTTP 301还是HTTP 302重定向,都需要依赖Location选项来指定资源的新位置。这个Location选项是一个标准的HTTP响应头部,用于告诉浏览器应该将请求重定向到哪个新的URL地址。
八.HTTP常见Header
1. 常见Header
-
Content-Type: 数据类型(text/html等); 查表:https://tool.oschina.net/commons
一张网页内,可能会有多种资源,网页自己+图片,获得网页,识别网页内还有其他资源,浏览器会发起二次请求。应答要告诉对方,我的有效载荷是什么。
-
Content-Length: Body的长度
-
Host: 客户端告知服务器, 所请求的资源是在哪个主机的哪个端口上;
-
User-Agent: 声明用户的操作系统和浏览器版本信息;
-
Referer: 当前页面是从哪个页面跳转过来的;
-
Location: 搭配3xx状态码使用, 告诉客户端接下来要去哪里访问;
-
Cookie: 用于在客户端存储少量信息. 通常用于实现会话(session)的功能;
-
Accept:表示客户端能接受的响应内容类型(MIME类型查HTTPContent-type对照表);
-
Accept-Encoding:表示客户端支持的内容压缩格式(编码方式).
2. 关于connection报头
HTTP中的Connection 字段是HTTP报文头的一部分,它主要用于控制和管理客户端与服务器之间的连接状态
核心作用
- 管理持久连接:
Connection字段还用于管理持久连接(也称为长连接)。持久连接允许客户端和服务器在请求/响应完成后不立即关闭TCP连接,以便在同一个连接上发送多个请求和接收多个响应。
持久连接(长连接)
- HTTP/1.1:在HTTP/1.1协议中,默认使用持久连接。当客户端和服务器都不明确指定关闭连接时,连接将保持打开状态,以便后续的请求和响应可以复用同一个连接。
- HTTP/1.0:在HTTP/1.0协议中,默认连接是非持久的。如果希望在HTTP/1.0上实现持久连接,需要在请求头中显式设置
Connection: keep-alive。
语法格式
-
Connection: keep-alive:表示希望保持连接以复用TCP连接。 -
Connection: close:表示请求/响应完成后,应该关闭TCP连接。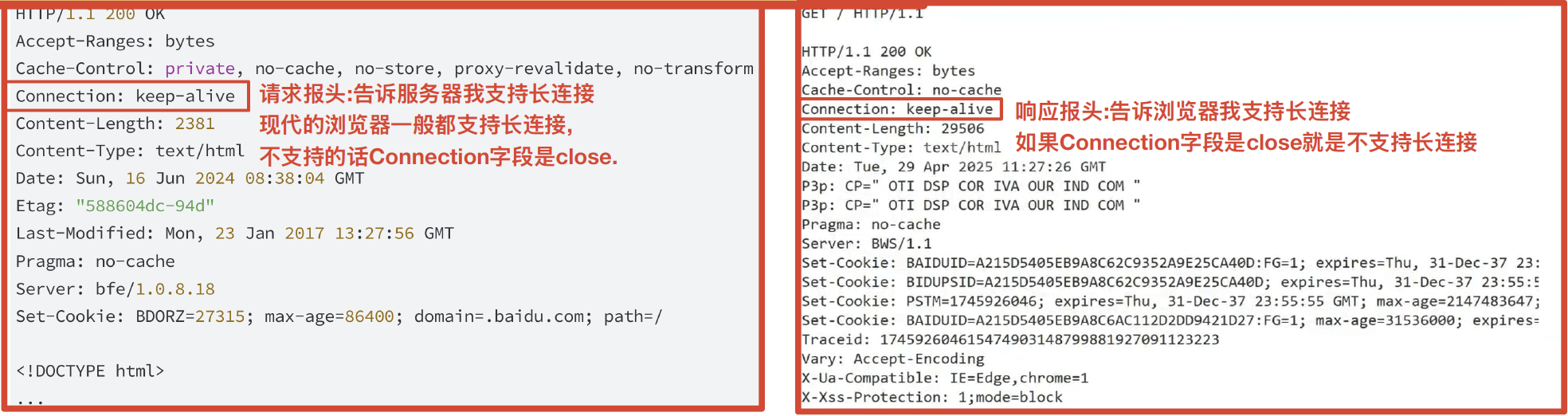
下面附上一张关于HTTP常见header的表格
| 字段名 | 含义 | 样例 |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | 客户端可接受的响应内容类型 | Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xm l;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8 |
| Accept-Encoding | 客户端支持的数据压缩格式 | Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br |
| Accept-Language | 客户端可接受的语言类型 | Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8 |
| Host | 请求的主机名和端口号 | Host: www.example.com:8080 |
| User-Agent | 客户端的软件环境信息 | User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 |
| Cookie | 客户端发送给服务器的 HTTP cookie信息 | Cookie: session_id=abcdefg12345; user_id=123 |
| Referer | 请求的来源URL | Referer: http://www.example.com/previous_page.html |
| Content-Type | 实体主体的媒体类型 | Content-Type: application/x-www-formurlencoded<br(对于表单提交) 或 Content-Type: application/json (对于JSON数据) |
| Content-Length | 实体主体的字节大小 | Content-Length: 150 |
| Authorization | 认证信息,如用户名和密码 | Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== (Base64编码后的用户 名:密码) |
| Cache-Control | 缓存控制指令 | 请求时: Cache-Control: no-cache 或 Cache- Control: max-age=3600 ;响应时: Cache- Control: public, max-age=3600 |
| Connection | 请求完后是关闭还是保持连接 | Connection: keep-alive 或 Connection: close |
| Date | 请求或响应的日期和时间 | Date: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 07:28:00 GMT |
| Location | 重定向的目标URL(与 3xx状态码配合使用) | Location: http://www.example.com/new_location.html (与 302状态码配合使用) |
| Server | 服务器类型 | Server: Apache/2.4.41 (Unix) |
| Last-Modified | 资源的最后修改时间 | Last-Modified: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 07:20:00 GMT |
| ETag | 资源的唯一标识符,用于缓存 | ETag: "3f80f-1b6-5f4e2512a4100" |
| Expires | 响应过期的日期和时间 | Expires: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 08:28:00 GMT |
九.最简单的HTTP服务器
实现一个最简单的HTTP服务器, 只在网页上输出 "hello world"; 只要我们按照HTTP协议的要求构造数据, 就很容易能做到;
client&&server,是如何保证自己读到的报文是完整的?
step1:读取字节流,分析读到的字节流,确认是否存在空行;
step2:提取Content-Length:获得正文长度,然后在读取或者截取指定长度的内容;
cpp
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Usage() {
printf("usage: ./server [ip] [port]\n");
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
Usage();
return 1;
}
int fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("socket");
return 1;
}
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]);
addr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2]));
int ret = bind(fd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr));
if (ret < 0) {
perror("bind");
return 1;
}
ret = listen(fd, 10);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("listen");
return 1;
}
for (;;) {
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t len;
int client_fd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &len);
if (client_fd < 0) {
perror("accept");
continue;
}
char input_buf[1024 * 10] = {0}; // 用一个足够大的缓冲区直接把数据读完.
ssize_t read_size = read(client_fd, input_buf, sizeof(input_buf) - 1);
if (read_size < 0) {
return 1;
}
printf("[Request] %s", input_buf);
char buf[1024] = {0};
const char* hello = "<h1>hello world</h1>";
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\nContent-Length:%lu\n\n%s", strlen(hello),
hello);
write(client_fd, buf, strlen(buf));
}
return 0;
}编译, 启动服务. 在浏览器中输入 http://[ip]:[port], 就能看到显示的结果 "Hello World"
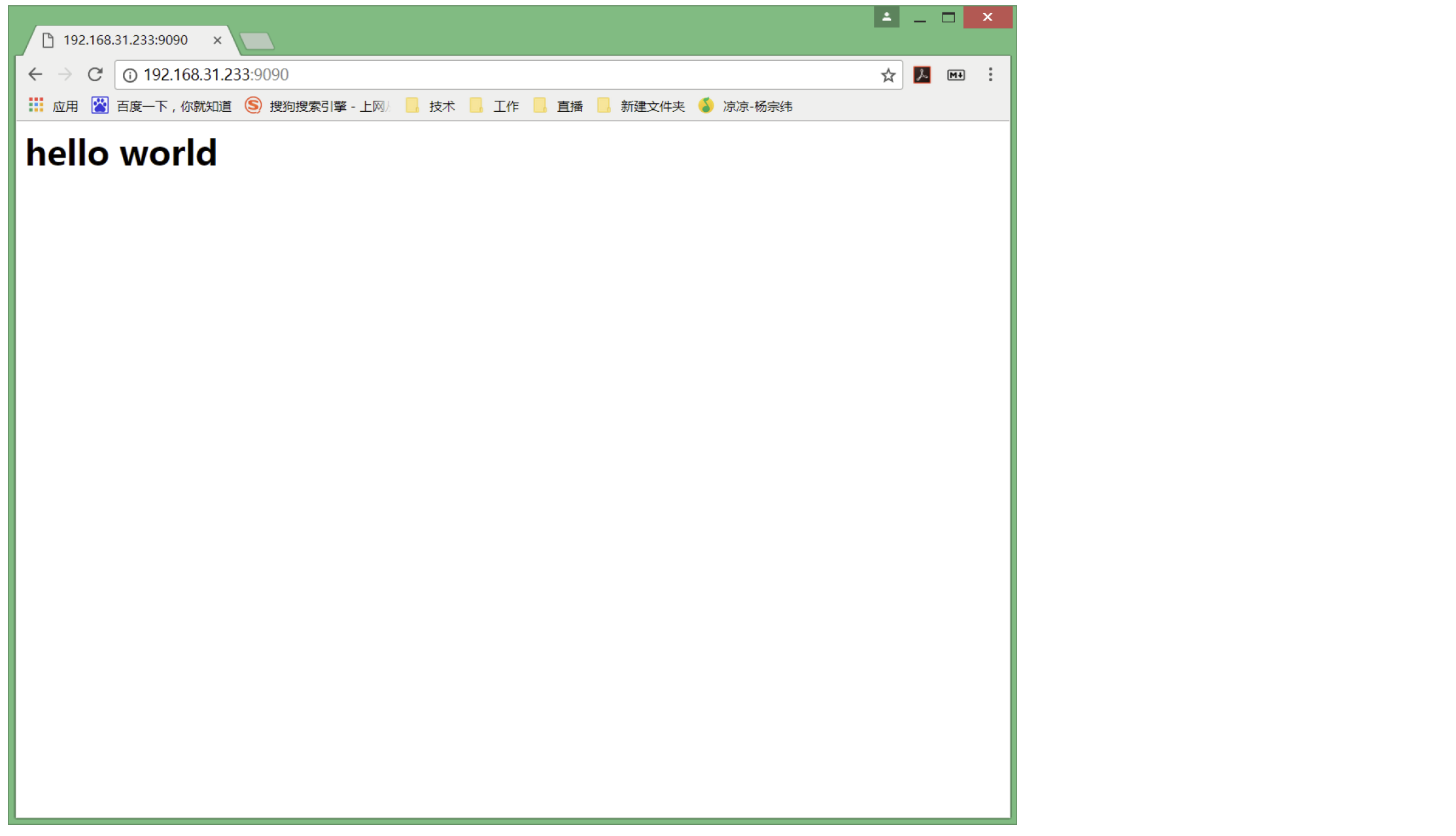
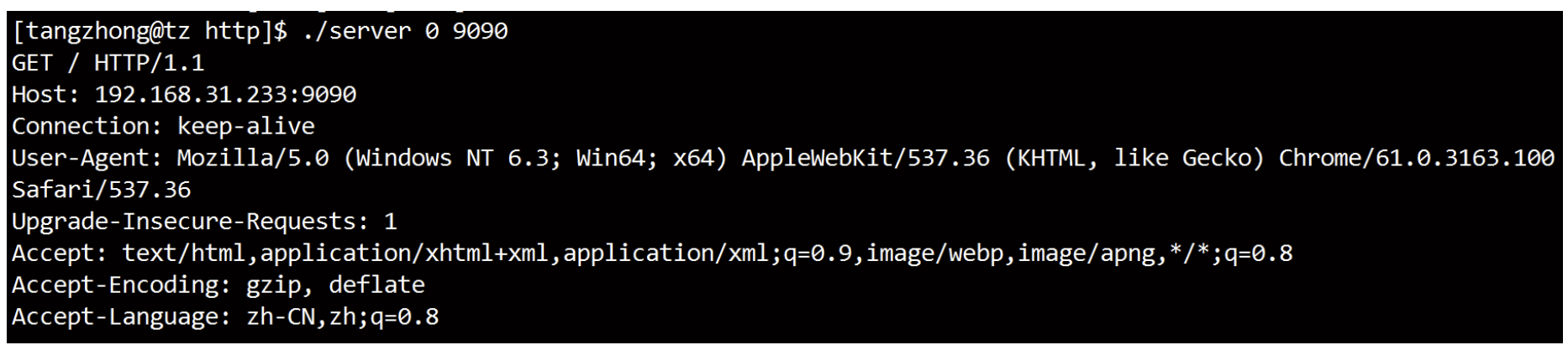
备注:
此处我们使用 9090 端口号启动了HTTP服务器. 虽然HTTP服务器一般使用80端口,
但这只是一个通用的习惯. 并不是说HTTP服务器就不能使用其他的端口号.
使用chrome测试我们的服务器时, 可以看到服务器打出的请求中还有一个
GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1这样的请求.
favicon.ico的作用: 网站标签页上的小图标.
十.完整http服务器
HTTP服务器(HttpServer)
实现一个基于TCP的HTTP服务器,支持静态资源返回和动态交互功能,支持长连接(keep-alive)和短连接
实现了一个完整的HTTP协议解析器,能够处理HTTP请求并返回响应,支持GET和POST方法,能够返回HTML、图片、视频等多种资源类型。
(1). Common.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <cstring>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
enum ExitCode
{
OK = 0,
USAGE_ERR,
SOCKET_ERR,
BIND_ERR,
LISTEN_ERR,
CONNECT_ERR,
FORK_ERROR,
OPEN_ERROR
};
class NoCopy
{
public:
NoCopy() {}
~NoCopy() {}
NoCopy(const NoCopy &) = delete;
const NoCopy &operator=(const NoCopy &) = delete;
};
#define CONV(addr) ((struct sockaddr*)&addr)(2). Inet_Addr.hpp
和网络版本计算器唯一的区别:添加 SetAddr 方法
cpp
#pragma once
#include "Common.hpp"
// 网络地址和主机地址之间进行转化的类
class InetAddr
{
public:
InetAddr(){}
// 网络转主机
InetAddr(struct sockaddr_in& addr)
{
SetAddr(addr);
}
// 主机转网络
InetAddr(const std::string& ip ,uint16_t port)
:_ip(ip)
,_port(port)
{
memset(&_addr, 0, sizeof(_addr));
_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
//法一(线程不安全)
//_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str());
//法二(线程安全)
inet_pton(AF_INET, _ip.c_str(), &_addr.sin_addr);
_addr.sin_port = htons(_port);
}
InetAddr(uint16_t port)
:_ip("0")
,_port(port)
{
memset(&_addr, 0, sizeof(_addr));
_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
_addr.sin_port = htons(_port);
}
void SetAddr(struct sockaddr_in& addr)
{
_addr = addr; //浅拷贝不会有影响
_port = ntohs(_addr.sin_port); // 从网络中拿到的!网络序列
// 4字节网络风格的IP -> 点分十进制的字符串风格的IP
//法一(线程不安全)
// _ip = inet_ntoa(_addr.sin_addr);
//法二(线程安全)
char ipbuffer[64];
inet_ntop(AF_INET,&_addr.sin_addr,ipbuffer,sizeof(ipbuffer));
_ip = ipbuffer;
}
uint16_t Port() const { return _port; }
std::string Ip() const { return _ip; }
// NetAddr需要引用,是因为Route.hpp的MessageRoute函数中
// sendto(sockfd, send_message.c_str(), send_message.size(), 0, (const struct sockaddr *)&user.NetAddr(), sizeof(user.NetAddr()));
// 的第五个参数需要可以修改,不能传右值(临时变量)
const struct sockaddr_in& NetAddr() { return _addr; }
const struct sockaddr* NetAddrPtr() { return CONV(_addr); }
socklen_t NetAddrLen()
{
return sizeof(_addr);
}
bool operator==(const InetAddr& addr)
{
return _ip == addr._ip && _port == addr._port;
}
std::string StringAddr()
{
return _ip + ":" + std::to_string(_port);
}
~InetAddr()
{}
private:
struct sockaddr_in _addr;
std::string _ip;
uint16_t _port;
};(3). Log.hpp
日志模块,支持控制台和文件两种输出策略(与远程控制和字典服务器项目(TcpEchoServer)和网络计算器(NetCal)中的Log.hpp完全相同)
(4). Mutex.hpp
互斥锁封装模块(与远程控制和字典服务器项目(TcpEchoServer)和网络计算器(NetCal)中的Mutex.hpp完全相同)
(5). Socket.hpp(模板方法模式)
和网络版本计算器唯一的区别:接收缓冲区大小扩大了
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Common.hpp"
#include "Inet_Addr.hpp"
namespace SocketModule
{
using namespace LogModule;
const static int gbacklog = 16;
// 模板方法模式(固定套路代码常用)
// 基类socket,大部分方法,都是纯虚方法
class Socket
{
public:
virtual ~Socket() {}
virtual void SocketOrDie() = 0;
virtual void BindOrDie(uint16_t port) = 0;
virtual void ListenOrDie(int blacklog) = 0;
virtual std::shared_ptr<Socket> Accept(InetAddr* client) = 0;
virtual void Close() = 0;
virtual int Recv(std::string *out) = 0;
virtual int Send(const std::string& message) = 0;
virtual int Connect(const std::string &server_ip, uint16_t server_port) = 0;
public:
void BuildTcpSocketMethod(uint16_t port, int blacklog = gbacklog)
{
SocketOrDie();
BindOrDie(port);
ListenOrDie(blacklog);
}
void BuildTcpClientSocketMethod()
{
SocketOrDie();
}
};
const static int defaultfd = -1;
class TcpSocket : public Socket
{
public:
TcpSocket():_sockfd(defaultfd)
{}
TcpSocket(int fd):_sockfd(fd)
{}
~TcpSocket() {}
void SocketOrDie() override
{
_sockfd = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); // ::表示默认使用更外部(全局)的socket函数
if(_sockfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "socket error";
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "socket success";
}
void BindOrDie(uint16_t port) override
{
InetAddr localaddr(port);
int n = ::bind(_sockfd, localaddr.NetAddrPtr(), localaddr.NetAddrLen());
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "bind error";
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "bind success";
}
void ListenOrDie(int blacklog) override
{
int n = ::listen(_sockfd, blacklog);
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "listen error";
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "listen success";
}
std::shared_ptr<Socket> Accept(InetAddr* client) override
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int fd = ::accept(_sockfd, CONV(peer), &len);
if(fd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "accept warning ...";
return nullptr; //TODO
}
client->SetAddr(peer);
return std::make_shared<TcpSocket>(fd);
}
int Recv(std::string *out) override //返回值等同read的返回值
{
// 流式读取,并不关心读到的是什么
char buffer[4096*4];
ssize_t n = ::recv(_sockfd,&buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1, 0);
if(n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
*out += buffer;
}
return n;
}
int Send(const std::string& message) override
{
return ::send(_sockfd, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0);
}
void Close() override
{
if(_sockfd > 0)
::close(_sockfd);
}
int Connect(const std::string &server_ip, uint16_t server_port) override
{
InetAddr server(server_ip, server_port);
return ::connect(_sockfd, server.NetAddrPtr(), server.NetAddrLen());
}
private:
int _sockfd; // _sockfd,listensockfd,sockfd
};
}(6). TcpServer.hpp
cpp
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <functional>
using namespace SocketModule;
using namespace LogModule;
using ioservice_t = std::function<void(std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock, InetAddr &client)>;
class TcpServer
{
public:
TcpServer(uint16_t port)
:_port(port)
,_listensockptr(std::make_unique<TcpSocket>())
,_isrunning(false)
{
_listensockptr->BuildTcpSocketMethod(_port);
}
void Start(ioservice_t callback)
{
_isrunning = true;
while(_isrunning)
{
InetAddr client;
auto sock = _listensockptr->Accept(&client); // 获得1.和client通信的sockfd 2.client网络地址
if(sock == nullptr)
{
continue;
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "accept success ..." << client.StringAddr();
// 获得了:1.与客户端通信socket;2.客户端地址和端口号
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "fork error ...";
exit(FORK_ERROR);
}
else if(id == 0)
{
//子进程 ->关闭listen socket
_listensockptr->Close();
if(fork() > 0)
exit(0);
//孙子进程在执行任务,已经是孤儿进程了
callback(sock,client);
sock->Close();
exit(OK);
}
else
{
//父进程 ->关闭clinet socket(即:auto sock)
sock->Close();
pid_t rid = ::waitpid(-1, nullptr, 0);
(void)rid;
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
~TcpServer() {}
private:
uint16_t _port;
std::unique_ptr<Socket> _listensockptr;
bool _isrunning;
};(7). Util.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
// 工具类
class Util
{
public:
Util() {}
~Util() {}
static bool ReadFileContent(const std::string &filename, std::string* out/*实际std::vector<char>常用*/)
{
// version 1:默认以文本方式读取文件的.图片是二进制的不能用这种方式读.
// std::ifstream in(filename, std::ios::out | std::ios::app);
// if (!in.is_open())
// {
// return false;
// }
// std::string line;
// while (std::getline(in,line))
// {
// *out += line;
// }
// in.close();
// return true;
// version 2:以二进制方式进行读取
int filesize = FileSize(filename);
if(filesize > 0)
{
std::ifstream in(filename, std::ios::binary);
if(!in.is_open())
return false;
out->resize(filesize);
in.read(&(*out)[0], filesize); //或in.read((char *)out->c_str(), filesize);
in.close();
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
static bool ReadOneLine(std::string &bigstr, std::string *out, const std::string &sep/*\r\n*/)
{
auto pos = bigstr.find(sep);
if(pos == std::string::npos)
return false;
*out = bigstr.substr(0, pos);
bigstr.erase(0, pos+sep.size());
return true;
}
static int FileSize(const std::string& filename)
{
std::ifstream in(filename,std::ios::binary);
if(!in.is_open())
return -1;
in.seekg(0, in.end);
int filesize = in.tellg();
in.seekg(0, in.beg);
in.close();
return filesize;
}
private:
};(8). Http.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include "TcpServer.hpp"
#include "Util.hpp"
#include <sstream>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <cctype>
const std::string gspace = " ";
const std::string glinespace = "\r\n";
const std::string glinesep = ": ";
const std::string webroot = "./wwwroot";
const std::string homepage = "index.html";
const std::string page_404 = "/404.html";
class HttpRequest
{
public:
HttpRequest()
:_is_interact(false)
,_has_header(false)
,_has_body(false)
{}
// 服务端浏览器写好了
std::string Serialize()
{
return std::string();
}
// 获取请求行
void ParseReqLine(std::string& reqline)
{
// GET / HTTP/1.1
std::stringstream ss(reqline);
ss >> _method >> _uri >> _version;
}
// 获取请求报头与正文
bool ParseReqHeadersAndBody(std::string& reqline)
{
std::string line;
int content_len = 0;
// 读取并解析 Header,直到空行
while (true)
{
bool ret = Util::ReadOneLine(reqline, &line, glinespace);
if (!ret)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "请求报头为空";
return true;
}
if (line.empty()) break; // 空行:头结束(因为ReadOneLine已去掉\r\n)
auto sep = line.find(glinesep);
if (sep != std::string::npos)
{
std::string key = line.substr(0, sep);
std::string value = line.substr(sep + glinesep.size());
_headers[key] = value;
if(!_has_header) _has_header = true;
if (key == "Content-Length" || key == "content-length")
{
content_len = std::stoi(value);
}
}
}
// 按 Content-Length 读取正文到 _text
_text.clear();
if (content_len > 0)
{
if ((int)reqline.size() >= content_len)
{
_has_body = true;
_text = reqline.substr(0, content_len);
reqline.erase(0, content_len);
}
else
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "报文异常";
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 实现(我们今天认为,reqstr是一个完整的http,没有写decode)
bool Deserialize(std::string& reqstr)
{
// 1.提取请求中的请求行
std::string reqline;
bool res = Util::ReadOneLine(reqstr, &reqline,glinespace);
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << reqline;
// 2.对请求行进行反序列化
// 获得请求行
ParseReqLine(reqline);
if(_uri=="/")
_uri = webroot + _uri + homepage;
else
_uri = webroot + _uri;
// 获得请求报头与正文
ParseReqHeadersAndBody(reqstr);
/*日志打印请求信息*/
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "_method: " << _method;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "_uri: " << _uri;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "_version: " << _version;
if(_has_header)
{
for(const auto &header : _headers)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "_header: " << header.first << glinesep << header.second;
}
}
if(_has_body)
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "_text: " << _text;
/*日志打印请求信息*/
// (1).POST特殊处理:
if (_method == "POST" || _method == "post")
{
_args = _text; //参数由请求正文发送
_is_interact = true;
return true;
}
// (2).GET特殊处理:
// 注:可能有这种_uri: ./wwwroot/login?username=zhangsan&password=123456
if (_method == "GET" || _method == "get")
{
const std::string temp = "?";
auto pos = _uri.find(temp);
if(pos == std::string::npos)
{
return true;
}
// _uri解析:
// _args: username=zhangsan&password=123456
// _uri: ./wwwroot/login
_args = _uri.substr(pos + temp.size());
_uri = _uri.substr(0, pos);
_is_interact = true;
return true;
}
// 其他请求方法(PUT、DELETE、HEAD等)
return true;
}
std::string Uri() { return _uri; }
bool isInteract() { return _is_interact; }
std::string Args() { return _args; }
// 检查是否支持长连接
bool KeepAlive()
{
auto iter = _headers.find("Connection");
if(iter != _headers.end())
{
// Connection字段:conn_val
std::string conn_val = iter->second;
// 转换为小写进行比较
for(char& c : conn_val)
{
c = std::tolower(c);
}
if(conn_val == "keep-alive")
return true;
}
// 检查 HTTP 版本,HTTP/1.1 默认支持长连接
if(_version == "HTTP/1.1" || _version == "http/1.1")
{
// HTTP/1.1 如果没有明确指定 Connection: close,则默认支持 keep-alive
auto iter2 = _headers.find("Connection");
if(iter2 != _headers.end())
{
std::string conn_val = iter2->second;
for(char& c : conn_val)
{
c = std::tolower(c);
}
if(conn_val == "close")
return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
~HttpRequest()
{}
private:
std::string _method;
std::string _uri;
std::string _version;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers; //请求报头
std::string _blankline; //空行
std::string _text; //正文
bool _has_header;
bool _has_body;
std::string _args; //uri后面跟的参数
bool _is_interact; //是否需要交互
};
class HttpResponse
{
public:
HttpResponse()
:_blankline(glinespace)
,_version("HTTP/1.0")
,_keep_alive(false)
{}
// 实现:成熟的http,应答做序列化,不需要依赖任何第三方库!
std::string Serialize()
{
std::string status_line = _version + gspace + std::to_string(_code) + gspace + _desc + glinespace;
std::string resp_header;
for(auto& header : _headers)
{
std::string line = header.first + glinesep + header.second + glinespace;
resp_header += line;
}
return status_line + resp_header + _blankline + _text;
}
// 服务端浏览器写好了
bool Deserialize()
{
return true;
}
void SetTargetFile(const std::string& target)
{
_targetfile = target;
}
void SetCode(int code)
{
_code = code;
switch(_code)
{
case 200:
_desc = "OK";
break;
case 404:
_desc = "Not Found";
break;
case 301:
_desc = "Moved Permanently";
break;
case 302:
_desc = "See Other";
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void SetHeader(const std::string& key, const std::string& value)
{
auto iter = _headers.find(key);
if(iter != _headers.end())
return;
_headers.emplace(key, value);
}
void SetText(const std::string & t)
{
_text = t;
}
// 设置是否保持连接
void SetKeepAlive(bool keep_alive)
{
_keep_alive = keep_alive;
if(_keep_alive)
{
SetHeader("Connection", "keep-alive");
// HTTP/1.1 版本以支持长连接
_version = "HTTP/1.1";
}
else
{
SetHeader("Connection", "close");
}
}
std::string Uri2Suffix(const std::string& targetfile)
{
// targetfile: ./wwwroot/a/b/c.html
auto pos = targetfile.rfind(".");
if(pos == std::string::npos)
{
return "text/html"; //应该报错的,简写默认是网页了
}
std::string suffix = targetfile.substr(pos);
if(suffix == ".html" || suffix == ".htm")
return "text/html";
else if (suffix == ".jpg")
return "image/jpeg";
else if (suffix == ".png")
return "image/png";
else if (suffix == ".mp4")
return "video/mpeg4";
else
return "text/html";//应该填完Content-Type整张表的,简写默认是网页了
}
bool MakeResponse()
{
if(_targetfile == "./wwwroot/favicon.ico")
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "用户请求: " << _targetfile << "忽略它";
return false;
}
// 临时重定向
if(_targetfile == "./wwwroot/redir_test")
{
SetCode(302);
SetHeader("Location", "https://www.qq.com/");
return true;
}
int filesize = 0;
bool res = Util::ReadFileContent(_targetfile, &_text); //ReadFileContent给_targetfile加好了./wwwroot
if(!res)
{
// 法一:
_text = "";
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "client want get : " << _targetfile << " but not found";
SetCode(404);
_targetfile = webroot + page_404;
Util::ReadFileContent(_targetfile, &_text);
std::string suffix = Uri2Suffix(_targetfile);
SetHeader("Content-Type", suffix);
// 法二:
// SetCode(302);
// SetHeader("Location", "http://115.190.2.155:8080/404.html"); //注意:这里没有域名,端口写死的,要注意!!!
// return true;
}
else
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "读取文件: " << _targetfile;
SetCode(200);
std::string suffix = Uri2Suffix(_targetfile);
SetHeader("Content-Type", suffix);
}
filesize = Util::FileSize(_targetfile);
SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(filesize));
return true;
}
~HttpResponse(){}
// private:
public:
std::string _version;
int _code; //404
std::string _desc; //"Not Found"
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers; //请求报头
std::string _blankline; //空行
std::string _text; //正文
// 其他属性
std::string _targetfile; //要获取资源的地址
bool _keep_alive; //是否保持连接
};
// Http要做到:
// 1.返回静态资源
// 2.提供动态交互的能力
using http_func_t = std::function<void(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp)>;
class Http
{
public:
Http(uint16_t port)
:tsvrp(std::make_unique<TcpServer>(port))
{
}
// 从缓冲区中提取一个完整的 HTTP 请求
// 返回值: true 表示提取到完整请求, false 表示数据不完整
bool ExtractOneRequest(std::string& buffer, std::string& request)
{
// 先检查是否至少有一个完整的请求行
size_t first_line_end = buffer.find(glinespace);
if(first_line_end == std::string::npos)
{
// 还没有收到完整的请求行
return false;
}
// 查找请求头结束标志 \r\n\r\n
std::string header_end = glinespace + glinespace; // "\r\n\r\n"
size_t header_end_pos = buffer.find(header_end);
if(header_end_pos == std::string::npos)
{
// 还没有收到完整的请求头
return false;
}
// 提取请求头部分(用于解析 Content-Length)
std::string header_part = buffer.substr(0, header_end_pos);
// 检查是否有 Content-Length
int content_len = 0;
size_t content_pos = header_part.find("Content-Length:");
if(content_pos == std::string::npos)
{
content_pos = header_part.find("content-length:");
}
if(content_pos != std::string::npos && content_pos < header_end_pos)
{
// 找到 Content-Length 头,解析其值
size_t len_start = header_part.find(":", content_pos) + 1;
// 跳过空格
while(len_start < header_part.size() && (header_part[len_start] == ' ' || header_part[len_start] == '\t'))
len_start++;
size_t len_end = header_part.find(glinespace, len_start);
if(len_end == std::string::npos)
len_end = header_part.size();
if(len_start < len_end)
{
std::string len_str = header_part.substr(len_start, len_end - len_start);
try {
content_len = std::stoi(len_str);
} catch(...) {
content_len = 0;
}
}
}
// 计算完整请求的结束位置
// header_end_pos 是 \r\n 的位置,header_end.size() 是 \r\n 的长度
// 所以请求头结束后的位置是 header_end_pos + header_end.size()
size_t header_end_offset = header_end_pos + header_end.size();
size_t request_end = header_end_offset + content_len;
if(buffer.size() < request_end)
{
// 数据不完整,还需要继续接收
return false;
}
// 提取完整的请求
request = buffer.substr(0, request_end);
buffer.erase(0, request_end);
return true;
}
void HandlerHttpRequest(std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock, InetAddr &client)
{
// 接收缓冲区,用于处理粘包
std::string recv_buffer;
bool should_close = false;
// 循环处理多个请求(支持长连接)
while(!should_close)
{
// 尝试从缓冲区提取完整请求
std::string httpreqstr;
bool has_complete_request = ExtractOneRequest(recv_buffer, httpreqstr);
// 如果没有完整请求,尝试接收更多数据
if(!has_complete_request)
{
std::string new_data;
int n = sock->Recv(&new_data);
if(n <= 0)
{
// 连接已关闭或出错
should_close = true;
break;
}
recv_buffer += new_data;
// 再次尝试提取完整请求
has_complete_request = ExtractOneRequest(recv_buffer, httpreqstr);
}
if(!has_complete_request)
{
// 如果还是没有完整请求,继续接收
continue;
}
std::cout << std::endl << "##########################" << std::endl;
std::cout << httpreqstr;
std::cout << "##########################" << std::endl << std::endl;
// 对字符串请求反序列化
HttpRequest req;
if(!req.Deserialize(httpreqstr))
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "请求解析失败,跳过该请求,继续处理下一个";
// 跳过这个有问题的请求,继续处理缓冲区中的下一个请求
continue;
}
// 构建http应答
HttpResponse resp;
// 根据请求决定是否保持连接
bool keep_alive = req.KeepAlive();
resp.SetKeepAlive(keep_alive);
if(req.isInteract())
{
// 1.交互
// _args: username=zhangsan&password=123456
// _uri: ./wwwroot/login
if(_route.find(req.Uri()) == _route.end())
{
// (1).无对应方法
resp.SetTargetFile(webroot + page_404);
if (resp.MakeResponse())
{
std::string response_str = resp.Serialize();
sock->Send(response_str);
}
}
else
{
// (2).有对应方法
_route[req.Uri()](req, resp);
std::string response_str = resp.Serialize();
sock->Send(response_str);
}
}
else
{
// 2.静态
resp.SetTargetFile(req.Uri());
if (resp.MakeResponse())
{
// 所以我们就不在担心,用户访问一个服务器上不存在的资源了(html,css,js,图片,视频这种资源--静态资源!)
std::string response_str = resp.Serialize();
sock->Send(response_str);
}
}
// 如果不保持连接,处理完这个请求后关闭
if(!keep_alive)
{
should_close = true;
}
}
}
void Start()
{
tsvrp->Start([this](std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock, InetAddr &client){
this->HandlerHttpRequest(sock, client);
});
}
void RegisterService(const std::string name, http_func_t h)
{
std::string key = webroot + name;
auto iter = _route.find(key);
if(iter == _route.end())
{
_route.emplace(key, h);
}
}
~Http()
{
}
private:
std::unique_ptr<TcpServer> tsvrp;
std::unordered_map<std::string, http_func_t> _route;
};(9). Main.cc
cpp
#include "Common.hpp"
#include "Http.hpp"
void Login(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << req.Args() << ",我们成功进入到了处理数据的逻辑";
std::string text = "hello: " + req.Args();
resp.SetCode(200);
resp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain"); //文字类型
resp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(text.size()));
resp.SetText(text);
}
void Register(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << req.Args() << ",我们成功进入到了处理数据的逻辑";
std::string text = "hello: " + req.Args();
resp.SetCode(200);
resp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain"); //文字类型
resp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(text.size()));
resp.SetText(text);
}
void VipCheck(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << req.Args() << ",我们成功进入到了处理数据的逻辑";
std::string text = "hello: " + req.Args();
resp.SetCode(200);
resp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain"); //文字类型
resp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(text.size()));
resp.SetText(text);
}
void Search(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << req.Args() << ",我们成功进入到了处理数据的逻辑";
std::string text = "hello: " + req.Args();
resp.SetCode(200);
resp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain"); //文字类型
resp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(text.size()));
resp.SetText(text);
}
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << proc << " port" << std::endl;
}
// http port
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
// std::cout << "服务器已经启动,已经是一个守护进程了" << std::endl;
// 守护进程化
// daemon(1, 0);
// Enable_File_Log_Strategy();
uint16_t port = std::stoi(argv[1]);
std::unique_ptr<Http> httpsvr = std::make_unique<Http>(port);
httpsvr->RegisterService("/login",Login);
httpsvr->RegisterService("/register", Register);
httpsvr->RegisterService("/vip_check", VipCheck);
httpsvr->RegisterService("/s", Search);
httpsvr->Start();
return 0;
}(10). Makefile
makefile
myhttp:Main.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf myhttp #/var/log/my.log (11). 项目结构
shell
Http/
├── Common.hpp
├── html
│ └── 20251027A041HW00
├── Http.hpp
├── Inet_Addr.hpp
├── Log.hpp
├── Main.cc
├── Makefile
├── Mutex.hpp
├── myhttp
├── Socket.hpp
├── TcpServer.hpp
├── Util.hpp
└── wwwroot
├── 404.html
├── About.html
├── board1.html
├── Contact.html
├── favicon.ico
├── image
├── index.html
├── landscape.html
├── Login.html
├── Register.html
├── robots.txt
├── test.html
└── video(12). 结果
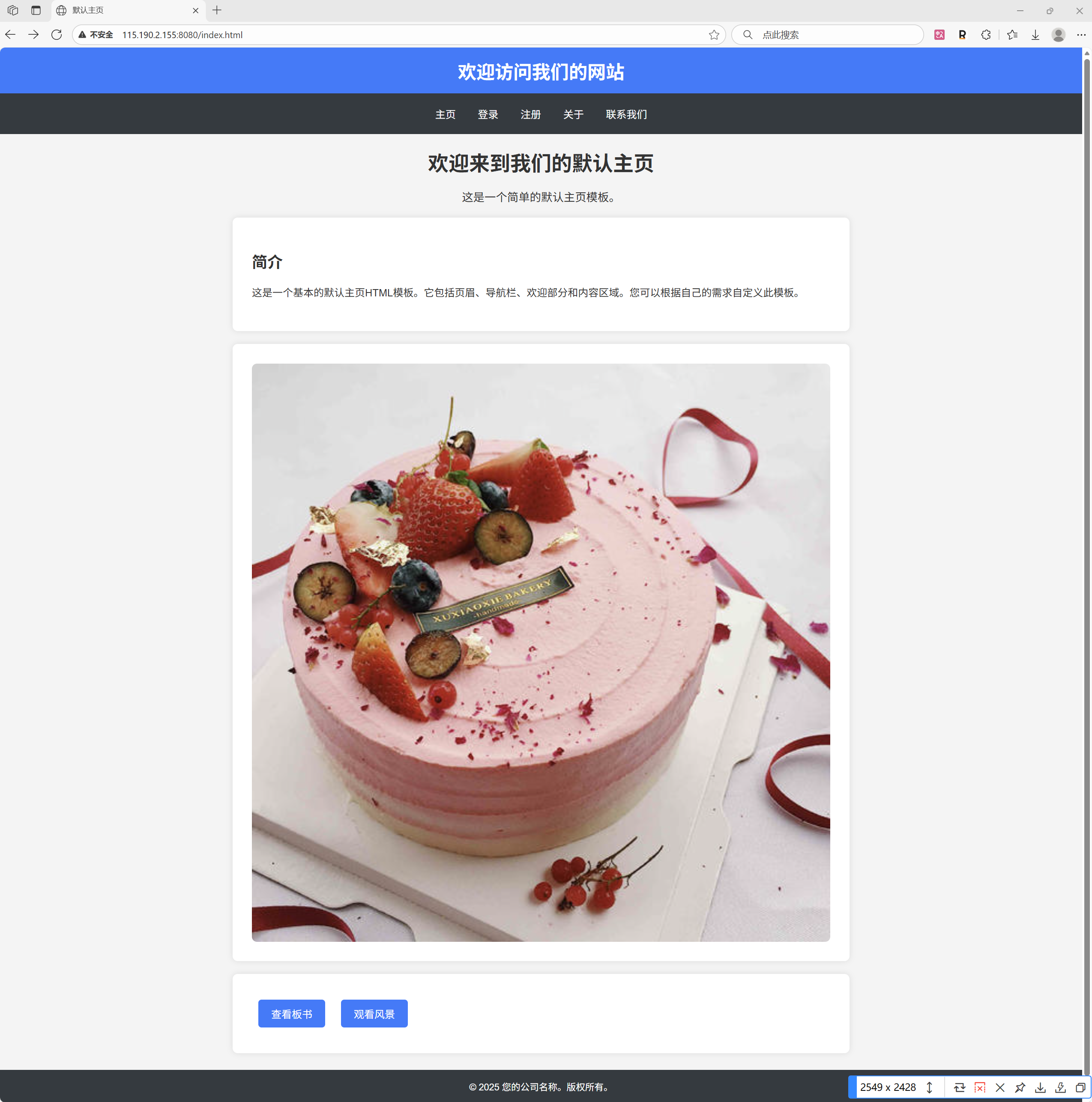
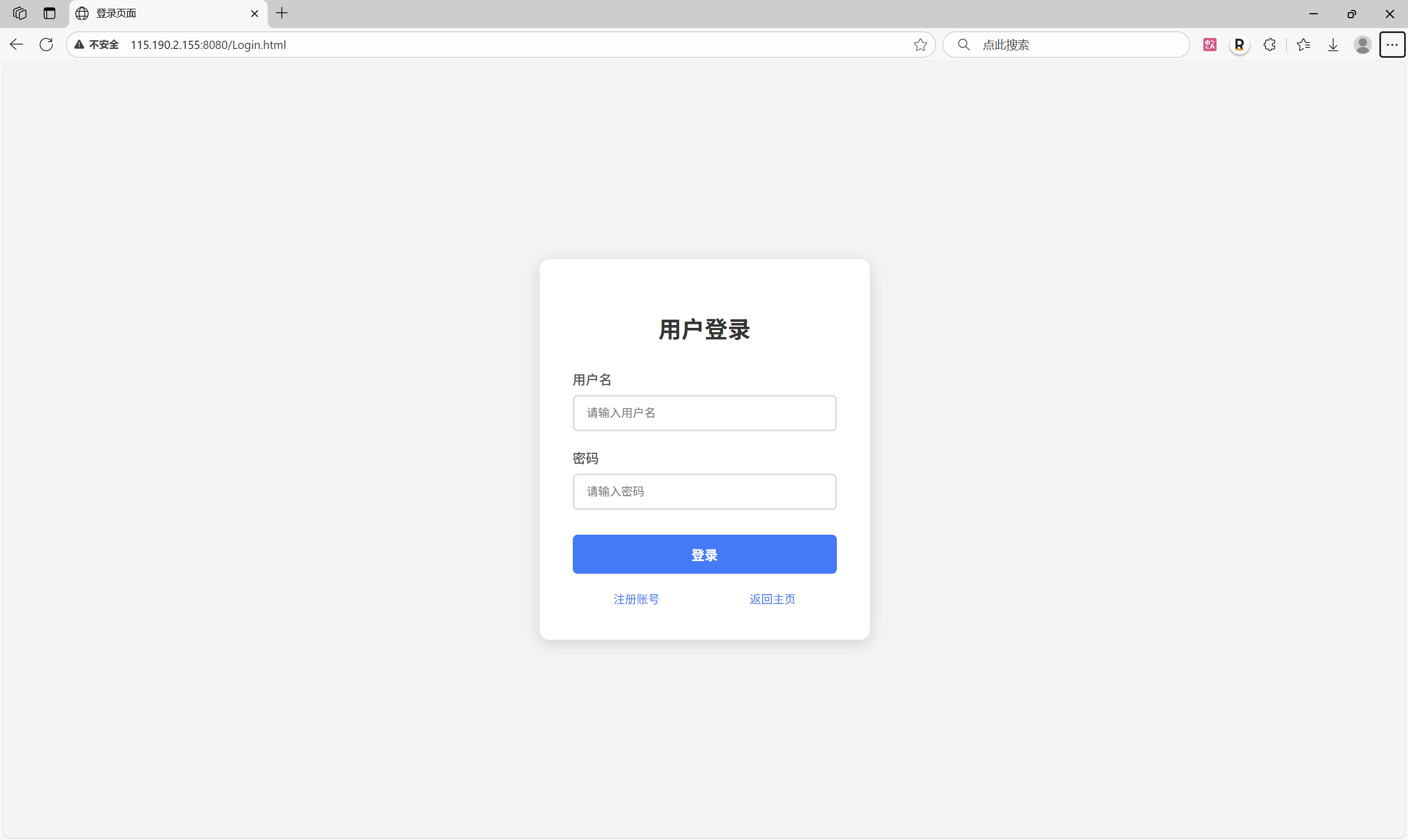
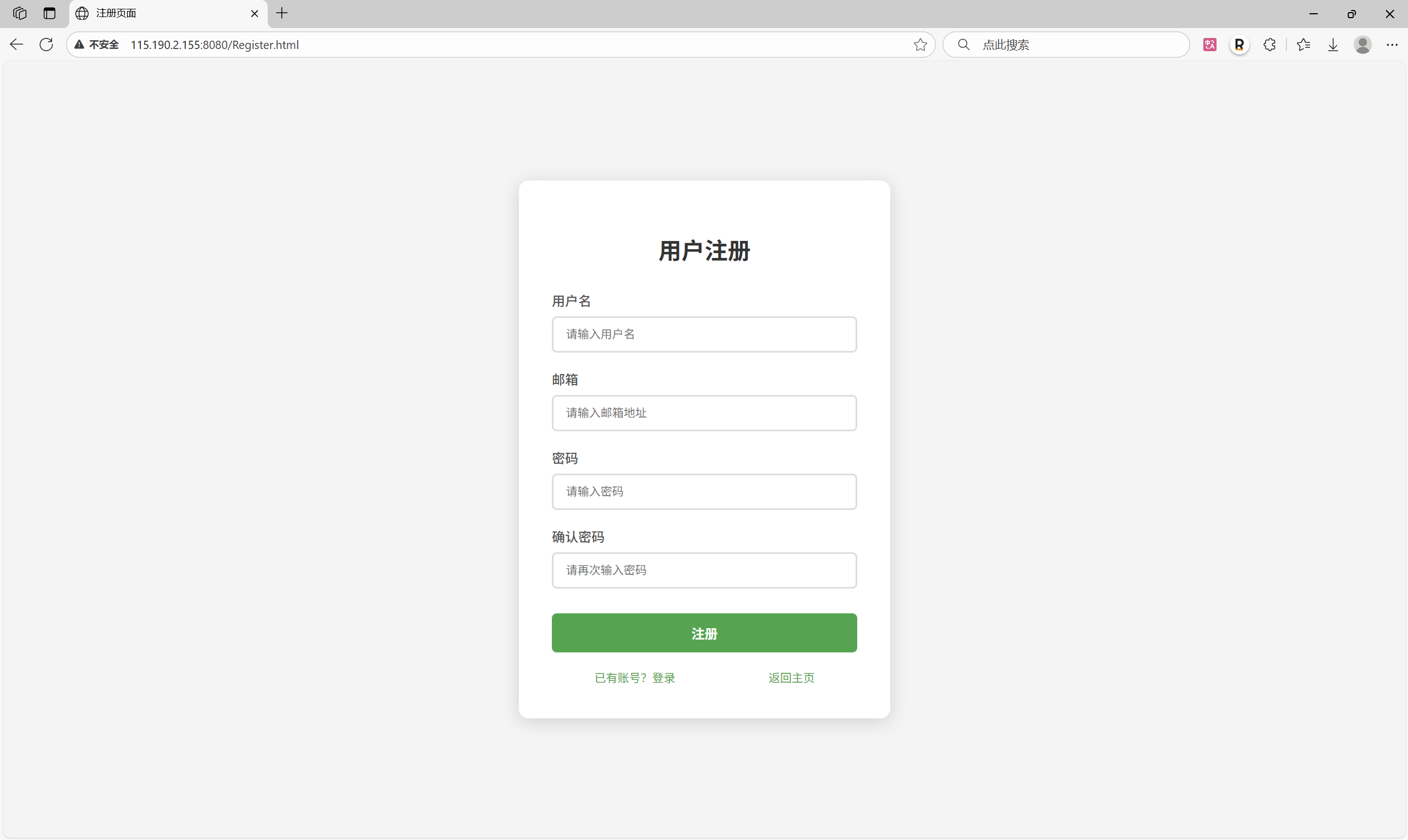
十一.附录:
1. HTTP历史及版本核心技术与时代背景
HTTP(Hypertext Transfer Protocol,超文本传输协议)作为互联网中浏览器和服务器间通信的基石,经历了从简单到复杂、从单一到多样的发展过程。以下将按照时间顺序,介绍HTTP的主要版本、核心技术及其对应的时代背景。
2. HTTP/0.9
(1).核心技术:
- 仅支持GET请求方法。
- 仅支持纯文本传输,主要是HTML格式。
- 无请求和响应头信息。
(2).时代背景:
- 1991年,HTTP/0.9版本作为HTTP协议的最初版本,用于传输基本的超文本HTML内容。
- 当时的互联网还处于起步阶段,网页内容相对简单,主要以文本为主。
3. HTTP/1.0
(1).核心技术:
- 引入POST和HEAD请求方法。
- 请求和响应头信息,支持多种数据格式(MIME)。
- 支持缓存(cache)。
- 状态码(status code)、多字符集支持等。
(2).时代背景:
- 1996年,随着互联网的快速发展,网页内容逐渐丰富,HTTP/1.0版本应运而生。
- 为了满足日益增长的网络应用需求,HTTP/1.0增加了更多的功能和灵活性。
- 然而,HTTP/1.0的工作方式是每次TCP连接只能发送一个请求,性能上存在一定局限。
4. HTTP/1.1
(1).核心技术:
- 引入持久连接(persistent connection),支持管道化(pipelining)。
- 允许在单个TCP连接上进行多个请求和响应,提高了性能。
- 引入分块传输编码(chunked transfer encoding)。
- 支持Host头,允许在一个IP地址上部署多个Web站点。
(2).时代背景:
- 1999年,随着网页加载的外部资源越来越多,HTTP/1.0的性能问题愈发突出。
- HTTP/1.1通过引入持久连接和管道化等技术,有效提高了数据传输效率。
- 同时,互联网应用开始呈现出多元化、复杂化的趋势,HTTP/1.1的出现满足了这些需求。
5. HTTP/2.0
(1).核心技术:
- 多路复用(multiplexing),一个TCP连接允许多个HTTP请求。
- 二进制帧格式(binary framing),优化数据传输。
- 头部压缩(header compression),减少传输开销。
- 服务器推送(server push),提前发送资源到客户端。
(2).时代背景:
- 2015年,随着移动互联网的兴起和云计算技术的发展,网络应用对性能的要求越来越高。
- HTTP/2.0通过多路复用、二进制帧格式等技术,显著提高了数据传输效率和网络性能。
- 同时,HTTP/2.0还支持加密传输(HTTPS),提高了数据传输的安全性。
6. HTTP/3.0
(1).核心技术:
- 使用QUIC协议替代TCP协议,基于UDP构建的多路复用传输协议。
- 减少了TCP三次握手及TLS握手时间,提高了连接建立速度。
- 解决了TCP中的线头阻塞问题,提高了数据传输效率。
(2).时代背景:
- 2022年,随着5G、物联网等技术的快速发展,网络应用对实时性、可靠性的要求越来越高。
- HTTP/3.0通过使用QUIC协议,提高了连接建立速度和数据传输效率,满足了这些需求。
- 同时,HTTP/3.0还支持加密传输(HTTPS),保证了数据传输的安全性。
7.爬虫
爬虫,本质就是用http客户端,来模拟浏览器行为,获取指定链接下的网页!
比如我们使用:wget+网页,就可以获取该网页的所有内容。