引言:从单一架构到多元生态
2017年,Vaswani等人发表的《Attention is All You Need》论文提出了Transformer架构,彻底改变了自然语言处理领域的发展轨迹。最初的Transformer采用编码器-解码器结构,为机器翻译任务而设计。然而,在随后的发展中,研究人员发现这种架构的各个组件具有独立的实用价值,从而衍生出三大主流技术路线:仅编码器架构 、仅解码器架构 和编码器-解码器架构。
本文将系统梳理Transformer架构的主要变体,分析其技术特点、适用场景及演化逻辑,为研究者和工程师提供全面的技术图谱。
1. 原始Transformer:技术基石
原始Transformer架构奠定了所有变体的基础,其核心组件包括:
1.1 自注意力机制
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_k = d_model // num_heads
self.W_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.W_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.W_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.W_o = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
def scaled_dot_product_attention(self, Q, K, V, mask=None):
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(self.d_k)
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
attention_weights = torch.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
output = torch.matmul(attention_weights, V)
return output, attention_weights1.2 位置编码
python
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, max_len=5000):
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model)
position = torch.arange(0, max_len, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(1)
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2).float() *
(-math.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0)
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.pe[:, :x.size(1)]2. 仅编码器架构:理解型模型的崛起
2.1 BERT:双向编码的代表
BERT(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)开启了预训练-微调范式的新时代。其核心创新在于:
技术特点:
- 掩码语言建模(MLM):随机遮盖15%的token进行预测
- 下一句预测(NSP):判断两个句子是否连续
- 纯编码器架构,适合理解任务
python
# BERT风格的掩码语言建模示例
class MLMHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, vocab_size):
super(MLMHead, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.decoder = nn.Linear(d_model, vocab_size)
def forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = torch.gelu(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.layer_norm(hidden_states)
prediction_scores = self.decoder(hidden_states)
return prediction_scores2.2 RoBERTa、ALBERT等改进变体
基于BERT的改进主要集中在预训练策略和模型效率上:
| 模型 | 核心改进 | 参数量 | 主要特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-base | 基准模型 | 110M | MLM + NSP, 12层 |
| RoBERTa | 优化训练 | 125M | 移除NSP, 更大批次, 更多数据 |
| ALBERT | 参数效率 | 12M | 参数共享, 因式分解嵌入 |
| DistilBERT | 模型压缩 | 66M | 知识蒸馏, 减少层数 |
| ELECTRA | 样本效率 | 110M | 替换token检测, 更高效预训练 |
3. 仅解码器架构:生成式模型的辉煌
3.1 GPT系列:自回归生成的演进
GPT(Generative Pre-trained Transformer)系列代表了仅解码器架构的发展主线:
技术演进路径:
- GPT-1:验证预训练+微调的有效性
- GPT-2:证明零样本学习能力,参数量15亿
- GPT-3:突破规模限制,参数量1750亿
- GPT-4:多模态能力,混合专家架构
python
class GPTBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, dropout=0.1):
super(GPTBlock, self).__init__()
self.ln1 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.attn = MultiHeadAttention(d_model, num_heads)
self.ln2 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(d_model, 4 * d_model),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(4 * d_model, d_model),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
)
def forward(self, x, attention_mask=None):
# 自注意力 + 残差连接
attn_output, _ = self.attn(self.ln1(x), self.ln1(x), self.ln1(x), attention_mask)
x = x + attn_output
# 前馈网络 + 残差连接
ff_output = self.mlp(self.ln2(x))
x = x + ff_output
return x3.2 因果自注意力机制
仅解码器架构的核心是因果自注意力,确保每个位置只能关注之前的位置:
python
def causal_attention_mask(seq_len, device):
"""生成因果注意力掩码"""
mask = torch.tril(torch.ones(seq_len, seq_len, device=device))
return mask.view(1, 1, seq_len, seq_len)
# 在注意力计算中的应用
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(d_k)
causal_mask = causal_attention_mask(seq_len, Q.device)
scores = scores.masked_fill(causal_mask == 0, -1e9)
attention_weights = torch.softmax(scores, dim=-1)4. 编码器-解码器架构:序列到学习的延续
4.1 T5:文本到文本的统一框架
T5(Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer)将所有NLP任务统一为文本到文本的格式:
python
class T5Architecture(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, d_model, num_layers, num_heads):
super(T5Architecture, self).__init__()
self.encoder = TransformerEncoder(vocab_size, d_model, num_layers, num_heads)
self.decoder = TransformerDecoder(vocab_size, d_model, num_layers, num_heads)
def forward(self, encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs):
encoder_output = self.encoder(encoder_inputs)
decoder_output = self.decoder(decoder_inputs, encoder_output)
return decoder_output4.2 BART:去噪自编码器方法
BART结合了BERT的去噪预训练和GPT的自回归生成:
预训练任务:
- 文本填充
- 句子重排
- 文档旋转
- token删除
5. 稀疏与高效架构:应对计算挑战
5.1 稀疏注意力变体
python
class SparseAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, block_size=64):
super(SparseAttention, self).__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.block_size = block_size
self.d_k = d_model // num_heads
def block_sparse_attention(self, Q, K, V):
batch_size, seq_len, d_model = Q.shape
# 将序列分块
num_blocks = seq_len // self.block_size
Q_blocks = Q.view(batch_size, num_blocks, self.block_size, d_model)
K_blocks = K.view(batch_size, num_blocks, self.block_size, d_model)
# 块间注意力计算
output_blocks = []
for i in range(num_blocks):
# 每个块只与相邻块计算注意力
start_block = max(0, i - 1)
end_block = min(num_blocks, i + 2)
relevant_K = K_blocks[:, start_block:end_block, :, :]
relevant_V = V_blocks[:, start_block:end_block, :, :]
# 计算块间注意力
block_output = self.compute_block_attention(
Q_blocks[:, i:i+1, :, :],
relevant_K,
relevant_V
)
output_blocks.append(block_output)
return torch.cat(output_blocks, dim=1)5.2 高效变体对比
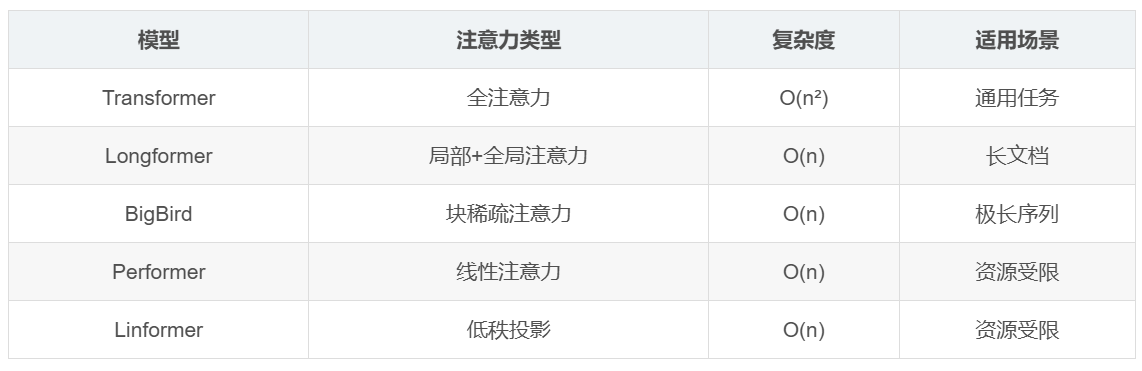
| 模型 | 注意力类型 | 复杂度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer | 全注意力 | O(n²) | 通用任务 |
| Longformer | 局部+全局注意力 | O(n) | 长文档 |
| BigBird | 块稀疏注意力 | O(n) | 极长序列 |
| Performer | 线性注意力 | O(n) | 资源受限 |
| Linformer | 低秩投影 | O(n) | 资源受限 |
6. 专家混合架构:规模化的新范式
6.1 Switch Transformer
python
class MoELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_experts, expert_capacity):
super(MoELayer, self).__init__()
self.experts = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(d_model, 4 * d_model),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(4 * d_model, d_model)
) for _ in range(num_experts)
])
self.gate = nn.Linear(d_model, num_experts)
self.num_experts = num_experts
self.expert_capacity = expert_capacity
def forward(self, x):
# 门控网络决定路由
gate_scores = self.gate(x)
routing_weights = torch.softmax(gate_scores, dim=-1)
# 选择top-k专家
top_k = 2 # 通常选择1或2个专家
routing_weights, selected_experts = torch.topk(routing_weights, top_k, dim=-1)
# 归一化权重
routing_weights = routing_weights / routing_weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
# 专家计算
final_output = torch.zeros_like(x)
for expert_idx in range(self.num_experts):
expert_mask = (selected_experts == expert_idx).any(dim=-1)
if expert_mask.any():
expert_input = x[expert_mask]
expert_output = self.experts[expert_idx](expert_input)
# 加权求和
expert_weights = routing_weights[expert_mask]
final_output[expert_mask] += expert_output * expert_weights.unsqueeze(-1)
return final_output7. 技术演进趋势与未来展望
7.1 架构融合趋势
当前的技术发展显示出明显的融合趋势:
- 编码器-解码器的边界模糊化:如UNILM统一了理解和生成任务
- 稀疏与稠密注意力结合:根据任务需求动态选择注意力模式
- 预训练范式统一:各种架构逐渐采用相似的预训练目标
7.2 关键技术挑战
python
# 未来架构可能的发展方向示例
class AdaptiveTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
# 动态选择注意力机制
self.attention_router = AttentionRouter(d_model=config.d_model)
# 可变的计算路径
self.computation_path = DynamicComputationPath()
def forward(self, x, task_type=None):
# 根据输入特性和任务类型选择最佳计算路径
attention_type = self.attention_router(x, task_type)
if attention_type == "sparse":
output = self.sparse_attention(x)
elif attention_type == "dense":
output = self.dense_attention(x)
elif attention_type == "linear":
output = self.linear_attention(x)
return output7.3 性能对比分析
下表展示了不同架构变体在各项指标上的表现:
| 架构类型 | 代表模型 | 训练效率 | 推理速度 | 可扩展性 | 任务适应性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 仅编码器 | BERT | 高 | 高 | 中等 | 理解任务优秀 |
| 仅解码器 | GPT系列 | 中等 | 中等 | 优秀 | 生成任务优秀 |
| 编码器-解码器 | T5 | 较低 | 较低 | 良好 | 通用性强 |
| 稀疏架构 | Longformer | 中等 | 高 | 优秀 | 长序列处理 |
| 混合专家 | Switch Transformer | 高 | 可变 | 极优秀 | 大规模预训练 |
结论
Transformer架构的演化路径体现了深度学习领域的技术发展逻辑:从通用架构到专用优化,从单一范式到多元融合。BERT和GPT作为两大技术路线代表,分别推动了理解型和生成型模型的发展,而后续的变体则在效率、规模和适用性方面不断突破。