day35文件的规范拆分和写法@浙大疏锦行
文件目录
day35_文件的规范拆分和写法/
├── data/
│ └── raw/
│ └── heart.csv # 已替换为 heart.csv 数据集
├── models/ # 用于存放训练好的模型
├── notebook/
│ └── main.ipynb # 主程序 Notebook,演示了完整的调用流程
├── src/ # 源代码目录
│ ├── init.py
│ ├── data/
│ │ ├── init.py
│ │ └── preprocessing.py # 数据加载与预处理(针对 heart.csv 进行了适配)
│ ├── models/
│ │ ├── init.py
│ │ └── train.py # 模型训练、评估与保存逻辑
│ └── visualization/
│ ├── init.py
│ └── plots.py # 可视化绘图(SHAP图、混淆矩阵)
├── README.md # 项目说明文档
└── requirements.txt # 依赖库列表
项目运行
python
import sys
import os
# 将项目根目录添加到系统路径
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "..")))
from src.data.preprocessing import load_data, encode_categorical_features, handle_missing_values
from src.models.train import train_model, evaluate_model, save_model
from src.visualization.plots import plot_feature_importance_shap, plot_confusion_matrix, set_plot_style
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split1. 数据加载与预处理
python
# 加载数据
data_path = "../data/raw/heart.csv"
data = load_data(data_path)
print("原始数据形状:", data.shape)
data.head()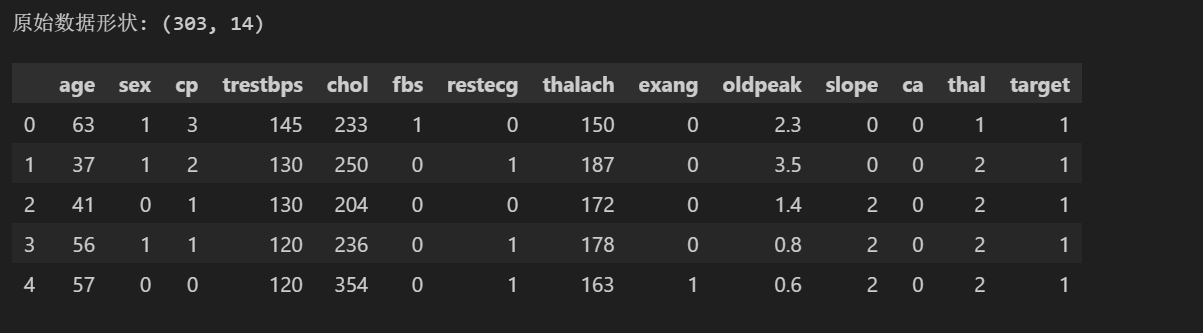
python
# 特征编码
data_encoded, _ = encode_categorical_features(data)
print("编码后数据形状:", data_encoded.shape)
data_encoded.head()编码后数据形状: (303, 24)
| age | sex | trestbps | chol | fbs | thalach | exang | oldpeak | ca | target | ... | restecg_0 | restecg_1 | restecg_2 | slope_0 | slope_1 | slope_2 | thal_0 | thal_1 | thal_2 | thal_3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 63 | 1 | 145 | 233 | 1 | 150 | 0 | 2.3 | 0 | 1 | ... | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 37 | 1 | 130 | 250 | 0 | 187 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 | 1 | ... | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 41 | 0 | 130 | 204 | 0 | 172 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 | 1 | ... | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 56 | 1 | 120 | 236 | 0 | 178 | 0 | 0.8 | 0 | 1 | ... | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 57 | 0 | 120 | 354 | 0 | 163 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 1 | ... | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
5 rows × 24 columns
python
# 处理缺失值
data_clean = handle_missing_values(data_encoded)
print("处理缺失值后数据形状:", data_clean.shape)处理缺失值后数据形状: (303, 24)
2. 模型训练
python
# 准备训练数据
X = data_clean.drop(['target'], axis=1)
y = data_clean['target']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练模型
model = train_model(X_train, y_train)
print("模型训练完成")3. 模型评估
python
evaluate_model(model, X_test, y_test)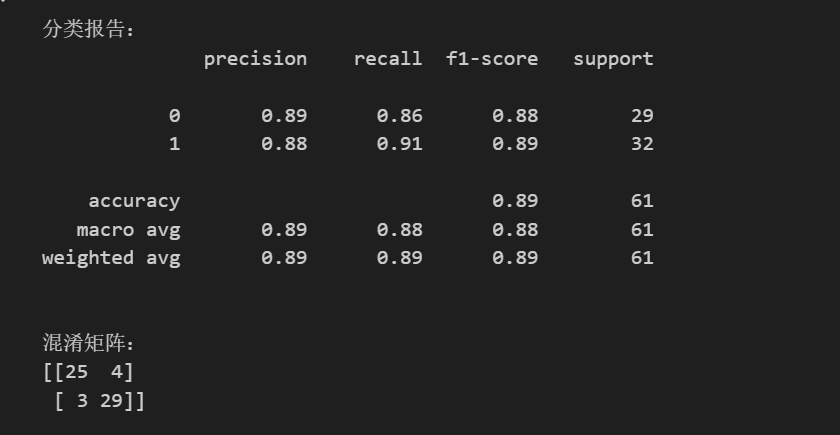
4. 可视化
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体和样式(直接在 Notebook 中设置,避免样式名兼容问题)
plt.style.use('ggplot')
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'Arial Unicode MS']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 绘制混淆矩阵
plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, model.predict(X_test))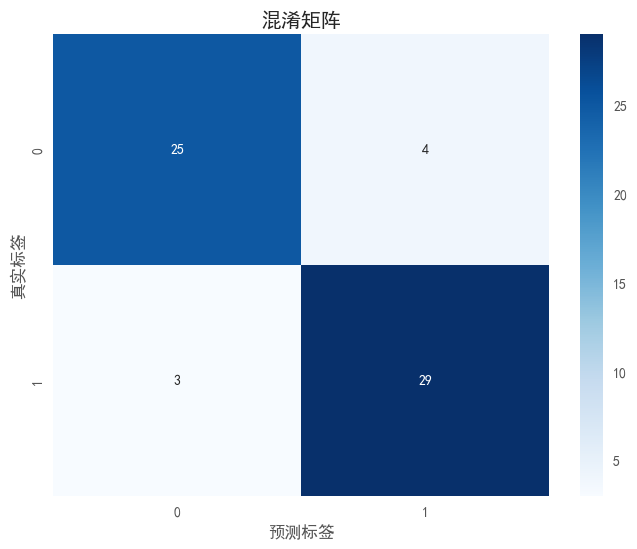
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 再次设置中文字体,确保 SHAP 图中文字正常显示
plt.style.use('ggplot')
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'Arial Unicode MS']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 绘制SHAP特征重要性
plot_feature_importance_shap(model, X_test)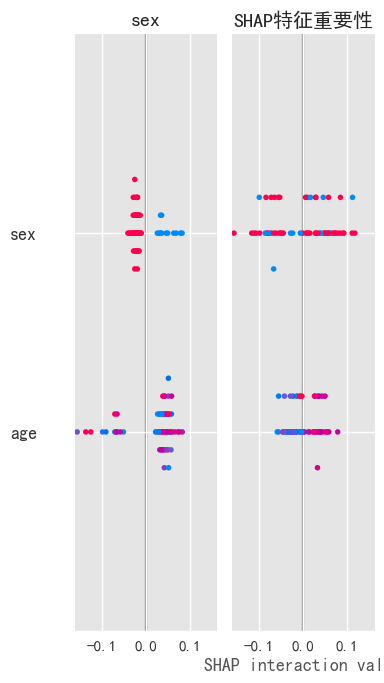
5. 保存模型
python
save_model(model, "../models/heart_disease_rf_model.joblib")