文章目录
-
- [📚 学习路径](#📚 学习路径)
- [🎯 第一步:理解基础概念](#🎯 第一步:理解基础概念)
-
- [🎨 什么是自定义Widget?](#🎨 什么是自定义Widget?)
- [🤔 什么时候需要自定义Widget?](#🤔 什么时候需要自定义Widget?)
- [📋 自定义Widget的分类](#📋 自定义Widget的分类)
- [🏗️ 第二步:掌握基本结构](#🏗️ 第二步:掌握基本结构)
-
- [🔍 StatelessWidget vs StatefulWidget](#🔍 StatelessWidget vs StatefulWidget)
-
- [📊 对比表格](#📊 对比表格)
- [🎯 选择原则](#🎯 选择原则)
- [🎨 第三步:实战简单组件](#🎨 第三步:实战简单组件)
-
- [🌟 入门级:简单文本按钮](#🌟 入门级:简单文本按钮)
- [🎨 进阶级:渐变按钮](#🎨 进阶级:渐变按钮)
- [🔮 高级级:玻璃态按钮](#🔮 高级级:玻璃态按钮)
- [📊 第四步:进阶复杂组件](#📊 第四步:进阶复杂组件)
-
- [🎯 理解CustomPainter](#🎯 理解CustomPainter)
- [📊 实战:圆形进度指示器](#📊 实战:圆形进度指示器)
- [🎮 完整演示应用](#🎮 完整演示应用)
- [🚀 第五步:优化与最佳实践](#🚀 第五步:优化与最佳实践)
-
- [🎯 核心知识点总结](#🎯 核心知识点总结)
-
- [🧱 自定义Widget的类型](#🧱 自定义Widget的类型)
- [🎨 设计原则](#🎨 设计原则)
- [💡 最佳实践](#💡 最佳实践)
-
- [✅ 推荐做法](#✅ 推荐做法)
- [❌ 避免的做法](#❌ 避免的做法)
- [🔧 性能优化技巧](#🔧 性能优化技巧)
-
- [1. 使用const构造函数](#1. 使用const构造函数)
- [2. 合理使用RepaintBoundary](#2. 合理使用RepaintBoundary)
- [3. 优化shouldRepaint逻辑](#3. 优化shouldRepaint逻辑)
- [🎯 组件组合示例](#🎯 组件组合示例)
- [📚 进阶学习方向](#📚 进阶学习方向)
- [🎉 总结](#🎉 总结)

📚 学习路径
本指南将带你从零开始掌握Flutter自定义Widget开发,学习路径如下:
- 🎯 理解基础概念 - 什么是自定义Widget,为什么需要它
- 🏗️ 掌握基本结构 - StatelessWidget vs StatefulWidget
- 🎨 实战简单组件 - 从最简单的自定义按钮开始
- 📊 进阶复杂组件 - 使用CustomPainter绘制图形
- 🚀 优化与最佳实践 - 性能优化和代码规范
🎯 第一步:理解基础概念
🎨 什么是自定义Widget?
自定义Widget就像是制作专属的乐高积木:
🧱 乐高积木比喻:
- 标准积木 = Flutter内置Widget:虽然功能齐全,但样式固定
- 自定义积木 = 自定义Widget:根据特殊需求设计的专属组件
- 积木组合 = Widget组合:将多个Widget组合成复杂功能
🤔 什么时候需要自定义Widget?
- 🎨 特殊UI需求:设计师给了特殊的UI设计,标准Widget无法实现
- 🔄 代码复用:需要在多个地方使用相同的UI组合
- 📦 业务封装:想要封装特定的业务逻辑和UI展示
- ⚡ 性能优化:需要更精细的控制渲染过程
📋 自定义Widget的分类
- 组合型Widget:将现有Widget组合成新功能
- 绘制型Widget:使用CustomPainter直接绘制
- 布局型Widget:自定义布局逻辑
- 交互型Widget:处理复杂的用户交互
🏗️ 第二步:掌握基本结构
🔍 StatelessWidget vs StatefulWidget
在开始编写自定义Widget之前,我们需要选择合适的基类:
📊 对比表格
| 特性 | StatelessWidget | StatefulWidget |
|---|---|---|
| 状态管理 | 无状态,不可变 | 有状态,可变 |
| 性能 | 更好 | 稍差 |
| 使用场景 | 静态UI | 动态UI |
| 重建触发 | 父组件重建 | setState()调用 |
| 生命周期 | 简单 | 复杂 |
🎯 选择原则
dart
// ✅ 使用StatelessWidget的场景
class MyStaticWidget extends StatelessWidget {
// 显示固定内容,不需要状态变化
// 例如:标题、图标、静态按钮等
}
// ✅ 使用StatefulWidget的场景
class MyDynamicWidget extends StatefulWidget {
// 需要响应用户交互或数据变化
// 例如:计数器、表单、动画等
}🎨 第三步:实战简单组件
让我们从最简单的自定义按钮开始,循序渐进地学习。
🌟 入门级:简单文本按钮
首先创建一个最基础的自定义按钮:
dart
/// 🎯 入门级:简单的自定义文本按钮
/// 这是最基础的自定义Widget示例,帮助理解基本结构
class SimpleTextButton extends StatelessWidget {
/// 按钮显示的文本
final String text;
/// 点击回调函数
final VoidCallback? onPressed;
/// 构造函数
const SimpleTextButton({
Key? key,
required this.text,
this.onPressed,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return GestureDetector(
onTap: onPressed,
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16, vertical: 8),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.blue,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
),
child: Text(
text,
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 16,
),
),
),
);
}
}🎨 进阶级:渐变按钮
在掌握基础结构后,我们来创建更复杂的渐变按钮:
这是一个自定义的渐变按钮组件,在简单按钮基础上增加了:
- 支持多种颜色的线性渐变背景
- 阴影效果,增加立体感
- 水波纹点击效果,提升交互体验
dart
/// 🎨 进阶级:渐变按钮组件(就像调色盘的渐变色彩)
class GradientButton extends StatelessWidget {
/// 按钮显示的文本内容
final String text;
/// 渐变颜色列表,至少需要两种颜色来创建渐变效果
/// 例如:[Colors.purple, Colors.blue] 创建紫色到蓝色的渐变
final List<Color> colors;
/// 按钮点击时的回调函数
final VoidCallback onPressed;
/// 🏗️ 构造函数
const GradientButton({
Key? key,
required this.text,
required this.colors,
required this.onPressed,
}) : super(key: key);
/// 🎨 构建渐变按钮的UI
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
height: 50, // 固定按钮高度
decoration: BoxDecoration(
// 🌈 创建线性渐变效果
gradient: LinearGradient(colors: colors),
// 🔘 设置圆角
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(25),
// ✨ 添加阴影效果
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black26,
blurRadius: 8,
offset: Offset(0, 4),
),
],
),
child: Material(
color: Colors.transparent,
child: InkWell(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(25),
onTap: onPressed,
child: Center(
child: Text(
text,
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
),
),
),
);
}
}🔮 高级级:玻璃态按钮
继续进阶,我们创建现代化的玻璃态按钮:
这是一个玻璃态设计风格的按钮组件,展示了:
- 半透明背景,创造毛玻璃效果
- 半透明边框,增加层次感
- 柔和的阴影,营造漂浮感
dart
/// 🔮 高级级:玻璃态按钮组件(就像毛玻璃的朦胧效果)
class GlassButton extends StatelessWidget {
final String text;
final VoidCallback onPressed;
const GlassButton({
Key? key,
required this.text,
required this.onPressed,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
height: 50,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
// 🌫️ 创建玻璃态效果
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.2),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(25),
// 🔳 添加半透明边框
border: Border.all(color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.3)),
// ✨ 添加柔和的阴影
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black12,
blurRadius: 10,
offset: Offset(0, 5),
),
],
),
child: Material(
color: Colors.transparent,
child: InkWell(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(25),
onTap: onPressed,
child: Center(
child: Text(
text,
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.black87,
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
),
),
),
);
}
}📊 第四步:进阶复杂组件
现在我们来学习使用CustomPainter创建完全自定义的绘制组件,这里先做了解,下一篇文章着重讲解。
🎯 理解CustomPainter
CustomPainter让我们可以直接在Canvas上绘制,就像画家在画布上作画:
- Canvas(画布):提供绘制表面
- Paint(画笔):定义绘制样式(颜色、粗细等)
- 绘制方法:drawCircle、drawRect、drawPath等
📊 实战:圆形进度指示器
让我们创建一个自定义的圆形进度指示器:
dart
/// 📊 圆形进度指示器(就像钟表的表盘)
///
/// 这个组件展示了CustomPainter的使用方法:
/// - 可自定义进度值(0.0-1.0)
/// - 可调节大小和线条粗细
/// - 中心显示百分比数值
class CircularProgressPainter extends StatelessWidget {
final double progress; // 进度值,范围 0.0-1.0
final double size; // 组件大小
final double strokeWidth; // 线条粗细
final Color color; // 进度颜色
const CircularProgressPainter({
Key? key,
required this.progress,
this.size = 100,
this.strokeWidth = 8,
this.color = Colors.blue,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return CustomPaint(
size: Size(size, size),
// 🖌️ 使用自定义绘制器
painter: _CircularProgressPainter(
progress: progress,
strokeWidth: strokeWidth,
color: color,
),
// 📝 在中心显示百分比
child: Container(
width: size,
height: size,
child: Center(
child: Text(
'${(progress * 100).toInt()}%',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: size * 0.15,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: color,
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
/// 🎨 自定义绘制器实现
class _CircularProgressPainter extends CustomPainter {
final double progress;
final double strokeWidth;
final Color color;
_CircularProgressPainter({
required this.progress,
required this.strokeWidth,
required this.color,
});
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
// 🎯 计算圆心和半径
final center = Offset(size.width / 2, size.height / 2);
final radius = (size.width - strokeWidth) / 2;
// 🔘 绘制背景圆环
final backgroundPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey[300]!
..strokeWidth = strokeWidth
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke;
canvas.drawCircle(center, radius, backgroundPaint);
// 🌈 绘制进度圆弧
final progressPaint = Paint()
..color = color
..strokeWidth = strokeWidth
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeCap = StrokeCap.round;
// 📊 计算进度对应的弧度
final sweepAngle = 2 * 3.14159 * progress;
canvas.drawArc(
Rect.fromCircle(center: center, radius: radius),
-3.14159 / 2, // 从顶部开始
sweepAngle, // 扫过角度
false, // 不连接到圆心
progressPaint,
);
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) => true;
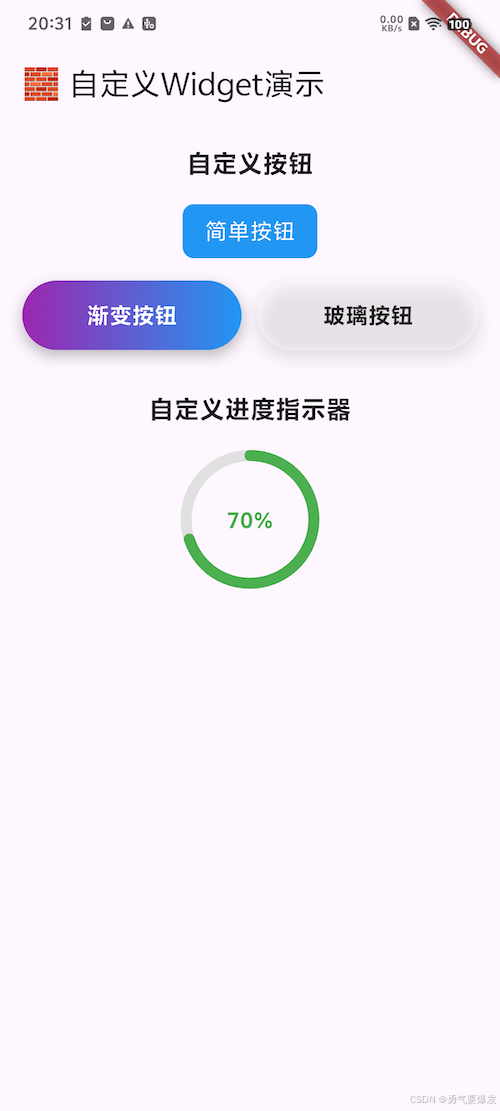
}🎮 完整演示应用
现在让我们把所有组件组合到一个演示应用中:
dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
/// 🚀 应用程序入口点
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(
home: CustomWidgetDemo(),
));
}
/// 📱 自定义Widget演示页面
class CustomWidgetDemo extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('🧱 自定义Widget演示')),
body: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
children: [
// 🎨 自定义按钮演示区域
Text('自定义按钮', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 18, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
SizedBox(height: 16),
SimpleTextButton(text:"简单按钮", onPressed: () => {
print('点击了普通按钮')
}, ),
SizedBox(height: 16),
// 📐 使用Row布局让两个按钮水平排列
Row(
children: [
// 🌈 渐变按钮
Expanded(
child: GradientButton(
text: '渐变按钮',
colors: [Colors.purple, Colors.blue],
onPressed: () => print('点击了渐变按钮'),
),
),
SizedBox(width: 12),
// 🔮 玻璃态按钮
Expanded(
child: GlassButton(
text: '玻璃按钮',
onPressed: () => print('点击了玻璃按钮'),
),
),
],
),
SizedBox(height: 30),
// 📊 自定义进度指示器演示区域
Text('自定义进度指示器', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 18, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
SizedBox(height: 16),
// 🎯 圆形进度指示器
CircularProgressPainter(
progress: 0.7,
size: 100,
strokeWidth: 8,
color: Colors.green,
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
🚀 第五步:优化与最佳实践
🎯 核心知识点总结
🧱 自定义Widget的类型
-
StatelessWidget - 无状态组件
- 适用于静态UI组件
- 性能更好,推荐优先使用
-
StatefulWidget - 有状态组件
- 适用于需要状态管理的动态组件
- 可以响应用户交互和数据变化
🎨 设计原则
- 单一职责:每个Widget只负责一个功能
- 可复用性:设计时考虑在不同场景下的复用
- 参数化:通过构造函数参数实现灵活配置
- 性能优化:合理使用const构造函数
💡 最佳实践
✅ 推荐做法
dart
// 1. 使用详细的文档注释
/// 📊 这是一个自定义的进度条组件
///
/// 支持以下功能:
/// - 自定义颜色和大小
/// - 动画效果
/// - 百分比显示
class MyProgressBar extends StatelessWidget {
// 2. 为必需参数添加required关键字
const MyProgressBar({
Key? key,
required this.progress,
this.color = Colors.blue, // 3. 提供合理的默认值
}) : super(key: key);
final double progress;
final Color color;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// 4. 使用const构造函数优化性能
return const SizedBox();
}
}❌ 避免的做法
dart
// ❌ 缺少文档注释
class BadWidget extends StatelessWidget {
// ❌ 没有使用required关键字
BadWidget({this.text, this.onPressed});
final String? text;
final VoidCallback? onPressed;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// ❌ 每次都创建新对象
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () => print('clicked'), // ❌ 硬编码逻辑
child: Container(
// ❌ 硬编码数值,缺乏灵活性
width: 200,
height: 50,
child: Text(text ?? ''),
),
);
}
}🔧 性能优化技巧
⭐️这些技巧会在后面的文章中着重讲解
1. 使用const构造函数
dart
// ✅ 好的做法
const GradientButton(
text: '按钮',
colors: [Colors.blue, Colors.purple],
onPressed: _handlePress,
)
// ❌ 避免:每次都创建新对象
GradientButton(
text: '按钮',
colors: [Colors.blue, Colors.purple],
onPressed: () => print('clicked'),
)2. 合理使用RepaintBoundary
dart
// 对于复杂的自定义绘制组件,使用RepaintBoundary隔离重绘
RepaintBoundary(
child: CustomPaint(
painter: MyComplexPainter(),
),
)3. 优化shouldRepaint逻辑
dart
class MyPainter extends CustomPainter {
final Color color;
final double progress;
MyPainter({required this.color, required this.progress});
@override
bool shouldRepaint(MyPainter oldDelegate) {
// 只有当关键属性改变时才重绘
return oldDelegate.color != color ||
oldDelegate.progress != progress;
}
}🎯 组件组合示例
dart
// 将多个自定义Widget组合使用
Widget buildActionButtons() {
return Row(
children: [
Expanded(
child: GradientButton(
text: '确认',
colors: [Colors.green, Colors.teal],
onPressed: _confirm,
),
),
SizedBox(width: 12),
Expanded(
child: GlassButton(
text: '取消',
onPressed: _cancel,
),
),
],
);
}📚 进阶学习方向
-
🎨 高级绘制技巧
- 贝塞尔曲线绘制
- 渐变和阴影效果
- 图片和文本绘制
-
🔄 状态管理集成
- 与Provider结合
- 与Bloc模式集成
- 响应式数据绑定
-
📱 平台适配
- iOS和Android差异处理
- 响应式设计
- 无障碍功能支持
-
⚡ 性能优化
- Widget树优化
- 内存管理
- 渲染性能调优
🎉 总结
通过本指南的学习,你已经掌握了:
- 🎯 基础概念:理解了什么是自定义Widget以及使用场景
- 🏗️ 基本结构:掌握了StatelessWidget和StatefulWidget的选择
- 🎨 实战技能:从简单按钮到复杂绘制组件的完整实现
- 📊 进阶技巧:学会了使用CustomPainter进行自定义绘制
- 🚀 最佳实践:了解了性能优化和代码规范
现在你可以:
- 创建美观实用的自定义UI组件
- 使用CustomPainter实现复杂的图形绘制
- 编写高性能、可维护的Flutter代码
- 将自定义Widget应用到实际项目中
欢迎点赞,关注,收藏,我们一起探索Flutter的无限可能,创造出更加精彩的用户界面!✨