目录
为什么需要Debug
编好的程序在执行过程中如果出现错误,该如何查找或定位错误呢?简单的代码直接就可以看出来,但如果代码比较复杂,就需要借助程序调试来查找错误了
运行编写好的程序时,可能出现的几种情况:
> 情况1:没有任何bug,程序执行正确!
===============如果出现如下的三种情况,都又必要使用debug===============
> 情况2:运行以后,出现了错误或异常信息。但是通过日志文件或控制台,显示了异常信息的位置。
> 情况3:运行以后,得到了结果,但是结果不是我们想要的。
> 情况4:运行以后,得到了结果,结果大概率是我们想要的。但是多次运行的话,可能会出现不是我们想要的情况。
比如:多线程情况下,处理线程安全问题。Debug(调试)
1 行断点
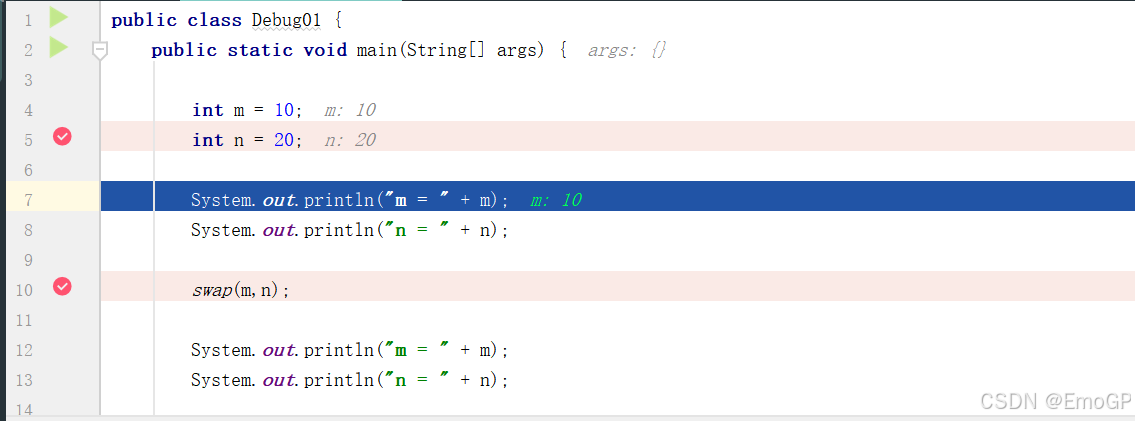
public class Debug01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m = 10;
int n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + m);
System.out.println("n = " + n);
swap(m,n);
System.out.println("m = " + m);
System.out.println("n = " + n);
}
public static void swap(int m,int n){
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
}添加如下断点
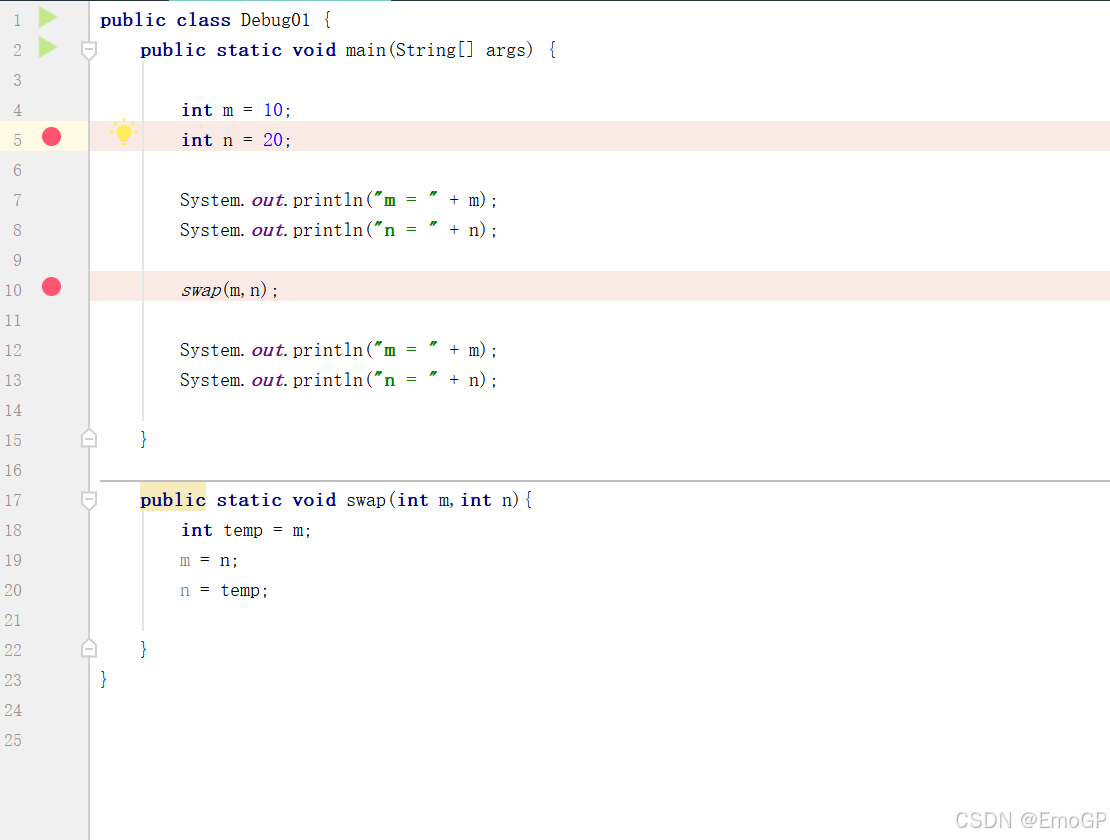
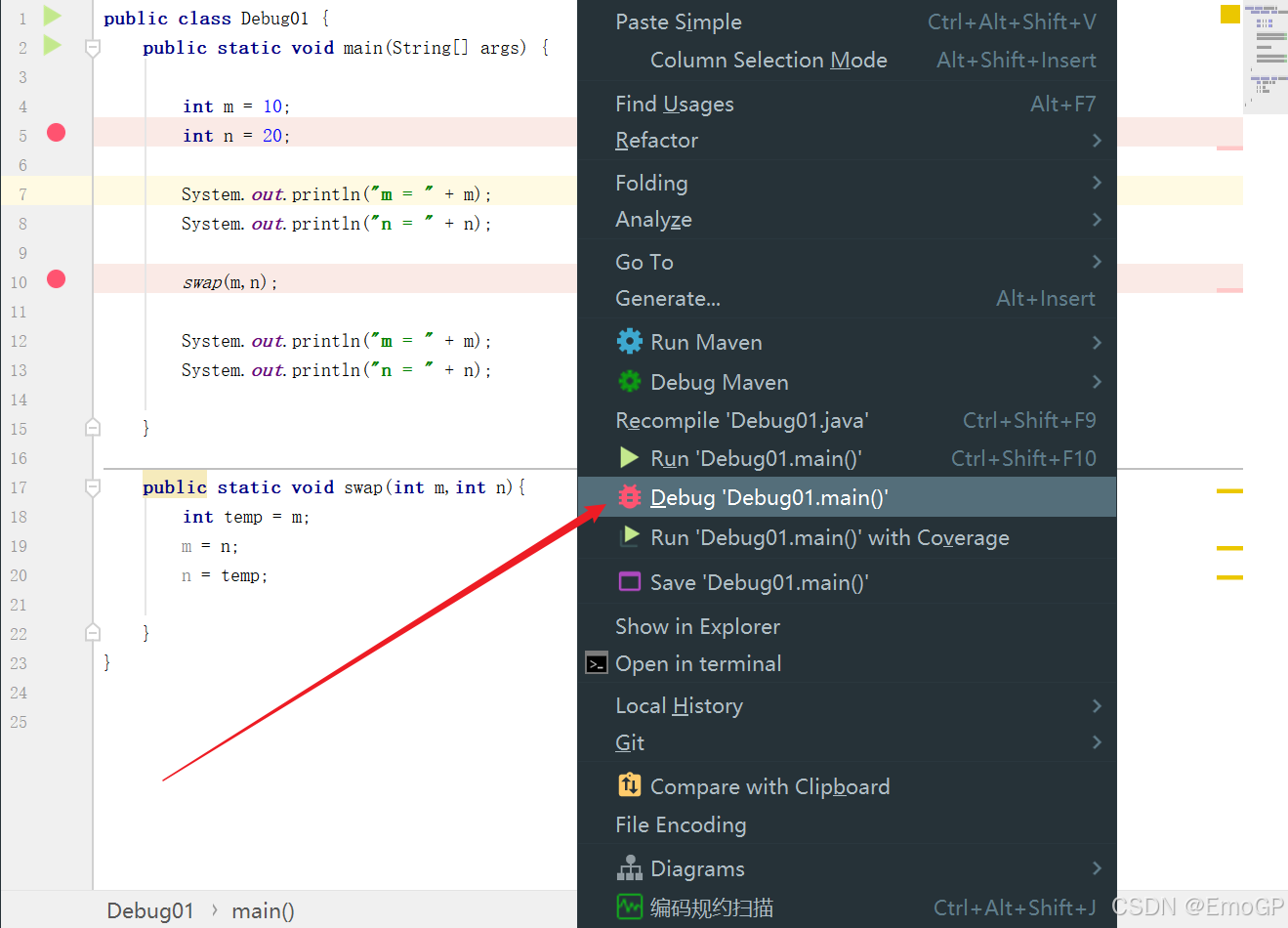
右键Debug运行
此时会运行到第一个断点的位置上
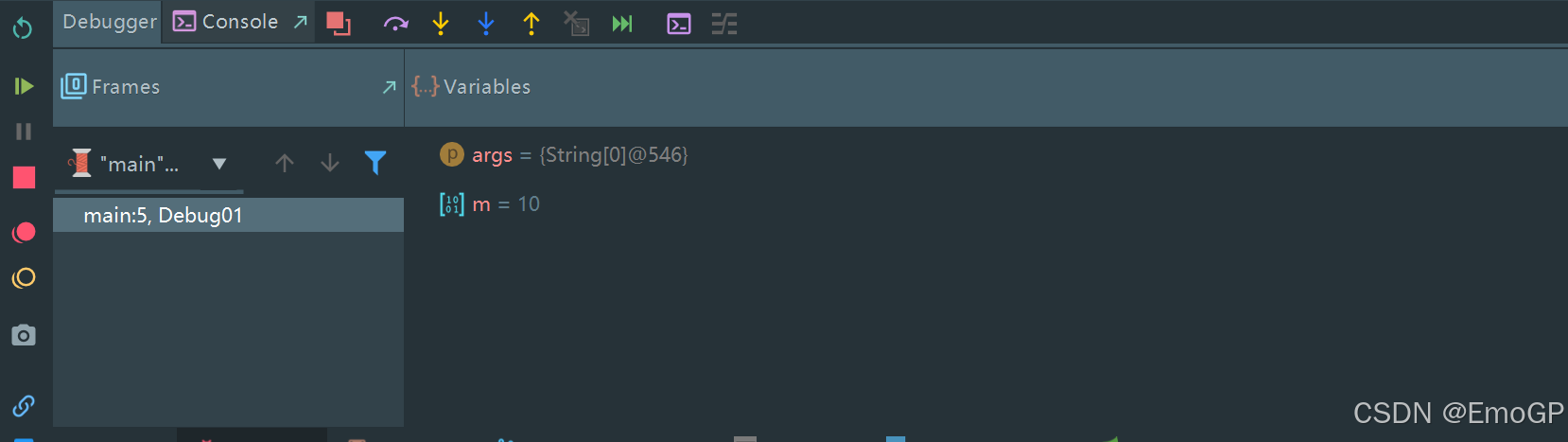
此时只是走到了断点的位置,实际上int n = 20;这一行还未执行
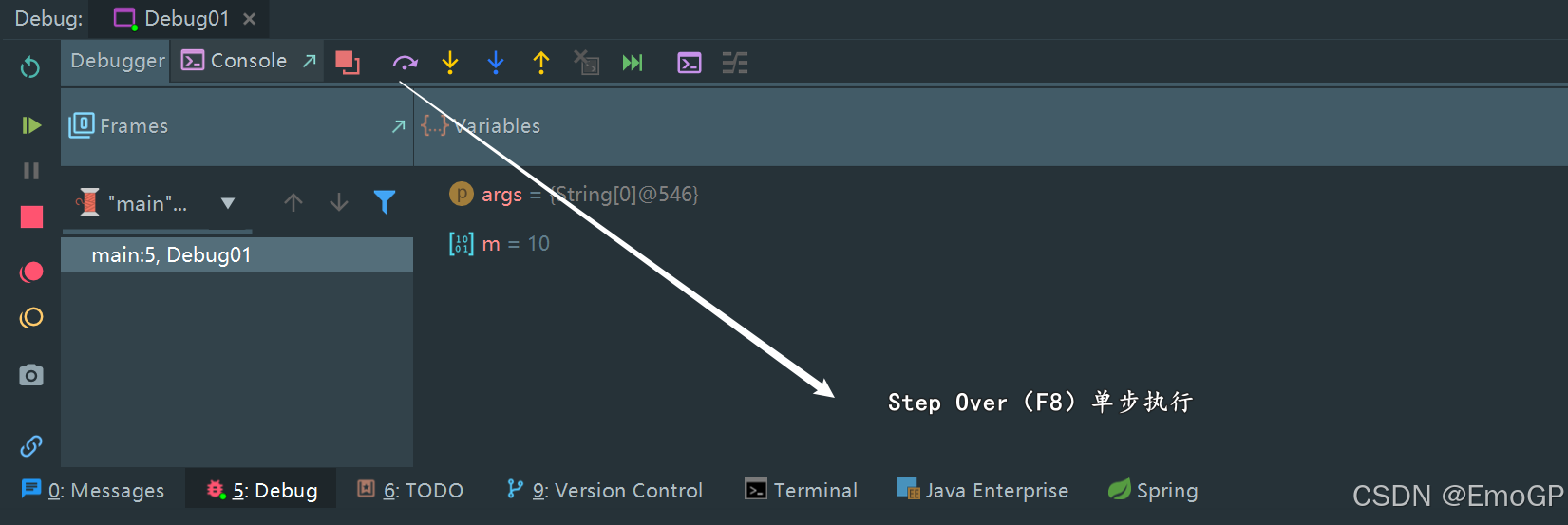
使用f8执行到如下位置
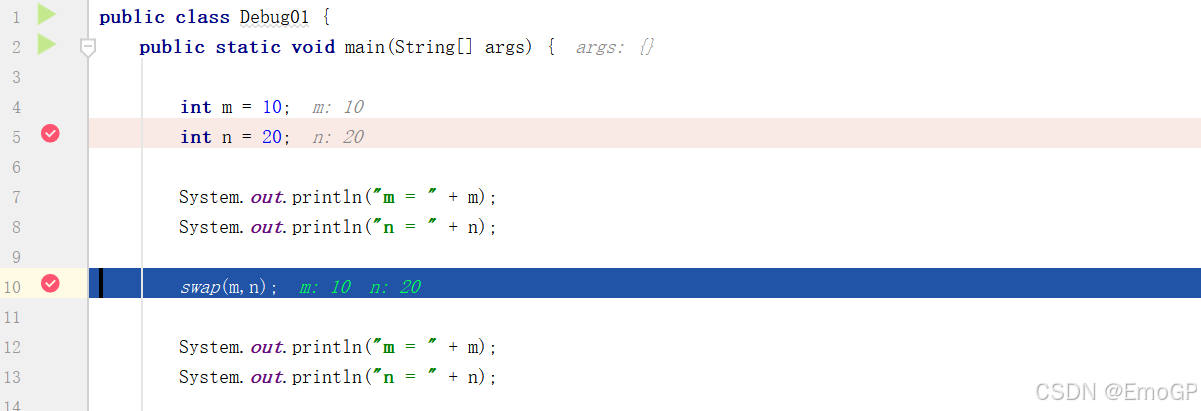
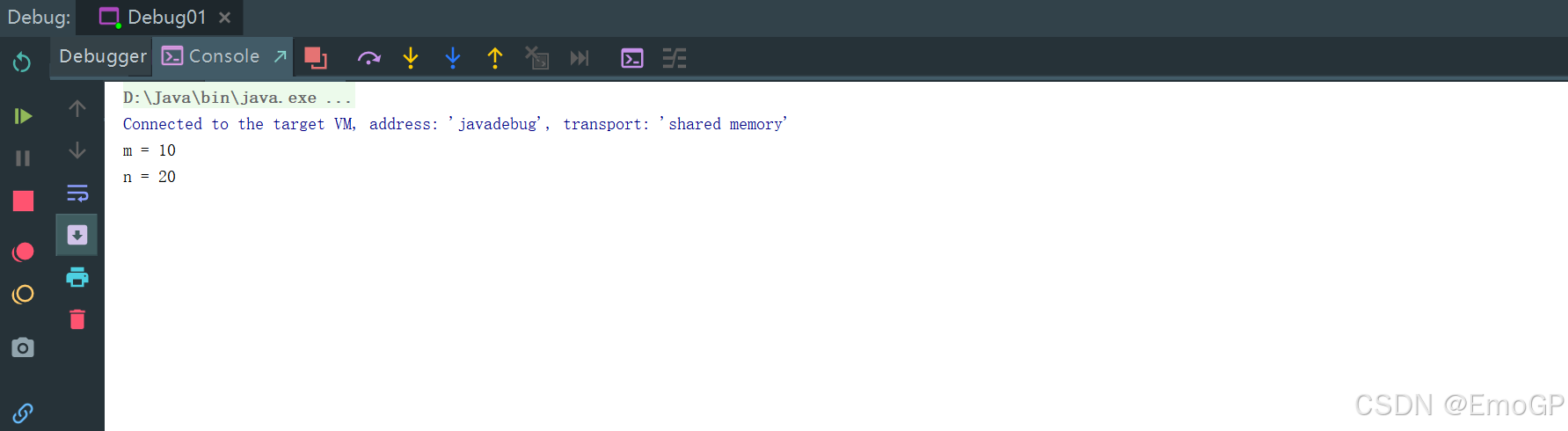
此时控制台输出如下
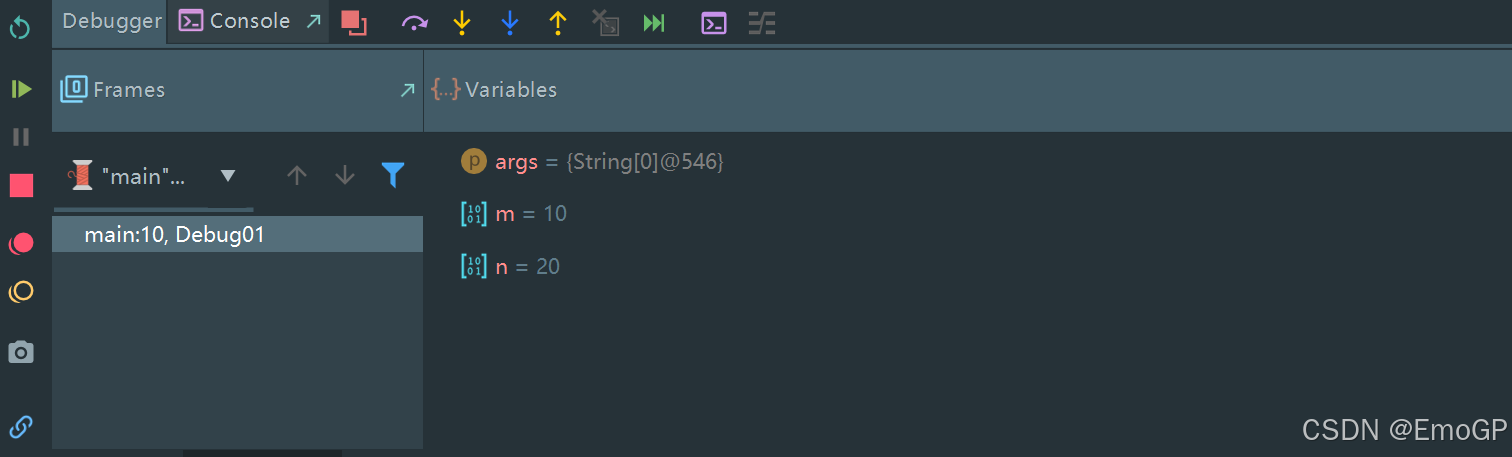

点击f7进入方法里面
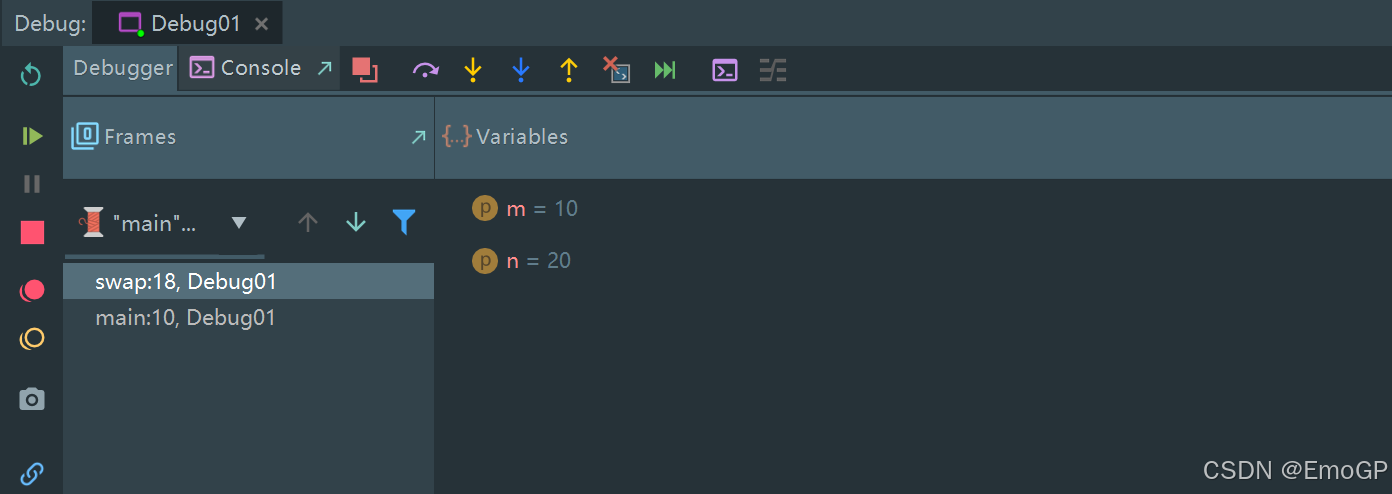
再单步执行
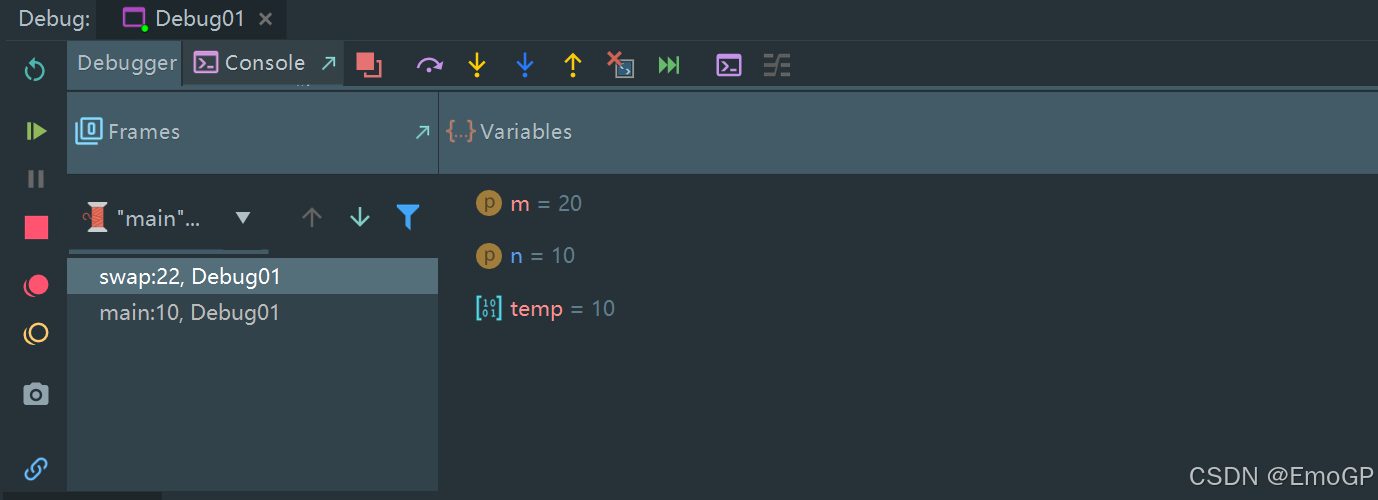
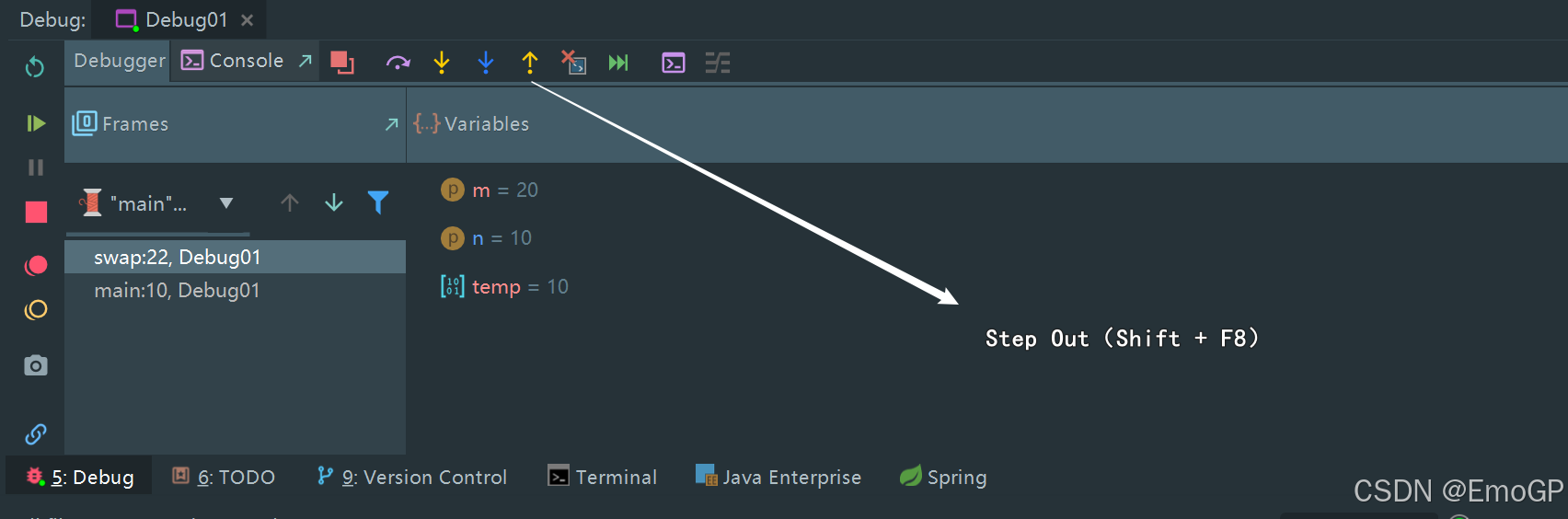
跳出方法
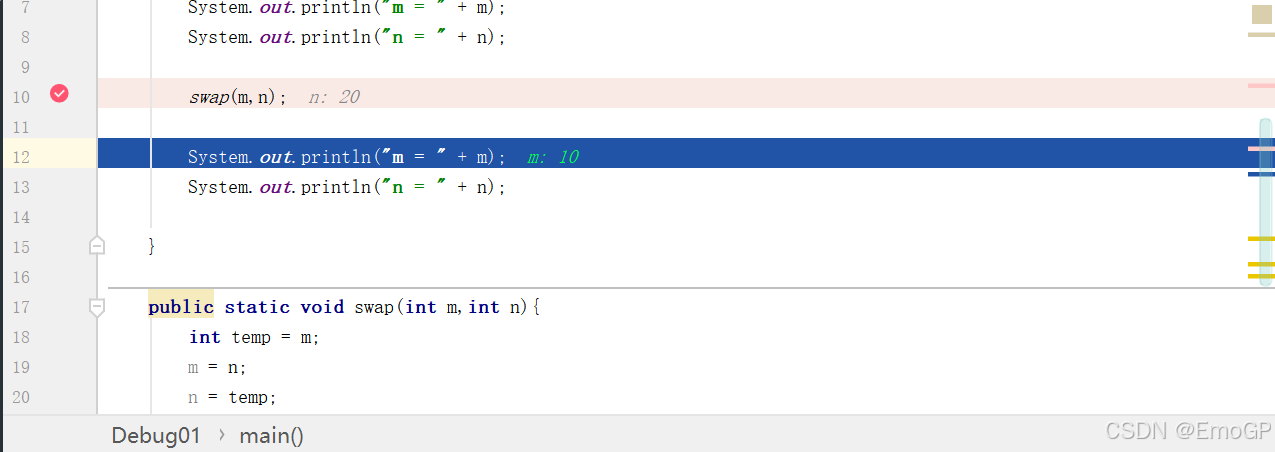
可以看到此时栈里面只有一个main方法
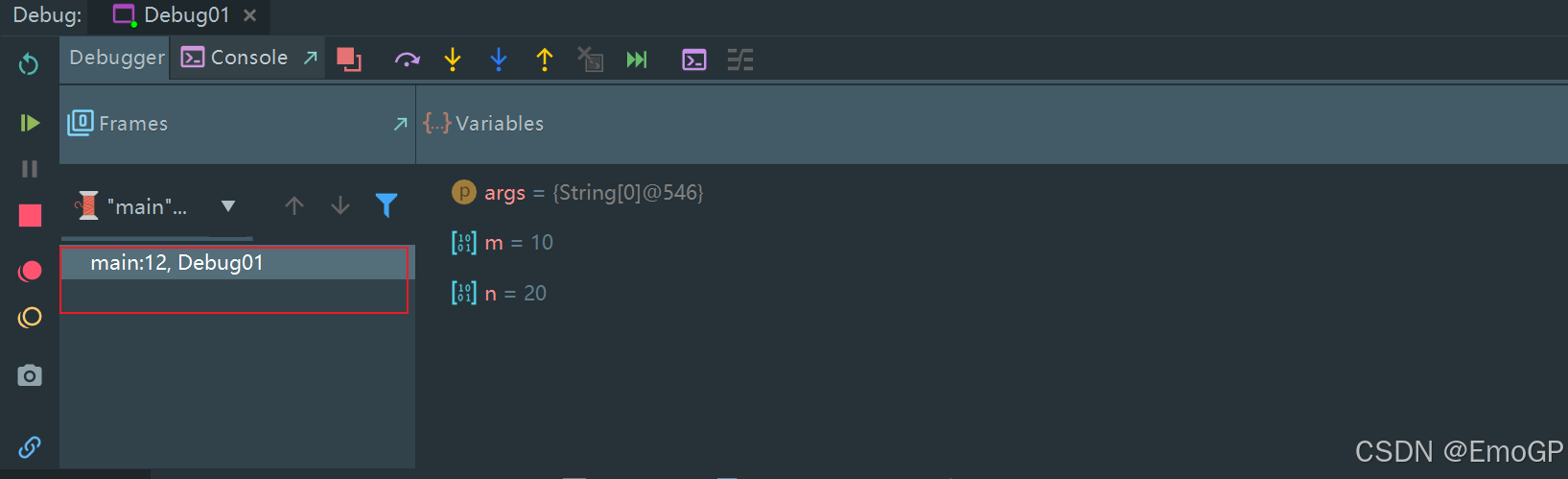
m和n的值并没有改变
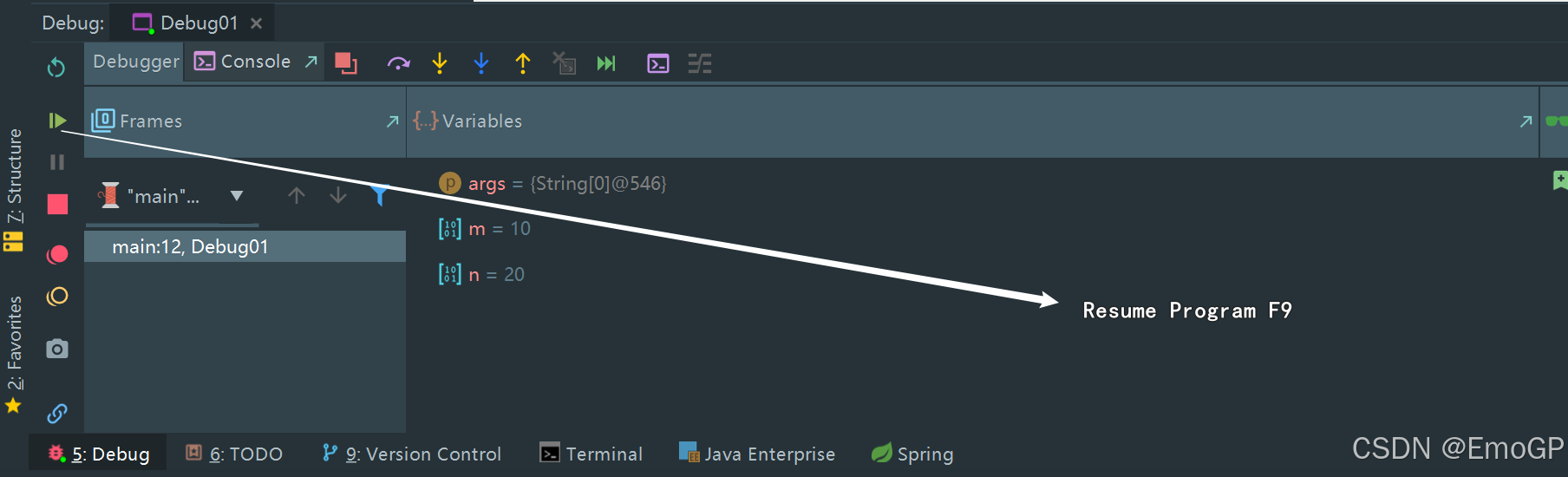
此时可以按f9,让程序结束
Resume Program:继续执行(到下一个断点 / 程序结束)
注意:
如果走到了下面这一步,想进入方法里面

此时Step Into 不起作用,需要Force Step Into
可再用Step Out退出
2 方法断点
断点设置在方法的签名上,默认当进入时,断点可以被唤醒
也可以设置在方法退出时,断点也被唤醒
在多态的场景下,在父类或接口的方法上打断点,会自动调入到子类或实现类的方法
3 字段断点
在类的属性声明上打断点,默认对属性的修改操作进行监控
4 条件断点
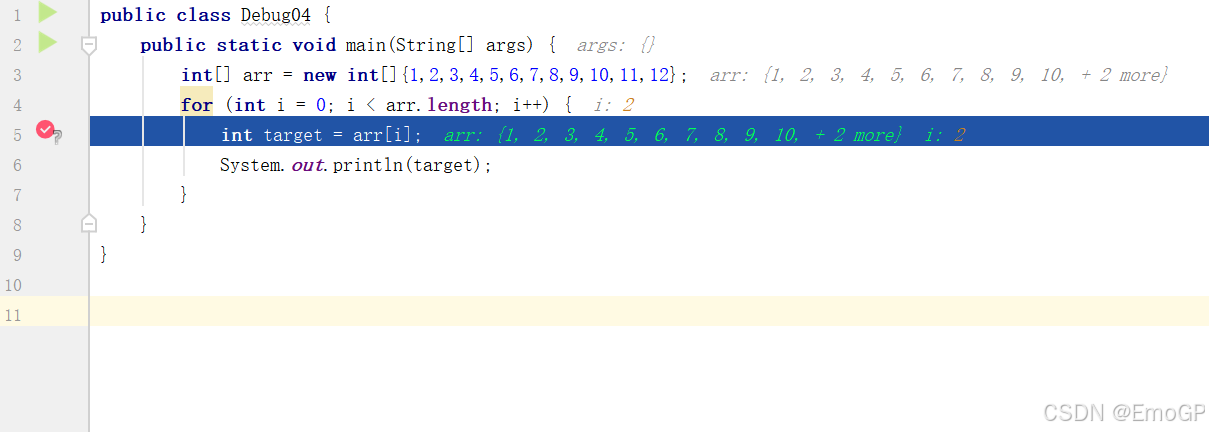
public class Debug04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int target = arr[i];
System.out.println(target);
}
}
}
添加条件
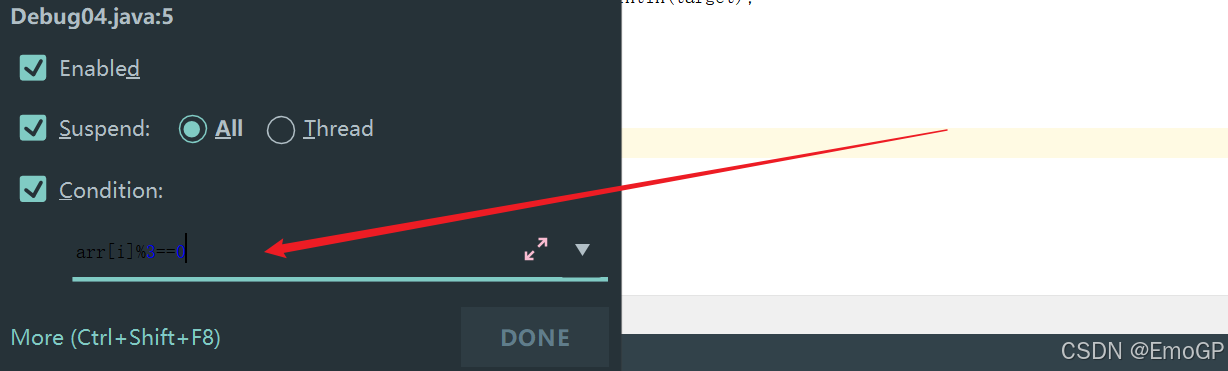
arr[i] % 3 ==05 异常断点
对异常进行跟踪,如果程序出现指定异常,程序就会执行断点,自动停住
public class Debug05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person(1001);
System.out.println(p1.getName().toUpperCase());
}
}
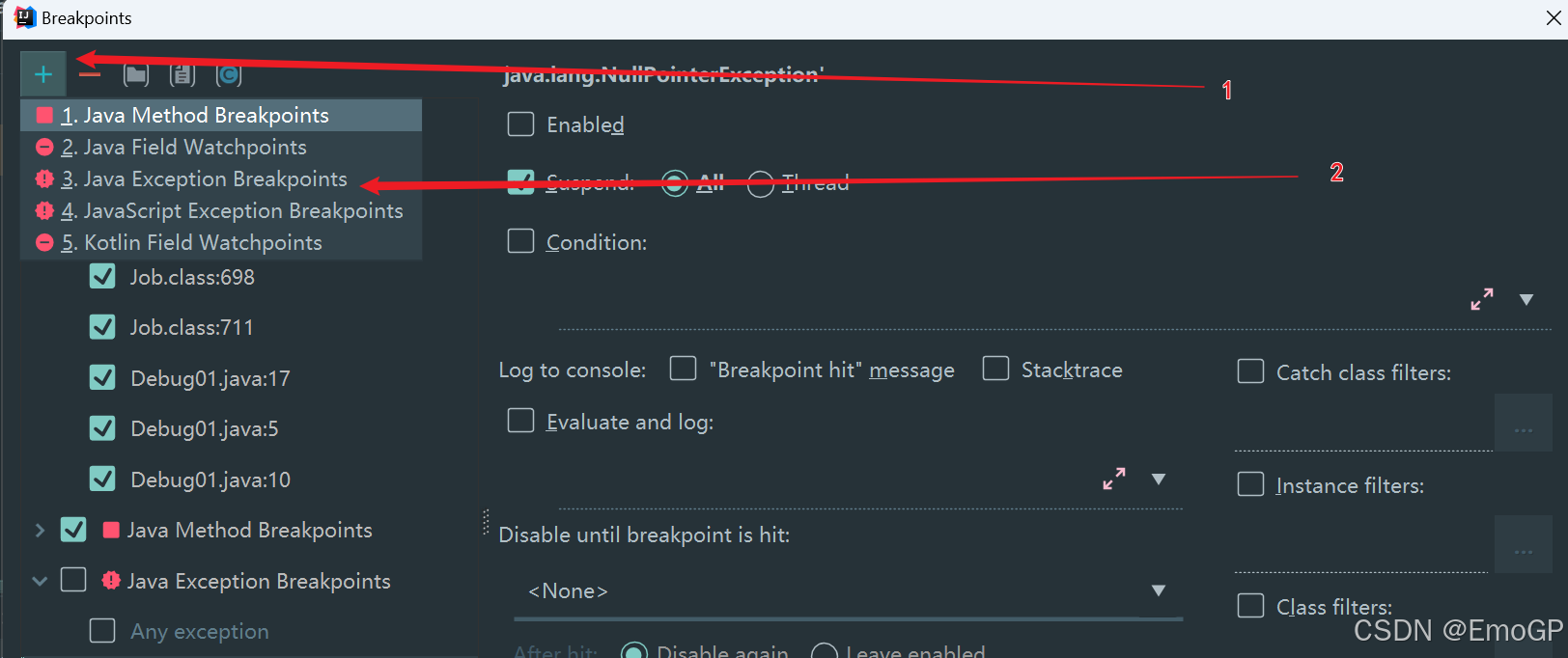
添加空指针异常
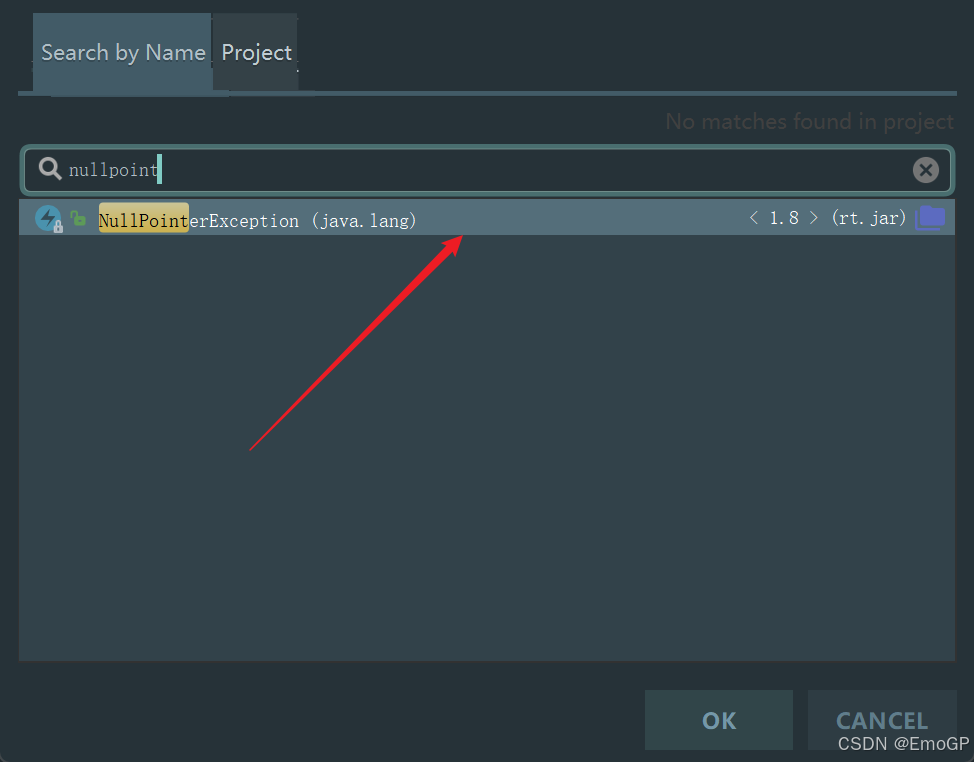
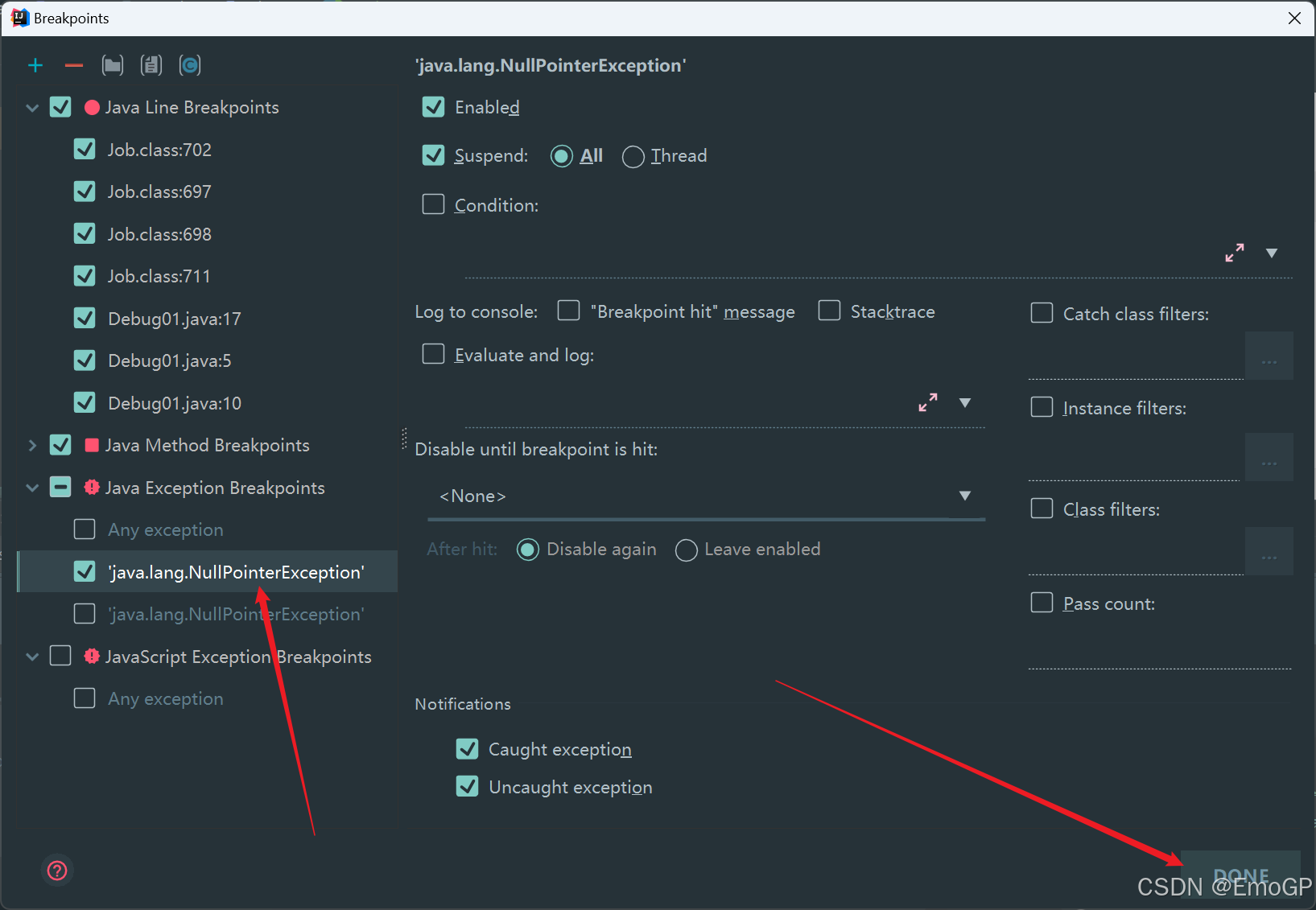
Debug程序
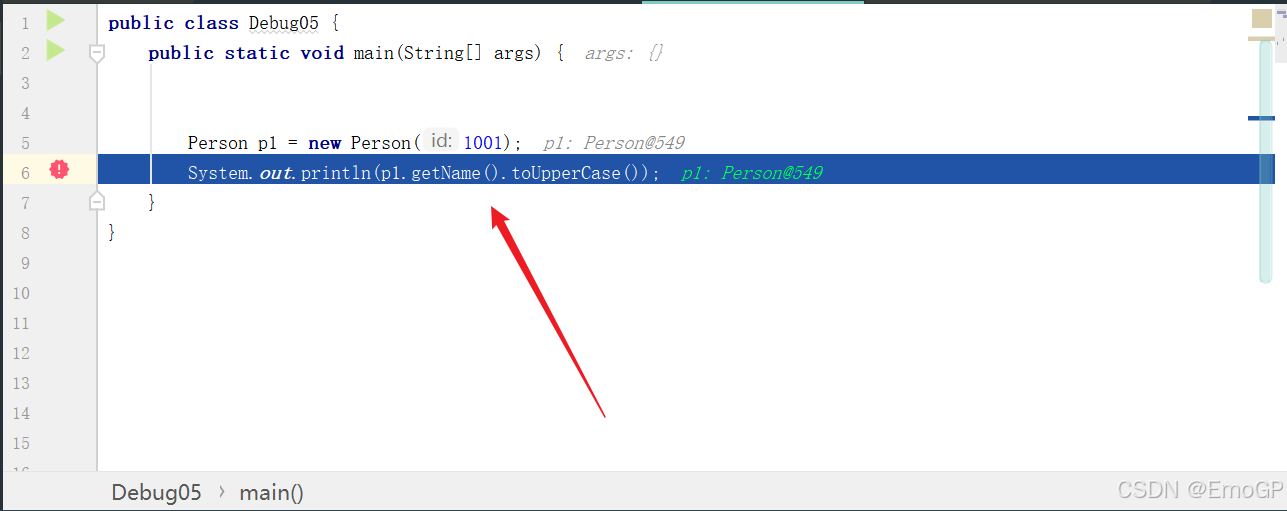
此时程序会自动停留在这行
6 线程调试
public class Debug06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test("Thread1");
test("Thread2");
}
public static void test(String threadName) {
new Thread(
() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
}
},
threadName
).start();
}
}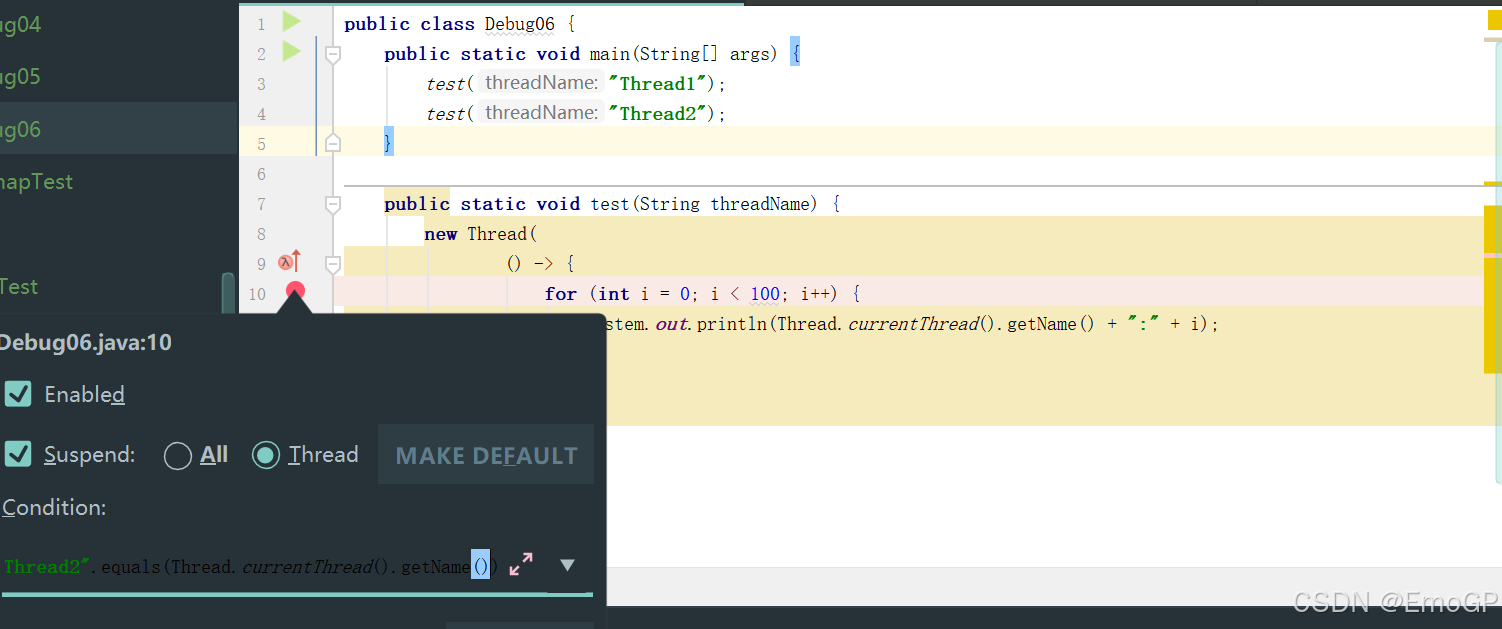
"Thread2".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())只针对Thread2进行调试
强制结束
public class Debug07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("获取请求的数据");
System.out.println("调用写入数据库的方法");
insert();
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
private static void insert() {
System.out.println("进入insert()方法");
System.out.println("获取数据库连接");
System.out.println("将数据写入数据表中");
System.out.println("写出操作完成");
System.out.println("断开连接");
}
}在如下地方添加断点
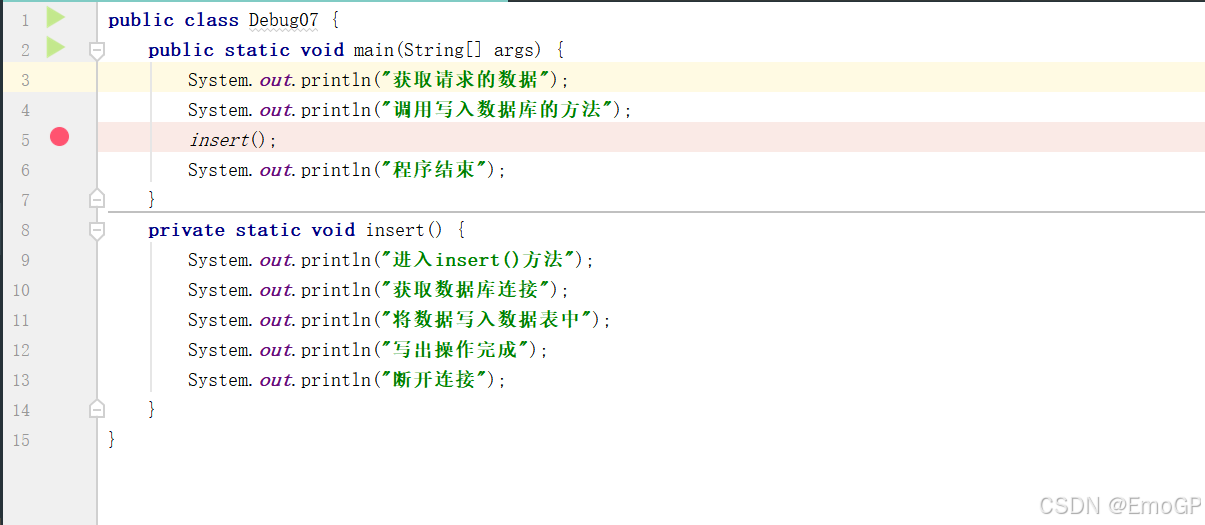
执行到如下程序的时候
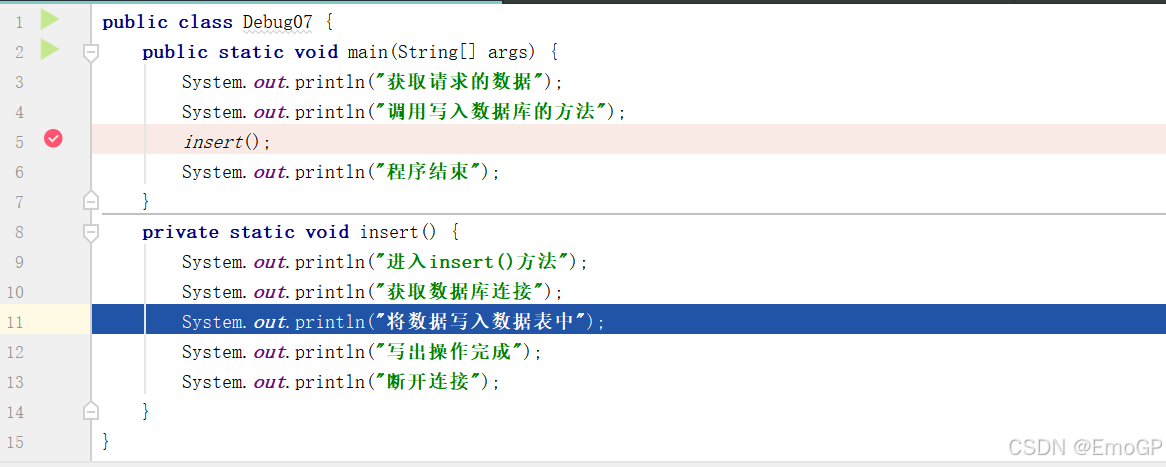
想要停止,可如下操作
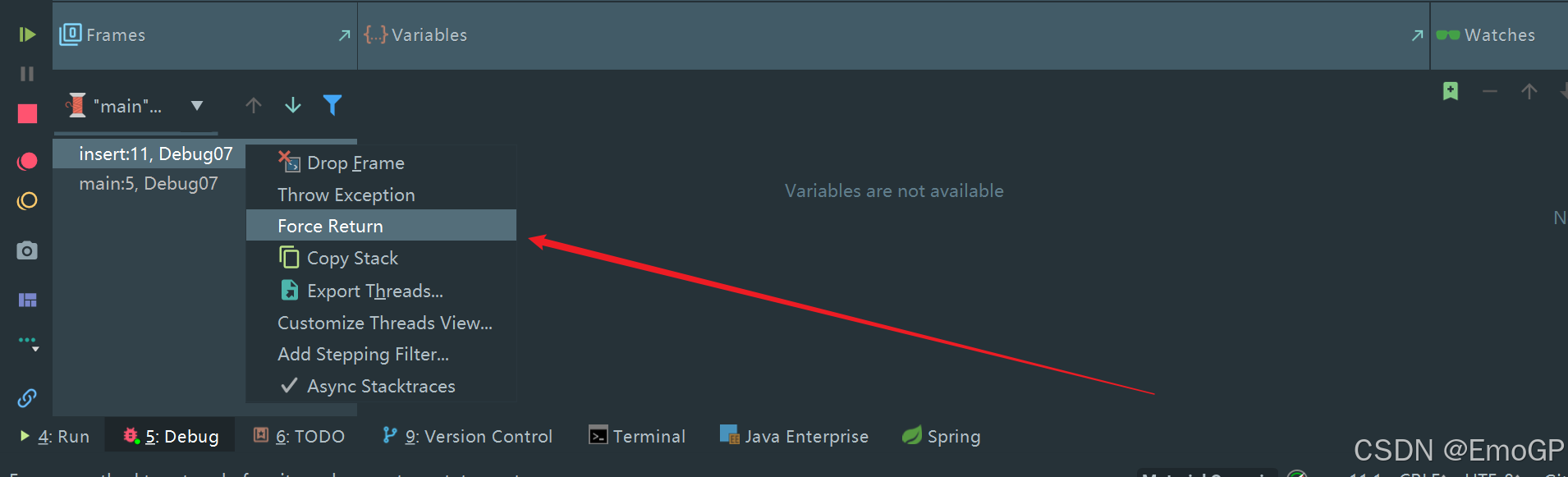
然后按f9,让剩余执行完

自定义调试数据视图
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Debug08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"高铁");
map.put(2,"网购");
map.put(3,"支付宝");
map.put(4,"共享单车");
System.out.println(map);
}
}在如下位置添加断点
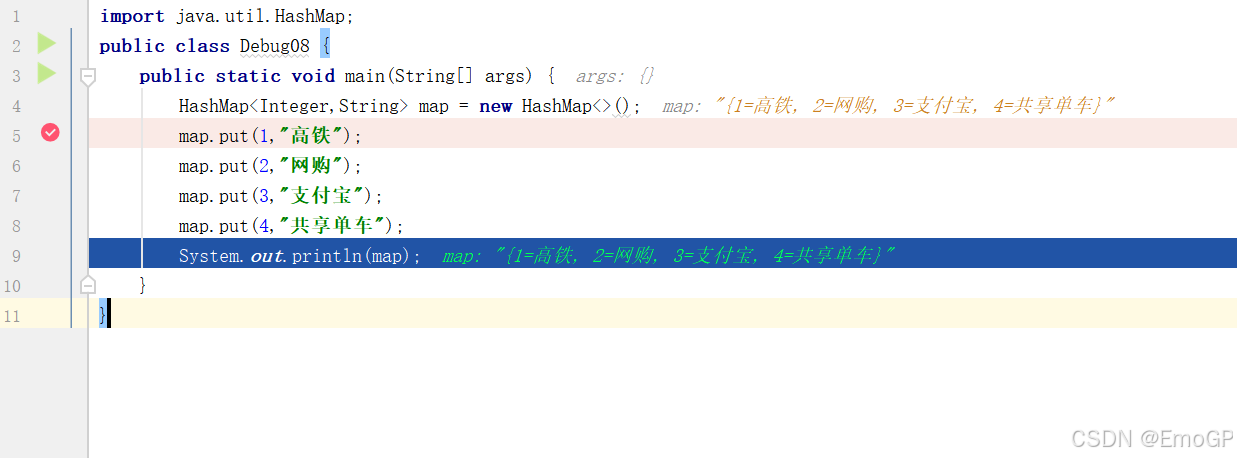
进行Debug
强制进入方法
Step out
再次强制进入
退出,单步执行
想要查看table内容,需要进行配置
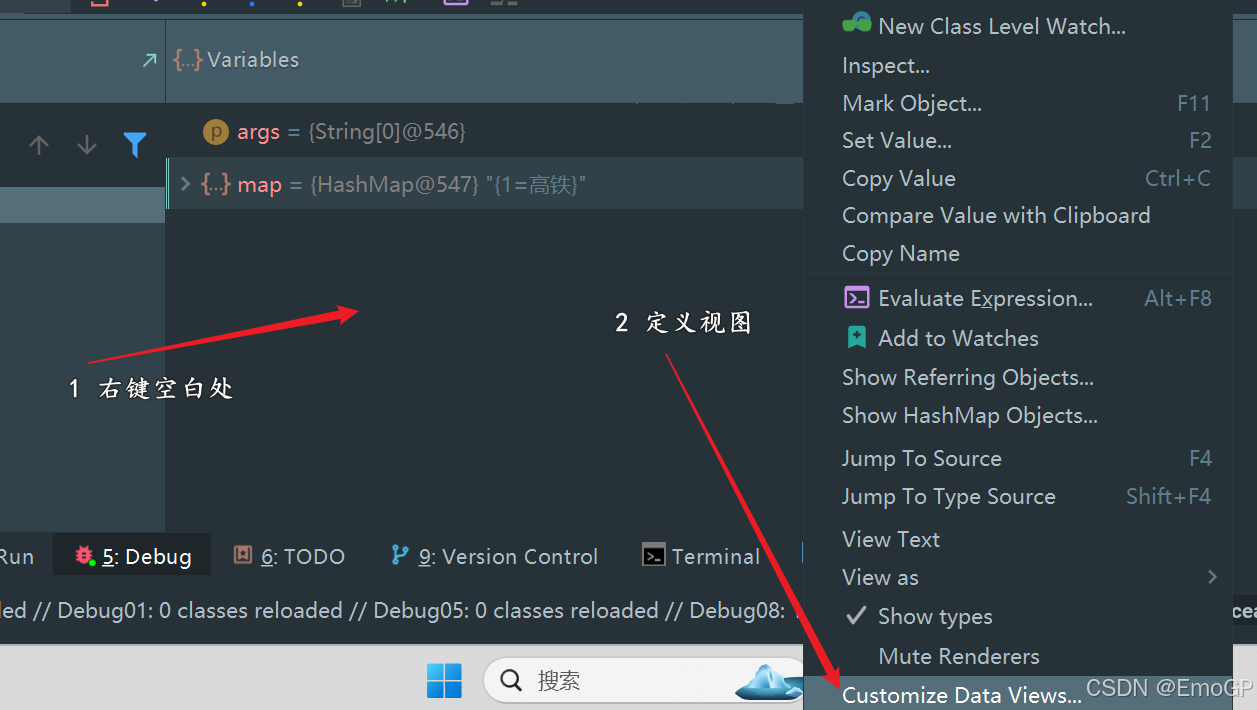

此时可以看到table内容
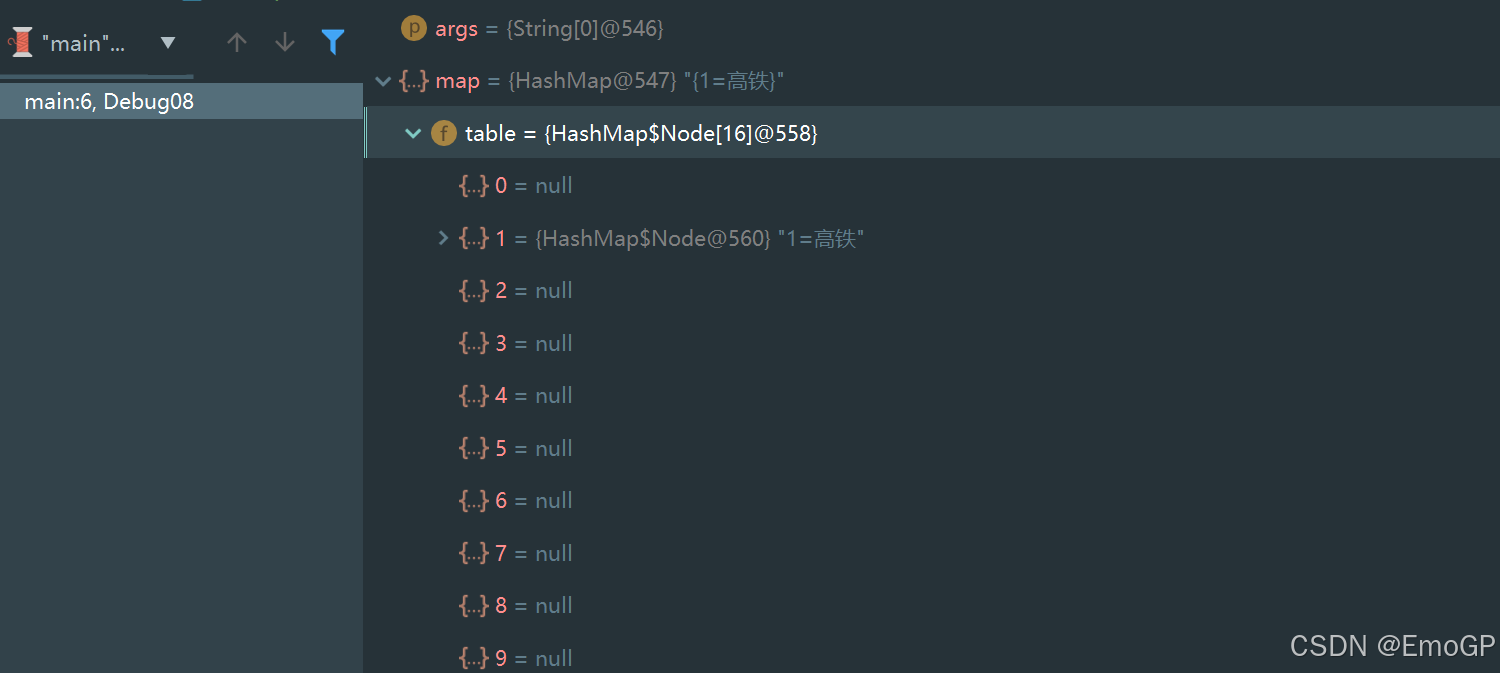
常见问题
使用Step Into时,会出现无法进入源码情况,如何解决?
方案1:使用force step into即可
方案2:点击Setting
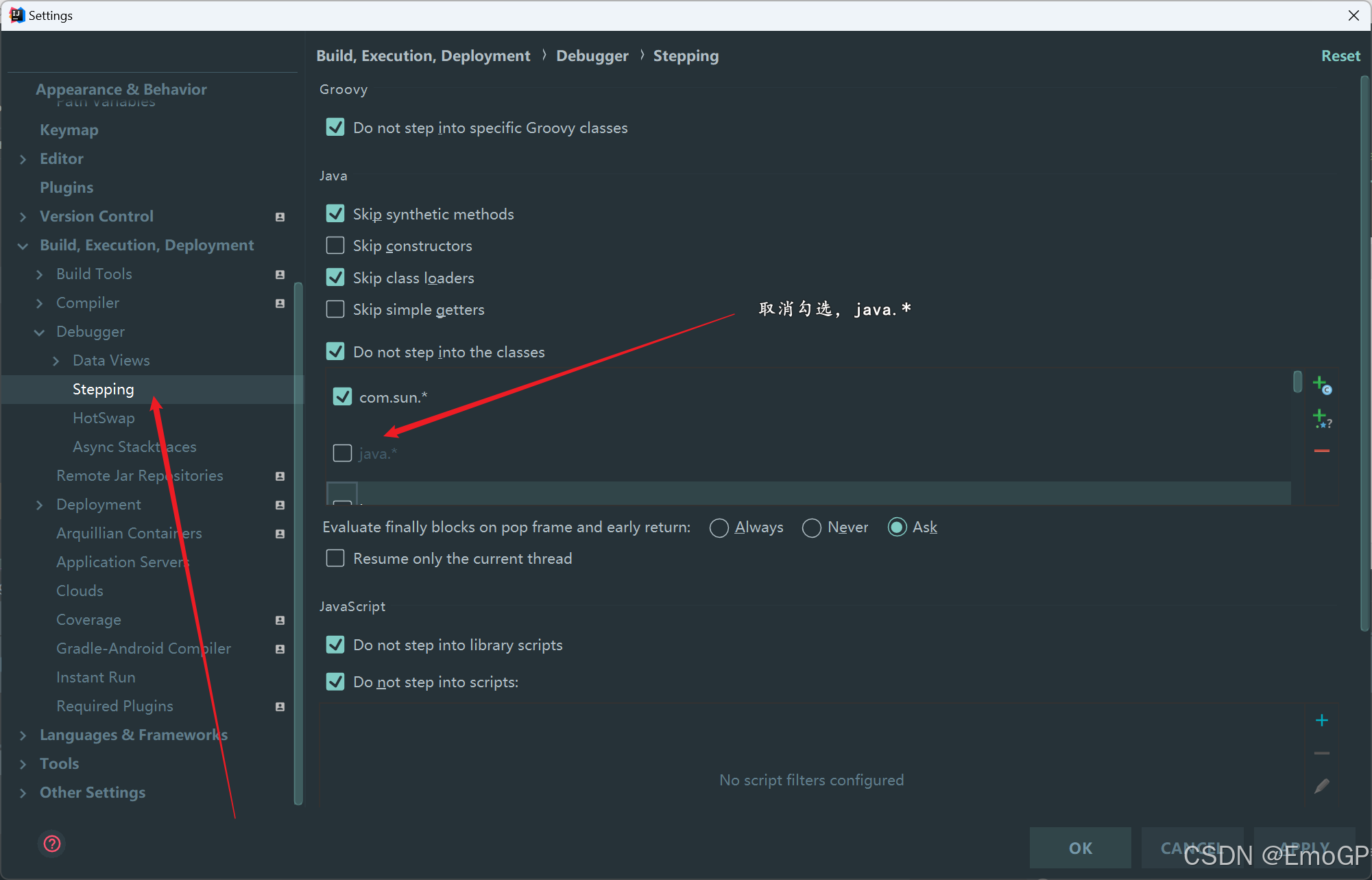
还有javax.*也要取消