桥接模式将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使二者可以独立变化。它通过提供抽象化和实现化之间的桥接结构,来实现二者的解耦(通过"组合"的方式建立两个类层次结构之间的联系,而不是继承);
这种模式涉及到一个作为桥接的接口 ,使得实体类的功能 独立于接口实现类,这两种类型的类可被结构化改变而互不影响。
桥接模式的目的是将抽象与实现分离,使它们可以独立地变化,该模式通过将一个对象的抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们可以独立地改变。它通过组合的方式,而不是继承的方式,将抽象和实现的部分连接起来。
介绍
1. 意图
- 将抽象部分与实现部分解耦,使二者可以独立变化;
- 避免类爆炸问题(当多个维度需要扩展时);
- 提高系统的可扩展性。
2. 主要解决的问题
- 当一个类存在多个变化维度时,使用继承会导致类的数量呈指数级增长(比如你有 m 种抽象和 n 种实现,用继承需要 m×n 个类,而桥接模式只需要 m+n 个类);
- 如果以继承的方式,会造成类爆炸问题,而桥接模式可以提供更灵活的扩展方式。
3. 使用场景
- 一个类存在两个或多个独立变化的维度,且这些维度都需要扩展;
- 不希望使用继承导致系统类的数量急剧增加;
- 需要在运行时切换实现;
例如:跨平台图形系统(形状+颜色)、消息发送系统(消息类型+发送方式)、数据库驱动(不同数据库+不同操作)
4. 实现方式
- 分离多角度分类:将不同角度的分类逻辑分离,允许它们独立变化。
- 减少耦合:降低抽象与实现之间的耦合度。
5. 关键代码
- 抽象类:定义一个抽象类,作为系统的一部分。
- 实现类:定义一个或多个实现类,与抽象类通过聚合(而非继承)关联。
6. 桥接模式抽象部分与现实部分的区分与定位
6.1. 定位口诀
- 实现部分:做事的方式、底层机制、平台相关;
- 抽象部分:做什么事、业务逻辑、功能扩展。
6.2. 判断标准:
- 实现部分:跟底层,更基础;
- 抽象部分:哪部分会调用另一部分,调用者就是抽象部分,被调用者就是实现部分
7. 结构
以下是桥接模式的几个关键角色:
- 抽象(Abstraction):定义抽象接口,通常包含对实现接口的引用;
- 扩展抽象(Refined Abstraction):对抽象的扩展,可以是抽象类的子类或具体实现类;
- 实现(Implementor):定义实现接口,提供基本操作的接口;
- 具体实现(Concrete Implementor):实现实现接口的具体类。
代码实现
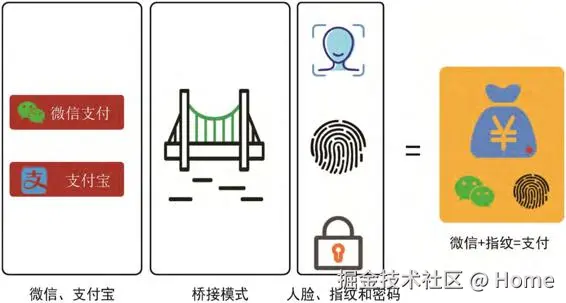
场景描述:商城项目中,集成微信支付和支付宝支付,其中支付方式开始可能只有密码支付,后面又拓展成指纹支付、人脸支付等等,这种拓展就很适合使用桥接设计模式进行拓展
1. 使用继承方式实现,导致实现类激增
java
public abstract class BasePayment {
// 风控校验
protected abstract boolean security(String uId);
// 交易
protected abstract void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount);
}
scala
public abstract class BaseWechatPayment extends BasePayment {
@Override
protected boolean security(String uId) {
System.out.println("微信支付风控校验环境安全");
return true;
}
@Override
protected abstract void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount);
}
scala
public class WeChatFacePayment extends BaseWechatPayment {
@Override
protected void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
System.out.println("微信人脸支付");
boolean securityStatus = this.security(uId);
if (securityStatus) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
public class WeChatPasswordPayment extends BaseWechatPayment {
@Override
protected void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
System.out.println("微信密码支付");
boolean securityStatus = this.security(uId);
if (securityStatus) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}
public class WeChatFingerprintPayment extends BaseWechatPayment {
@Override
protected void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
System.out.println("微信指纹支付");
boolean securityStatus = this.security(uId);
if (securityStatus) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}
scala
public class BaseAlipayPayment extends BasePayment {
@Override
protected boolean security(String uId) {
System.out.println("支付宝支付风控校验环境安全");
return true;
}
@Override
protected abstract void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount);
}
scala
public class AlipayFacePayment extends BaseAlipayPayment {
@Override
protected void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
System.out.println("支付宝人脸支付");
boolean securityStatus = this.security(uId);
if (securityStatus) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}
public class AlipayPasswordPayment extends BaseAlipayPayment {
@Override
protected void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
System.out.println("支付宝密码支付");
boolean securityStatus = this.security(uId);
if (securityStatus) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}
public class AlipayFingerprintPayment extends BaseAlipayPayment {
@Override
protected void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
System.out.println("支付宝指纹支付");
boolean securityStatus = this.security(uId);
if (securityStatus) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}2. 使用桥接模式实现
2.1. 分析:
支付功能有两个维度变化:
- 维度1:支付渠道(微信、支付宝);
- 维度2:支付方式(人脸、密码、指纹)。
符合当一个类存在多个变化维度时,使用继承会导致类的数量呈指数级增长的先决条件
2.2. 定位抽象和实现
关键是判断:哪个是底层机制(怎么做),哪个是业务功能(做什么)
- 实现部分:支付方式(人脸、密码、指纹)
- 支付方式里面有 "支付的具体认证机制"、"验证身份"、"验证后扣款" 等,表明了要做什么,怎么做;
- 更底层、更基础
- 抽象部分:支付渠道(微信、支付宝)
- 支付渠道只是"业务层的支付通道", 指出我们要做支付宝支付和微信支付,只要知道做什么,不需要关注具体怎么做;
- 更高层、面向业务
2.3. 桥接模式代码实现
2.3.1. 抽象部分
csharp
public abstract class BasePayment {
// 桥!连接支付方式
protected IPayMode payMode;
public BasePayment(IPayMode payMode) {
this.payMode = payMode;
}
// 交易
public abstract void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount);
}
scala
public class AliPayment extends BasePayment {
public AliPayment(IPayMode payMode) {
super(payMode);
}
@Override
public void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
if (payMode.security(uId)) {
System.out.println("支付成功");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}
scala
public class WxPayment extends BasePayment{
public WxPayment(IPayMode payMode) {
super(payMode);
}
@Override
public void transfer(String uId, BigDecimal amount) {
if (payMode.security(uId)) {
System.out.println("微信支付完成");
} else {
System.out.println("支付存在风险!");
}
}
}
typescript
@Configuration
public class PayConfig {
// ========================= 微信支付 ===============================
// 微信人脸支付
@Bean("wxFacePayment")
public BasePayment wxFacePayment(FacePayment facePayment) {
return new WxPayment(facePayment);
}
// 微信指纹支付
@Bean("wxFingerPayment")
public BasePayment wxFingerPayment(FingerprintPayment fingerprintPayment) {
return new WxPayment(fingerprintPayment);
}
// 微信密码支付
@Bean("wxPasswordPayment")
public BasePayment wxPasswordPayment(PasswordPayment passwordPayment) {
return new WxPayment(passwordPayment);
}
// ========================= 支付宝支付 ===============================
// 支付宝人脸支付
@Bean("aliFacePayment")
public BasePayment aliFacePayment(FacePayment facePayment) {
return new AliPayment(facePayment);
}
// 支付宝指纹支付
@Bean("aliFingerprintPayment")
public BasePayment aliFingerprintPayment(FingerprintPayment fingerprintPayment) {
return new AliPayment(fingerprintPayment);
}
// 密码支付
@Bean("aliPasswordPayment")
public BasePayment aliPasswordPayment(PasswordPayment passwordPayment) {
return new AliPayment(passwordPayment);
}
}2.3.2. 实现部分
arduino
public interface IPayMode {
// 支付风控校验
boolean security(String uId);
}
typescript
@Component
public class FacePayment implements IPayMode {
@Override
public boolean security(String uId) {
System.out.println("人脸支付,风控校验-人脸识别");
System.out.println("用户 " + uId + " 人脸识别成功");
return true;
}
}
typescript
@Component
public class FingerprintPayment implements IPayMode {
@Override
public boolean security(String uId) {
System.out.println("指纹支付,风控校验-指纹识别");
System.out.println("用户 " + uId + " 指纹识别成功");
return true;
}
}
typescript
@Component
public class PasswordPayment implements IPayMode {
@Override
public boolean security(String uId) {
System.out.println("密码支付,风控校验-密码验证");
System.out.println("用户 " + uId + " 密码验证成功");
return true;
}
}2.3.3. 代码调用
less
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/portal/test")
public class TestController {
@Resource
private Map<String,BasePayment> paymentMap;
@GetMapping(value = "/pay/test")
public CommonResult<String> payTest() {
// 支付宝密码支付
BasePayment aliPasswordPayment = paymentMap.get("aliPasswordPayment");
aliPasswordPayment.transfer("U10001", new BigDecimal("88.88"));
return CommonResult.success();
}
}