前言
目前在做自己的后台管理系统,采用React构建,利用Antd加了Tabs可关闭页签,结合dnd-kit实现了可拖拽Tabs,页面渲染之前参考网上采用Map缓存,结果实际到手发现不是缓存失效,就是刷新、清除影响缓存,反正问题挺多。
Vue是有自带的Keep-Alive控件,咱小胳膊小腿的,也不敢比,也没那时间精力去研究🧐,但React百度搜了是没有自带的Keep-Alive的,网上的教程也仅止于静态实例(可能我没搜到,万望大佬勿喷),但自己又很想要学这个功能。
最近AI确实很🔥很👍,之前使用过字节的Trae,当时效果还不错,刚好赶上Clude的末班车,自从Clude不让用后,Trae的体验一言难尽。于是抱着体验的态度,花了20$买了Cursor,于是就拿缓存Keep-Alive开🔪,从昨晚开始搞到现在,在我不断测试不断调教下,终于有了成果,但代价也不一般,直接上图
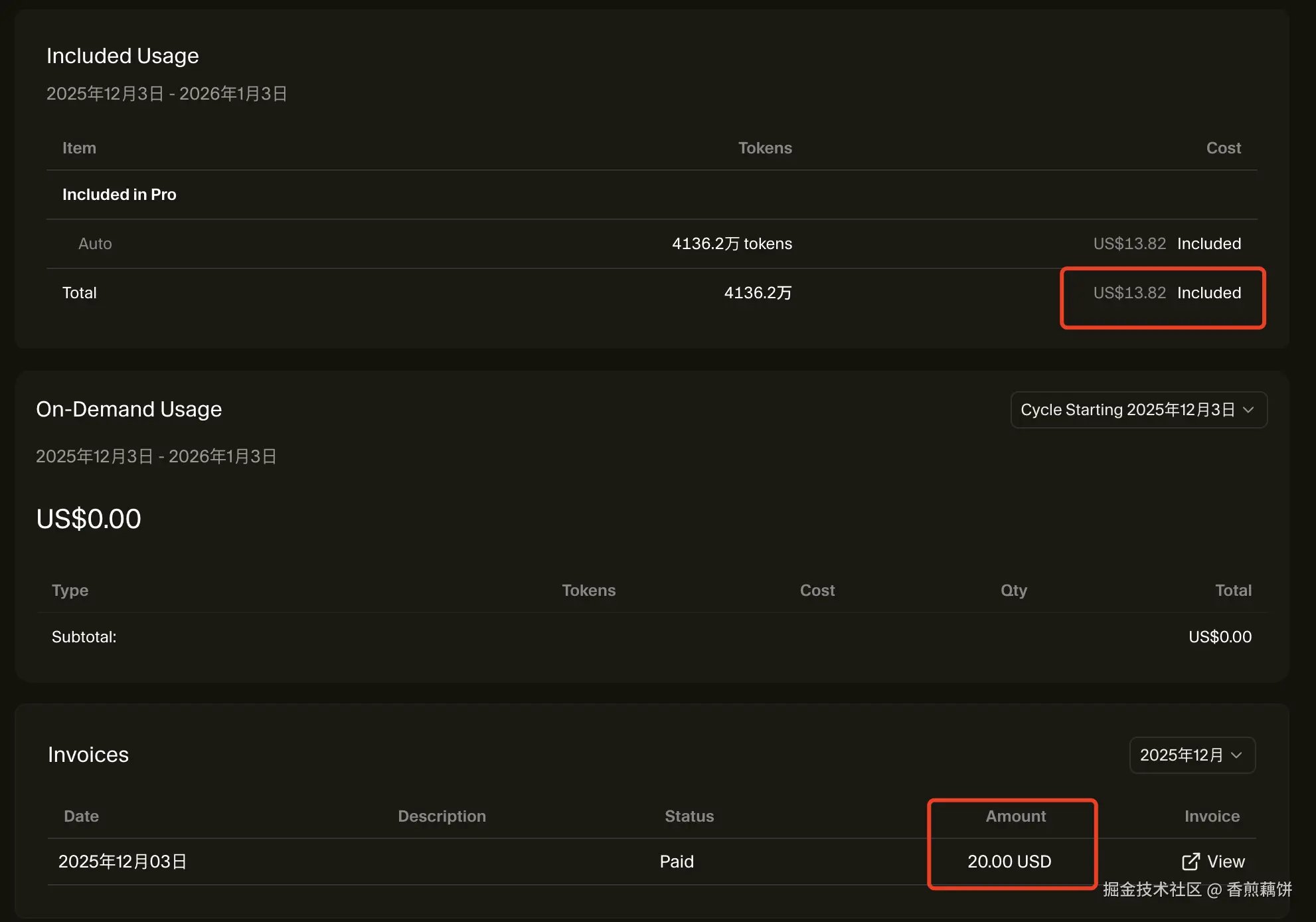 一天过去,直接烧掉100大洋,欢迎品尝
一天过去,直接烧掉100大洋,欢迎品尝
线上地址:www.liyq666.top/
git仓库:gitee.com/lyqjob/proj...
项目实例图
附上AI生成的使用文档,以下内容AI生成
概述
什么是页面缓存?
想象一下,你在浏览器中打开了多个标签页(比如:用户管理、角色管理、菜单管理)。当你从一个标签页切换到另一个标签页时,页面缓存系统会帮你:
- 保存页面状态:切换标签页时,页面不会重新加载,之前填写的数据、滚动位置等都会保留
- 避免重复请求:切换回之前的标签页时,不会重新请求接口,直接显示之前的数据
- 提升用户体验:页面切换更流畅,没有闪烁和重新加载的感觉
为什么需要缓存?
- 性能优化:减少不必要的 API 请求,提升页面响应速度
- 用户体验:保持页面状态,用户不会丢失已填写的数据
- 资源节约:避免重复渲染组件,节省浏览器资源
核心概念
1. 缓存存储(Cache Store)
缓存系统使用 Map 数据结构来存储页面组件:
javascript
// 三个核心存储结构
const cacheStore = new Map() // 存储:key -> ReactElement(页面组件)
const locationStore = new Map() // 存储:key -> Location(路由信息)
const accessOrder = [] // 存储:访问顺序数组,用于 LRU 算法简单理解:
cacheStore:就像一个大仓库,每个页面都有一个编号(key),对应一个页面组件locationStore:记录每个页面的路由信息(路径、参数等)accessOrder:记录页面的访问顺序,最近访问的排在最后
2. 缓存 Key(Cache Key)
每个页面都有一个唯一的标识符,由 路径 + 查询参数 组成:
javascript
// 例如:
'/setting/user' // 用户管理页面
'/setting/user?page=2' // 用户管理页面,第2页(不同的 key!)
'/setting/role' // 角色管理页面重要:即使路径相同,查询参数不同,也会被视为不同的页面,需要分别缓存。
3. 白名单机制(Whitelist)
有些页面不需要缓存,每次访问都重新渲染。这些页面在白名单中:
javascript
const CACHE_WHITELIST = [
'/', // 首页
'/dashboard', // 数据看板
'/setting/cache', // 缓存管理页面
'/setting/log/loginlog', // 登录日志
'/setting/log/operlog', // 操作日志
'/monitor/online', // 在线用户
'/setting/role/info' // 角色详情
]为什么需要白名单?
- 首页、看板等页面需要实时数据,不应该缓存
- 日志类页面需要显示最新数据,缓存会导致数据不准确
4. LRU 算法(Least Recently Used)
LRU = 最近最少使用
当缓存数量超过限制(默认 8 个)时,系统会自动删除最久未使用的页面缓存。
工作原理:
- 每次访问页面时,将该页面移到访问顺序数组的最后
- 当缓存超过 8 个时,删除访问顺序数组第一个(最久未使用的)
- 这样保证最常用的页面始终在缓存中
示例:
bash
访问顺序:['/page1', '/page2', '/page3', '/page4', '/page5', '/page6', '/page7', '/page8']
访问 /page1 → ['/page2', '/page3', '/page4', '/page5', '/page6', '/page7', '/page8', '/page1']
访问 /page9 → 缓存已满,删除 /page2(最久未使用)系统架构
整体架构图
arduino
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ BasicLayout(布局组件) │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ TabsContainer(标签页容器) │ │
│ │ - 显示标签页 │ │
│ │ - 右键菜单(刷新、关闭等) │ │
│ │ - 拖拽排序 │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ KeepAliveOutlet(缓存核心组件) │ │
│ │ - 管理页面缓存 │ │
│ │ - LRU 算法 │ │
│ │ - 渲染缓存的页面 │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ 订阅/发布消息
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ useGlobalMessage(全局消息系统) │
│ - 发布 keep:alive:drop(删除单个缓存) │
│ - 发布 keep:alive:clear(清除所有缓存) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ 管理标签页状态
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ useTabsManager(标签页管理) │
│ - 添加/关闭标签页 │
│ - 切换标签页 │
│ - 发送清除缓存消息 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ 确保数据只加载一次
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ useCacheableEffect(可缓存的 Effect) │
│ - 跟踪已初始化的组件 │
│ - 防止重复加载数据 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘组件关系
- BasicLayout:最外层布局,包含所有组件
- TabsContainer:显示和管理标签页
- KeepAliveOutlet:核心缓存组件,管理页面缓存
- useTabsManager:管理标签页状态,发送清除缓存指令
- useGlobalMessage:全局消息系统,用于组件间通信
- useCacheableEffect:确保页面数据只加载一次
核心组件详解
1. KeepAliveOutlet(缓存核心组件)
位置 :src/components/KeepAlive/index.jsx
职责:
- 管理页面缓存的生命周期
- 实现 LRU 算法
- 渲染缓存的页面组件
核心数据结构
javascript
// 缓存存储(模块级变量,所有实例共享)
const cacheStore = new Map() // key -> { element: ReactElement, location: Location }
const accessOrder = [] // 访问顺序数组,用于 LRU 算法
// 暴露到全局的工具函数
window.__checkCache = (key) => cacheStore.has(key) // 检查是否有缓存
window.__isWhitelisted = (pathname) => isWhitelisted(pathname) // 检查是否在白名单注意 :locationStore 已被移除,位置信息直接存储在 cacheStore 的 value 中。
关键函数
1. getCacheKey(pathname, search)
javascript
// 生成缓存 key
const getCacheKey = (pathname, search) => {
return pathname + search // 例如:'/setting/user?page=2'
}2. isWhitelisted(pathname)
javascript
// 检查路径是否在白名单中
const isWhitelisted = (pathname) => {
return CACHE_WHITELIST.some(route => {
if (pathname === route) return true
if (pathname.startsWith(route + '/')) return true
return false
})
}3. moveToRecent(key)
javascript
// 将 key 移到访问顺序数组的最后(标记为最近使用)
const moveToRecent = (key) => {
const index = accessOrder.indexOf(key)
if (index >= 0) {
accessOrder.splice(index, 1) // 从原位置删除
}
accessOrder.push(key) // 添加到末尾
}4. evictLRU(excludeKey)
javascript
// LRU 清理:删除最久未使用的缓存(排除当前正在访问的)
const evictLRU = (excludeKey) => {
while (cacheStore.size >= CACHE_LIMIT) { // 默认 8 个
// 找到第一个不是 excludeKey 的 key(最久未使用的)
const keyToRemove = accessOrder.find(k => k !== excludeKey)
if (keyToRemove) {
removeCache(keyToRemove) // 删除缓存
} else {
break
}
}
}5. removeCache(key)
javascript
// 移除指定 key 的缓存
const removeCache = (key) => {
if (cacheStore.has(key)) {
cacheStore.delete(key) // 删除组件缓存
const index = accessOrder.indexOf(key)
if (index >= 0) {
accessOrder.splice(index, 1) // 从访问顺序中删除
}
return true
}
return false
}缓存管理流程
步骤 1:检查是否需要缓存
javascript
const shouldNotCache = useMemo(() => isWhitelisted(location.pathname), [location.pathname])步骤 2:生成缓存 key
javascript
const cacheKey = getCacheKey(location.pathname, location.search)步骤 3:处理缓存逻辑
javascript
useEffect(() => {
// 1. 白名单路由:不缓存,直接返回
if (shouldNotCache) {
if (removeCache(cacheKey)) {
setCacheVersion(v => v + 1) // 触发重新渲染
}
return
}
// 2. 如果 key 没变化,只更新访问顺序
if (prevKeyRef.current === cacheKey) {
if (cacheStore.has(cacheKey)) {
moveToRecent(cacheKey) // 标记为最近使用
}
return
}
// 3. key 变化了,处理新页面
prevKeyRef.current = cacheKey
// 如果还没有缓存,添加缓存
if (!cacheStore.has(cacheKey)) {
// 使用 setTimeout 确保 outlet 已经准备好
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
const currentOutlet = outletRef.current
if (currentOutlet) {
cacheStore.set(cacheKey, {
element: currentOutlet,
location: {
pathname: location.pathname,
search: location.search,
hash: location.hash,
state: location.state,
key: location.key
}
})
if (!accessOrder.includes(cacheKey)) {
accessOrder.push(cacheKey)
} else {
moveToRecent(cacheKey)
}
evictLRU(cacheKey) // 如果超过限制,删除最久未使用的
setCacheVersion(v => v + 1)
}
}, 0)
return () => {
clearTimeout(timer)
}
} else {
// 已缓存,只更新访问顺序
moveToRecent(cacheKey)
}
}, [cacheKey, shouldNotCache, outlet, location.pathname, location.search])渲染逻辑
javascript
const nodes = useMemo(() => {
const list = []
// 1. 白名单路由:直接渲染,不缓存
if (shouldNotCache) {
if (outlet) {
list.push(<div key={cacheKey}>{outlet}</div>)
}
return list
}
// 2. 如果还没有缓存,但 outlet 存在,临时渲染(首次加载)
if (!cacheStore.has(cacheKey) && outlet) {
list.push(<div key={cacheKey}>{outlet}</div>)
}
// 3. 渲染所有缓存的组件(通过 display 控制显示/隐藏)
for (const [key, cache] of cacheStore.entries()) {
const isActive = key === cacheKey
list.push(
<div
key={key}
style={{
display: isActive ? 'block' : 'none', // 只有当前页面显示
height: '100%',
width: '100%'
}}
>
<CachedComponent cacheKey={key}>
{cache.element}
</CachedComponent>
</div>
)
}
return list
}, [cacheKey, cacheVersion, shouldNotCache, outlet])消息订阅(接收清除缓存指令)
javascript
useEffect(() => {
// 订阅 'keep:alive:drop' 事件(删除单个缓存)
const onDrop = (detail) => {
const key = detail?.key
if (!key) return
// 🌟 只有在明确要求清除缓存时才清除(比如刷新标签页)
// 关闭标签页时不应该清除缓存,这样重新打开时可以快速恢复
const shouldRemove = detail?.remove === true
if (shouldRemove) {
if (removeCache(key)) {
setCacheVersion(v => v + 1)
}
// 清除组件初始化状态(刷新时才清除)
if (window.__clearComponentInit) {
window.__clearComponentInit(key)
}
}
// 关闭标签页时:不清除缓存,也不清除初始化状态
}
// 订阅 'keep:alive:clear' 事件(清除所有缓存)
const onClear = () => {
cacheStore.clear()
accessOrder.splice(0, accessOrder.length)
// 清除所有组件初始化状态
if (window.__clearAllInit) {
window.__clearAllInit()
}
setCacheVersion(v => v + 1)
}
const unsubscribeDrop = subscribe('keep:alive:drop', onDrop)
const unsubscribeClear = subscribe('keep:alive:clear', onClear)
return () => {
unsubscribeDrop()
unsubscribeClear()
}
}, [subscribe, error])重要变化:
- 关闭标签页时:不清除缓存(
remove: false),保留页面状态,重新打开时可以快速恢复 - 刷新标签页时:清除缓存(
remove: true),强制重新加载数据 - 使用
window.__clearComponentInit和window.__clearAllInit清除初始化状态
2. useCacheableEffect(可缓存的 Effect Hook)
位置 :src/hooks/useCacheableEffect.js
职责:
- 确保
useEffect只在首次挂载时执行 - 防止切换标签页时重复加载数据
核心数据结构
javascript
// 全局存储已初始化的组件(模块级变量)
const initializedComponents = new Set()
// 存储格式:'pathname+search::depsStr'
// 例如:'/setting/user::[]' 或 '/setting/role::[null,null]'工作原理
javascript
export const useCacheableEffect = (effect, deps = [], options = {}) => {
const { cacheable = true, cacheKey } = options
const location = useLocation()
// 生成组件唯一标识
const componentKey = cacheKey || (location.pathname + location.search)
const depsStr = JSON.stringify(deps) // 依赖项的 JSON 字符串
const initKey = `${componentKey}::${depsStr}`
// 使用 ref 存储 effect 和是否已执行
const effectRef = useRef(effect)
const hasExecutedRef = useRef(false)
// 更新 effect 引用
useEffect(() => {
effectRef.current = effect
}, [effect])
useEffect(() => {
// 如果不可缓存,每次都执行
if (!cacheable) {
const cleanup = effectRef.current()
return cleanup
}
// 检查是否已初始化(全局检查)
if (initializedComponents.has(initKey)) {
window.process.done() // 关闭进度条
return // 已初始化,跳过执行
}
// 检查是否已执行(组件级别检查,防止重复执行)
if (hasExecutedRef.current) {
// 确保已标记为已初始化
if (!initializedComponents.has(initKey)) {
initializedComponents.add(initKey)
}
return
}
// 首次执行
hasExecutedRef.current = true
initializedComponents.add(initKey)
const cleanup = effectRef.current()
return () => {
if (typeof cleanup === 'function') {
cleanup()
}
}
}, [componentKey, cacheable, depsStr]) // 不包含 effect,使用 effectRef 存储最新引用
}关键改进:
- 使用
Set而不是Map存储初始化状态 - 使用
effectRef存储最新的 effect 函数,避免依赖项变化导致的问题 - 双重检查机制:全局检查(
initializedComponents)和组件级别检查(hasExecutedRef) - 自动关闭进度条:当检测到已初始化时,自动调用
window.process.done()
使用示例
非白名单页面(需要缓存):
javascript
// 在页面组件中使用
const UserManagement = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([])
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
// ✅ 首次加载数据 - 使用 useCacheableEffect,必须添加 cacheable: true
useCacheableEffect(() => {
getList(current, pageSize)
getDepartmentList()
}, [], { cacheable: true }) // 空依赖数组,确保只在首次挂载时执行
// ✅ 分页变化时单独处理(使用普通 useEffect)
useEffect(() => {
getList(current, pageSize)
}, [current, pageSize])
// ✅ 数据恢复机制:当检测到缓存但数据为空时,自动重新加载
const location = useLocation();
useEffect(() => {
const cacheKey = location.pathname + location.search;
const isUsingCache = window.__checkCache && window.__checkCache(cacheKey);
if (loading && isUsingCache && !hasTriedRestoreRef.current) {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
if (data.length === 0 && total === 0) {
// 数据为空,重新加载
getList(current, pageSize);
} else {
// 数据存在,重置 loading
setLoading(false);
}
hasTriedRestoreRef.current = true;
}, 100);
return () => clearTimeout(timer);
}
}, [loading, data.length, total, location.pathname, location.search]);
// ...
}白名单页面(不需要缓存):
javascript
// 白名单页面使用普通 useEffect,不使用 useCacheableEffect
const LoginLog = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([])
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
// ✅ 白名单页面,使用普通 useEffect
useEffect(() => {
getList(current, pageSize)
}, [])
// ...
}为什么需要 useCacheableEffect?
当页面被 KeepAlive 缓存后,组件不会重新挂载 ,但 useEffect 仍然会在某些情况下执行。使用 useCacheableEffect 可以确保数据只在首次加载时请求一次,避免重复请求。
数据恢复机制:
当从白名单页面切换回缓存页面时,可能会出现组件状态丢失的情况(数据为空)。系统会自动检测并重新加载数据,确保页面正常显示。
3. useTabsManager(标签页管理 Hook)
位置 :src/hooks/useTabsManager.js
职责:
- 管理标签页的状态(添加、关闭、切换等)
- 发送清除缓存的指令
核心功能
1. 添加标签页
javascript
const addTab = useCallback((pathname, search) => {
const fullPathKey = pathname + (search || '')
setTabs(prevTabs => {
// 检查是否已存在
const existingTab = prevTabs.find(tab => tab.key === fullPathKey)
if (existingTab) {
return prevTabs // 已存在,不重复添加
}
// 创建新标签页
const newTab = getRouteInfo(pathname, search)
return [...prevTabs, newTab]
})
setActiveKey(fullPathKey)
}, [getRouteInfo])2. 关闭标签页
javascript
const closeTab = useCallback((key) => {
setTabs(prevTabs => {
const targetTab = prevTabs.find(tab => tab.key === key)
if (!targetTab || targetTab.isPinned) return prevTabs
const newTabs = prevTabs.filter(tab => tab.key !== key)
// 如果关闭的是当前激活标签页,切换到其他标签页
if (activeKey === key) {
const nextTab = newTabs[0] || newTabs[newTabs.length - 1]
if (nextTab) {
setActiveKey(nextTab.key)
navigate(nextTab.key)
}
}
return newTabs
})
// 🌟 关闭标签页时不清除缓存,只清除初始化状态
// 这样重新打开时可以快速恢复,但会重新加载数据
globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key, remove: false })
}, [activeKey, navigate])注意 :关闭标签页时,缓存不会被清除(remove: false),这样重新打开时可以快速恢复页面。只有刷新标签页时才会清除缓存。
3. 关闭所有标签页
javascript
const closeAllTabs = useCallback(() => {
// 发送全局清除消息
globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('clear')
// 重置状态
setTabs(DEFAULT_PINNED_TABS)
setActiveKey('/')
navigate('/')
}, [navigate, success])4. 刷新标签页
javascript
const refreshTab = useCallback((key) => {
// 🌟 刷新标签页时清除缓存和初始化状态,强制重新加载
globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key, remove: true })
}, [success])5. 关闭其他标签页
javascript
const closeOtherTabs = useCallback((keepKey) => {
setTabs(prevTabs => {
// 找出即将被关闭的标签页的 key
const keysToDrop = prevTabs
.filter(tab => !tab.isPinned && tab.key !== keepKey)
.map(tab => tab.key);
// 清除其他标签页的缓存
keysToDrop.forEach(key => {
globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key });
});
// 🌟 如果保留的标签页不是当前激活的,清除其初始化状态
// 这样会重新加载数据,确保页面状态正确
if (activeKey !== keepKey) {
if (window.__clearComponentInit) {
window.__clearComponentInit(keepKey);
}
}
// 返回保留的标签页列表
return prevTabs.filter(tab =>
tab.isPinned || tab.key === keepKey
);
});
// 激活目标 Key 并导航
setActiveKey(keepKey);
navigate(keepKey);
}, [success, navigate, activeKey]);4. useGlobalMessage(全局消息系统)
位置 :src/hooks/useGlobalMessage.js
职责:
- 实现发布-订阅模式
- 处理组件间通信
核心机制
发布消息
javascript
const publish = useCallback((eventType, payload = {}) => {
// 1. 通知订阅者
if (subscribersRef.current.has(eventType)) {
const subscribers = subscribersRef.current.get(eventType)
subscribers.forEach(callback => {
callback({ detail: payload })
})
}
// 2. 发送浏览器原生事件
const event = new CustomEvent(eventType, { detail: payload })
window.dispatchEvent(event)
}, [])订阅消息
javascript
const subscribe = useCallback((eventType, callback, options = {}) => {
const { once = false } = options
if (!subscribersRef.current.has(eventType)) {
subscribersRef.current.set(eventType, new Set())
}
const subscribers = subscribersRef.current.get(eventType)
const wrappedCallback = (event) => {
try {
callback(event.detail)
if (once) unsubscribe(eventType, wrappedCallback)
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error in subscriber for ${eventType}:`, error)
}
}
subscribers.add(wrappedCallback)
return () => unsubscribe(eventType, wrappedCallback)
}, [])处理 keepAlive 事件
javascript
const handleKeepAlive = useCallback((detail) => {
const action = detail?.action || detail?.message || 'drop'
const options = detail?.options || {}
let eventType = EVENT_TYPES.KEEP_ALIVE + ':' + action // 'keep:alive:drop' 或 'keep:alive:clear'
publish(eventType, options)
}, [publish])工具函数
javascript
export const globalMessageUtils = {
// 发送 keepAlive 消息
keepAlive(message = 'keepAlive', options = {}) {
window.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent(EVENT_TYPES.KEEP_ALIVE, {
detail: { message, options }
}))
}
}数据流转过程
场景 1:首次访问页面
markdown
1. 用户点击菜单 → 路由变化 → location.pathname = '/setting/user'
2. KeepAliveOutlet 检测到路由变化
3. 生成 cacheKey = '/setting/user'
4. 检查白名单 → 不在白名单中,需要缓存
5. 检查 cacheStore → 没有缓存
6. 等待 outlet(页面组件)加载完成
7. 保存到 cacheStore:cacheStore.set('/setting/user', outlet)
8. 保存到 locationStore:locationStore.set('/setting/user', location)
9. 添加到 accessOrder:accessOrder.push('/setting/user')
10. 执行 LRU 清理(如果超过 8 个)
11. 触发重新渲染,显示页面
12. 页面组件使用 useCacheableEffect 加载数据
13. 数据加载完成,标记为已初始化场景 2:切换标签页
markdown
1. 用户点击其他标签页 → 路由变化 → location.pathname = '/setting/role'
2. KeepAliveOutlet 检测到路由变化
3. 生成 cacheKey = '/setting/role'
4. 检查 cacheStore → 已有缓存
5. 更新访问顺序:moveToRecent('/setting/role')
6. 触发重新渲染
7. 渲染逻辑:
- 显示 '/setting/role'(display: 'block')
- 隐藏 '/setting/user'(display: 'none')
8. 页面组件不会重新挂载,useCacheableEffect 不会执行
9. 直接显示缓存的数据,无需重新请求接口场景 3:关闭标签页
php
1. 用户点击关闭按钮 → closeTab('/setting/user')
2. useTabsManager 更新 tabs 状态(移除该标签页)
3. 发送消息:globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key: '/setting/user', remove: false })
4. useGlobalMessage 处理消息 → publish('keep:alive:drop', { key: '/setting/user', remove: false })
5. KeepAliveOutlet 订阅到消息 → onDrop({ key: '/setting/user', remove: false })
6. 检查 shouldRemove = false
7. 🌟 不清除缓存,保留页面状态(这样重新打开时可以快速恢复)
8. 触发重新渲染注意:关闭标签页时,缓存会被保留,这样重新打开时可以快速恢复页面状态。
场景 4:关闭所有标签页
scss
1. 用户点击"关闭所有" → closeAllTabs()
2. 发送全局清除消息:globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('clear')
3. useGlobalMessage 处理消息 → publish('keep:alive:clear', {})
4. KeepAliveOutlet 订阅到消息 → onClear()
5. 执行清除操作:
- cacheStore.clear()
- locationStore.clear()
- accessOrder.splice(0, accessOrder.length)
- window.clearAllInitialized()
6. 重置标签页状态:setTabs(DEFAULT_PINNED_TABS)
7. 导航到首页:navigate('/')场景 5:刷新标签页
php
1. 用户右键点击标签页 → 选择"刷新" → refreshTab('/setting/user')
2. 发送删除缓存消息:globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key: '/setting/user', remove: true })
3. KeepAliveOutlet 检查 shouldRemove = true
4. 执行 removeCache('/setting/user')
- cacheStore.delete('/setting/user')
- accessOrder 中删除 '/setting/user'
5. 清除组件初始化状态:window.__clearComponentInit('/setting/user')
6. 触发重新渲染
7. 由于缓存已删除,会重新渲染 outlet
8. 页面组件重新挂载,useCacheableEffect 重新执行
9. 重新加载数据场景 6:关闭其他标签页
javascript
1. 用户右键点击标签页 → 选择"关闭其他" → closeOtherTabs('/setting/user')
2. 找出其他标签页的 key:['/setting/role', '/setting/menu']
3. 清除其他标签页的缓存:globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key: '/setting/role' })
4. 如果保留的标签页不是当前激活的:
- 清除初始化状态:window.__clearComponentInit('/setting/user')
- 这样会重新加载数据,确保页面状态正确
5. 更新 tabs 状态,只保留目标标签页
6. 导航到目标标签页
7. 目标标签页重新加载数据(因为初始化状态被清除)场景 7:数据恢复机制
bash
1. 用户从白名单页面(如 /setting/cache)切换回缓存页面(如 /setting/user)
2. KeepAliveOutlet 恢复缓存的组件
3. 页面组件检测到使用缓存:window.__checkCache('/setting/user') === true
4. 检查数据状态:
- 如果数据为空且 total === 0,可能是状态丢失
- 延迟 100ms 后重新检查
5. 如果数据仍然为空,自动重新加载数据
6. 如果数据存在,重置 loading 状态数据恢复机制的作用:
- 解决从白名单页面切换回缓存页面时,可能出现的数据丢失问题
- 自动检测并恢复数据,确保页面正常显示
LRU 缓存策略
算法原理
LRU(Least Recently Used):最近最少使用算法
核心思想:当缓存空间不足时,删除最久未使用的缓存。
实现细节
1. 访问顺序数组
javascript
const accessOrder = [] // 存储访问顺序,数组第一个是最久未使用的2. 访问页面时
javascript
// 将页面移到数组末尾(标记为最近使用)
const moveToRecent = (key) => {
const index = accessOrder.indexOf(key)
if (index >= 0) {
accessOrder.splice(index, 1) // 从原位置删除
}
accessOrder.push(key) // 添加到末尾
}3. 缓存满时清理
javascript
const evictLRU = (excludeKey) => {
while (cacheStore.size >= CACHE_LIMIT) { // 默认 8 个
// 找到第一个不是 excludeKey 的 key(最久未使用的)
const keyToRemove = accessOrder.find(k => k !== excludeKey)
if (keyToRemove) {
removeCache(keyToRemove) // 删除缓存
} else {
break
}
}
}示例演示
假设 CACHE_LIMIT = 3(为了演示方便,实际是 8):
css
初始状态:
cacheStore: {}
accessOrder: []
访问 /page1:
cacheStore: { '/page1': <Component1> }
accessOrder: ['/page1']
访问 /page2:
cacheStore: { '/page1': <Component1>, '/page2': <Component2> }
accessOrder: ['/page1', '/page2']
访问 /page3:
cacheStore: { '/page1': <Component1>, '/page2': <Component2>, '/page3': <Component3> }
accessOrder: ['/page1', '/page2', '/page3']
访问 /page4(缓存已满):
1. 添加 /page4
2. 执行 evictLRU('/page4')
3. 删除 accessOrder[0] = '/page1'(最久未使用)
cacheStore: { '/page2': <Component2>, '/page3': <Component3>, '/page4': <Component4> }
accessOrder: ['/page2', '/page3', '/page4']
再次访问 /page2:
1. moveToRecent('/page2') → 移到末尾
cacheStore: { '/page2': <Component2>, '/page3': <Component3>, '/page4': <Component4> }
accessOrder: ['/page3', '/page4', '/page2']
访问 /page5(缓存已满):
1. 添加 /page5
2. 执行 evictLRU('/page5')
3. 删除 accessOrder[0] = '/page3'(最久未使用)
cacheStore: { '/page4': <Component4>, '/page2': <Component2>, '/page5': <Component5> }
accessOrder: ['/page4', '/page2', '/page5']为什么使用 LRU?
- 符合用户习惯:用户经常访问的页面会保留在缓存中
- 自动管理:无需手动清理,系统自动管理缓存大小
- 性能优化:最常用的页面始终在缓存中,切换速度快
使用指南
1. 在页面组件中使用 useCacheableEffect
非白名单页面(需要缓存):
javascript
import { useCacheableEffect } from '@/hooks/useCacheableEffect'
import { useLocation } from 'react-router-dom'
import { useRef } from 'react'
const UserManagement = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([])
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
const [total, setTotal] = useState(0)
const hasTriedRestoreRef = useRef(false)
const prevCacheKeyRef = useRef('')
const location = useLocation()
// ✅ 首次加载数据 - 使用 useCacheableEffect,必须添加 cacheable: true
useCacheableEffect(() => {
getList(current, pageSize)
getDepartmentList()
}, [], { cacheable: true }) // 空依赖数组,确保只在首次挂载时执行
// ✅ 数据恢复机制:当检测到缓存但数据为空时,自动重新加载
useEffect(() => {
const cacheKey = location.pathname + location.search
const isUsingCache = window.__checkCache && window.__checkCache(cacheKey)
if (prevCacheKeyRef.current !== cacheKey) {
hasTriedRestoreRef.current = false
prevCacheKeyRef.current = cacheKey
}
if (loading && isUsingCache && !hasTriedRestoreRef.current) {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
if (data.length === 0 && total === 0) {
console.log('[User] 检测到缓存但数据为空,重新加载数据')
hasTriedRestoreRef.current = true
getList(current, pageSize)
} else {
setLoading(false)
hasTriedRestoreRef.current = true
}
}, 100)
return () => clearTimeout(timer)
}
if (loading && data.length > 0) {
setLoading(false)
}
}, [loading, data.length, total, location.pathname, location.search])
// ✅ 分页变化时单独处理(使用普通 useEffect)
useEffect(() => {
getList(current, pageSize)
}, [current, pageSize])
// ❌ 不要这样做(会导致每次切换标签页都重新加载)
useEffect(() => {
getList()
}, [])
}白名单页面(不需要缓存):
javascript
// 白名单页面使用普通 useEffect,不使用 useCacheableEffect
const LoginLog = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([])
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
// ✅ 白名单页面,使用普通 useEffect
useEffect(() => {
getList(current, pageSize)
}, [])
// ...
}2. 添加页面到白名单
如果某个页面不需要缓存,添加到白名单:
javascript
// src/components/KeepAlive/index.jsx
const CACHE_WHITELIST = [
'/',
'/dashboard',
'/your-new-page' // 添加新页面
]3. 手动清除缓存
javascript
import { globalMessageUtils } from '@/hooks/useGlobalMessage'
// 清除单个页面缓存
globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key: '/setting/user' })
// 清除所有缓存
globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('clear')4. 调整缓存数量限制
javascript
// src/components/KeepAlive/index.jsx
const CACHE_LIMIT = 8 // 修改为你需要的数量常见问题
Q1: 为什么切换标签页后,页面数据没有更新?
A: 这是因为页面被缓存了,组件不会重新挂载。如果需要实时数据,应该:
- 将页面添加到白名单(不缓存)
- 使用刷新功能(右键菜单 → 刷新)
- 在数据变化时手动刷新(例如:保存成功后刷新列表)
Q2: 为什么有些页面切换时会重新加载?
A: 可能的原因:
- 页面在白名单中:这些页面每次访问都会重新加载
- 缓存已满:LRU 算法删除了该页面的缓存
- 页面刷新:浏览器刷新会清空所有缓存
Q3: 如何调试缓存问题?
A: 在开发环境下,KeepAlive 组件会输出调试日志:
javascript
// 查看控制台输出
[KeepAlive] 新增缓存: { cacheKey: '/setting/user', cacheSize: 1, ... }
[KeepAlive] 使用缓存: '/setting/user'
[KeepAlive] 清除所有缓存,清除前: { cacheSize: 3, cachedKeys: [...] }Q4: 为什么 useCacheableEffect 不执行?
A: 检查以下几点:
- 是否设置了
cacheable: true(非白名单页面必须设置) - 组件是否已被标记为已初始化 (检查
initializedComponentsSet) - 缓存 key 是否正确(路径 + 查询参数)
- 是否是白名单页面 (白名单页面应该使用普通
useEffect,不使用useCacheableEffect)
调试方法:
javascript
// 在浏览器控制台查看初始化状态
console.log(window.__clearComponentInit) // 应该是一个函数
console.log(window.__clearAllInit) // 应该是一个函数
// 查看缓存状态
console.log(window.__checkCache('/setting/user')) // 检查是否有缓存Q5: 如何强制刷新页面数据?
A: 有几种方式:
-
右键菜单 → 刷新 :清除缓存并重新加载(
remove: true) -
关闭标签页后重新打开:会重新加载数据(因为初始化状态被清除)
-
在代码中手动清除缓存 :
javascript// 清除缓存和初始化状态(强制刷新) globalMessageUtils.keepAlive('drop', { key: location.pathname + location.search, remove: true }) // 只清除初始化状态(保留缓存,但会重新加载数据) if (window.__clearComponentInit) { window.__clearComponentInit(location.pathname + location.search) }
Q8: 为什么切换回缓存页面时数据是空的?
A : 这可能是组件状态丢失导致的。系统已经实现了数据恢复机制:
- 自动检测:当检测到使用缓存但数据为空时,会自动重新加载数据
- 延迟检查:延迟 100ms 检查,确保组件状态已恢复
- 避免重复:使用 ref 跟踪,避免重复加载
如果仍然出现问题,检查:
- 数据恢复机制的
useEffect是否正确实现 hasTriedRestoreRef和prevCacheKeyRef是否正确设置- 数据判断条件是否正确(
data.length === 0 && total === 0)
Q6: 缓存会占用多少内存?
A: 缓存的是 React 组件实例,内存占用取决于:
- 组件复杂度:组件越复杂,占用内存越多
- 数据量:页面数据越多,占用内存越多
- 缓存数量:默认最多 8 个页面
如果内存紧张,可以:
- 减少
CACHE_LIMIT(默认 8) - 将不需要缓存的页面添加到白名单
Q7: 页面刷新后缓存会丢失吗?
A : 是的。缓存存储在内存中(Map 对象),页面刷新后会清空。这是正常行为,因为:
- 页面刷新意味着用户想要重新加载应用
- 缓存数据可能已过期,需要重新获取
- 避免内存泄漏
总结
核心要点
- 缓存存储 :使用
Map存储页面组件,accessOrder数组记录访问顺序 - LRU 算法:自动删除最久未使用的缓存,保持缓存数量在限制内
- 白名单机制 :某些页面不缓存,每次访问都重新加载(使用普通
useEffect) - 消息系统:通过发布-订阅模式实现组件间通信
- useCacheableEffect :确保页面数据只加载一次(非白名单页面必须使用,并添加
cacheable: true) - 数据恢复机制:自动检测并恢复丢失的数据,确保页面正常显示
- 智能缓存管理:关闭标签页时保留缓存,刷新时才清除缓存
最佳实践
- ✅ 非白名单页面使用 useCacheableEffect 加载初始数据,并添加
cacheable: true - ✅ 白名单页面使用普通 useEffect ,不使用
useCacheableEffect - ✅ 使用普通 useEffect 处理依赖变化(如分页、搜索等)
- ✅ 实现数据恢复机制,确保从白名单页面切换回缓存页面时数据正常
- ✅ 将实时数据页面添加到白名单(如日志、看板等)
- ✅ 合理设置缓存数量限制(默认 8 个)
- ✅ 关闭标签页时保留缓存,刷新时才清除缓存
- ❌ 不要在 useCacheableEffect 中处理依赖变化 (应该使用普通
useEffect) - ❌ 不要在白名单页面使用 useCacheableEffect (应该使用普通
useEffect) - ❌ 不要在 useCacheableEffect 的依赖数组中包含函数引用 (应该使用空数组
[])
相关文件
src/components/KeepAlive/index.jsx- 缓存核心组件src/hooks/useCacheableEffect.js- 可缓存的 Effect Hooksrc/hooks/useTabsManager.js- 标签页管理src/hooks/useGlobalMessage.js- 全局消息系统src/components/TabsContainer/index.jsx- 标签页容器src/layouts/BasicLayout.jsx- 基础布局
总结
不知道这次尝试是否值得,如果不是沉没成本太大,我可能已经中断尝试了,还好有了成果,也可能我测试不够全面,导致有遗留Bug,欢迎告知我,也欢迎后来者继续前进,技术实现的代码总在一步步往前走不是嘛
或许前端终将被AI替代,但路在脚下,你我共勉
好了,我也要去学习研究这个缓存了,看到这里,如果对你有帮助,欢迎git仓库给个⭐️标,谢谢了🙏