背景说明
1、源端是AWS、目标端是阿里云
2、最后个割接环境,客户能接受停机迁移
3、源端数据量比较大,大概3T
官方迁移文档
Elasticsearch迁移方案选取指南_检索分析服务 Elasticsearch版(ES)-阿里云帮助中心
将AWS中的ES数据迁移到阿里云ES中_检索分析服务 Elasticsearch版(ES)-阿里云帮助中心
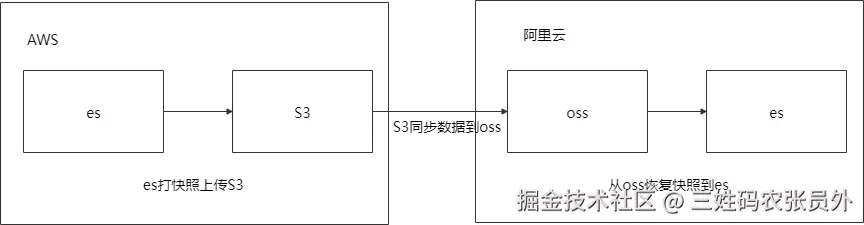
ES迁移整体流程
优化目标端ES配置项
修改下面的配置可以有效加速快照恢复的速度。
增加恢复带宽
bash
PUT /_cluster/settings
{
"transient": {
"indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec": "300mb"
}
}
GET /_cluster/settings?include_defaults=true&flat_settings=true1、限制恢复带宽: 将 indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec 参数设置为 300mb(默认是40mb)
2、临时生效: 使用 transient 配置,重启后失效
3、影响范围: 控制分片恢复、重新平衡等操作的网络传输速度
调整集群分片分配并发度: 配置 Elasticsearch 集群中分片恢复和分配的并发数量
默认值是4
bash
PUT _cluster/settings
{
"persistent": {
"cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries" : "16",
"cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries" : "16"
}
}cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries:
- 设置每个节点上同时进行的分片恢复操作数量为 16
- 影响集群重新平衡、节点重启后的数据恢复速度
cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries:
- 设置每个节点上同时进行的主分片初始恢复操作数量为 16
- 主要影响新索引创建或集群启动时的主分片分配速度
配置特点
- 持久化设置: 使用 persistent 配置,重启后仍然有效
- 性能优化: 增加并发度可以加快集群恢复和重新平衡速度
- 资源管理: 需要根据节点硬件资源合理设置,避免过度消耗系统资源
适用场景
- 集群扩容或缩容时加速分片重新分配
- 节点维护后快速恢复服务
- 大规模数据迁移时提高效率
总结的迁移步骤
第一次快照恢复动作
1、在AWS上的es创建快照并上传到S3
bash
GET _snapshot
# 创建仓库
PUT _snapshot/ali_backup
{
"type": "s3",
"settings": {
"bucket": "AWS云S3桶名称",
"base_path": "桶下面的路径",
"region": "cn-north-1",
"endpoint": "s3.cn-north-1.amazonaws.com.cn"
}
}
# 第一个版本快照
PUT _snapshot/ali_backup/prd_01
{
"indices": "*",
"ignore_unavailable": true,
"include_global_state": false
}
# 查看快照进度
GET _cat/snapshots/ali_backup?v2、启动S3到oss的数据同步任务:经过上面的步骤AWS的es数据已经同步到S3,配置数据同步将S3数据同步到阿里云OSS并观察数据同步结果
3、在阿里云ES上恢复快照
bash
# 更新仓库
PUT _snapshot/ali_backup
{
"type": "oss",
"settings": {
"base_path": "桶下面的路径",
"endpoint": "http://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com",
"access_key_id": "*************",
"secret_access_key": "*************",
"bucket": "oss桶",
"compress": true
}
}
# 查看快照
GET _snapshot/ali_backup/prd_01
# 全量恢复快照(排除系统索引,注意这里是第一次恢复所以不需要关闭索引)
POST _snapshot/ali_backup/prd_01/_restore
{
"indices": "*,-.*,-system*,-ilm*,-kibana*,-.kibana*"
}
# * 恢复镜像中的所有索引
# -.* 排除系统索引
# -system*
# -ilm* 排除ILM索引
# -kibana*,-.kibana* 排除kibana索引第二次快照恢复动作
1、在AWS上的es创建快照并上传到S3,第2个版本prd_02
bash
# 第2个版本快照
PUT _snapshot/ali_backup/prd_02
{
"indices": "*",
"ignore_unavailable": true,
"include_global_state": false
}
# 查看快照进度
GET _cat/snapshots/ali_backup?v2、启动S3到oss的数据同步任务
3、在阿里云ES上恢复快照
bash
# 查看快照
GET _snapshot/ali_backup/prd_02
# 关闭所有索引主要要排除系统索引,不然kibana会报错就没法操作了
POST /*,-.*,-system*,-ilm*,-kibana*,-.kibana*/_close
# 全量恢复快照排除系统索引
POST _snapshot/ali_backup/prd_02/_restore
{
"indices": "*,-.*,-system*,-ilm*,-kibana*,-.kibana*"
}总结说明
快照恢复比较简单高效,当据量大的情况下第一次打快照和恢复快照时间较长,后面做增量快照和恢复增量快照比较快。
es生成快照脚本
下面是基于python开发的生成快照、关闭索引、恢复索引、打开索引、查看恢复状态、查看索引版本的工具,方便进行多次打快照恢复快照避免在kibana上频繁操作误操作。
es_ba_config.toml
ini
[AWS-es01]
es_host = "xxxxx.ssss.net.cn"
es_port = 9200
protocol = "https"
username = "elastic" # 用户名
password = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxx" # 密码
[AWS-es02]
es_host = "xxxxx.ssss.cn"
es_port = 9200
protocol = "https"
username = "elastic" # 用户名
password = "XXXXXXXXP" # 密码es_re_config.toml
ini
[ALI-es-01]
es_host = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXxx.aliyuncs.com"
es_port = 9200
protocol = "https"
username = "elastic" # 用户名
password = "XXXXXXXXX" # 密码
[ALI-es-02]
es_host = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXxx.aliyuncs.com"
es_port = 9200
protocol = "https"
username = "elastic" # 用户名
password = "XXXXXXXXX" # 密码
python
import requests
import toml
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
app = Flask(__name__)
#----------------------------加载配置文件---------------------------#
def set_config(config_name):
"""
获取配置信息并设置全局变量
"""
global ES_HOST, ES_PORT, PROTOCOL, USERNAME, PASSWORD
try:
file_path = r"D:\work\es_ba_config.toml"
config = toml.load(file_path)[config_name]
# 设置全局变量
ES_HOST = config.get('es_host')
ES_PORT = config.get('es_port')
PROTOCOL = config.get('protocol')
USERNAME = config.get('username')
PASSWORD = config.get('password')
print({
'ES_HOST': ES_HOST,
'ES_PORT': ES_PORT,
'PROTOCOL': PROTOCOL,
'USERNAME': USERNAME,
'PASSWORD': PASSWORD
})
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载配置失败: {e}")
return None
#----------------------------加载配置文件---------------------------#
@app.route('/api/get_snapshot_status', methods=['POST'])
def api_get_snapshot_status():
"""
API接口:获取快照状态
执行命令: GET _cat/snapshots/plrs_target_ps_visit_precondition?v
"""
data = request.get_json()
repository = data.get('repository')
config_name = data.get('config_name')
set_config(config_name)
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/_cat/snapshots/{repository}?v"
# 设置请求参数
params = {
'v': 'true' # 显示详细信息
}
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if USERNAME and PASSWORD:
auth = (USERNAME, PASSWORD)
try:
# 发送 GET 请求,添加认证信息和参数
response = requests.get(url, params=params, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
print(response.text)
return jsonify({
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": response.text
})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return jsonify({
"code": 500,
"message": f"获取快照状态失败: {str(e)}",
"data": None
})
@app.route('/api/create_snapshot', methods=['POST'])
def api_create_snapshot():
"""
API接口:创建快照
执行命令: PUT _snapshot/plrs_target_ps_visit_precondition/prd_01
"""
# 使用默认参数匹配指定的快照创建命令
ignore_unavailable = True
include_global_state = False
data = request.get_json()
repository = data.get('repository')
snapshot = data.get('snapshot')
indices = data.get('indices')
config_name = data.get('config_name')
set_config(config_name)
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/_snapshot/{repository}/{snapshot}"
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if USERNAME and PASSWORD:
auth = (USERNAME, PASSWORD)
# 设置请求体
body = {
"indices": indices,
"ignore_unavailable": ignore_unavailable,
"include_global_state": include_global_state
}
try:
# 发送 PUT 请求,添加认证信息和请求体
response = requests.put(url, auth=auth, json=body)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
# 返回 JSON 响应数据
return jsonify({
"code": 200,
"message": "快照创建成功",
"data": response.json()
})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return jsonify({
"code": 500,
"message": "创建快照失败",
"data": None
})
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8888, debug=True)
python
import requests
import toml
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
app = Flask(__name__)
#----------------------------加载配置文件---------------------------#
def set_config(config_name):
"""
获取配置信息并设置全局变量
"""
global ES_HOST, ES_PORT, PROTOCOL, USERNAME, PASSWORD
try:
file_path = r"D:\work\es_re_config.toml"
config = toml.load(file_path)[config_name]
# 设置全局变量
ES_HOST = config.get('es_host')
ES_PORT = config.get('es_port')
PROTOCOL = config.get('protocol')
USERNAME = config.get('username')
PASSWORD = config.get('password')
print({
'ES_HOST': ES_HOST,
'ES_PORT': ES_PORT,
'PROTOCOL': PROTOCOL,
'USERNAME': USERNAME,
'PASSWORD': PASSWORD
})
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载配置失败: {e}")
return None
#----------------------------加载配置文件---------------------------#
def get_es_indices_status(es_host, es_port=9200, protocol='http', username=None, password=None):
"""
获取 Elasticsearch 所有索引的状态信息
Args:
es_host (str): Elasticsearch 主机地址
es_port (int): Elasticsearch 端口号,默认为 9200
protocol (str): 协议类型,默认为 'http'
username (str): 用户名,用于基本认证
password (str): 密码,用于基本认证
Returns:
dict: 索引状态信息
"""
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{protocol}://{es_host}:{es_port}/_cat/indices/*"
# 设置请求参数
params = {
'h': 'index,status', # 只返回索引名和状态
'expand_wildcards': 'all' # 展开所有通配符匹配的索引
}
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if username and password:
auth = (username, password)
try:
# 发送 GET 请求,添加认证信息
response = requests.get(url, params=params, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
# 处理响应数据
indices_data = response.text.strip()
if indices_data:
# 按行分割并处理数据
lines = indices_data.split('\n')
indices_status = {}
for line in lines:
if line.strip():
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) >= 2:
index_name = parts[0]
status = parts[1]
indices_status[index_name] = status
# 2. 过滤出非系统索引
print("\n正在过滤非系统索引...")
non_system_indices = filter_non_system_indices(indices_status)
print(f"共找到 {len(non_system_indices)} 个非系统索引:")
for index in non_system_indices:
print(f" - {index}")
return non_system_indices
else:
return {}
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"请求 Elasticsearch 失败: {e}")
return None
def filter_non_system_indices(indices_status):
"""
过滤出所有非系统索引(不以 . 开头的索引)
Args:
indices_status (dict): 所有索引及其状态
Returns:
list: 非系统索引列表
"""
non_system_indices = []
for index_name in indices_status.keys():
# 过滤掉以 . 开头的系统索引
if not index_name.startswith('.'):
non_system_indices.append(index_name)
return non_system_indices
# 逐个关闭索引
@app.route('/api/close_individual_indices', methods=['POST'])
def close_individual_indices():
data = request.get_json()
indices_list = data.get('indices_list')
config_name = data.get('config_name')
set_config(config_name)
"""
逐个关闭索引(更安全的方式)
Args:
es_host (str): Elasticsearch 主机地址
es_port (int): Elasticsearch 端口号
protocol (str): 协议类型
username (str): 用户名
password (str): 密码
indices_list (list): 要关闭的索引列表,依赖接口传递,如果是空就获取全部
Returns:
dict: 关闭操作结果统计
"""
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if USERNAME and PASSWORD:
auth = (USERNAME, PASSWORD)
success_count = 0
failed_count = 0
details = []
if not indices_list:
try:
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/*,-.*,-system*,-ilm*,-kibana*,-.kibana*/_close"
# 发送 POST 请求关闭单个索引
response = requests.post(url, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"关闭索引 * 失败: {e}")
details.append({"index": "*", "status": "failed", "error": str(e)})
else:
for index_name in indices_list:
try:
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/{index_name}/_close"
# 发送 POST 请求关闭单个索引
response = requests.post(url, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status()
print(f"成功关闭索引: {index_name}")
success_count += 1
details.append({"index": index_name, "status": "success"})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"关闭索引 {index_name} 失败: {e}")
failed_count += 1
details.append({"index": index_name, "status": "failed", "error": str(e)})
return jsonify({
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": {
"success": success_count,
"failed": failed_count,
"details": details
}
})
@app.route('/api/open_individual_indices', methods=['POST'])
def open_individual_indices():
data = request.get_json()
indices_list = data.get('indices_list')
config_name = data.get('config_name')
set_config(config_name)
"""
逐个开启索引(更安全的方式)
Args:
es_host (str): Elasticsearch 主机地址
es_port (int): Elasticsearch 端口号
protocol (str): 协议类型
username (str): 用户名
password (str): 密码
indices_list (list): 要开启的索引列表
Returns:
dict: 开启操作结果统计
"""
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if USERNAME and PASSWORD:
auth = (USERNAME, PASSWORD)
success_count = 0
failed_count = 0
details = []
if not indices_list:
# 开启所有索引
try:
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/_all/_open"
# 发送 POST 请求开启单个索引
response = requests.post(url, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"开启索引_all失败: {e}")
details.append({"index": "_all", "status": "failed", "error": str(e)})
else:
for index_name in indices_list:
try:
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/{index_name}/_open"
# 发送 POST 请求开启单个索引
response = requests.post(url, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status()
print(f"成功开启索引: {index_name}")
success_count += 1
details.append({"index": index_name, "status": "success"})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"开启索引 {index_name} 失败: {e}")
failed_count += 1
details.append({"index": index_name, "status": "failed", "error": str(e)})
return jsonify({
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": {
"success": success_count,
"failed": failed_count,
"details": details
}
})
@app.route('/api/restore_snapshot', methods=['POST'])
def api_restore_snapshot():
"""
API接口:恢复快照
执行命令: POST _snapshot/ali_es_backup/prd_01/_restore
"""
# 使用固定的参数来匹配指定的恢复命令
data = request.get_json()
repository = data.get('repository')
snapshot = data.get('snapshot')
indices = data.get('indices')
config_name = data.get('config_name')
set_config(config_name)
# 构建请求 URL
get_url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/_snapshot/{repository}/{snapshot}"
post_url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/_snapshot/{repository}/{snapshot}/_restore"
print(get_url)
print(post_url)
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if USERNAME and PASSWORD:
auth = (USERNAME, PASSWORD)
# 设置请求体 - 匹配指定命令的参数
body = {
"indices": indices
}
print(body)
try:
# 发送 POST 请求,添加认证信息和请求体
response = requests.get(get_url, auth=auth, json=body)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
pass
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return jsonify({
"code": 500,
"message": f"获取快照失败: {str(e)}",
"data": None
})
try:
# 发送 POST 请求,添加认证信息和请求体
response = requests.post(post_url, auth=auth, json=body)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
return jsonify({
"code": 200,
"message": f"快照恢复成功",
"data": response.json()
})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return jsonify({
"code": 500,
"message": f"恢复快照失败: {str(e)}",
"data": None
})
@app.route('/api/get_all_snapshots', methods=['POST'])
def get_all_snapshots():
"""
获取指定仓库下所有快照的信息
Args:
es_host (str): Elasticsearch 主机地址
es_port (int): Elasticsearch 端口号,默认为 9200
protocol (str): 协议类型,默认为 'http'
username (str): 用户名,用于基本认证
password (str): 密码,用于基本认证
repository (str): 快照仓库名称
Returns:
dict: 快照信息
"""
data = request.get_json()
repository = data.get('repository')
config_name = data.get('config_name')
set_config(config_name)
# 构建请求 URL
url = f"{PROTOCOL}://{ES_HOST}:{ES_PORT}/_snapshot/{repository}/_all"
# 设置请求参数
params = {
'filter_path': 'snapshots.name,snapshots.snapshot,snapshots.state,snapshots.start_time,snapshots.end_time'
}
# 设置认证信息
auth = None
if USERNAME and PASSWORD:
auth = (USERNAME, PASSWORD)
try:
# 发送 GET 请求,添加认证信息和参数
response = requests.get(url, params=params, auth=auth)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
# 返回 JSON 响应数据
return jsonify({
"code": 200,
"message": "获取成功",
"data": response.json()
})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return jsonify({
"code": 500,
"message": f"获取信息失败: {str(e)}",
"data": None
})
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=6666, debug=True)