如何录制浏览器播放的音频?虚拟音频线与Python采集步骤
-
- 一、为什么要录制浏览器音频?
- 二、技术原理
-
- [1. 虚拟音频线 (Virtual Audio Cable)](#1. 虚拟音频线 (Virtual Audio Cable))
- [2. Python音频采集](#2. Python音频采集)
- 三、完整操作步骤
一、为什么要录制浏览器音频?
- 直接录音的问题:使用普通麦克风录制电脑播放的音频会引入环境噪音,音质差
- 版权保护限制:许多流媒体平台禁止直接下载内容
- 内容保存需求:你可能想要保存在线课程、会议录音或喜欢的音乐
- 音频处理需求:需要对网络音频进行编辑、转录或分析
二、技术原理
1. 虚拟音频线 (Virtual Audio Cable)
想象一下,你的电脑有真实的音频线连接扬声器和麦克风。虚拟音频线在软件层面创建了这样的"虚拟线路",允许将一个应用程序的音频输出直接"路由"到另一个应用程序的音频输入,就像用一根虚拟的线将它们连接起来。
2. Python音频采集
使用Python的PyAudio库直接从系统音频输入(现在变成了虚拟音频线的输出)捕获音频数据,并保存为文件。
三、完整操作步骤
1、安装虚拟音频线 (VAC)
1.1、为什么需要VAC?
Windows系统默认不会让应用程序直接捕获另一个应用程序的音频输出。VAC创建了一个虚拟的音频设备,可以将浏览器音频"重定向"到Python程序可以访问的地方。
1.2、如何安装
- 访问 Virtual Audio Cable 官网
- 下载适合你系统的版本(32位或64位)
- 运行安装程序,按照提示完成安装
- 安装后可能需要重启电脑
1.3、安装验证
- 安装完成后,在系统声音设置中会出现新的音频设备
- 这些设备通常命名为"Virtual Audio Cable"
2、在浏览器中打开你想要录制的音频内容
3、配置音频路由
- 打开音量合成器 :
- 右键点击系统任务栏的音量图标
- 选择"打开音量合成器"
- 配置应用程序输出 :
- 在音量合成器中找到你的浏览器应用
- 点击下拉菜单,将输出设备从"扬声器"改为"Virtual Cable"
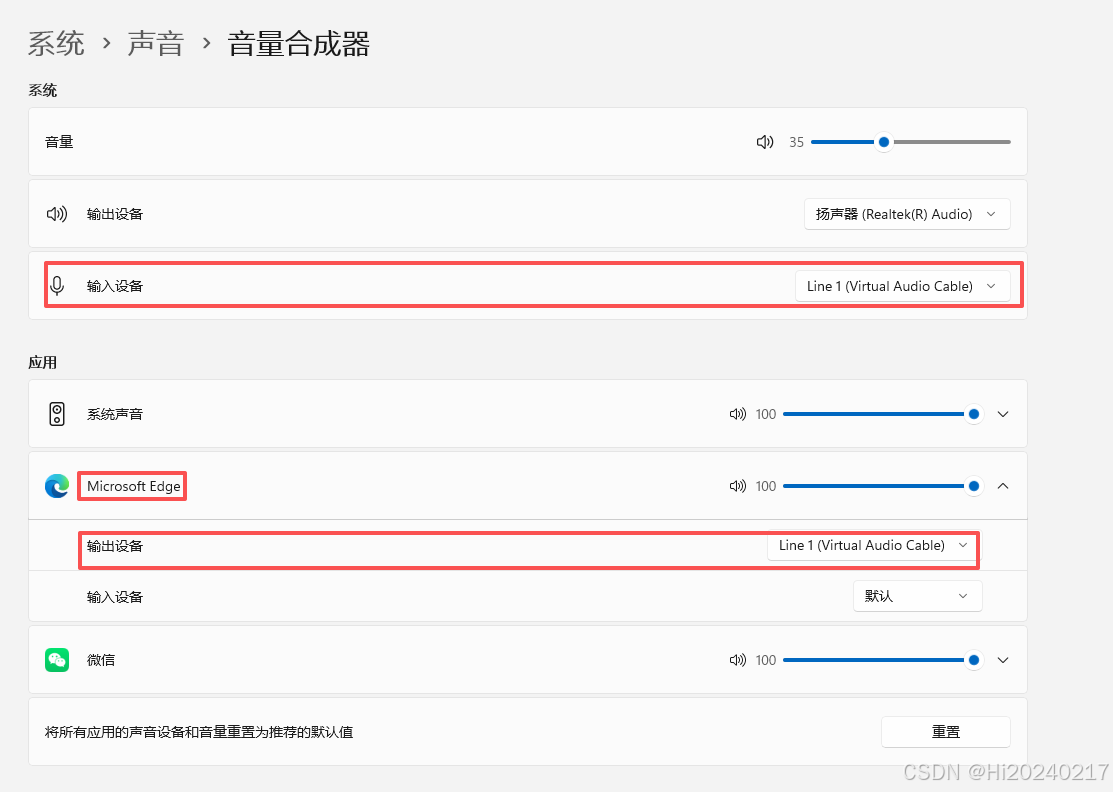
- 验证配置 :
- 播放音频时,声音应该不会从扬声器发出(因为被重定向了)
- 你可以在声音设置中看到虚拟音频线设备有音频活动
4、创建Python采集脚本
我们的Python脚本使用PyAudio库从默认音频输入设备(虚拟音频线)读取数据
python
import pyaudio
import numpy as np
import wave
from datetime import datetime
import time
import signal
import sys
class PCMRecorder:
def __init__(self, sample_rate=44100, channels=2, chunk_size=1024):
self.sample_rate = sample_rate
self.channels = channels
self.chunk_size = chunk_size
self.audio_format = pyaudio.paInt16
self.p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
self.is_recording = False
self.recording_start_time = None
def record_until_interrupt(self, output_file=None, device_index=None):
"""
持续录制音频直到用户按下 Ctrl+C
参数:
output_file: 输出文件路径(可选)
device_index: 设备索引,None使用默认设备
"""
self.is_recording = True
self.recording_start_time = time.time()
# 设置信号处理,捕获 Ctrl+C
original_sigint = signal.getsignal(signal.SIGINT)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, self._signal_handler)
# 打开音频流
stream = self.p.open(
format=self.audio_format,
channels=self.channels,
rate=self.sample_rate,
input=True,
input_device_index=device_index,
frames_per_buffer=self.chunk_size
)
print("开始录制... 按 Ctrl+C 结束录制")
print("正在录制...")
frames = []
chunk_count = 0
last_display_time = time.time()
try:
while self.is_recording:
# 读取音频数据
data = stream.read(self.chunk_size, exception_on_overflow=False)
frames.append(data)
chunk_count += 1
# 每1秒显示一次录制时长
current_time = time.time()
if current_time - last_display_time >= 1:
elapsed_time = current_time - self.recording_start_time
print(f"\r已录制: {self._format_time(elapsed_time)}", end="", flush=True)
last_display_time = current_time
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n检测到中断信号...")
finally:
# 恢复原来的信号处理
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, original_sigint)
# 停止并关闭流
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
# 合并所有音频数据
if frames:
audio_data = b''.join(frames)
recording_duration = time.time() - self.recording_start_time
print(f"\n录制结束!")
print(f"总录制时长: {self._format_time(recording_duration)}")
print(f"总采样点数: {len(audio_data) // 2}") # 每个采样点2字节
# 保存文件
if output_file:
# 如果没有指定输出文件,生成带时间戳的文件名
if not output_file:
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
output_file = f"recording_{timestamp}.pcm"
# 保存原始PCM
with open(output_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(audio_data)
print(f"PCM数据已保存到: {output_file}")
# 同时保存WAV文件
wav_file = output_file.replace('.pcm', '.wav')
if wav_file == output_file: # 如果没有.pcm扩展名
wav_file = output_file + '.wav'
self.save_wav(audio_data, wav_file)
print(f"WAV文件已保存到: {wav_file}")
# 转换为numpy数组并返回
np_audio = np.frombuffer(audio_data, dtype=np.int16)
if self.channels > 1:
np_audio = np_audio.reshape(-1, self.channels)
return np_audio, recording_duration
else:
print("未录制到任何音频数据")
return None, 0
def _signal_handler(self, sig, frame):
"""处理Ctrl+C信号"""
print("\n正在停止录制...")
self.is_recording = False
def _format_time(self, seconds):
"""格式化时间显示"""
hours = int(seconds // 3600)
minutes = int((seconds % 3600) // 60)
seconds = int(seconds % 60)
if hours > 0:
return f"{hours:02d}:{minutes:02d}:{seconds:02d}"
else:
return f"{minutes:02d}:{seconds:02d}"
def record(self, duration=10, device_index=None, output_file=None):
"""
录制指定时长的PCM音频
参数:
duration: 录制时长(秒)
device_index: 设备索引,None使用默认设备
output_file: 输出文件路径
"""
# 打开音频流
stream = self.p.open(
format=self.audio_format,
channels=self.channels,
rate=self.sample_rate,
input=True,
input_device_index=device_index,
frames_per_buffer=self.chunk_size
)
print(f"开始录制 {duration} 秒...")
# 录制音频
frames = []
total_chunks = int(self.sample_rate / self.chunk_size * duration)
for i in range(total_chunks):
data = stream.read(self.chunk_size, exception_on_overflow=False)
frames.append(data)
# 显示进度
if i % 50 == 0:
progress = (i + 1) / total_chunks * 100
print(f"\r进度: {progress:.1f}%", end="")
print("\n录制完成!")
# 停止并关闭流
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
# 合并所有音频数据
audio_data = b''.join(frames)
# 转换为numpy数组
np_audio = np.frombuffer(audio_data, dtype=np.int16)
# 如果是立体声,重新整形
if self.channels > 1:
np_audio = np_audio.reshape(-1, self.channels)
# 保存文件
if output_file:
# 保存原始PCM
with open(output_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(audio_data)
print(f"PCM数据已保存到: {output_file}")
# 同时保存WAV文件
wav_file = output_file.replace('.pcm', '.wav')
if wav_file == output_file: # 如果没有.pcm扩展名
wav_file = output_file + '.wav'
self.save_wav(audio_data, wav_file)
print(f"WAV文件已保存到: {wav_file}")
return np_audio
def save_wav(self, audio_data, filename):
"""保存为WAV文件"""
wf = wave.open(filename, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(self.channels)
wf.setsampwidth(self.p.get_sample_size(self.audio_format))
wf.setframerate(self.sample_rate)
wf.writeframes(audio_data)
wf.close()
def __del__(self):
"""清理资源"""
self.p.terminate()
if __name__ == "__main__":
recorder = PCMRecorder()
print("音频录制程序")
print("=" * 50)
print("1. 按 Ctrl+C 结束录制")
print("2. 输出文件将自动保存为 PCM 和 WAV 格式")
print("=" * 50)
# 使用新的持续录制功能
output_file = f"recording_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')}.pcm"
try:
audio_data, duration = recorder.record_until_interrupt(
output_file=output_file,
device_index=None
)
if audio_data is not None:
# 显示信息
print(f"\n录制信息:")
print(f" 总采样点数: {len(audio_data)}")
print(f" 声道数: {recorder.channels}")
print(f" 采样率: {recorder.sample_rate} Hz")
print(f" 时长: {duration:.2f} 秒")
print(f" 文件大小: {len(audio_data) * 2} 字节")
except Exception as e:
print(f"录制过程中发生错误: {e}")脚本使用说明:
-
安装依赖:首先需要安装PyAudio库
bashpip install pyaudio numpy wave -
运行脚本:
bashpython audio_recorder.py -
开始录制:
- 脚本启动后会自动开始录制
- 确保浏览器音频正在播放
- 控制台会显示录制时长
-
停止录制:
- 按
Ctrl+C停止录制 - 脚本会自动保存两个文件:
.pcm文件:原始音频数据,适合进一步处理.wav文件:标准音频格式,可以直接播放
- 按
-
文件命名 :
文件会自动以时间戳命名,如
recording_20251205_143000.wav