1. React 工程架构
React 工程项目使用 Monorepo 架构进行管理,因为 React 团队为了将不同职责包拆分,使得源码更具可读性与维护性。所以我们在开始看 React 源码之前,需要先稍微熟悉一下 Monorepo 架构,与 React 整体分包设计。
1.1. react
React 工程的基础包,也叫入口包,我们使用 React 的相关 API 都是从它导出的。
该包定义了 React 对外 API 协议,并且这个包也仅仅是暴露协议,真正的实现并不在它里面。如果是浏览器端,核心 Dom 相关实现在 React-Dom,如果是在手机端,核心元素操作是在 React-Native 中。
1.2. react-dom
针对于 Web 应用的渲染器实现,完成 React 与 Web 的桥接。该包主要提供应用初始化挂载 API,例如:createRoot 。
javascript
function createRoot(
container: Element | Document | DocumentFragment,
options?: CreateRootOptions,
): RootType {
// 创建根节点实例
return createRootImpl(container, options);
}1.3. react-reconciler
react 的大总管,负责整体协调 react-dom、react、scheduler 之间的调用和职责交接。
主要包括:
-
/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.new.js
-
/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.new.js
-
/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberClassComponent.new.js
-
/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.new.js
整个与 scheduler 的联系,发生在:/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.new.js
1.4. scheduler
react 整体调度机制的核心实现,控制上面提到的 react-reconciler 包推入的执行任务的具体执行时机。 concurrent 模式下,任务切片、可中断更新等都是该包的功劳。
1.5. react-noop-renderer
react 的演示渲染器,没有渲染目标输出,用来单独演示调和器的内部结构。不过有一点需要强调,我们可以依照这个包,写一个自定义渲染器哦。
javascript
const hostConfig = {
getRootHostContext: () => {
return rootHostContext;
},
getChildHostContext: () => {
return childHostContext;
},
shouldSetTextContent: (type, props) => {
return (
typeof props.children === "string" || typeof props.children === "number"
);
},
prepareForCommit: () => {},
resetAfterCommit: () => {},
createTextInstance: (text) => {
return document.createTextNode(text);
},
createInstance: (
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
_currentHostContext,
workInProgress
) => {
const domElement = document.createElement(type);
Object.keys(newProps).forEach((propName) => {
const propValue = newProps[propName];
if (propName === "children") {
if (typeof propValue === "string" || typeof propValue === "number") {
domElement.textContent = propValue;
}
} else if (propName === "onClick") {
domElement.addEventListener("click", propValue);
} else if (propName === "className") {
domElement.setAttribute("class", propValue);
} else if (propName === "style") {
const propValue = newProps[propName];
const propValueKeys = Object.keys(propValue);
const propValueStr = propValueKeys.map(k => `${k}: ${propValue[k]}`).join(";")
domElement.setAttribute(propName, propValueStr);
} else {
const propValue = newProps[propName];
domElement.setAttribute(propName, propValue);
}
});
return domElement;
},
appendInitialChild: (parent, child) => {
parent.appendChild(child);
},
appendChild(parent, child) {
parent.appendChild(child);
},
finalizeInitialChildren: (domElement, type, props) => {},
supportsMutation: true,
appendChildToContainer: (parent, child) => {
parent.appendChild(child);
},
prepareUpdate(domElement, oldProps, newProps) {
return true;
},
commitUpdate(domElement, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps) {
Object.keys(newProps).forEach((propName) => {
const propValue = newProps[propName];
if (propName === "children") {
if (typeof propValue === "string" || typeof propValue === "number") {
domElement.textContent = propValue;
}
// TODO 还要考虑数组的情况
} else if (propName === "style") {
const propValue = newProps[propName];
const propValueKeys = Object.keys(propValue);
const propValueStr = propValueKeys.map(k => `${k}: ${propValue[k]}`).join(";")
domElement.setAttribute(propName, propValueStr);
} else {
const propValue = newProps[propName];
domElement.setAttribute(propName, propValue);
}
});
},
commitTextUpdate(textInstance, oldText, newText) {
textInstance.text = newText;
},
removeChild(parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.removeChild(child);
},
};2. JSX编译
2.1. 编译器
可以转化 JSX 的编译工具有很多,我们最熟知的是:Babel,其实还有很多的编译构建工具,例如 ESBuild、SWC等,他们都可以将 JSX 转为 React 运行时代码。我们以 Babel 为例,探讨 JSX 编译过程。
2.2. 编译配置与编译过程
Babel 是一个 JavaScript 编译器,它可以将 JSX 代码转换为纯 JavaScript 代码。这个转换过程涉及几个步骤,从解析 JSX 到生成等效的 JavaScript。以下是详细的转换过程及其对应的代码示例:
2.2.1. JSX代码
假设我们有一段简单的 JSX 代码:
javascript
const element = <h1 className="greeting">Hello, world!</h1>;2.2.2. Babel 的 JSX 转换
Babel 将 JSX 代码转换为 React.createElement 调用。我们来看一下具体的转换过程。
- 解析 JSX
Babel 解析器首先将 JSX 代码解析成抽象语法树(AST)。这个步骤中,JSX 被识别为特定的节点类型。
- 转换 JSX 元素
Babel 插件 @babel/plugin-transform-react-jsx 会将 JSX 元素转换为 React.createElement 调用。
具体的转换规则是:
-
JSX 标签名被转换为 React.createElement 的第一个参数。
-
JSX 属性被转换为一个对象,作为 React.createElement 的第二个参数。
-
JSX 子元素被转换为 React.createElement 的后续参数。
对于我们的示例代码,转换后的 JavaScript 代码如下:
javascript
const element = React.createElement(
'h1',
{ className: 'greeting' },
'Hello, world!'
);2.2.3. Babel 配置
为了进行这个转换,我们需要配置 Babel。以下是一个示例配置文件 .babelrc:
javascript
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-react"]
}这个配置使用了 @babel/preset-react 预设,它包含了用于转换 JSX 的插件。
2.2.4. 示例代码
我们通过一个完整例子,了解 babel 的配置与转换过程。
- 原始 JSX 文件 App.jsx
javascript
// App.jsx
import React from 'react';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1 className="greeting">Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is a JSX example.</p>
</div>
);
};
export default App;- 使用 Babel CLI 转换 JSX
安装 babel、预设以及 babel cli:
javascript
pnpm add -D @babel/core @babel/preset-react可以使用 Babel CLI 来转换这个文件:
javascript
babel App.jsx --out-file App.js- 转换后的文件 App.js
javascript
// App.js
import React from 'react';
const App = () => {
return React.createElement(
'div',
null,
React.createElement(
'h1',
{ className: 'greeting' },
'Hello, world!'
),
React.createElement(
'p',
null,
'This is a JSX example.'
)
);
};
export default App;3. React 核心流程
React 执行流程我们拆解为两部分,分别为:创建与更新。
创建阶段,主要完成的工作包含:容器创建、元素对应 Fiber 创建、更新队列初始化等操作。
更新阶段,主要包含:状态更新触发任务入队、scheduler 调度、重新构建 fiber、完成 fiber 到元素映射更新视图。
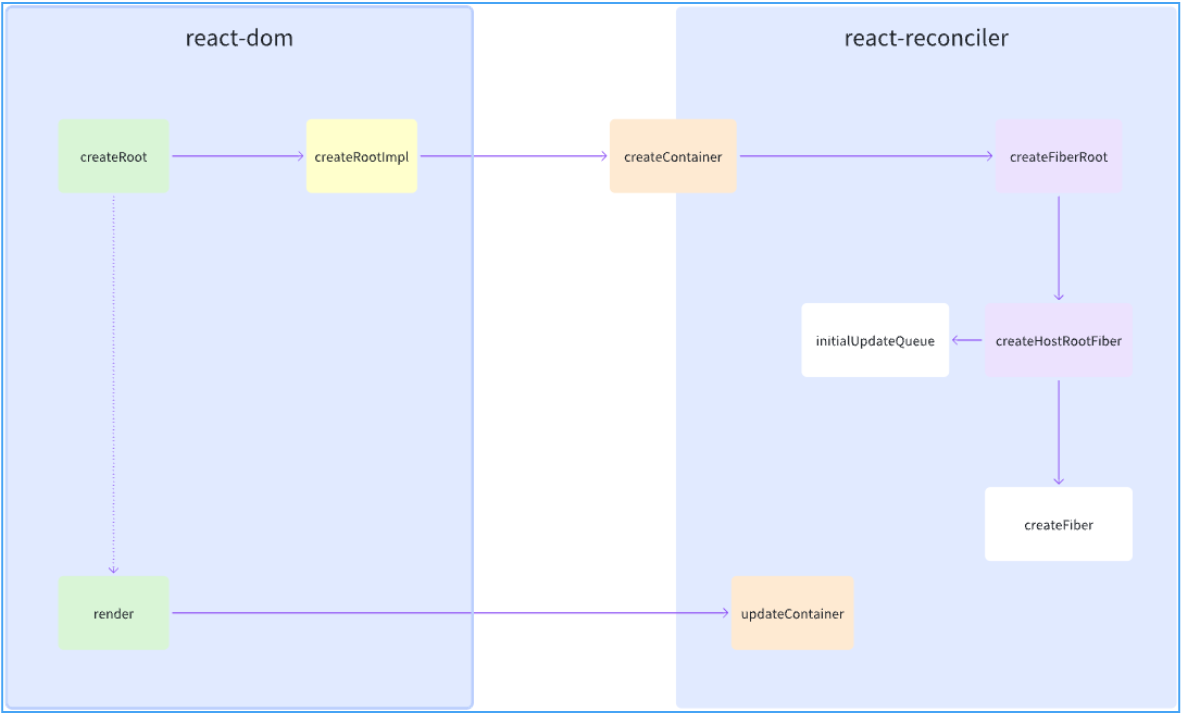
3.1. 创建
此处只先探讨 concurrent 模式启动,这也是最最常用的模式。
完整执行顺序及核心文件:
- react-dom
-
ReactDOM.createRoot
-
createRootImpl
- react-reconciler
-
createContainer
-
createFiberRoot
-
createHostRootFiber
-
createFiber
-
initializeUpdateQueue
- react-dom
-
ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render
-
markContainerAsRoot
-
updateContainer
-
此处省略,在更新处探讨
3.2. 更新
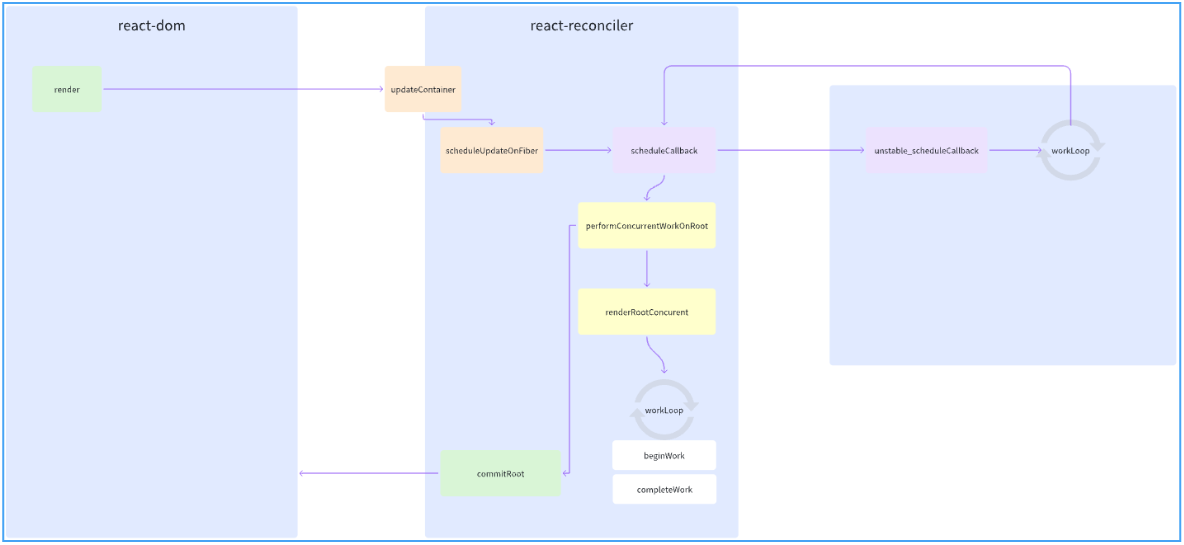
上文提到,react 应用创建会先初始化所需数据,包含 fiberRoot、rootFiber、updateQueue 等,然后调用 render 方法,我们可以看到在 render 时,却是调用了与状态更新时所调用的同一方法 updateContainer,这正是其设计的精妙之处。
javascript
ReactDOMHydrationRoot.prototype.render = ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render = function(
children: ReactNodeList,
): void {
const root = this._internalRoot;
if (root === null) {
throw new Error('Cannot update an unmounted root.');
}
// ...
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
};完整执行顺序及核心文件:
- react-reconciler
-
updateContainer
-
requestUpdateLane
-
enqueueUpdate
-
scheduleUpdateOnFiber
- scheduler
-
unstable_scheduleCallback
-
workLoop
- react-reconciler
-
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
-
renderRootConcurrent
-
workLoop
-
performUnitOfWork (beginWork、completeWork)
-
commitRoot
4. 数据结构与算法导引
4.1. 数据结构
在 React 源码中,主要使用堆、栈、链表数据结构完成执行环节的核心逻辑。
4.1.1. 堆
堆在 scheduler 中用于任务排序。由于堆顶元素数值最小,提取元素时直接从堆顶获取。排序利用二叉堆特性,循环提取根节点实现排序,本质是一种选择排序,时间复杂度为 O(nlog n)。
堆的特性如下:
-
父节点的值 >= 子节点的值为最大堆,父节点的值 <= 子节点的值为最小堆。每个节点的左子树和右子树都是一个二叉堆。
-
假设一个数组 [k₀, k₁, k₂, ... kₙ] 下标从 0 开始,则:kᵢ <= k₂ᵢ₊₁, kᵢ <= k₂ᵢ₊₂ 或 kᵢ >= k₂ᵢ₊₁, kᵢ >= k₂ᵢ₊₂ ,i值为0到n/2。
React中应用如下:
javascript
/**
* Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
*
* This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
*
* @flow strict
*/
type Heap = Array<Node>;
type Node = {|
id: number,
sortIndex: number,
|};
export function push(heap: Heap, node: Node): void {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
siftUp(heap, node, index);
}
export function peek(heap: Heap): Node | null {
return heap.length === 0 ? null : heap[0];
}
export function pop(heap: Heap): Node | null {
if (heap.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const first = heap[0];
const last = heap.pop();
if (last !== first) {
heap[0] = last;
siftDown(heap, last, 0);
}
return first;
}
function siftUp(heap, node, i) {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
// The parent is larger. Swap positions.
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
// The parent is smaller. Exit.
return;
}
}
}
function siftDown(heap, node, i) {
let index = i;
const length = heap.length;
const halfLength = length >>> 1;
while (index < halfLength) {
const leftIndex = (index + 1) * 2 - 1;
const left = heap[leftIndex];
const rightIndex = leftIndex + 1;
const right = heap[rightIndex];
// If the left or right node is smaller, swap with the smaller of those.
if (compare(left, node) < 0) {
if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, left) < 0) {
heap[index] = right;
heap[rightIndex] = node;
index = rightIndex;
} else {
heap[index] = left;
heap[leftIndex] = node;
index = leftIndex;
}
} else if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, node) < 0) {
heap[index] = right;
heap[rightIndex] = node;
index = rightIndex;
} else {
// Neither child is smaller. Exit.
return;
}
}
}
function compare(a, b) {
// Compare sort index first, then task id.
const diff = a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex;
return diff !== 0 ? diff : a.id - b.id;
}-
peek函数:查看堆顶元素,也就是优先级最高的task或timer。
-
pop函数:将堆顶元素弹出并删除,随后需调用siftDown函数向下调整堆。
-
push函数:添加新节点,添加之后需要调用siftUp函数向上调整堆。
-
siftDown函数:向下调整堆结构,保证数组是一个最小堆。
-
siftUp函数:插入节点后向上调整堆结构,保证数组是一个最小堆。
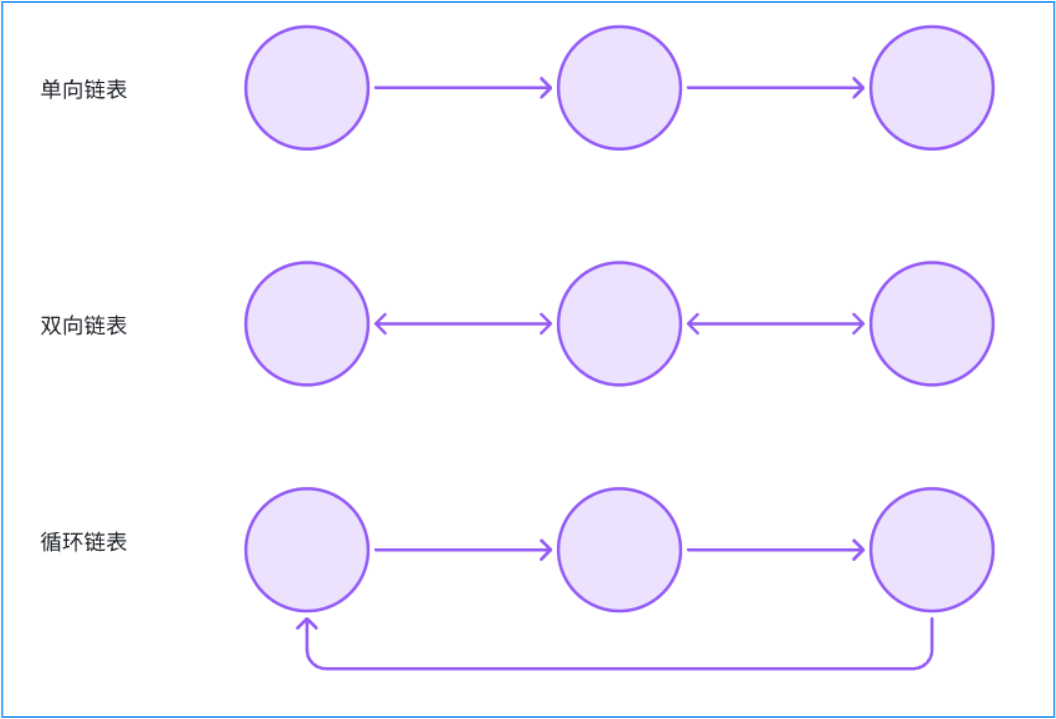
4.1.2. 链表
链表是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的指针。由于不必按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到 O(1)的复杂度,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要 O(n)的时间.
按指针指向特点可分为:
-
单向链表
-
双向链表
-
循环链表
基本使用如下:
javascript
// 定义Node节点类型
function Node(name) {
this.name = name;
this.next = null;
}
// 链表
function LinkedList() {
this.head = new Node('head');
// 查找node节点的前一个节点
this.findPrevious = function (node) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode && currentNode.next !== node) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode;
};
// 在node后插入新节点newElement
this.insert = function (name, node) {
const newNode = new Node(name);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
};
// 删除节点
this.remove = function (node) {
const previousNode = this.findPrevious(node);
if (previousNode) {
previousNode.next = node.next;
}
};
// 反转链表
this.reverse = function () {
let prev = null;
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
const tempNode = current.next;
// 重新设置next指针,使其指向前一个节点
current.next = prev;
// 游标后移
prev = current;
current = tempNode;
}
// 重新设置head节点
this.head = prev;
};
}-
节点插入, 时间复杂度 O(1)
-
节点查找, 时间复杂度 O(n)
-
节点删除, 时间复杂度 O(1)
-
反转链表, 时间复杂度 O(n)
在 React 源码中,要大量使用链表的场景,包含:fiber、hook、更新队列。
- fiber
javascript
// 一个Fiber对象代表一个即将渲染或者已经渲染的组件(ReactElement),一个组件可能对应两个fiber(current和WorkInProgress)
// 单个属性的解释在后文(在注释中无法添加超链接)
export type Fiber = {
tag: WorkTag,
key: null | string,
elementType: any,
type: any,
stateNode: any,
return: Fiber | null,
child: Fiber | null,
sibling: Fiber | null,
index: number,
ref:
| null
| (((handle: mixed) => void) & { _stringRef?: string, ... })
| RefObject,
pendingProps: any, // 从`ReactElement`对象传入的 props。用于和 fiber.memoizedProps`比较可以得出属性是否变动
memoizedProps: any, // 上一次生成子节点时用到的属性,生成子节点之后保持在内存中
updateQueue: mixed, // 存储state更新的队列,当前节点的state改动之后,都会创建一个update对象添加到这个队列中。
memoizedState: any, // 用于输出的state,最终渲染所使用的state
dependencies: Dependencies | null, // 该fiber节点所依赖的(contexts, events)等
mode: TypeOfMode, // 二进制位bitfield, 继承至父节点, 影响本fiber节点及其子树中所有节点。与react应用的运行模式有关(有ConcurrentMode, BlockingMode, NoMode等选项)。
// Effect 副作用相关
flags: Flags, // 标志位
subtreeFlags: Flags, // 替代16.x版本中的 firstEffect, nextEffect。当设置了enableNewReconciler=true才会启用
deletions: Array<Fiber> | null, // 存储将要被删除的子节点。当设置了 enableNewReconciler=true 才会启用
nextEffect: Fiber | null, // 单向链表,指向下一个有副作用的fiber节点
firstEffect: Fiber | null, // 指向副作用链表中的第一个fiber节点
lastEffect: Fiber | null, // 指向副作用链表中的最后一个fiber节点
// 优先级相关
lanes: Lanes, // 本fiber节点的优先级
childLanes: Lanes, // 子节点的优先级
alternate: Fiber | null, // 指向内存中的另一个fiber,每个被更新过fiber节点在内存中都是成对出现(current和WorkInProgress)
// 性能统计相关(开启enableProfilerTimer后才会统计)
// react-dev-tool 会根据这些时间统计来评估性能
actualDuration?: number, // 本次更新过程,本节点以及子树所消耗的总时间
actualStartTime?: number, // 标记本fiber节点开始构建的时间
selfBaseDuration?: number, // 用于最近一次生成本fiber节点所消耗的时间
treeBaseDuration?: number, // 生成子树所消耗的时间的总和
};- UpdateQueue
javascript
export type Update<State> = {
eventTime: number, // 发起update事件的时间(17.0.2中作为临时字段,即将移出
lane: Lane, // update所属的优先级
tag: 0 | 1 | 2 | 3, //
payload: any, // 载荷,根据场景可以设置成一个回调函数或者对象
callback: (() => mixed) | null, // 回调函数
next: Update<State> | null, // 指向链表中的下一个,由于UpdateQueue是一个环形链表,最后一个update.next指向第一个Update对象
};
// ============= UpdateQueue ==============
type SharedQueue<State> = {
pending: Update<State> | null,
};
export type UpdateQueue<State> = {
baseState: State,
firstBaseUpdate: Update<State> | null,
lastBaseUpdate: Update<State> | null,
shared: SharedQueue<State>,
effects: Array<Update<State>> | null,
};4.1.3. 栈
栈,这个数据结构很普遍了,只允许在有序的线性资料集合的一端进行加入数据和移除数据的运算. 因而按照后进先出的原理运作,通常用在匹配逻辑等问题。
基本使用:
javascript
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.dataStore = [];
this.top = 0;
}
// 压栈
push(element) {
this.dataStore[this.top++] = element;
}
// 弹栈
pop() {
return this.dataStore[--this.top];
}
// 预览栈顶元素
peek() {
return this.dataStore[this.top - 1];
}
// 检测栈内存储了多少个元素
length() {
return this.top;
}
// 清空栈
clear() {
this.top = 0;
}
}React中的应用:
- Context状态管理
React内部会维护一个栈来保存提供者的状态,供给消费者使用。
javascript
/**
* Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
*
* This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
*
* @flow
*/
import type {Fiber} from './ReactInternalTypes';
export type StackCursor<T> = {|current: T|};
const valueStack: Array<any> = [];
let fiberStack: Array<Fiber | null> = null;
if (__DEV__) {
fiberStack = [];
}
let index = -1;
function createCursor<T>(defaultValue: T): StackCursor<T> {
return {
current: defaultValue,
};
}
function isEmpty(): boolean {
return index === -1;
}
function pop<T>(cursor: StackCursor<T>, fiber: Fiber): void {
if (index < 0) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.error('Unexpected pop.');
}
return;
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (fiber !== fiberStack[index]) {
console.error('Unexpected Fiber popped.');
}
}
cursor.current = valueStack[index];
valueStack[index] = null;
if (__DEV__) {
fiberStack[index] = null;
}
index--;
}
function push<T>(cursor: StackCursor<T>, value: T, fiber: Fiber): void {
index++;
valueStack[index] = cursor.current;
if (__DEV__) {
fiberStack[index] = fiber;
}
cursor.current = value;
}
function checkThatStackIsEmpty() {
if (__DEV__) {
if (index !== -1) {
console.error(
'Expected an empty stack. Something was not reset properly.',
);
}
}
}
function resetStackAfterFatalErrorInDev() {
if (__DEV__) {
index = -1;
valueStack.length = 0;
fiberStack.length = 0;
}
}
export {
createCursor,
isEmpty,
pop,
push,
// DEV only:
checkThatStackIsEmpty,
resetStackAfterFatalErrorInDev,
};结合 Context 的逻辑处理。
javascript
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberNewContext.old.js
export function pushProvider<T>(
providerFiber: Fiber,
context: ReactContext<T>,
nextValue: T,
): void {
if (isPrimaryRenderer) {
push(valueCursor, context._currentValue, providerFiber);
context._currentValue = nextValue;
if (__DEV__) {
if (
context._currentRenderer !== undefined &&
context._currentRenderer !== null &&
context._currentRenderer !== rendererSigil
) {
console.error(
'Detected multiple renderers concurrently rendering the ' +
'same context provider. This is currently unsupported.',
);
}
context._currentRenderer = rendererSigil;
}
} else {
push(valueCursor2, context._currentValue2, providerFiber);
context._currentValue2 = nextValue;
if (__DEV__) {
if (
context._currentRenderer2 !== undefined &&
context._currentRenderer2 !== null &&
context._currentRenderer2 !== rendererSigil
) {
console.error(
'Detected multiple renderers concurrently rendering the ' +
'same context provider. This is currently unsupported.',
);
}
context._currentRenderer2 = rendererSigil;
}
}
}4.2. 算法
4.2.1. 调和过程
- Diff 算法的核心策略
React 的 diff 算法基于两个重要假设:
-
不同类型元素生成不同树结构
-
通过 key 属性标识稳定节点
基本比较逻辑:
javascript
// React 源码中的简化比较逻辑
function reconcileChildren(current, workInProgress, nextChildren) {
if (current === null) {
// 挂载阶段
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren
);
} else {
// 更新阶段 - 执行 diff
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren
);
}
}- 节点 Diff 的具体过程
- 单节点 Diff
javascript
// 示例:单节点比较
function reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
element,
lanes
) {
const key = element.key;
let child = currentFirstChild;
while (child !== null) {
// 首先比较 key
if (child.key === key) {
// key 相同,再比较 type
if (child.type === element.type) {
// 可以复用现有节点
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child.sibling);
const existing = useFiber(child, element.props);
existing.return = returnFiber;
return existing;
} else {
// key相同但type不同,删除旧节点及其兄弟节点
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child);
break;
}
} else {
// key不同,标记删除当前节点
deleteChild(returnFiber, child);
}
child = child.sibling;
}
// 创建新节点
const created = createFiberFromElement(element, returnFiber.mode, lanes);
created.return = returnFiber;
return created;
}- 多节点 Diff
javascript
function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChildren,
lanes
) {
let resultingFirstChild = null;
let previousNewFiber = null;
let oldFiber = currentFirstChild;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
let newIdx = 0;
let nextOldFiber = null;
// 第一轮遍历:处理可复用的节点
for (; oldFiber !== null && newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
if (oldFiber.index > newIdx) {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber;
oldFiber = null;
} else {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
const newFiber = updateSlot(
returnFiber,
oldFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes
);
if (newFiber === null) {
// 无法复用,跳出第一轮遍历
if (oldFiber === null) {
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
break;
}
// 记录节点移动
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
// 构建新fiber链表
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
// 第二轮遍历:处理剩余情况
if (newIdx === newChildren.length) {
// 新children遍历完成,删除剩余oldFiber
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
return resultingFirstChild;
}
if (oldFiber === null) {
// 旧children遍历完成,创建新节点
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = createChild(returnFiber, newChildren[newIdx], lanes);
if (newFiber !== null) {
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
// 添加到链表...
}
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}
// 第三轮遍历:处理节点移动和复用
const existingChildren = mapRemainingChildren(oldFiber);
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = updateFromMap(
existingChildren,
returnFiber,
newIdx,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes
);
if (newFiber !== null) {
// 处理节点移动逻辑...
}
}
// 删除未使用的旧节点
existingChildren.forEach(child => deleteChild(returnFiber, child));
return resultingFirstChild;
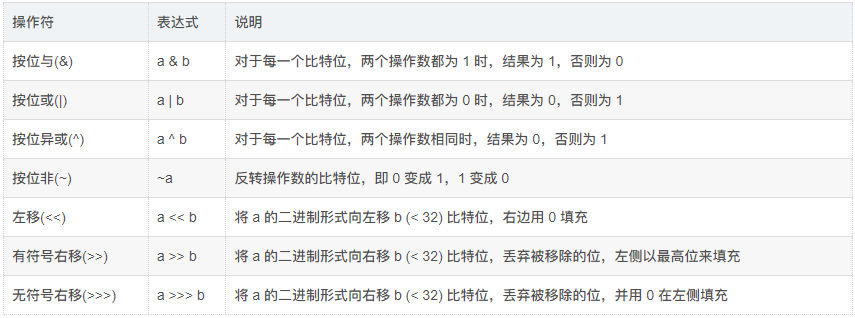
}4.2.2. 位运算
位运算用在任务的优先级判断、执行上下文判断上,通过位运算可以轻松得出给定某个对象是否具有某项约定特征。
- 位运算基础
- 位运算求解
位运算求解非常简单,我们一般的方式是按位与求得当下某个参数是否蕴含着某项特征,例如在 React 优先级判断中按位与可直接计算出 lanes 是否包含给定 xxxLane。
javascript
export const NoLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const NoLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const SyncLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000001;
// 早期版本
function getHighestPriorityLanes(lanes: Lanes | Lane): Lanes {
// 判断 Lanes中是否包含 SyncLane
if ((SyncLane & lanes) !== NoLanes) {
return_highestLanePriority = SyncLanePriority;
return SyncLane;
}
// ...
// ... 省略其他代码
return lanes;
}
// 18.3.1
export function getHighestPriorityLane(lanes: Lanes): Lane {
return lanes & -lanes;
}
function getHighestPriorityLanes(lanes: Lanes | Lane): Lanes {
switch (getHighestPriorityLane(lanes)) {
case SyncLane:
return SyncLane;
}
}- React 中的应用
- 在优先级管理中的应用
文件:/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberLane.new.js
核心代码:
javascript
export const TotalLanes = 31;
export const NoLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const NoLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const SyncLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000001;
export const InputContinuousHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000010;
export const InputContinuousLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000100;
export const DefaultHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000001000;
export const DefaultLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000010000;
const TransitionHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000100000;
const TransitionLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000111111111111111111000000;
const TransitionLane1: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000001000000;
const TransitionLane2: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000010000000;
const TransitionLane3: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000100000000;
const TransitionLane4: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000001000000000;
const TransitionLane5: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000010000000000;
const TransitionLane6: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000100000000000;
const TransitionLane7: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000001000000000000;
const TransitionLane8: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000010000000000000;
const TransitionLane9: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000100000000000000;
const TransitionLane10: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000001000000000000000;
const TransitionLane11: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000010000000000000000;
const TransitionLane12: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000100000000000000000;
const TransitionLane13: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000001000000000000000000;
const TransitionLane14: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000010000000000000000000;
const TransitionLane15: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000100000000000000000000;
const TransitionLane16: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000001000000000000000000000;
const RetryLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000011111110000000000000000000;
const RetryLane1: Lane = /* */ 0b0000001000000000000000000000000;
const RetryLane2: Lane = /* */ 0b0000010000000000000000000000000;
const RetryLane3: Lane = /* */ 0b0000100000000000000000000000000;
const RetryLane4: Lane = /* */ 0b0001000000000000000000000000000;
const RetryLane5: Lane = /* */ 0b0010000000000000000000000000000;
export const SomeRetryLane: Lane = RetryLane1;
export const SelectiveHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000100000000000000000000000000;
const NonIdleLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000011111111111111111111111111;
export const IdleHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0100000000000000000000000000000;
export const IdleLane: Lane = /* */ 0b1000000000000000000000000000000;
export const OffscreenLane: Lane = /* */ 0b1000000000000000000000000000000;
function getHighestPriorityLanes(lanes: Lanes | Lane): Lanes {
switch (getHighestPriorityLane(lanes)) {
case SyncLane:
return SyncLane;
case InputContinuousHydrationLane:
return InputContinuousHydrationLane;
case InputContinuousLane:
return InputContinuousLane;
case DefaultHydrationLane:
return DefaultHydrationLane;
case DefaultLane:
return DefaultLane;
case TransitionHydrationLane:
return TransitionHydrationLane;
case TransitionLane1:
case TransitionLane2:
case TransitionLane3:
case TransitionLane4:
case TransitionLane5:
case TransitionLane6:
case TransitionLane7:
case TransitionLane8:
case TransitionLane9:
case TransitionLane10:
case TransitionLane11:
case TransitionLane12:
case TransitionLane13:
case TransitionLane14:
case TransitionLane15:
case TransitionLane16:
return lanes & TransitionLanes;
case RetryLane1:
case RetryLane2:
case RetryLane3:
case RetryLane4:
case RetryLane5:
return lanes & RetryLanes;
case SelectiveHydrationLane:
return SelectiveHydrationLane;
case IdleHydrationLane:
return IdleHydrationLane;
case IdleLane:
return IdleLane;
case OffscreenLane:
return OffscreenLane;
default:
if (__DEV__) {
console.error(
'Should have found matching lanes. This is a bug in React.',
);
}
return lanes;
}
}- workLoop 上下文
文件:/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.new.js
核心代码:
javascript
export const NoContext = /* */ 0b0000;
const BatchedContext = /* */ 0b0001;
const RenderContext = /* */ 0b0010;
const CommitContext = /* */ 0b0100;
type RootExitStatus = 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6;
const RootInProgress = 0;
const RootFatalErrored = 1;
const RootErrored = 2;
const RootSuspended = 3;
const RootSuspendedWithDelay = 4;
const RootCompleted = 5;
const RootDidNotComplete = 6;
export function batchedUpdates<A, R>(fn: (a: A) => R, a: A): R {
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext;
executionContext |= BatchedContext;
try {
return fn(a);
} finally {
executionContext = prevExecutionContext;
// If there were Legacy sync updates, flush them at the end of the outer
// most batchedUpdates-like method.
if (
executionContext === NoContext &&
// Treat `act` as if it's inside `batchedUpdates`, even in Legacy mode.
!(__DEV__ && ReactCurrentActQueue.isBatchingLegacy)
) {
resetRenderTimer();
flushSyncCallbacksOnlyInLegacyMode();
}
}
}注意这里的 |executionContext |= BatchedContext;按位或然后将值付给 executionContext,这样进来的 context 自动打上批处理标记。比如:
javascript
let A = 0b001;
const BC = 0b010;
A |= BC
// 此时 A 的值为: 0b0114.2.3. 图遍历
对于树或图结构的遍历来讲,分为深度优先和广度优先。
- 概念
深度优先遍历:DFS是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。
- 实现方式
DFS 的主流实现方式有 2 种:
- 递归
javascript
function Node() {
this.name = '';
this.children = [];
}
function dfs(node) {
console.log('探寻阶段:', node.name);
node.children.forEach((child) => {
dfs(child);
});
console.log('回溯阶段:', node.name);
}- 利用 栈 存储遍历路径
javascript
function Node() {
this.name = '';
this.children = [];
// 因为要分辨探寻阶段和回溯阶段,所以必须要一个属性来记录是否已经访问过该节点
// 如果不打印探寻和回溯,就不需要此属性
this.visited = false;
}
function dfs(node) {
const stack = [];
stack.push(node);
// 栈顶元素还存在,就继续循环
while ((node = stack[stack.length - 1])) {
if (node.visited) {
console.log('回溯阶段:', node.name);
// 回溯完成,弹出该元素
stack.pop();
} else {
console.log('探寻阶段:', node.name);
node.visited = true;
// 利用栈的先进后出的特性,倒序将节点送入栈中
for (let i = node.children.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
stack.push(node.children[i]);
}
}
}
}- React 中的应用
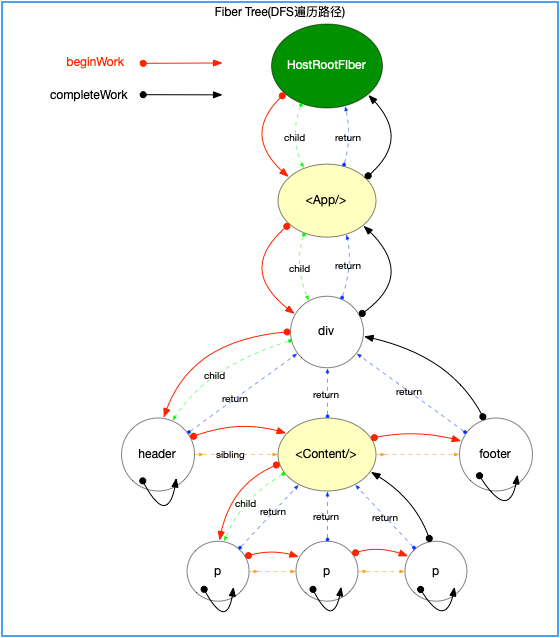
- fiber 树的构造
在 ReactElement 的构造过程中,同时伴随着 fiber 树的构造,fiber 树同样也是在 beginWork 阶段生成的。绘制遍历路径如下:
- 查找 context 的消费节点
在 React 应用中,当 context 改变之后,需要找出依赖该 context 的所有子节点。
javascript
function propagateContextChanges<T>(
workInProgress: Fiber,
contexts: Array<any>,
renderLanes: Lanes,
forcePropagateEntireTree: boolean,
): void {
// Only used by Lazy implementation
if (!enableLazyContextPropagation) {
return;
}
let fiber = workInProgress.child;
if (fiber !== null) {
// Set the return pointer of the child to the work-in-progress fiber.
fiber.return = workInProgress;
}
while (fiber !== null) {
let nextFiber;
// Visit this fiber.
const list = fiber.dependencies;
if (list !== null) {
nextFiber = fiber.child;
let dep = list.firstContext;
findChangedDep: while (dep !== null) {
// Assigning these to constants to help Flow
const dependency = dep;
const consumer = fiber;
findContext: for (let i = 0; i < contexts.length; i++) {
const context: ReactContext<T> = contexts[i];
// Check if the context matches.
// TODO: Compare selected values to bail out early.
if (dependency.context === context) {
// Match! Schedule an update on this fiber.
// In the Lazy implementation, don't mark a dirty flag on the
// dependency itself. Not all changes are propagated, so we can't
// rely on the propagation function alone to determine whether
// something has changed; the consumer will check. In the future, we
// could add back a dirty flag as an optimization to avoid double
// checking, but until we have selectors it's not really worth
// the trouble.
consumer.lanes = mergeLanes(consumer.lanes, renderLanes);
const alternate = consumer.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, renderLanes);
}
scheduleContextWorkOnParentPath(
consumer.return,
renderLanes,
workInProgress,
);
}
}
if (!forcePropagateEntireTree) {
// During lazy propagation, when we find a match, we can defer
// propagating changes to the children, because we're going to
// visit them during render. We should continue propagating the
// siblings, though
nextFiber = null;
}
// Since we already found a match, we can stop traversing the
// dependency list.
break findChangedDep;
}
dep = dependency.next;
}
} else if (fiber.tag === DehydratedFragment) {
// If a dehydrated suspense boundary is in this subtree, we don't know
// if it will have any context consumers in it. The best we can do is
// mark it as having updates.
const parentSuspense = fiber.return;
if (parentSuspense === null) {
throw new Error(
'We just came from a parent so we must have had a parent. This is a bug in React.',
);
}
parentSuspense.lanes = mergeLanes(parentSuspense.lanes, renderLanes);
const alternate = parentSuspense.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, renderLanes);
}
// This is intentionally passing this fiber as the parent
// because we want to schedule this fiber as having work
// on its children. We'll use the childLanes on
// this fiber to indicate that a context has changed.
scheduleContextWorkOnParentPath(
parentSuspense,
renderLanes,
workInProgress,
);
nextFiber = null;
} else {
// Traverse down.
nextFiber = fiber.child;
}
if (nextFiber !== null) {
// Set the return pointer of the child to the work-in-progress fiber.
nextFiber.return = fiber;
} else {
// No child. Traverse to next sibling.
nextFiber = fiber;
while (nextFiber !== null) {
if (nextFiber === workInProgress) {
// We're back to the root of this subtree. Exit.
nextFiber = null;
break;
}
const sibling = nextFiber.sibling;
if (sibling !== null) {
// Set the return pointer of the sibling to the work-in-progress fiber.
sibling.return = nextFiber.return;
nextFiber = sibling;
break;
}
// No more siblings. Traverse up.
nextFiber = nextFiber.return;
}
fiber = nextFiber;
}
}
}5. 补充资料
-
补充 Babel 编译 jsx:Babel · The compiler for next generation JavaScript
-
Min Heap 可视化:https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Heap.html
-
关于 monorepo:https://pnpm.io/workspaces
-
核心包:https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/main/packages/react
-
调和:https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/main/packages/react-reconciler
-
调度:https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/main/packages/scheduler
-
视图:https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/main/packages/react-dom