手写Tomcat:深入理解Servlet容器工作原理
在Java Web开发中,Tomcat作为最常用的Servlet容器,其工作原理是每个Java开发人员都应该掌握的核心知识。本文将带领大家通过手写一个简易版的Tomcat,深入剖析Servlet容器的工作原理。我们将按照代码结构,逐个解析每个Java类的实现。
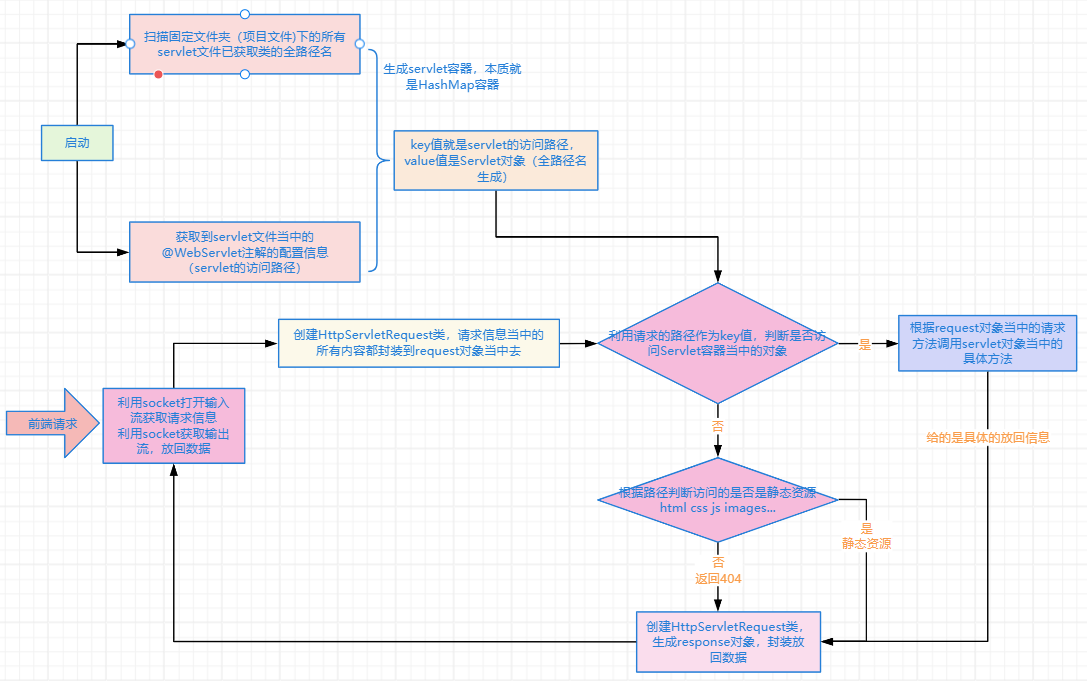
手写Tomcat流程分析图
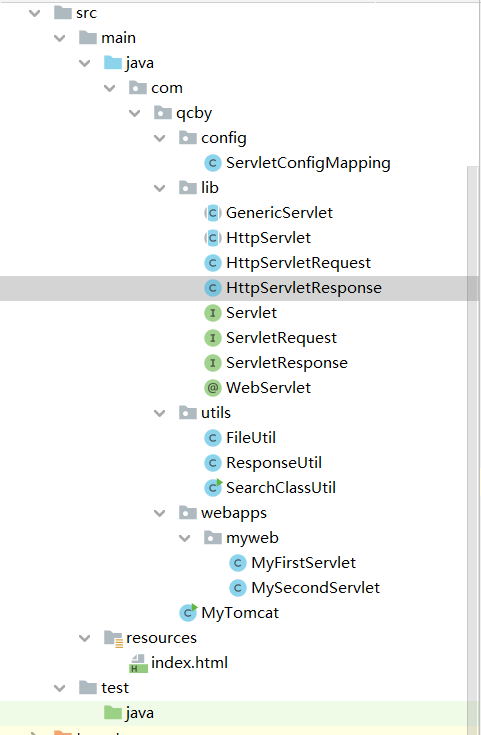
项目结构概览
1. ServletConfigMapping类 - Servlet配置映射
java
package com.qcby.config;
import com.qcby.lib.HttpServlet;
import com.qcby.lib.WebServlet;
import com.qcby.utils.SearchClassUtil;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class ServletConfigMapping {
public static Map<String, HttpServlet> classmapping=new HashMap<>();
static {
//通过反射获取路径呗
List<String>paths= SearchClassUtil.searchClass("com.qcby.webapps.myweb");
for(String path:paths){
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName(path);
WebServlet webServlet=(WebServlet) clazz.getAnnotation(WebServlet.class);
String value=webServlet.value();
HttpServlet httpServlet=(HttpServlet) clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
classmapping.put(value,httpServlet);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}核心功能:
- 在静态块中初始化Servlet容器
- 使用反射扫描指定包下的所有类
- 获取@WebServlet注解中的路径配置
- 创建Servlet实例并存入HashMap容器
2. GenericServlet类 - Servlet通用抽象类
java
package com.qcby.lib;
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet{
@Override
public void init() {
}
@Override
public abstract void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception;
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}核心功能:
- 实现了Servlet接口的基本生命周期方法
- 提供了默认的空实现(init和destroy)
- 将service方法声明为抽象方法,由子类实现
3. HttpServlet类 - HTTP Servlet抽象类
java
package com.qcby.lib;
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet{
public abstract void doGet(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception;
public abstract void doPost(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception;
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
if(req.getMethod().equals("GET")){
this.doGet(req,resp);
//这个地址就是子类对象的地址
}else{
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
}
}核心功能:
- 扩展了GenericServlet,专门处理HTTP协议
- 定义了doGet和doPost两个抽象方法
- 实现了service方法,根据请求方法分发到具体的处理方法
4. HttpServletRequest类 - HTTP请求对象
java
package com.qcby.lib;
public class HttpServletRequest implements ServletRequest{
private String method;
private String path;
@Override
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
@Override
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
@Override
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method=method;
}
@Override
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path=path;
}
}核心功能:
- 封装HTTP请求信息
- 提供getter和setter方法访问请求方法和路径
- 实现了ServletRequest接口
5. HttpServletResponse类 - HTTP响应对象
java
package com.qcby.lib;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import com.qcby.utils.FileUtil;
import com.qcby.utils.ResponseUtil;
public class HttpServletResponse implements ServletResponse {
private OutputStream outputStream;
@Override
public OutputStream getOutputStream() {
return this.outputStream;
}
@Override
public void setOutputStream(OutputStream outputStream) {
this.outputStream=outputStream;
}
//还有两个方法 返回静态资源 返回动态资源 说白了都是outputStream.write(); 写入输出流进行字节输出 参数是一个字节数组
@Override
public void append(String content) throws Exception {
this.outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}
public void returnStatic(String path) throws Exception {
//利用file工具包 找到path 在工具包里利用 输出流write
String resoucePath = FileUtil.getResoucePath(path);
File file=new File(resoucePath);
FileUtil.writeFile(file,outputStream);
}
}核心功能:
- 封装HTTP响应信息
- 管理输出流
- 提供append方法写入动态内容
- 提供returnStatic方法返回静态资源
6. Servlet接口 - Servlet标准接口
java
package com.qcby.lib;
public interface Servlet {
public void init();
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception;
public void destroy();
}核心功能:
- 定义了Servlet的生命周期方法
- 标准化Servlet的行为规范
7. ServletRequest接口 - 请求接口
java
package com.qcby.lib;
public interface ServletRequest {
public String getMethod();
public String getPath();
public void setMethod(String method);
public void setPath(String path);
}核心功能:
- 定义了请求对象的基本操作
- 提供获取和设置请求方法和路径的方法
8. ServletResponse接口 - 响应接口
java
package com.qcby.lib;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public interface ServletResponse {
public OutputStream getOutputStream();
public void setOutputStream(OutputStream outputStream);
public void append(String content) throws Exception;
}核心功能:
- 定义了响应对象的基本操作
- 管理输出流和内容写入
9. WebServlet注解 - Servlet配置注解
java
package com.qcby.lib;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface WebServlet {
String value(); //定义注解的参数吧 传过来的是 访问路径
}核心功能:
- 运行时保留的注解
- 只能用于类上
- 包含一个value参数,用于指定Servlet的访问路径
10. FileUtil类 - 文件工具类
java
package com.qcby.utils;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 该类的主要作用是进行读取文件
*/
public class FileUtil {
public static boolean witeFile(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream){
boolean success = false ;
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream ;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream;
try {
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
bufferedOutputStream.write(ResponseUtil.responseHeader200.getBytes());
int count = 0;
while (count == 0){
count = inputStream.available();
}
int fileSize = inputStream.available();
long written = 0;
int beteSize = 1024;
byte[] bytes = new byte[beteSize];
while (written < fileSize){
if(written + beteSize > fileSize){
beteSize = (int)(fileSize - written);
bytes = new byte[beteSize];
}
bufferedInputStream.read(bytes);
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes);
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
written += beteSize;
}
success = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return success;
}
public static boolean writeFile(File file,OutputStream outputStream) throws Exception{
return witeFile(new FileInputStream(file),outputStream);
}
public static String getResoucePath(String path){
String resource = FileUtil.class.getResource("/").getPath();
return resource + "\\" + path;
}
}核心功能:
- 提供文件读取和写入功能
- 支持大文件分块读取
- 获取资源文件路径
11. ResponseUtil类 - 响应工具类
java
package com.qcby.utils;
public class ResponseUtil {
public static String responseHeader200 = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html\r\n" +
"Connection: keep-alive\r\n" +
"Content-Length: %d\r\n" +
"\r\n";
public static String responseHeader404 = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html\r\n" +
"Connection: keep-alive\r\n" +
"Content-Length: %d\r\n" +
"\r\n";
public static String getResponseHeader200(String content){
return "HTTP/1.1 200 \r\n" +
"Content-Type:text/html \r\n"+"\r\n" + content;
}
}核心功能:
- 提供标准的HTTP响应头
- 简化响应消息的构建
12. SearchClassUtil类 - 类搜索工具类
java
package com.qcby.utils;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 扫描指定包,获取该包下所有的类的全路径信息
*/
public class SearchClassUtil {
public static List<String> classPaths = new ArrayList<String>();
public static List<String> searchClass(String path){
//需要扫描的包名
String basePack = path;
//将获取到的包名转换为路径
String classPath = SearchClassUtil.class.getResource("/").getPath();
basePack = basePack.replace(".", File.separator);
String searchPath = classPath + basePack;
doPath(new File(searchPath),classPath);
//这个时候我们已经得到了指定包下所有的类的绝对路径了。我们现在利用这些绝对路径和java的反射机制得到他们的类对象
return classPaths;
}
/**
* 该方法会得到所有的类,将类的绝对路径写入到classPaths中
* @param file
*/
private static void doPath(File file,String classpath) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {//文件夹
//文件夹我们就递归
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f1 : files) {
doPath(f1,classpath);
}
} else {//标准文件
//标准文件我们就判断是否是class文件
if (file.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
String path = file.getPath().replace(classpath.replace("/","\\").
replaceFirst("\\\\",""),"").replace("\\",".").
replace(".class","");
//如果是class文件我们就放入我们的集合中。
classPaths.add(path);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> classes = SearchClassUtil.searchClass("com.qcby.webapps.myweb");
for (String s: classes) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}核心功能:
- 递归扫描指定包下的所有.class文件
- 获取类的全限定名
- 支持包名到路径的转换
13. MyFirstServlet类 - 第一个Servlet示例
java
package com.qcby.webapps.myweb;
import com.qcby.lib.HttpServlet;
import com.qcby.lib.ServletResponse;
import com.qcby.lib.ServletRequest;
import com.qcby.lib.WebServlet;
import com.qcby.utils.ResponseUtil;
@WebServlet("/first")
public class MyFirstServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收到了get请求,正在处理");
resp.append(ResponseUtil.getResponseHeader200("<h1>你好</h1>"));
}
@Override
public void doPost(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收到了post请求,正在处理");
resp.append(ResponseUtil.getResponseHeader200("<h1>你好</h1>"));
}
}核心功能:
- 使用@WebServlet注解配置访问路径为"/first"
- 实现了doGet和doPost方法
- 处理HTTP GET和POST请求
14. MySecondServlet类 - 第二个Servlet示例
java
package com.qcby.webapps.myweb;
import com.qcby.lib.HttpServlet;
import com.qcby.lib.ServletResponse;
import com.qcby.lib.ServletRequest;
import com.qcby.lib.WebServlet;
import com.qcby.utils.ResponseUtil;
@WebServlet("/second")
public class MySecondServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收到了get请求,正在处理");
resp.append(ResponseUtil.getResponseHeader200("<h1>你好</h1>"));
}
@Override
public void doPost(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收到了Post请求,正在处理");
resp.append(ResponseUtil.getResponseHeader200("<h1>你好</h1>"));
}
}核心功能:
- 使用@WebServlet注解配置访问路径为"/second"
- 实现了doGet和doPost方法
- 处理HTTP GET和POST请求
15. MyTomcat类 - Tomcat主启动类
java
package com.qcby;
import com.qcby.lib.HttpServlet;
import com.qcby.lib.HttpServletRequest;
import com.qcby.lib.HttpServletResponse;
import com.qcby.utils.ResponseUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import static com.qcby.config.ServletConfigMapping.classmapping;
public class MyTomcat {
private static HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest=new HttpServletRequest();
private static HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse=new HttpServletResponse();
public static final Integer PROT=6677;
public static void start() throws Exception {
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(PROT);
while(true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); //得到socket对象
//获取输入流
InputStream stream= socket.getInputStream(); //此时是 01
httpServletResponse.setOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
handler(stream);
}
}
public static void handler(InputStream stream) throws Exception {
int count=0;
while(count==0){
count=stream.available();
}
byte[] bytes=new byte[count];
int read= stream.read(bytes);
String msg=new String(bytes,0,read);
//截取
String firstLine=msg.split("\n")[0];
String method=firstLine.split("\\s")[0];
String path=firstLine.split("\\s")[1];
System.out.println("method:"+method+" path:"+path);
httpServletRequest.setMethod(method);
httpServletRequest.setPath(path);
//对path进行判断
if(path==""){
System.out.println("是空请求");
// httpServletResponse.append(ResponseUtil.responseHeader404);
}else if(classmapping.get(path)!=null){
HttpServlet httpServlet=classmapping.get(path); //我在栈空间设置一个父类引用 指向 子类对象
httpServlet.service(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse);
}else{
//处理静态资源
httpServletResponse.returnStatic(path);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
start();
}
}核心功能:
- 启动Socket服务器监听6677端口
- 解析HTTP请求报文
- 根据请求路径分发到对应的Servlet或静态资源
- 管理请求-响应处理流程
总结
通过手写这个简易版的Tomcat,我们深入理解了以下核心概念:
- Servlet容器本质:一个以URL路径为key,Servlet实例为value的Map
- 请求响应流程:Socket接收请求 → 解析HTTP报文 → 路由分发 → 处理并返回
- 注解驱动配置:通过反射和注解实现零配置部署
- 静态动态资源分离:统一入口,根据路径判断资源类型
这个简易版Tomcat虽然功能有限,但已经实现了Servlet容器的核心思想。真正的Tomcat在此基础上增加了更多功能,如连接池、会话管理、JSP编译等,但基本原理是相通的。
希望这篇文章能够帮助你深入理解Tomcat和Servlet容器的工作原理!