1. 引言
Vericut是一款专业的数控加工仿真软件,广泛应用于航空航天、汽车制造和精密加工等领域。MCH(Machine Configuration)文件是Vericut中定义机床几何结构、运动学参数和控制系统配置的核心文件。本文将通过一个典型的5轴联动加工中心配置实例,深入解析MCH文件的结构和构建方法。
该机床采用典型的"双摆台"结构,工件安装在B轴和C轴(实际为A轴)组成的双转台上,刀具通过Z轴和Y轴进行线性运动。这种结构特别适合于复杂曲面零件的多角度加工,是航空航天领域叶片、叶盘等零件加工的常用配置。
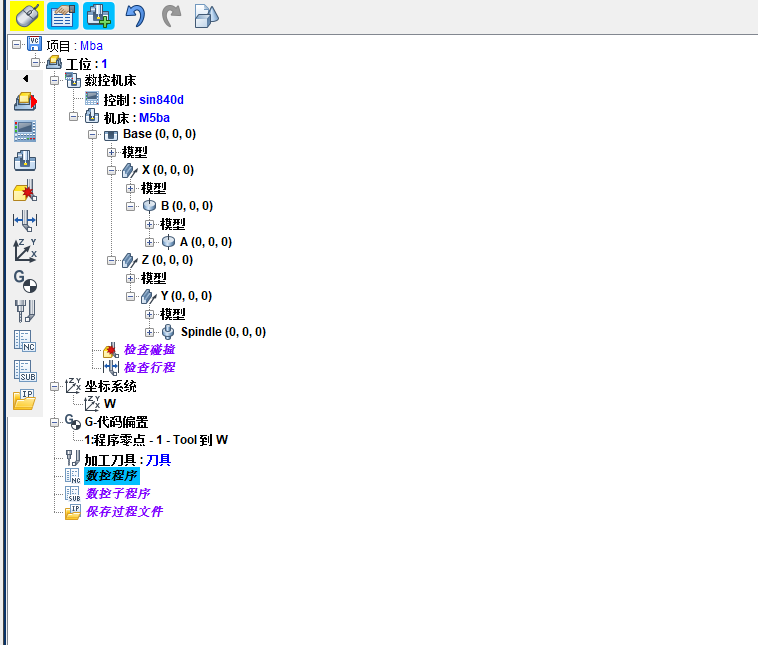
2. MCH文件基础结构
MCH文件采用XML格式,包含机床的基本信息、组件定义、运动链关系和几何模型等核心内容。以下是完整的基础结构框架:
xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<VcMachine Version="9.1.1" Machine="5Am" Unit="millimeter">
<!-- 文件信息部分 -->
<Information>
<InfoUserName>Workstation</InfoUserName>
<InfoDateTime>Mon Jul 7 17:03:44 2025</InfoDateTime>
<InfoVericutVersion>9.5</InfoVericutVersion>
<InfoBuildDate>June 20, 2024</InfoBuildDate>
<InfoLibraryDate>06/20/24</InfoLibraryDate>
</Information>
<!-- 运动优先级类型 -->
<PriorityType>single</PriorityType>
<!-- 碰撞检测设置 -->
<Collision>
</Collision>
<!-- 机床组件定义区域 -->
<!-- 各组件将在后续详细定义 -->
<!-- 预览图像 -->
<Preview Image="iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAQAAAADYCAYAAAAEaD2QAACAAElEQVR4XuydB5RUxfb1WevziWSVLBJUcgYxgIAiOShIUHJO..."/>
</VcMachine>每个MCH文件都必须以<VcMachine>为根元素,其中Version属性指定Vericut版本兼容性,Machine属性定义机床名称,Unit属性设置全局单位系统。单位设置直接影响后续所有几何尺寸的解析,常用单位包括毫米(millimeter)和英寸(inch),其转换关系为:
1 inch = 25.4 mm 1\ \text{inch} = 25.4\ \text{mm} 1 inch=25.4 mm
3. 机床组件定义与运动学建模
机床组件是MCH文件的核心,每个组件通过<Component>元素定义,包含类型、可见性、运动参数和几何模型等信息。组件类型主要包括:
base:机床基础(床身)linear:线性运动轴rotary:旋转运动轴spindle:主轴组件tool:刀具安装点attach:工件夹具
3.1 基础组件定义
机床基础是运动链的参考基准,所有其他组件都直接或间接安装于基础之上。基础组件通常包含机床的主要结构几何模型:
xml
<Component Name="Base"
Subsystem="1"
Type="base" Visible="machine" Enabled="on" Draw="shaded" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0">
<Attach></Attach>
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0"/>
<STL Unit="millimeter" Normal="outward" Visible="on" Enabled="on"
HasOpenSurface="off" XRGB="0x0040E0D0">
<File>G:\54yuikAm\床身.stl</File>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x0040E0D0"/>
<EdgeAngle>30</EdgeAngle>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>组件的位置和方向通过<Position>和<Rotation>元素定义。位置使用笛卡尔坐标系 ( X , Y , Z ) (X, Y, Z) (X,Y,Z)表示,旋转采用欧拉角 ( I , J , K ) (I, J, K) (I,J,K)系统,分别绕X、Y、Z轴旋转。旋转矩阵 R R R的计算公式为:
R = R z ( K ) ⋅ R y ( J ) ⋅ R x ( I ) R = R_z(K) \cdot R_y(J) \cdot R_x(I) R=Rz(K)⋅Ry(J)⋅Rx(I)
其中绕X、Y、Z轴的旋转矩阵分别为:
R x ( θ ) = [ 1 0 0 0 cos θ − sin θ 0 sin θ cos θ ] R_x(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \cos\theta & -\sin\theta \\ 0 & \sin\theta & \cos\theta \end{bmatrix} Rx(θ)=⎣⎡1000cosθsinθ0−sinθcosθ⎦⎤
R y ( θ ) = [ cos θ 0 sin θ 0 1 0 − sin θ 0 cos θ ] R_y(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} \cos\theta & 0 & \sin\theta \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ -\sin\theta & 0 & \cos\theta \end{bmatrix} Ry(θ)=⎣⎡cosθ0−sinθ010sinθ0cosθ⎦⎤
R z ( θ ) = [ cos θ − sin θ 0 sin θ cos θ 0 0 0 1 ] R_z(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} \cos\theta & -\sin\theta & 0 \\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} Rz(θ)=⎣⎡cosθsinθ0−sinθcosθ0001⎦⎤
3.2 线性轴组件
线性轴组件定义机床的平移运动,包括X、Y、Z轴。每个线性轴通过<Link>元素定义运动参数:
xml
<Component Name="X"
Subsystem="1"
Type="linear" Visible="machine" Enabled="on" Draw="shaded" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0">
<Attach>Base</Attach>
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0"/>
<Link Axis="-X" PartSide="auto" Register="X"
RapidRate="5000" Accel="125" Decel="125"
MaxLinearVelocity="5000" MaxCornerVelocity="600">
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter" Normal="outward" Visible="on" Enabled="on"
HasOpenSurface="off" XRGB="0x007CFC00">
<File>G:\5Am\X轴.stl</File>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x007CFC00"/>
<EdgeAngle>30</EdgeAngle>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>运动参数中,RapidRate定义快速移动速度,Accel和Decel分别定义加速度和减速度,MaxLinearVelocity限制最大线速度,MaxCornerVelocity控制拐角处最大速度。这些参数直接影响加工效率和表面质量。
对于线性插补运动,当机床同时移动多个轴时,各轴的实际速度 v i v_i vi需要满足:
v i = Δ L i T ≤ v i , max v_i = \frac{\Delta L_i}{T} \leq v_{i,\text{max}} vi=TΔLi≤vi,max
其中 Δ L i \Delta L_i ΔLi为第 i i i轴的移动距离, T T T为运动时间, v i , max v_{i,\text{max}} vi,max为该轴的最大允许速度。
3.3 旋转轴组件
旋转轴组件定义机床的旋转运动,通常为A、B、C轴。旋转轴的运动参数与线性轴类似,但运动类型为旋转:
xml
<Component Name="B"
Subsystem="1"
Type="rotary" Visible="machine" Enabled="on" Draw="shaded"
XRGB="0x00A0A0A0" RotarySpin="off">
<Attach>X</Attach>
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="180" J="0" K="180"/>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0"/>
<Link Axis="Y" PartSide="auto" Register="B"
RapidRate="5000" Accel="125" Decel="125"
MaxLinearVelocity="5000" MaxCornerVelocity="600">
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter" Normal="outward" Visible="on" Enabled="on"
HasOpenSurface="off" XRGB="0x00FFFFFF">
<File>G:\5Am\B轴.stl</File>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x00FFFFFF"/>
<EdgeAngle>30</EdgeAngle>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="6.12323399574e-17" Y="0" Z="-1"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="6.12323399574e-17"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>旋转轴的Rotation属性定义了组件的初始方向。示例中B轴的初始旋转为 I = 180 ° I=180° I=180°, K = 180 ° K=180° K=180°,这通常用于调整转台的初始姿态。旋转矩阵中的小数值(如 6.12323399574 × 1 0 − 17 6.12323399574 \times 10^{-17} 6.12323399574×10−17)实际上是浮点数计算误差,理论值应为0,表示由于有限精度计算产生的舍入误差。
对于5轴机床,旋转轴的运动范围通常有限制。B轴常见的运动范围为 − 120 ° -120° −120°到 + 120 ° +120° +120°,C轴为 0 ° 0° 0°到 360 ° 360° 360°连续旋转。这些限制需要在机床控制器中设置,并在Vericut中通过行程限制参数定义。
3.4 主轴和刀具组件
主轴组件是刀具的安装基准,刀具组件定义刀具的安装位置和方向:
xml
<Component Name="Spindle"
Subsystem="1"
Type="spindle" Visible="machine" Enabled="on" Draw="shaded" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0">
<Attach>Y</Attach>
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0"/>
<Link Axis="Z" PartSide="no" Register="">
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter" Normal="outward" Visible="off" Enabled="on"
HasOpenSurface="off" XRGB="0x80000000">
<File>G:\5Am\主轴.stl</File>
<EdgeAngle>30</EdgeAngle>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="-162.9065" Y="110.58" Z="162.0667"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
xml
<Component Name="Tool"
Subsystem="1"
Type="tool" Visible="all" Enabled="on" Draw="shaded" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0">
<Attach>Spindle</Attach>
<Position X="-162.9065" Y="110.58" Z="162.0667"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Appearance Name="Machine Component" Ambient="0.2" Diffuse="0.7"
Reflect="0.2" Specular="1" Shininess="6"
Translucency="1" XRGB="0x00A0A0A0"/>
<Tool TurretIndex="1"/>
<Link Axis="Z" PartSide="auto" Register="">
</Link>
</Component>刀具位置(-162.9065, 110.58, 162.0667)定义了刀具相对于主轴的安装点。在5轴加工中,刀具中心点(Tool Center Point, TCP)的位置计算需要考虑所有运动轴的变换。对于本文的双摆台结构,工件坐标系到机床坐标系的变换矩阵为:
T machine = T base ⋅ T X ⋅ T B ⋅ T C ⋅ T workpiece T_{\text{machine}} = T_{\text{base}} \cdot T_X \cdot T_B \cdot T_C \cdot T_{\text{workpiece}} Tmachine=Tbase⋅TX⋅TB⋅TC⋅Tworkpiece
其中 T base T_{\text{base}} Tbase为机床基础变换, T X T_X TX为X轴变换, T B T_B TB为B轴变换, T C T_C TC为C轴变换, T workpiece T_{\text{workpiece}} Tworkpiece为工件坐标系变换。
4. 运动链分析与运动学计算
4.1 运动链结构分析
从MCH文件可以提取出完整的运动链结构:
xml
<!-- 工件侧运动链 -->
<Component Name="Base" Type="base">...</Component>
<Component Name="X" Type="linear" Attach="Base">...</Component>
<Component Name="B" Type="rotary" Attach="X">...</Component>
<Component Name="C" Type="rotary" Attach="B">...</Component>
<Component Name="Attach" Type="attach" Attach="C">...</Component>
<!-- 刀具侧运动链 -->
<Component Name="Base" Type="base">...</Component>
<Component Name="Z" Type="linear" Attach="Base">...</Component>
<Component Name="Y" Type="linear" Attach="Z">...</Component>
<Component Name="Spindle" Type="spindle" Attach="Y">...</Component>
<Component Name="Tool" Type="tool" Attach="Spindle">...</Component>这种运动链结构在运动学上属于"混合型5轴机床",工件通过X、B、C三轴运动,刀具通过Z、Y两轴运动。运动学正解计算刀具中心点位置时,需要将刀具坐标系转换到工件坐标系:
P workpiece = ( T workpiece ) − 1 ⋅ ( T C ) − 1 ⋅ ( T B ) − 1 ⋅ ( T X ) − 1 ⋅ T base − 1 ⋅ T base ⋅ T Z ⋅ T Y ⋅ T spindle ⋅ P tool P_{\text{workpiece}} = (T_{\text{workpiece}})^{-1} \cdot (T_C)^{-1} \cdot (T_B)^{-1} \cdot (T_X)^{-1} \cdot T_{\text{base}}^{-1} \cdot T_{\text{base}} \cdot T_Z \cdot T_Y \cdot T_{\text{spindle}} \cdot P_{\text{tool}} Pworkpiece=(Tworkpiece)−1⋅(TC)−1⋅(TB)−1⋅(TX)−1⋅Tbase−1⋅Tbase⋅TZ⋅TY⋅Tspindle⋅Ptool
4.2 运动学逆解算法
对于5轴加工,通常给定刀具轴线方向向量 n ⃗ = ( n x , n y , n z ) \vec{n} = (n_x, n_y, n_z) n =(nx,ny,nz)和刀具中心点位置 P = ( x , y , z ) P = (x, y, z) P=(x,y,z),需要求解各轴位置 ( X , Y , Z , B , C ) (X, Y, Z, B, C) (X,Y,Z,B,C)。对于双摆台结构,逆解算法如下:
python
import numpy as np
import math
def inverse_kinematics_5axis(tool_position, tool_orientation, machine_params):
"""
5轴机床逆运动学求解
tool_position: 刀具中心点坐标 (x, y, z)
tool_orientation: 刀具方向向量 (nx, ny, nz)
machine_params: 机床结构参数
返回: 各轴位置 (X, Y, Z, B, C)
"""
# 提取机床参数
pivot_distance = machine_params['pivot_distance'] # 转台旋转中心到工件坐标系原点距离
tool_length = machine_params['tool_length'] # 刀具长度
# 归一化刀具方向向量
n = np.array(tool_orientation)
n = n / np.linalg.norm(n)
# 计算旋转轴角度
# B轴角度计算(绕Y轴旋转)
B = math.atan2(math.sqrt(n[0]**2 + n[2]**2), n[1])
# C轴角度计算(绕Z轴旋转)
if abs(B) < 1e-6: # B接近0时,C角任意
C = 0
else:
C = math.atan2(n[0], n[2])
# 计算旋转矩阵
R_B = np.array([
[math.cos(B), 0, math.sin(B)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-math.sin(B), 0, math.cos(B)]
])
R_C = np.array([
[math.cos(C), -math.sin(C), 0],
[math.sin(C), math.cos(C), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
# 完整旋转矩阵
R = R_C @ R_B
# 计算线性轴位置
# 考虑转台旋转中心偏移
pivot_offset = np.array([0, pivot_distance, 0])
# 刀具在转台坐标系中的位置
tool_in_rotary = np.array(tool_position) - pivot_offset
# 反向旋转到初始位置
tool_in_initial = R.T @ tool_in_rotary
# 考虑刀具长度补偿
tool_tip_offset = np.array([0, 0, -tool_length])
tool_in_initial = tool_in_initial - tool_tip_offset
# 提取线性轴位置
X = tool_in_initial[0]
Y = tool_in_initial[1] - machine_params['y_offset'] # Y轴偏移补偿
Z = tool_in_initial[2]
# 角度单位转换(弧度转度)
B_deg = math.degrees(B)
C_deg = math.degrees(C)
return X, Y, Z, B_deg, C_deg
# 示例使用
machine_params = {
'pivot_distance': 150.0, # 转台旋转中心到工件距离
'tool_length': 100.0, # 刀具长度
'y_offset': 110.58 # Y轴初始偏移
}
# 测试数据
tool_position = [100, 200, 150]
tool_orientation = [0, 0, 1] # 垂直向下
result = inverse_kinematics_5axis(tool_position, tool_orientation, machine_params)
print(f"各轴位置: X={result[0]:.3f}, Y={result[1]:.3f}, Z={result[2]:.3f}, "
f"B={result[3]:.3f}°, C={result[4]:.3f}°")4.3 速度规划和插补算法
5轴联动加工需要协调多个轴的运动,确保加工精度和表面质量。常用的插补算法包括线性插补和样条插补:
python
class FiveAxisInterpolator:
"""5轴插补器"""
def __init__(self, feed_rate, acceleration, jerk_limit):
self.feed_rate = feed_rate # 进给速度 mm/min
self.acceleration = acceleration # 加速度 mm/s²
self.jerk_limit = jerk_limit # 加加速度限制 mm/s³
self.tolerance = 1e-6 # 计算容差
def linear_interpolation(self, start_pose, end_pose, delta_time):
"""
5轴线性插补
start_pose: 起始位姿 [X, Y, Z, B, C]
end_pose: 终止位姿 [X, Y, Z, B, C]
delta_time: 时间间隔 s
返回: 插补点位姿列表
"""
start = np.array(start_pose)
end = np.array(end_pose)
# 计算总位移
linear_distance = np.linalg.norm(end[:3] - start[:3])
angular_distance = np.linalg.norm(end[3:] - start[3:])
# 计算总时间(考虑线性运动和旋转运动的协调)
linear_time = linear_distance / (self.feed_rate / 60.0) # 转换为mm/s
angular_time = angular_distance / (self.feed_rate / 60.0 * 0.1) # 旋转轴速度限制
total_time = max(linear_time, angular_time)
# S曲线速度规划
def s_curve_velocity(t, T_total):
"""S型速度曲线"""
if t < 0:
return 0
elif t < T_total / 3:
# 加速段
return self.acceleration * t
elif t < 2 * T_total / 3:
# 匀速段
return self.feed_rate / 60.0
elif t <= T_total:
# 减速段
return self.feed_rate / 60.0 - self.acceleration * (t - 2 * T_total / 3)
else:
return 0
# 生成插补点
interpolated_poses = []
current_time = 0
while current_time <= total_time:
# 计算当前时间比例(考虑速度曲线)
if total_time > 0:
# 基于S曲线计算实际运动比例
current_speed = s_curve_velocity(current_time, total_time)
if current_time > 0:
distance_ratio = current_speed * current_time / linear_distance
else:
distance_ratio = 0
else:
distance_ratio = 1
distance_ratio = np.clip(distance_ratio, 0, 1)
# 线性插补
current_pose = start + (end - start) * distance_ratio
interpolated_poses.append(current_pose.tolist())
current_time += delta_time
return interpolated_poses
def tool_center_point_control(self, poses, tool_length):
"""
刀具中心点控制(TCP控制)
保持刀具中心点轨迹,自动计算各轴补偿
poses: 刀具中心点位姿 [X, Y, Z, B, C]
tool_length: 刀具长度
返回: 各轴实际位置
"""
actual_positions = []
for pose in poses:
x, y, z, b, c = pose
# 将角度转换为弧度
b_rad = np.radians(b)
c_rad = np.radians(c)
# 计算旋转矩阵
R_b = np.array([
[np.cos(b_rad), 0, np.sin(b_rad)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(b_rad), 0, np.cos(b_rad)]
])
R_c = np.array([
[np.cos(c_rad), -np.sin(c_rad), 0],
[np.sin(c_rad), np.cos(c_rad), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
R_total = R_c @ R_b
# 刀具方向向量
tool_direction = R_total @ np.array([0, 0, 1])
# 计算实际主轴位置(考虑刀具长度)
spindle_position = np.array([x, y, z]) - tool_direction * tool_length
actual_positions.append([*spindle_position, b, c])
return actual_positions
# 使用示例
interpolator = FiveAxisInterpolator(
feed_rate=1000, # 1000 mm/min
acceleration=100, # 100 mm/s²
jerk_limit=1000 # 1000 mm/s³
)
start_pose = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
end_pose = [100, 50, 30, 45, 90]
interpolated = interpolator.linear_interpolation(start_pose, end_pose, 0.01)
print(f"生成 {len(interpolated)} 个插补点")
print(f"第一个点: {interpolated[0]}")
print(f"最后一个点: {interpolated[-1]}")5. 碰撞检测与验证
Vericut提供强大的碰撞检测功能,可以检测刀具与工件、夹具、机床组件之间的干涉。碰撞检测基于各组件的几何模型和实时位置计算:
python
class CollisionDetector:
"""碰撞检测器"""
def __init__(self, machine_components):
self.components = machine_components
self.collision_pairs = []
def setup_collision_pairs(self):
"""设置需要检测的碰撞对"""
# 通常需要检测:
# 1. 刀具 vs 工件
# 2. 刀具 vs 夹具
# 3. 刀具 vs 机床组件
# 4. 主轴 vs 机床组件
# 5. 工件 vs 机床组件
self.collision_pairs = [
('Tool', 'Workpiece'),
('Tool', 'Fixture'),
('Spindle', 'Machine'),
('Workpiece', 'Machine')
]
def check_collision(self, component1, component2, positions):
"""
检查两个组件是否碰撞
使用分离轴定理(Separating Axis Theorem)进行OBB碰撞检测
"""
# 获取组件的包围盒(Oriented Bounding Box)
obb1 = self.get_oriented_bounding_box(component1, positions)
obb2 = self.get_oriented_bounding_box(component2, positions)
# 分离轴定理检测
axes = []
# 组件1的三个轴
for i in range(3):
axes.append(obb1['axes'][i])
# 组件2的三个轴
for i in range(3):
axes.append(obb2['axes'][i])
# 轴之间的叉积
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
cross_axis = np.cross(obb1['axes'][i], obb2['axes'][j])
if np.linalg.norm(cross_axis) > 1e-6:
axes.append(cross_axis / np.linalg.norm(cross_axis))
# 检查所有分离轴
for axis in axes:
# 计算两个包围盒在轴上的投影
proj1 = self.project_obb(obb1, axis)
proj2 = self.project_obb(obb2, axis)
# 检查投影是否重叠
if not self.overlap(proj1, proj2):
return False # 找到分离轴,无碰撞
return True # 所有轴都重叠,发生碰撞
def get_oriented_bounding_box(self, component, positions):
"""获取组件的定向包围盒"""
# 实际实现中需要从STL文件计算
# 这里简化为基于位置和尺寸的估计
pos = positions.get(component, {'position': [0,0,0], 'rotation': [0,0,0]})
# 假设组件尺寸(实际应从几何模型获取)
dimensions = {'Tool': [10, 10, 100],
'Workpiece': [200, 100, 50],
'Fixture': [150, 150, 30],
'Spindle': [80, 80, 200],
'Machine': [1000, 800, 600]}
size = dimensions.get(component, [100, 100, 100])
# 计算旋转矩阵
rx, ry, rz = pos['rotation']
R = self.euler_to_matrix(rx, ry, rz)
# 三个轴方向
axes = [R[:,0], R[:,1], R[:,2]]
return {
'center': np.array(pos['position']),
'axes': axes,
'extents': np.array(size) / 2
}
def euler_to_matrix(self, rx, ry, rz):
"""欧拉角转旋转矩阵"""
Rx = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(rx), -np.sin(rx)],
[0, np.sin(rx), np.cos(rx)]])
Ry = np.array([[np.cos(ry), 0, np.sin(ry)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(ry), 0, np.cos(ry)]])
Rz = np.array([[np.cos(rz), -np.sin(rz), 0],
[np.sin(rz), np.cos(rz), 0],
[0, 0, 1]])
return Rz @ Ry @ Rx
def project_obb(self, obb, axis):
"""计算OBB在轴上的投影区间"""
center_projection = np.dot(obb['center'], axis)
# 计算半长
half_length = 0
for i in range(3):
half_length += abs(np.dot(obb['axes'][i], axis)) * obb['extents'][i]
return (center_projection - half_length, center_projection + half_length)
def overlap(self, interval1, interval2):
"""检查两个区间是否重叠"""
return not (interval1[1] < interval2[0] or interval2[1] < interval1[0])
def batch_collision_check(self, all_positions):
"""批量碰撞检测"""
collisions = []
for comp1, comp2 in self.collision_pairs:
if comp1 in all_positions and comp2 in all_positions:
if self.check_collision(comp1, comp2, all_positions):
collisions.append((comp1, comp2))
return collisions
# 使用示例
components = ['Tool', 'Workpiece', 'Fixture', 'Spindle', 'Machine']
detector = CollisionDetector(components)
detector.setup_collision_pairs()
# 模拟位置数据
positions = {
'Tool': {'position': [100, 50, 30], 'rotation': [0, 0, 0]},
'Workpiece': {'position': [0, 0, 0], 'rotation': [0, 0, 0]},
'Fixture': {'position': [0, 0, -20], 'rotation': [0, 0, 0]},
'Spindle': {'position': [100, 50, 130], 'rotation': [0, 0, 0]},
'Machine': {'position': [0, 0, 0], 'rotation': [0, 0, 0]}
}
collisions = detector.batch_collision_check(positions)
if collisions:
print(f"检测到碰撞: {collisions}")
else:
print("无碰撞")6. 机床精度分析与补偿
机床精度受几何误差、热误差和负载变形等多种因素影响。通过误差建模和补偿可以提高加工精度:
python
class MachineErrorCompensation:
"""机床误差补偿"""
def __init__(self, machine_type):
self.machine_type = machine_type
self.error_models = {}
self.setup_error_models()
def setup_error_models(self):
"""设置误差模型"""
# 几何误差模型参数
# 对于5轴机床,典型几何误差有21项
if self.machine_type == '5axis_double_swivel':
# 线性轴误差
self.error_models['linear'] = {
'position_errors': { # 定位误差
'X': self.polynomial_error_model,
'Y': self.polynomial_error_model,
'Z': self.polynomial_error_model
},
'straightness_errors': { # 直线度误差
'XY': self.polynomial_error_model,
'XZ': self.polynomial_error_model,
'YX': self.polynomial_error_model,
'YZ': self.polynomial_error_model,
'ZX': self.polynomial_error_model,
'ZY': self.polynomial_error_model
},
'angular_errors': { # 角度误差
'roll': self.polynomial_error_model, # 滚转
'pitch': self.polynomial_error_model, # 俯仰
'yaw': self.polynomial_error_model # 偏航
}
}
# 旋转轴误差
self.error_models['rotary'] = {
'position_errors': {
'B': self.polynomial_error_model,
'C': self.polynomial_error_model
},
'tilt_errors': {
'Bx': self.polynomial_error_model,
'By': self.polynomial_error_model,
'Cx': self.polynomial_error_model,
'Cy': self.polynomial_error_model
}
}
def polynomial_error_model(self, position, coefficients):
"""多项式误差模型"""
# 系数: [c0, c1, c2, c3, ...]
error = 0
for i, coeff in enumerate(coefficients):
error += coeff * (position ** i)
return error
def homogeneous_transformation_matrix(self, errors):
"""基于误差生成齐次变换矩阵"""
# 误差向量: [δx, δy, δz, εx, εy, εz]
δx, δy, δz, εx, εy, εz = errors
# 小角度近似旋转矩阵
R = np.array([
[1, -εz, εy],
[εz, 1, -εx],
[-εy, εx, 1]
])
# 齐次变换矩阵
T = np.eye(4)
T[:3, :3] = R
T[:3, 3] = [δx, δy, δz]
return T
def calculate_volumetric_error(self, commanded_position, actual_position):
"""
计算体积误差
Volumetric Error = ||实际位置 - 指令位置||
"""
return np.linalg.norm(np.array(actual_position) - np.array(commanded_position))
def error_compensation(self, commanded_pose, error_params):
"""
误差补偿计算
commanded_pose: 指令位姿 [X, Y, Z, B, C]
error_params: 误差参数
返回: 补偿后的指令位姿
"""
x, y, z, b, c = commanded_pose
# 计算各轴误差
errors = {}
# 线性轴误差
for axis in ['X', 'Y', 'Z']:
pos = {'X': x, 'Y': y, 'Z': z}[axis]
# 定位误差
pos_error = self.error_models['linear']['position_errors'][axis](
pos, error_params.get(f'{axis}_pos', [0,0,0,0])
)
# 直线度误差
straightness_error = 0
for dir_axis in ['X', 'Y', 'Z']:
if dir_axis != axis:
key = f'{axis}{dir_axis}'
if key in self.error_models['linear']['straightness_errors']:
coeff = error_params.get(f'{key}_straight', [0,0,0,0])
straightness_error += self.error_models['linear']['straightness_errors'][key](pos, coeff)
# 角度误差
angular_error = 0
for angle_type in ['roll', 'pitch', 'yaw']:
coeff = error_params.get(f'{axis}_{angle_type}', [0,0,0,0])
angular_error += self.error_models['linear']['angular_errors'][angle_type](pos, coeff)
errors[axis] = {
'position': pos_error + straightness_error,
'angle': angular_error
}
# 旋转轴误差(简化处理)
b_error = self.error_models['rotary']['position_errors']['B'](
b, error_params.get('B_pos', [0,0,0,0])
)
c_error = self.error_models['rotary']['position_errors']['C'](
c, error_params.get('C_pos', [0,0,0,0])
)
# 应用补偿
compensated_x = x - errors['X']['position']
compensated_y = y - errors['Y']['position']
compensated_z = z - errors['Z']['position']
compensated_b = b - b_error
compensated_c = c - c_error
return [compensated_x, compensated_y, compensated_z, compensated_b, compensated_c]
def thermal_error_model(self, temperature_data, time_elapsed):
"""
热误差模型
机床在运行过程中因温度变化产生的误差
"""
# 简化线性热误差模型
thermal_expansion_coeff = 11.7e-6 # 钢的线膨胀系数 /°C
# 假设温度梯度
temp_gradient = {
'spindle': temperature_data.get('spindle', 25),
'bed': temperature_data.get('bed', 25),
'ambient': temperature_data.get('ambient', 25)
}
# 计算热变形
length = 500 # 典型机床结构长度 mm
delta_temp = temp_gradient['spindle'] - temp_gradient['bed']
thermal_error = thermal_expansion_coeff * length * delta_temp
# 时间相关项(热惯性)
time_constant = 3600 # 热时间常数 s
time_factor = 1 - np.exp(-time_elapsed / time_constant)
return thermal_error * time_factor
# 使用示例
compensator = MachineErrorCompensation('5axis_double_swivel')
# 误差参数(示例值,实际需要通过测量获得)
error_params = {
'X_pos': [0.001, 0.00002, 0, 0], # X轴定位误差多项式系数
'Y_pos': [0.002, 0.00001, 0, 0], # Y轴定位误差
'Z_pos': [0.0015, 0.000015, 0, 0], # Z轴定位误差
'XY_straight': [0, 0.00001, 0, 0], # X轴在Y方向的直线度
'B_pos': [0.05, 0.0001, 0, 0], # B轴定位误差
'C_pos': [0.03, 0.00005, 0, 0] # C轴定位误差
}
commanded_pose = [100.0, 50.0, 30.0, 45.0, 90.0]
compensated_pose = compensator.error_compensation(commanded_pose, error_params)
print(f"指令位姿: {commanded_pose}")
print(f"补偿后位姿: {[f'{v:.4f}' for v in compensated_pose]}")
# 热误差计算
temp_data = {'spindle': 35, 'bed': 28, 'ambient': 25}
thermal_error = compensator.thermal_error_model(temp_data, 7200) # 运行2小时
print(f"热误差估计: {thermal_error:.6f} mm")7. 完整机床配置文件生成
基于上述分析,可以生成完整的5轴机床MCH配置文件:
xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<VcMachine Version="9.1.1" Machine="5Axis_Mill" Unit="millimeter">
<!-- 文件信息 -->
<Information>
<InfoUserName>CNC_Programmer</InfoUserName>
<InfoDateTime>2024-01-15 10:30:00</InfoDateTime>
<InfoVericutVersion>9.5</InfoVericutVersion>
<InfoBuildDate>June 20, 2024</InfoBuildDate>
<InfoLibraryDate>06/20/24</InfoLibraryDate>
<InfoDescription>5-Axis Double Swivel Table Milling Machine</InfoDescription>
</Information>
<!-- 运动优先级 -->
<PriorityType>single</PriorityType>
<!-- 碰撞检测设置 -->
<Collision>
<CheckComponentPairs>
<Pair Component1="Tool" Component2="Workpiece"/>
<Pair Component1="Tool" Component2="Fixture"/>
<Pair Component1="Spindle" Component2="MachineBase"/>
<Pair Component1="Workpiece" Component2="MachineBase"/>
</CheckComponentPairs>
<Clearance Value="1.0"/>
</Collision>
<!-- 机床组件定义 -->
<!-- 基础组件 -->
<Component Name="MachineBase" Type="base" Subsystem="1">
<Attach></Attach>
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/MachineBase.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- X轴线性运动 -->
<Component Name="X_Axis" Type="linear" Subsystem="1" Attach="MachineBase">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Link Axis="-X" Register="X" RapidRate="6000"
MaxLinearVelocity="6000" Accel="200" Decel="200">
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/X_Axis.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- B轴旋转运动 -->
<Component Name="B_Axis" Type="rotary" Subsystem="1" Attach="X_Axis">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="180" J="0" K="180"/>
<Link Axis="Y" Register="B" RapidRate="360"
MaxLinearVelocity="5000" Accel="100" Decel="100">
<Limits Minimum="-120" Maximum="120"/>
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/B_Axis.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="-1"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- C轴旋转运动 -->
<Component Name="C_Axis" Type="rotary" Subsystem="1" Attach="B_Axis">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Link Axis="X" Register="C" RapidRate="360"
MaxLinearVelocity="5000" Accel="100" Decel="100">
<Limits Minimum="-999999" Maximum="999999"/> <!-- 无限旋转 -->
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/C_Axis.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- 工件夹具 -->
<Component Name="WorkpieceFixture" Type="attach" Subsystem="1" Attach="C_Axis">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/WorkpieceFixture.stl</File>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- Z轴线性运动 -->
<Component Name="Z_Axis" Type="linear" Subsystem="1" Attach="MachineBase">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Link Axis="Z" Register="Z" RapidRate="5000"
MaxLinearVelocity="5000" Accel="150" Decel="150">
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/Z_Axis.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="-162.9065" Y="-110.58" Z="162.0667"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- Y轴线性运动 -->
<Component Name="Y_Axis" Type="linear" Subsystem="1" Attach="Z_Axis">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Link Axis="Y" Register="Y" RapidRate="5000"
MaxLinearVelocity="5000" Accel="150" Decel="150">
<AxisPriority PriorityGroup="0" PriorityPos="1"
InterpolatedPos="on" PriorityNeg="1" InterpolatedNeg="on"/>
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter">
<File>Models/Y_Axis.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="-162.9065" Y="110.58" Z="162.0667"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- 主轴组件 -->
<Component Name="Spindle" Type="spindle" Subsystem="1" Attach="Y_Axis">
<Position X="0" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Link Axis="Z" PartSide="no" Register="">
</Link>
<STL Unit="millimeter" Visible="off">
<File>Models/Spindle.stl</File>
<ModelMatrix>
<MatrixXAxis X="1" Y="0" Z="0"/>
<MatrixYAxis X="0" Y="1" Z="0"/>
<MatrixZAxis X="0" Y="0" Z="1"/>
<MatrixOrigin X="-162.9065" Y="110.58" Z="162.0667"/>
</ModelMatrix>
</STL>
</Component>
<!-- 刀具安装点 -->
<Component Name="Tool" Type="tool" Subsystem="1" Attach="Spindle">
<Position X="-162.9065" Y="110.58" Z="162.0667"/>
<Rotation I="0" J="0" K="0"/>
<Tool TurretIndex="1"/>
<Link Axis="Z" PartSide="auto" Register="">
</Link>
</Component>
<!-- 机床行程限制 -->
<TravelLimits>
<Axis Name="X" Minimum="-500" Maximum="500"/>
<Axis Name="Y" Minimum="-400" Maximum="400"/>
<Axis Name="Z" Minimum="-300" Maximum="300"/>
<Axis Name="B" Minimum="-120" Maximum="120"/>
<Axis Name="C" Minimum="-999999" Maximum="999999"/>
</TravelLimits>
<!-- 机床性能参数 -->
<Performance>
<MaxFeedRate Value="10000"/> <!-- mm/min -->
<MaxSpindleSpeed Value="24000"/> <!-- RPM -->
<PositioningAccuracy Value="0.005"/> <!-- mm -->
<Repeatability Value="0.002"/> <!-- mm -->
</Performance>
<!-- 预览图像 -->
<Preview Image="iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAA...(Base64编码图像数据)"/>
</VcMachine>8. 总结
本文详细解析了Vericut 5轴机床MCH文件的结构与构建方法,涵盖了从基础组件定义到高级运动学计算的完整流程。关键要点包括:
- MCH文件采用XML格式,通过组件树结构描述机床的几何和运动关系
- 运动链定义决定机床类型,本文的双摆台结构适合复杂曲面加工
- 运动学计算是5轴加工的核心,包括正解、逆解和插补算法
- 碰撞检测确保加工安全,基于几何模型的实时干涉检查
- 误差补偿提高加工精度,通过几何误差和热误差建模改善加工质量
实际应用中,需要根据具体机床的机械结构调整运动链定义,并通过激光干涉仪等测量设备获取准确的误差参数。Vericut的MCH文件为机床仿真提供了完整的数字孪生模型,是实现虚拟加工、程序验证和工艺优化的基础。
通过合理配置MCH文件,可以最大限度发挥5轴机床的加工能力,实现复杂零件的高效、高精度加工,在航空航天、模具制造和精密加工等领域具有重要应用价值。