并行工具,FutureTask 的增强版,也可以叫完全体,超级强大
- Runable 是没有返回结果的行为
- Callable 是有返回结果的行为
- Future封装了 Callable 和 Runnable,委托给线程池执行,需要取回返回结果 --> 同步阻塞
- CompletableFuture封装了Future ,拥有回调功能,在某个行为执行完成之后,可以继续进行下一个动作 --> 异步非阻塞
真是业务场景中,都是多任务组合来进行处理
一、FutureTask存在的问题
FutureTask是一个同步阻塞处理任务的方式 --> 很多人说是同步非阻塞,但是调用get()方法会阻塞调用线程,个人认为这块还是同步阻塞,但是任务是异步执行
问题1:FutureTask获取线程执行的结果前,其他线程调用get()方法一直阻塞,需要等待FutureTask执行完call方法,才可以拿到返回结果。
问题2:如果不通过get()方法去挂起线程,通过while循环,不停的判断任务的状态是否结束,结束后,再拿结果,如果任务长时间没执行完毕,CPU 会一直调度查看任务状态,浪费 CPU 资源
以上两个问题,用 CompletableFuture就可以解决,CompletableFuture是一个异步非阻塞的方式,实现了 Future接口,提供了各种丰富的函数去执行各种操作
二、简单案例
写个简单案例,入个门,底层原理留在后续进行研究。
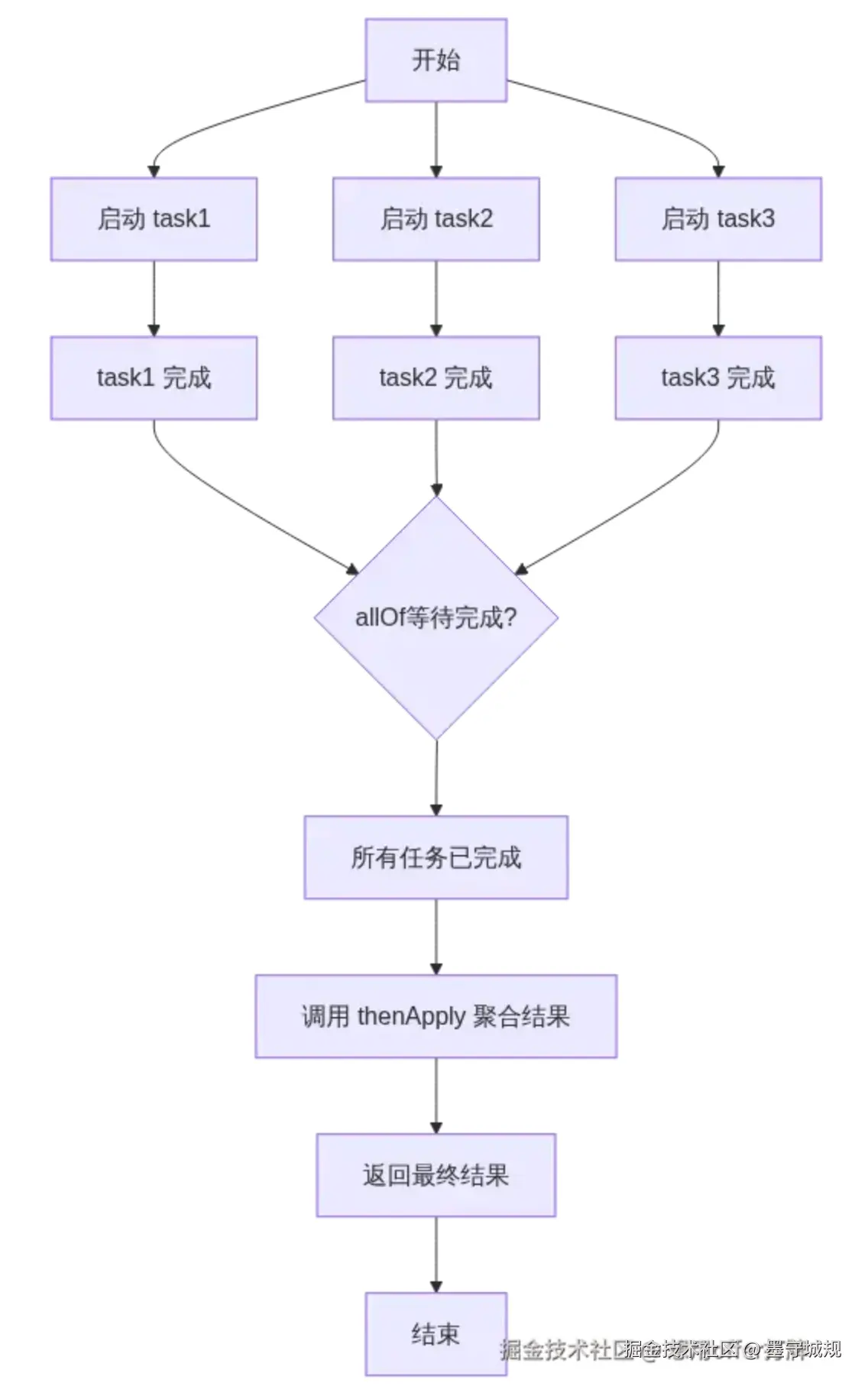
在真实的业务场景中,一个接口里用到了互不影响的几个流程,就可以用并行编排来进行性能优化。
csharp
public boolean checkOrder1(){
if (!basicCheck()){
return false;
}
List<CompletableFuture> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 异步编排 supplyAsync 有返回结果 创建编排任务
CompletableFuture<Boolean> checkRiskControl = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务 1");
return true;
});
list.add(checkRiskControl);
CompletableFuture<Boolean> checkCoupon = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务 2");
return true;
});
list.add(checkCoupon);
CompletableFuture<Boolean> checkGoods = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务 3");
return true;
});
list.add(checkGoods);
CompletableFuture<Boolean> checkInventory = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务 4");
return true;
});
list.add(checkInventory);
// 编排到一块 allof --> 所有的任务都执行完后,才执行allof
CompletableFuture<Boolean> result = CompletableFuture.allOf(
list.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])
).thenApply(res -> { // thenApply 拿到所有的结果 进行下一步
System.out.println("thenApply 拿到了所有结果 最后进行执行!!");
return checkGoods.join() && checkInventory.join() && checkCoupon.join()&& checkRiskControl.join();
});
// get方法 与 join方法区别:get是阻塞的 get 拿不到返回值一直到 join是非阻塞的
System.out.println("订单完成前置校验结果为:" + result.join());
return true;
}这里用到了三个CompletableFuture的功能:
- supplyAsync() --> 异步执行,有返回值
- allof() --> 全部执行完成,进行下一步
- thenApply() --> 依赖上一步的执行结果,有传参(上一个任务的结果就是入参),有返回值
- join() --> 获取执行结果 【这个方法是非阻塞的】 get() --> 是阻塞的
三、源码分析
以 JDK21 版本为例,着重分析异步回调是怎么实现的
着重以runAsync()方法以及then()方法为例子来进行分析,后续所有的方法大同小异
kotlin
// 再来一个没有返回结果的任务
// 默认使用的是 ForkJoin线程池 --> 守护线程,当主线程执行结束,守护线程也跟着结束,所有这个打印结果有可能输出,也有可能不输出
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("没有返回结果!!!");
});
voidCompletableFuture.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("11"));
voidCompletableFuture.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("22"));
voidCompletableFuture.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("33"));1、CompletableFuture的关键属性
就看下面的两个关键属性
arduino
// 存放任务返回的最终结果,即使返回值为 void 类型的,也会封装结果,封装的结果为NIL
volatile Object result;
// 一些then方法,后继要执行的任务存储的栈结构
volatile Completion stack;stack底层其实通过链表来实现的

2、runAsync()方法

没有指定线程池,默认使用ForkJoinPool

javascript
static CompletableFuture<Void> asyncRunStage(Executor e, Runnable f) {
// 边界判断,如果传进来的runable的lambda是空的,抛异常
if (f == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 声明当前任务的CompletableFuture对象,主要是为了触发后续任务的执行
CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>();
// 将任务和CompletableFuture封装到一起,作为 AsyncRun对象,交给线程池进行执行
e.execute(new AsyncRun(d, f));
return d;
}交给线程池执行,具体会运行到 AsyncRun对象的run方法
scala
static final class AsyncRun extends ForkJoinTask<Void>implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {
// 当前 CompletableFuture对象
CompletableFuture<Void> dep;
// 具体任务
Runnable fn;
// 构造器
AsyncRun(CompletableFuture<Void> dep, Runnable fn) {
this.dep = dep; this.fn = fn;
}
public void run() {
CompletableFuture<Void> d;
Runnable f;
// 源码编写人的编码风格 --> 判空处理的同时,将成员变量做临时存储
if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {
// 方便 GC,将成员变量置null
dep = null; fn = null;
// 判断当前任务是否已经执行完毕
if (d.result == null) { // 等于null 说明任务还没有执行
try {
// 执行任务
f.run();
// 设置结果 --> runAsync()没有返回结果,给当前CompletableFuture对象封装返回结果
// 为null的结果是NIL
d.completeNull();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 抛出异常,封装异常
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
// 从栈里取后续任务进行执行
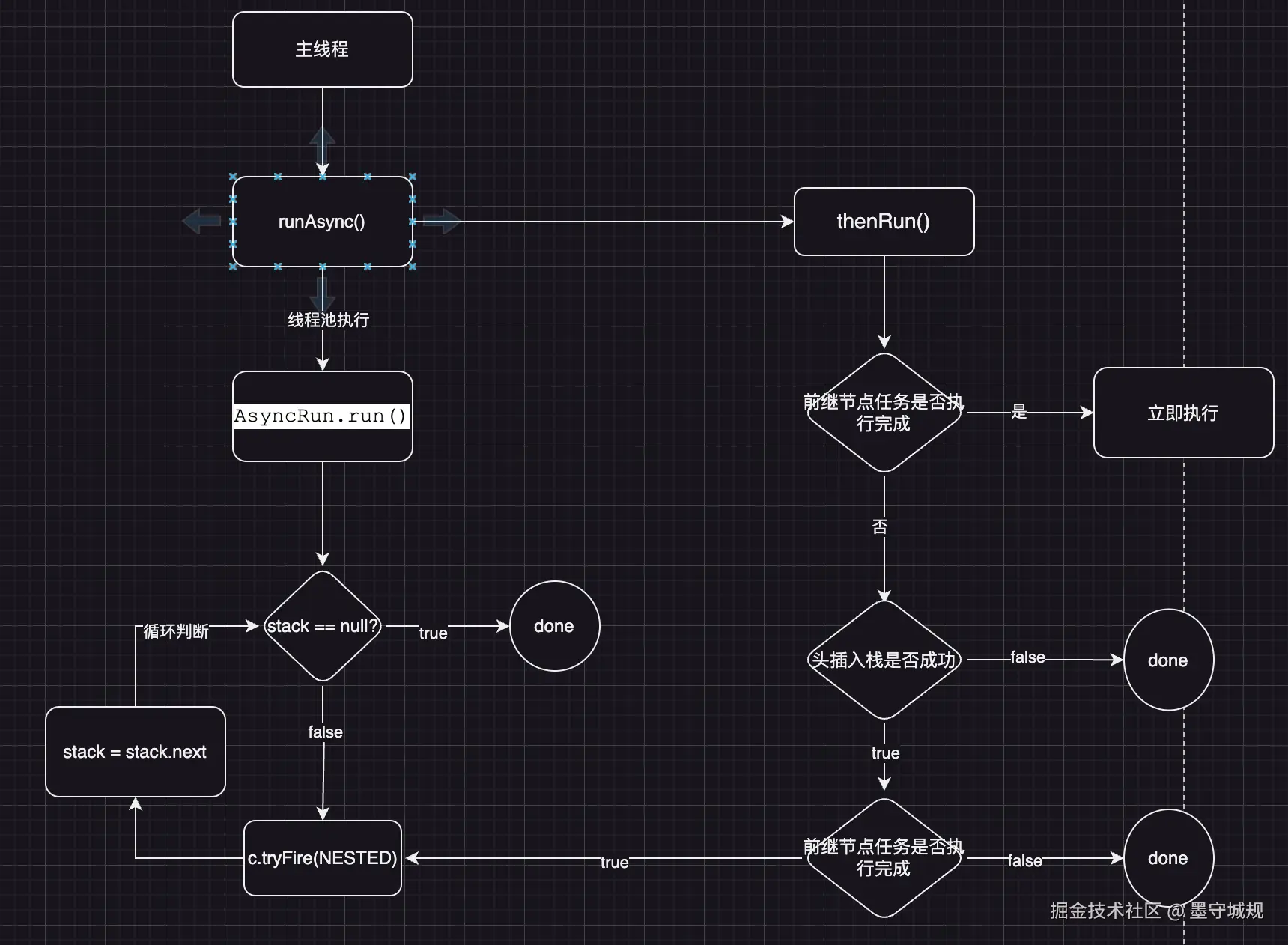
d.postComplete();
}
}
}这里分析一下d.completeNull()方法 和 d.completeThrowable(ex)这两个方法是怎么封装结果的
java
final boolean completeNull() {
// 通过 CAS 将result设置为 NIL
return RESULT.compareAndSet(this, null, NIL);
}
final boolean completeThrowable(Throwable x) {
// 通过 CAS 的方式将result封装异常结果
return RESULT.compareAndSet(this, null, encodeThrowable(x));
}接着分析,当前任务执行完毕后,后续栈里的任务具体是怎么处理的 --> d.postComplete()方法
kotlin
/*
* 总结:
* 1、栈里没值跳过
* 2、栈里有值从栈顶开始依次取值,执行具体任务
*/
final void postComplete() {
// 拿到当前的CompletableFuture对象
CompletableFuture<?> f = this;
// 局部栈变量
Completion h;
// 拆开来看
// (h = f.stack) != null --> 把当前CompletableFuture对象的stack变量赋值给局部变量h 并且判断 是不是为null --> 如果为空:说明没有后继任务,不需要往下执行
// (f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null) ---> 完全是为了健壮性判断,f如果不是当前对象,赋值成当前对象再进行判断
while ((h = f.stack) != null || (f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) { // 这个目的就是判断当前CompletableFuture对象的stack属性值是否为空 并且将栈顶数据赋值给h
CompletableFuture<?> d;
Completion t;
// 将当前CompletableFuture对象的 Stack 值设置为 h.next [栈顶换为next], h为栈顶元素
if (STACK.compareAndSet(f, h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) { // next不为null
if (f != this) { // f不是当前对象
pushStack(h); // 还原,再给压回去
continue;
}
// 移除掉h的next值 --> 删除h节点
NEXT.compareAndSet(h, t, null); // try to detach
}
// 具体执行栈顶的任务
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;
}
}
}具体执行任务的方法 h.tryFire(NESTED) ,这个tryFire()就得看具体的实现类是怎么执行的,怎么看具体的实现类 --> 就得知道调用完runAsync()方法, 后继方法调用的是什么,给栈里存放的具体任务的值 --> 后继方法调用的thenRun()这个方法
csharp
// 调用的后续方法是thenRun() ---> 看这个方法的具体实现类
task.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("11"));查看调用链,发现最后封装成一个UniRun对象
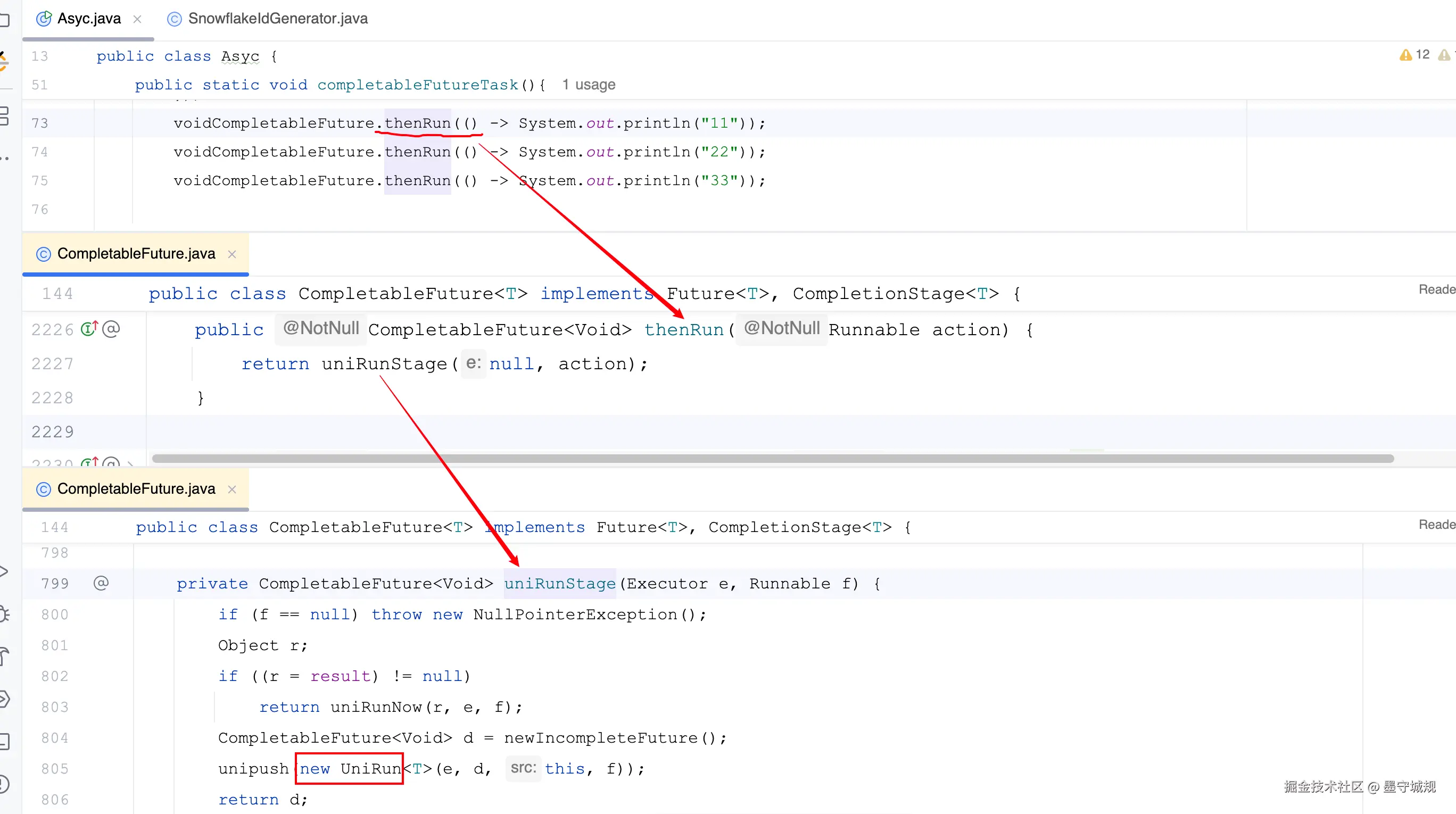
UniRun 继承 UniCompletion , UniCompletion 继承了 Completion
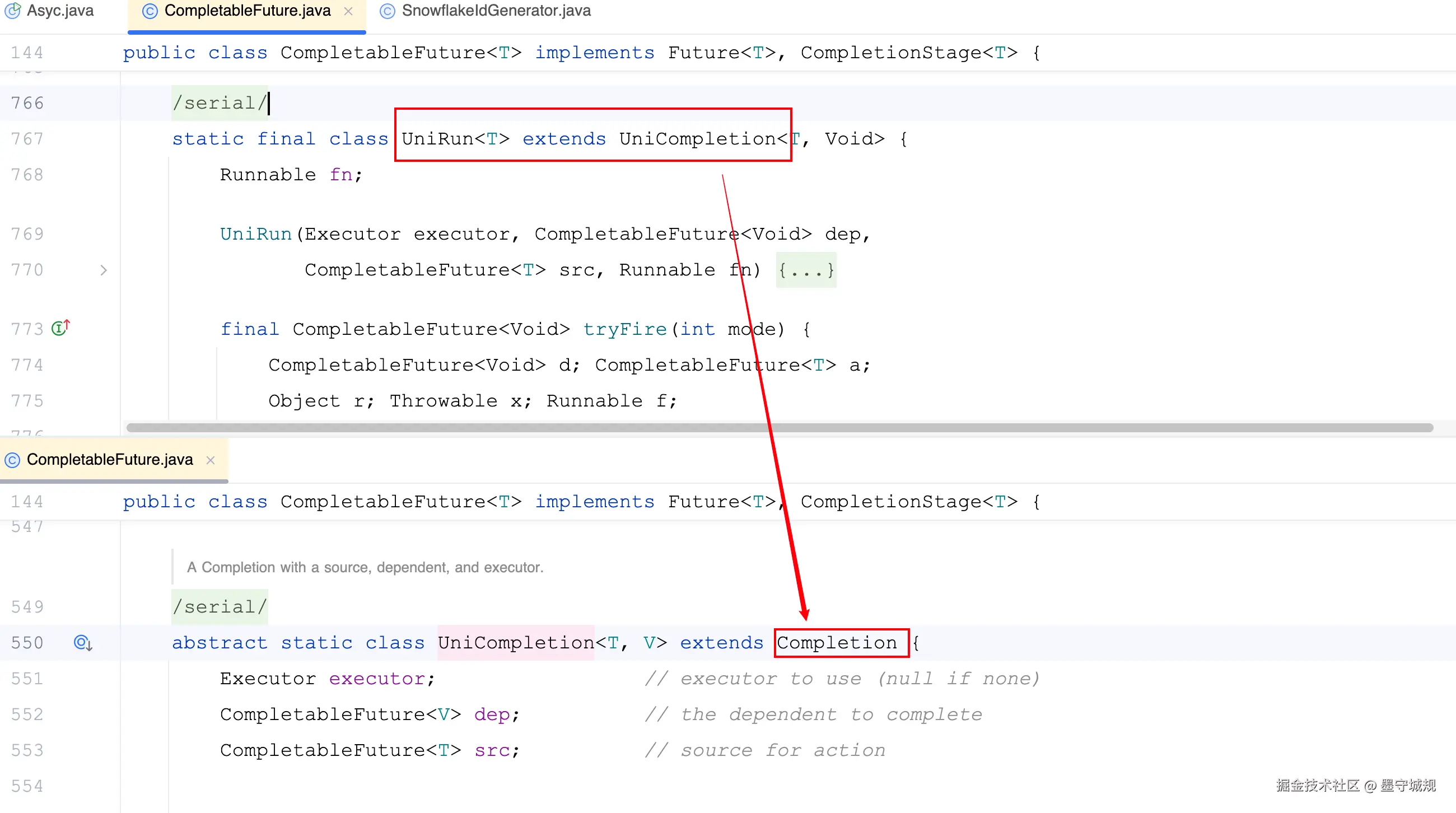
所以具体执行任务的 tryFire方法,就先看 UniRun内部类的实现
php
// Modes for Completion.tryFire. Signedness matters.
static final int SYNC = 0; // 异步执行
static final int ASYNC = 1; // 同步执行
static final int NESTED = -1; // 嵌套执行
// mode模式 --> 分为 同步、异步、嵌套
final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) {
CompletableFuture<Void> d; // 后继任务
CompletableFuture<T> a; // 前继任务
Object r; // 前继任务的结果
Throwable x; // 前继任务出现了异常
Runnable f; // 当前具体任务
// src表示前继任务
// dep表示后继任务
// fn表示具体任务
// 边界判断
if ((a = src) == null || (r = a.result) == null || (d = dep) == null || (f = fn) == null){
return null;
}
// 判断后继任务是否执行
if (d.result == null) {
// 后继任务没执行
if (r instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null){
// 前继任务执行中出现了异常,后续任务就不再执行,封装异常
d.completeThrowable(x, r);
}else{ // 执行后继任务
try {
// 根据模式进行判断,是否交由线程池来执行
// 具体异步执行任务方法 claim() --> 交给线程池来执行
if (mode <= 0 && !claim()){
return null;
}else { // mode == 1 同步执行 另一种情况:线程池为null 也会走到else 同步执行
f.run(); // 直接执行具体的run方法
d.completeNull(); // 封装结果
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 出现异常,封装异常
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
}
// 方便 GC,将成员变量置null
src = null;
dep = null;
fn = null;
// 继续执行前继任务的后续任务
return d.postFire(a, mode);
}claim()方法 --> 用线程池来执行任务
java
// 异步/嵌套执行后继任务
final boolean claim() {
// 赋值线程池给局部变量
Executor e = executor;
// 判断当前任务标记是否已经执行
if (compareAndSetForkJoinTaskTag((short)0, (short)1)) {
if (e == null){
// 线程池为null 说明是同步执行,直接返回true
return true;
}
executor = null; // 方便 GC,成员变量置为null
// 异步执行,使用线程池来执行
e.execute(this);
}
return false;
}3、thenRun()方法
这里就是具体分析看看后继任务是怎么执行的
发现问题:是通过压栈来具体进行执行的,但是在实际的代码测试中,发现后继任务的执行,并不是严格按照先进后出来进行打印的,而是随机顺序。
原因:如果前继任务执行完,就直接执行后继任务,不入栈
thenRun()相同的功能有三种方法,这里分析thenRun不带线程池的方式
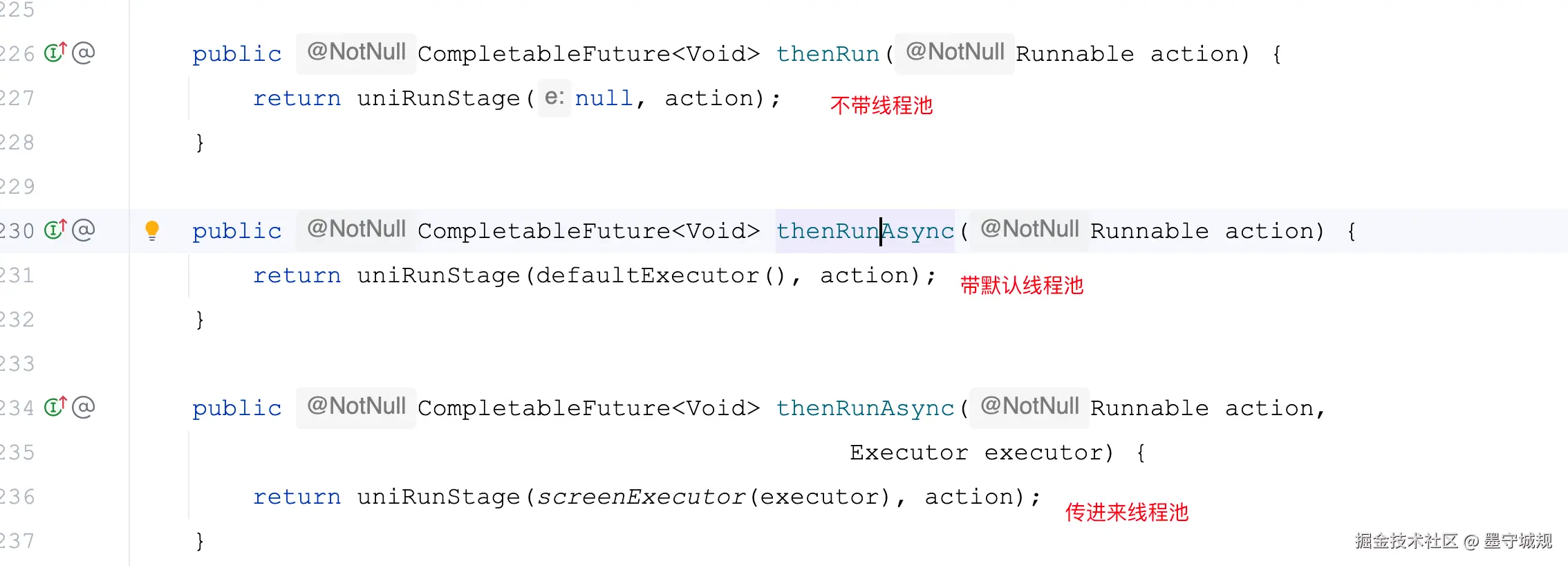
分析uniRunStage()方法
kotlin
private CompletableFuture<Void> uniRunStage(Executor e, Runnable f) {
// 边界处理
if (f == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Object r;
// result是this.result 代表当前任务的是否已经执行完毕
if ((r = result) != null){
// 如果当前任务已经执行完毕,不需要入栈,直接执行后继任务
return uniRunNow(r, e, f);
}
// 构建后继任务的CompletableFuture d --> 方便后继任务的后继任务执行
CompletableFuture<Void> d = newIncompleteFuture();
// 压栈
// e --> 线程池
// d --> 后继任务的 CompletableFuture 对象
// this --> 当前对象的 CompletableFuture
// f --> 后继任务的具体任务
unipush(new UniRun<T>(e, d, this, f));
return d;
}分析到这就可以回答开头的问题:如果task.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("11"));这个task任务已经执行完了,那就不需要压栈,直接执行 () -> {System.out.println("11")},如果task没执行完,才需要压栈。
uniRunNow()立即执行后继任务的源码
typescript
// 立即执行的源码
private CompletableFuture<Void> uniRunNow(Object r, Executor e, Runnable f) {
Throwable x;
// 还是得构建一个继任务的CompletableFuture d
CompletableFuture<Void> d = newIncompleteFuture();
if (r instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null){
// 前继任务出现了异常,后继任务也不需要执行
d.result = encodeThrowable(x, r);
}else{
try {
if (e != null) {
// 线程池不为空,用线程池异步来执行
e.execute(new UniRun<T>(null, d, this, f));
} else {
// 直接同步执行
f.run();
// 封装后继任务的结果
d.result = NIL;
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 出现异常,封装后继任务的异常结果
d.result = encodeThrowable(ex);
}
}
return d;
}在执行入栈时,会构造一个 UniRun 对象,我们先分析一下这个构造器
scala
// UniRun 继承 UniCompletion 抽象类
static final class UniRun<T> extends UniCompletion<T,Void> {
Runnable fn;
// executor 线程池
// dep 后继任务
// src 前继任务
// fn 具体的任务
UniRun(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<Void> dep,CompletableFuture<T> src, Runnable fn) {
super(executor, dep, src);
this.fn = fn;
}
}
abstract static class UniCompletion<T,V> extends Completion {
Executor executor; // executor to use (null if none)
CompletableFuture<V> dep; // the dependent to complete
CompletableFuture<T> src; // source for action
UniCompletion(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,
CompletableFuture<T> src) {
this.executor = executor; this.dep = dep; this.src = src;
}
}再看具体的入栈方法unipush()
csharp
// 入栈源码
final void unipush(Completion c) {
if (c != null) { // 边界判断,这个一定是true,不为空
// 自旋入栈
while (!tryPushStack(c)) {
// CAS 入栈失败
if (result != null) { // 前继任务已经执行完了
NEXT.set(c, null); // 将c的next设置为null
break;
}
}
// 前继任务已经执行完了,开始执行后继任务
if (result != null){
// 同步执行c这个节点任务
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
}
}头插法入栈
arduino
final boolean tryPushStack(Completion c) {
// 当前前继任务的stack属性赋值给局部变量h
Completion h = stack;
// 头插法,将c的next指向h --> 模拟栈
NEXT.set(c, h);
// 当前前继任务的stack值变为c
return STACK.compareAndSet(this, h, c);
}4、总结
runAsync()与thenRun()方法是配合使用的
为了方便理解,做如下声明
runAsync()存放的是前继任务
thenRun()存放的是后继任务