9.3 线程池
在 Java 中 , 线程池是一种管理线程的机制 , 它通过预先创建一定数量的线程 , 避免了频繁创建和销毁线程带来的性能开销 , 提高了系统的相应速度和资源利用率
Java 中线程池的核心实现位于 java.util.concurrent 包下 , 主要涉及 Executor , ExecutorServuce , ThreadPoolExecutor 等类和接口
① 标准库中的线程池
java
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class demo31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
pool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
});
}
}- 使用 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10) : 创建一个包含 10 个线程的固定大小的线程池
- pool.submit(new Runnable(){... ...}) : 向线程池提交一个任务 , 任务是打印 hello
- 问题 : 线程池在提交任务后会保持运行状态 , 等待新任务 , 因此程序会一直处于运行状态 , 不会自动结束
②ThreadPoolExecutor 的构造方法(参数较多)
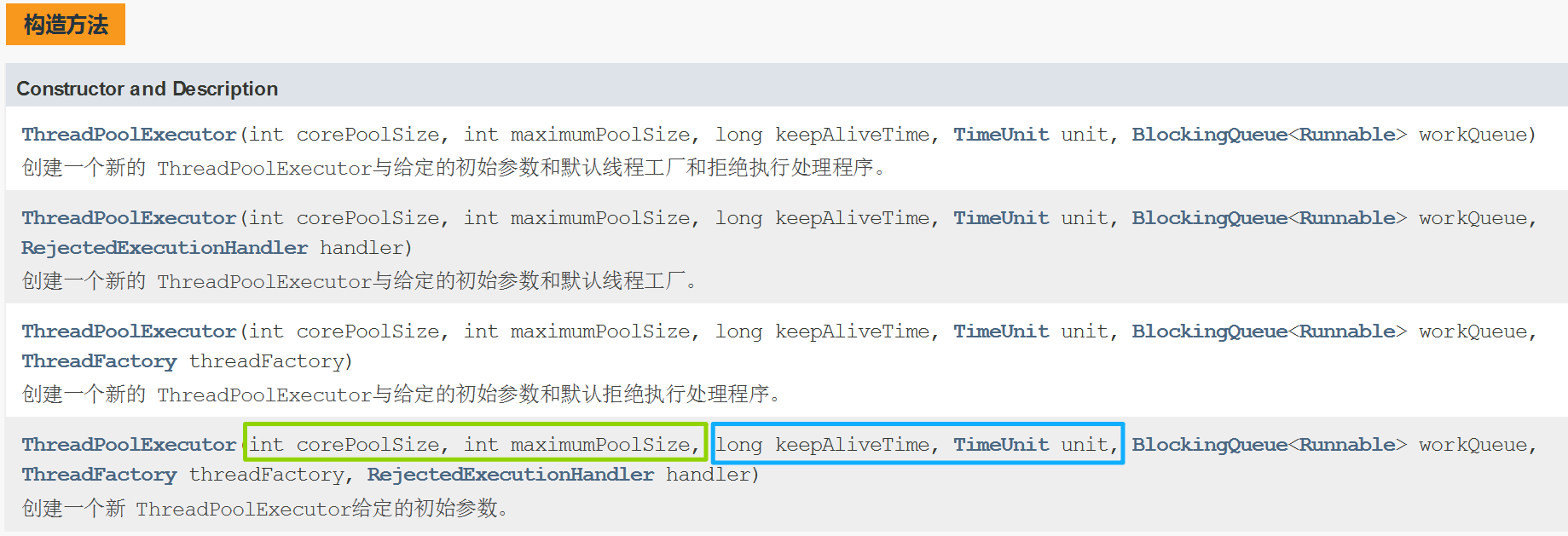
- int corePoolSize :核心线程数,即线程池长期维持的最小线程数量 ; 线程池一单创建,这些线程也要随之创建,直到整个线程池销毁,这些线程才会销毁
- int maximumPoolSize :最大线程数,即任务繁忙时可扩容到的最大线程数量 ; 核心线程数+非核心线程数,不繁忙就销毁,繁忙就再创建
- long keepAliveTime : 非核心线程允许空闲的最大时间,即任务减少后超出 corePoolSize 的线程会再改时间后被销毁
- TimeUnit unit : keepAliveTime 的时间单位(枚举类型)
- BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue : 传递任务的阻塞队列 , 即当核心线程都在工作时,新任务会暂时存到该队列 ; 调用 submit 就是在生产任务
- ThreadFactory threadFactory : 创建线程的工厂(工厂模式) ,参与具体的创建线程工作,通过不同线程工厂创建出的线程相当于对一些属性进行了不同的初始化设置(用于自定义线程的创建逻辑,如命名,优先级等)
- RejectedExecutionHandler handler : 拒绝策略 , 如果任务超出负荷了如何处理新的任务
AbortPolicy() : 超出负荷直接爬出异常(可能无法正常工作)
CallerRunsPolicy(): 调用者负责处理多出来的任务(让调用 submit 的线程自行执行任务)
DiscardOldestPolicy() : 丢弃队列中最老的任务
DiscardPolicy() : 丢弃新来的任务(当前 submit 的这个任务)
③Executors 创建线程池的几种方式
Executors 提供了快速创建线程池的静态方法 , 但不推荐在生产环境中使用 , 因为其默认参数可能导致资源耗尽(如无界队列可能导致 OOM)
Executors 本质上是对 ThreadPoolExecutor 类的封装
- Executors.newFixedThreadPool(n) : 创建固定线程数的线程池
- Executors.newCachedThreadPool() : 创建线程数目动态增长的线程池
- Executors.newSingleThreadPool() : 创建只包含单个线程的线程池
- Executors.newScheduledThreadPool() : 设定延迟时间后执行 , 或定期执行命令 , 是进阶版的 Timer
使用 Executors 的部分示例 :
java
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class demo32 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
//ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0;i<1000;i++){
int id = i;
threadPool.submit(()->{
System.out.println("hello "+id + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}④ 实现一个线程池
- 核心操作 submit , 将任务加入线程池中
- 使用 Worker 类描述一个工作线程 , 使用 Runnable 描述一个任务
- 使用 BlockingQueue 组织所有任务
java
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
class MyThread{
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = null;
public MyThread(int n){
queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
Runnable task = null;
try {
task = queue.take();
task.run();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
}
}
public void submit(Runnable task) throws InterruptedException {
queue.put(task);
}
}
public class demo33 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread pool = new MyThread(4);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
pool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"hello");
}
});
}
}
}9.4 定时器
在 Java 中 , 定时器(Timer)用于按指定时间或周期性执行任务 , 常用方式有 : java.util,Timer 和 java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService
以下提供标准库的两个定时器
① Timer 类(传统方式)
schedule(TimerTask task, long delay):延迟delay毫秒后执行一次任务schedule(TimerTask task, Date time):在指定时间time执行一次任务schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period):延迟delay毫秒后,每隔period毫秒重复执行任务(以任务开始时间为基准)scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period):延迟delay毫秒后,每隔period毫秒重复执行任务(以任务计划时间为基准,可能追赶执行)
java
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class demo34 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 3000");
}
},3000);
TimerTask task2 = new TimerTask() {
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
count++;
System.out.println("hello task");
if(count>=5){
this.cancel();//取消当前任务
timer.cancel();//关闭定时器
System.out.println("定时器已关闭");
}
}
};
timer.schedule(task2,1000,1000);
}
}②ScheduledExecutorService
以后再说
实现一个定时器
java
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
class MyTimerTsak implements Comparable<MyTimerTsak> {
private Runnable task;
private long time;
public MyTimerTsak(Runnable task, long time) {
this.task = task;
this.time = time;
}
public int compareTo(MyTimerTsak o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void run() {
task.run();
}
}
class MyTimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTsak> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
private Object locker = new Object();
public void schedule(Runnable task, long delay) {
synchronized(locker){
MyTimerTsak timertask = new MyTimerTsak(task, System.currentTimeMillis() + delay);
queue.offer(timertask);
}
}
public MyTimer() {
Thread t =
new Thread(
() -> {
while (true) {
synchronized (locker) {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
MyTimerTsak task = queue.peek();
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < task.getTime()) {
continue;
} else {
task.run();
queue.poll();
}
}
}
});
t.start();
}
}问题 :构造方法存在无限空循环导致 cpu 占用过高;即使是队列为空或者未到任务执行时间,也会抢占 cpu
解决方法:使用两个 wait(),在添加任务后使用 notify ()
java
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
class MyTimerTask implements Comparable<MyTimerTask> {
private Runnable task;
// 记录任务要执行的时刻
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long time) {
this.task = task;
this.time = time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
// return (int) (o.time - this.time);
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void run() {
task.run();
}
}
// 自己实现一个定时器
class MyTimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 直接使用 this 作为锁对象, 当然也是 ok 的
private Object locker = new Object();
public void schedule(Runnable task, long delay) {
synchronized (locker) {
// 以入队列这个时刻作为时间基准.
MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask(task, System.currentTimeMillis() + delay);
queue.offer(timerTask);
locker.notify();
}
}
public MyTimer() {
// 创建一个线程, 负责执行队列中的任务
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (true) {
synchronized (locker) {
// 取出队首元素
// 还是加上 while
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
// 这里的 sleep 时间不好设定!!
locker.wait();
}
MyTimerTask task = queue.peek();
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < task.getTime()) {
// 当前任务时间, 如果比系统时间大, 说明任务执行的时机未到
locker.wait(task.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis());
} else {
// 时间到了, 执行任务
task.run();
queue.poll();
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
t.start();
}
}
public class Demo38 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTimer timer = new MyTimer();
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 3000");
}
}, 3000);
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 2000");
}
}, 2000);
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 1000");
}
}, 1000);
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(4);
}
}核心逻辑:
- Task 类用于描述一个任务(作为 Timer 的内部类) , 里面包含一个 Runnable 对象和一个 time(毫秒级时间戳) ; 这个对象需要放到优先级队列中 , 需要实现 Comparable 接口
- Timer 类提供的核心接口为 schedule , 用于注册一个任务 , 并指定这个任务多长时间后执行 ; Timer 实例中 , 通过 PriorityQueue 来组织若干个 Task 对象 , 通过 schedule 来往队列中插入一个个 Task 对象 ; Timer 类中存在一个 worker 线程 , 一直不停扫描队首元素 , 看能否执行这个任务