说到redis的分布式锁容易想到了setNx,好处是实现简单,但是会有一些问题比如误删锁问题、锁不可重入问题。所以Redisson并没有通过setNx命令来实现加锁,而是自己实现了一套完成的加锁的逻辑
加锁与解锁
RLock继承了Java的lock接口,RedissonLock继承自RedissonBaseLock(抽象类),而RedissonBaseLock又实现了RLock。
typescript
//调用getLock时候就是new了一个RedissonLock
public RLock getLock(String name) {
return new RedissonLock(this.commandExecutor, name);
}我们重点看lock方法:
kotlin
public void lock() {
try {
this.lock(-1L, (TimeUnit)null, false);
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
//调用了tryAcquire获取锁,这里传入了-1L代表没有指定锁的释放时间,正常情况下如果不释放是永久持有。
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(-1L, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
//以下代码先忽略
//.....
}
private Long tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
//这里调用get,等待future返回。
return (Long)this.get(this.tryAcquireAsync0(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
private RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync0(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
//使用了线程池去获取锁
return this.getServiceManager().execute(() -> {
return this.tryAcquireAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
});
}
//重点方法来了
private RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
RFuture ttlRemainingFuture;
if (leaseTime > 0L) {
//如果这里leaseTime不为0说明用户设置了锁的租约时间直接传入。
ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
//如果这里leaseTime为0说明用户没有限制锁的租约时间,但是这里仍然会传30秒的持有时间
ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, this.internalLockLeaseTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
CompletionStage<Long> s = this.handleNoSync(threadId, ttlRemainingFuture);
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = new CompletableFutureWrapper(s);
CompletionStage<Long> f = ttlRemainingFuture.thenApply((ttlRemaining) -> {
//如果为空说明lua获取锁脚本获得了锁
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
//判断是否开启看门狗机制。
if (leaseTime > 0L) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
return ttlRemaining;
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper(f);
}
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
return this.evalWriteSyncedNoRetryAsync(this.getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if ((redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) or (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1)) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); "+
"return nil; "+
"end;"+
//返回锁的过期时间。
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(this.getRawName()), new Object[]{unit.toMillis(leaseTime), this.getLockName(threadId)});
}获取锁的整个逻辑是: 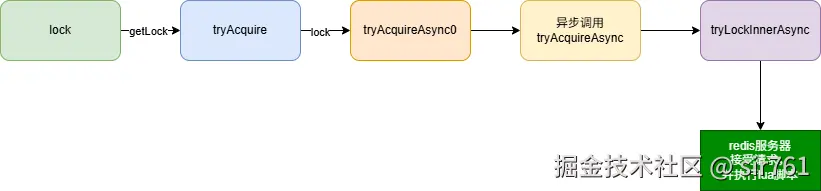 首先,如果用户调用获取锁时候没有限制租约时间,redisson会自动给tryLockInnerAsync加上一个30秒的租约时间,并调用scheduleExpirationRenewal进行看门狗机制
首先,如果用户调用获取锁时候没有限制租约时间,redisson会自动给tryLockInnerAsync加上一个30秒的租约时间,并调用scheduleExpirationRenewal进行看门狗机制
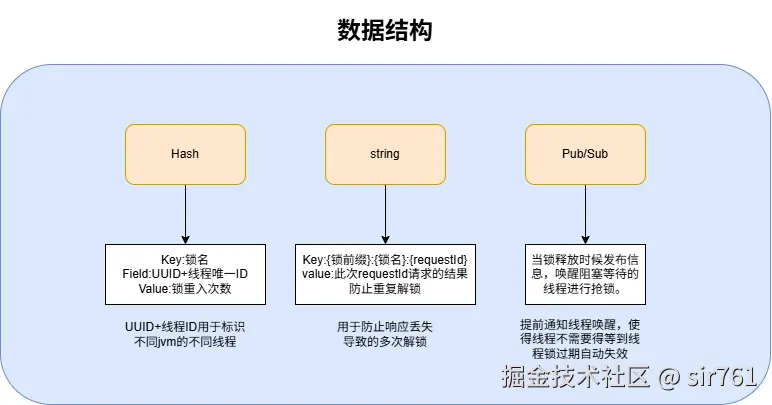
tryLockInnerAsync是执行了一个lua脚本,首先redisson他采用的是hash来存放这个锁,key是锁的名字,field由UUID和线程id组成(UUID是区分不同客户端,防止不同客户端但是线程名恰好相同),value是锁的重入次数。这样就避免了锁的误删,重入和死锁问题了。lua的大致流程为:
- 先判断当前锁是否被持有或者持有者是否是当前线程,如果是的话重入次数加1,并设置/重置整个锁 Key 的过期时间(防止死锁)然后返回。
- 如果上面if不成立说明锁被别人持有了,则返回当前锁剩余的存活时间(TTL)。客户端拿到这个时间后,会等待这么久再重试。
回到刚刚我们忽略的代码:
java
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(-1L, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
//如果这里ttl不为空说明锁被人占有了。
if (ttl != null) {
//此时使用pub/sub订阅这个管道
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
this.pubSub.timeout(future);
//内部维护了一个Semaphore用于控制本地线程的阻塞和唤醒
RedissonLockEntry entry;
if (interruptibly) {
entry = (RedissonLockEntry)this.commandExecutor.getInterrupted(future);
} else {
entry = (RedissonLockEntry)this.commandExecutor.get(future);
}
try {
//死循环直到获取锁或者被中断
while(true) {
//先乐观查询一次
ttl = this.tryAcquire(-1L, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
//仍然没有获取到锁则进入阻塞阶段
if (ttl >= 0L) {
try {
//通过ttl时间判断锁还有多久释放,从而判断阻塞多久,避免cpu空转带来性能消耗,精准在锁释放时候唤醒
//当有人释放锁了,redisson监听到了之后调用entry.getLatch().release(),或者到达ttl了都会使线程被唤醒
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException var14) {
InterruptedException e = var14;
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
//出现异常了,重新抢锁
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else if (interruptibly) {
entry.getLatch().acquire();
} else {
entry.getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
} finally {
//最后终止订阅。
this.unsubscribe(entry, threadId);
}
}
}解锁的逻辑:
跟加锁逻辑一样都是异步转换同步。
java
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
String requestId = this.getServiceManager().generateId();
return this.getServiceManager().execute(() -> {
return this.unlockAsync0(threadId, requestId);
});
}
private RFuture<Void> unlockAsync0(long threadId, String requestId) {
CompletionStage<Boolean> future = this.unlockInnerAsync(threadId, requestId);
//处理异常
CompletionStage<Void> f = future.handle((res, e) -> {
this.cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId, res);
if (e != null) {
if (e instanceof CompletionException) {
throw (CompletionException)e;
} else {
throw new CompletionException(e);
}
} else if (res == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: " + this.id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
throw new CompletionException(cause);
} else {
return null;
}
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper(f);
}
protected final RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId, String requestId) {
if (requestId == null) {
requestId = this.getServiceManager().generateId();
}
MasterSlaveServersConfig config = this.getServiceManager().getConfig();
long timeout = ((long)config.getTimeout() + config.getRetryDelay().calcDelay(config.getRetryAttempts()).toMillis()) * (long)config.getRetryAttempts();
timeout = Math.max(timeout, 1L);
//异步释放锁
RFuture<Boolean> r = this.unlockInnerAsync(threadId, requestId, (int)timeout);
CompletionStage<Boolean> ff = r.thenApply((v) -> {
CommandAsyncExecutor ce = this.commandExecutor;
if (ce instanceof CommandBatchService) {
ce = new CommandBatchService(this.commandExecutor);
}
((CommandAsyncExecutor)ce).writeAsync(this.getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.DEL, new Object[]{this.getUnlockLatchName(this.id)});
if (ce instanceof CommandBatchService) {
((CommandBatchService)ce).executeAsync();
}
return v;
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper(ff);
}
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId, String requestId, int timeout) {
return this.evalWriteSyncedNoRetryAsync(this.getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
//防重检查(幂等性)
"local val = redis.call('get', KEYS[3]);"+
"if val ~= false then "+
"return tonumber(val);"+
"end;"+
//判断是否持有锁
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then "+
"return nil;"+
"end; "+
//扣减重入次数
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); "+
//判断是"重入释放"还是"彻底释放"
"if (counter > 0) then "+
//重入次数减1
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); "+
"redis.call('set', KEYS[3], 0, 'px', ARGV[5]); "+
"return 0; "+
"else "+
//彻底释放锁
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); "+
//发送队列消息
"redis.call(ARGV[4], KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); "+
"redis.call('set', KEYS[3], 1, 'px', ARGV[5]); "+
"return 1; "+
"end; ",
Arrays.asList(this.getRawName(), this.getChannelName(), this.getUnlockLatchName(requestId)), new Object[]{LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId), this.getSubscribeService().getPublishCommand(), timeout});
}lua的流程为:
先去查一下 KEYS[3](查看解锁请求的结果缓存)是否存在。如果存在,说明这个请求之前已经处理过了 (可能是网络波动导致客户端以为超时了,重发了请求)。直接返回之前缓存的结果(0 或 1),不需要再执行后面的逻辑。这保证了幂等性。
- 检查 Hash KEYS[1] 中是否存在当前线程 ARGV[3]。如果不存在(== 0),说明当前线程根本没有持有这把锁。返回 nil(Java 客户端会抛出 IllegalMonitorStateException)。
- 将该线程的加锁计数器减 1,counter 是减完之后剩下的次数。
- 如果counter > 0,说明锁重入了。pexpire:刷新锁的过期时间(看门狗时间),只要锁还没彻底释放,就得给它续命。set KEYS[3] 0:记录本次请求结果为 0(表示未完全释放)。返回 0,代表还未释放锁。
- 如果counter<=0,说明锁此时可以释放了,这里会先删除这个锁对应的key,然后调用
redis.call(ARGV[4], KEYS[2], ARGV[1]);这里ARGC[4]其实通常是publish发送消息,之所以不写死是因为集群下可以用spublish加快性能。这里发送消息是为了前文提到的,告诉监听者锁已经释放。set KEYS[3] 1:缓存本次请求结果为 1,并将1返回,代表锁成功释放了
这里之所以要多出一个KEY[3]是为了做幂等。KEY[3]命名一般为{锁前缀}:{锁名}:{requestId},每次请求时候都会带上不同的requestId,vlaue是requestId请求的解锁结果
存在一种可能,客户端重入了2次锁,客户端第一次调用unlock时候,redis正常执行了解锁逻辑,并扣减了1次锁记录,但是由于网络波动,响应丢失了,此时客户端会重新发起一次请求,导致重复扣减。为了解决这个问题,就利用key[3],判断一下相同的请求id是否有记录如果是就代表确实发送了响应丢失,直接将上次的数据返回,避免重复解锁。
公平锁
以上锁是默认非公平锁,所有线程都去争抢锁,而公平锁则是进入队列等待,防止饥饿问题。
当我们getFairLock时候其实是new了一个RedissonFairLock
typescript
public RLock getFairLock(String name) {
return new RedissonFairLock(this.commandExecutor, name);
}RedissonFairLock继承自RedissonLock也就是说加锁的流程都是大致相同的。RedissonFairLock重写了tryLockInnerAsync方法
ini
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
long wait = this.threadWaitTime;
if (waitTime > 0L) {
wait = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
}
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (command == RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN) {
return this.commandExecutor.syncedEvalNoRetry(
this.getRawName(),
LongCodec.INSTANCE,
command,
// Lua脚本 - 用于获取锁
"while true do " +
" local firstThreadId2 = redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], 0); " +
" if firstThreadId2 == false then " +
" break; " +
" end; " +
" local timeout = redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], firstThreadId2); " +
" if timeout ~= false and tonumber(timeout) <= tonumber(ARGV[3]) then " +
" redis.call('zrem', KEYS[3], firstThreadId2); " +
" redis.call('lpop', KEYS[2]); " +
" else " +
" break; " +
" end; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) and ((redis.call('exists', KEYS[2]) == 0) or (redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], 0) == ARGV[2])) then " +
" redis.call('lpop', KEYS[2]); " +
" redis.call('zrem', KEYS[3], ARGV[2]); " +
" local keys = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[3], 0, -1); " +
" for i = 1, #keys, 1 do " +
" redis.call('zincrby', KEYS[3], -tonumber(ARGV[4]), keys[i]); " +
" end; " +
" redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
" redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return 1;",
Arrays.asList(this.getRawName(), this.threadsQueueName, this.timeoutSetName),
new Object[]{unit.toMillis(leaseTime), this.getLockName(threadId), currentTime, wait}
);
} else if (command == RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG) {
return this.commandExecutor.syncedEvalNoRetry(
this.getRawName(),
LongCodec.INSTANCE,
command,
// Lua脚本 - 用于尝试获取锁并返回TTL
"while true do " +
" local firstThreadId2 = redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], 0); " +
" if firstThreadId2 == false then " +
" break; " +
" end; " +
" local timeout = redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], firstThreadId2); " +
" if timeout ~= false and tonumber(timeout) <= tonumber(ARGV[4]) then " +
" redis.call('zrem', KEYS[3], firstThreadId2); " +
" redis.call('lpop', KEYS[2]); " +
" else " +
" break; " +
" end; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) and ((redis.call('exists', KEYS[2]) == 0) or (redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], 0) == ARGV[2])) then " +
" redis.call('lpop', KEYS[2]); " +
" redis.call('zrem', KEYS[3], ARGV[2]); " +
" local keys = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[3], 0, -1); " +
" for i = 1, #keys, 1 do " +
" redis.call('zincrby', KEYS[3], -tonumber(ARGV[3]), keys[i]); " +
" end; " +
" redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1 then " +
" redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return nil; " +
"end; " +
"local timeout = redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], ARGV[2]); " +
"if timeout ~= false then " +
" local ttl = redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]); " +
" return math.max(0, ttl); " +
"end; " +
"local lastThreadId = redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], -1); " +
"local ttl; " +
"if lastThreadId ~= false and lastThreadId ~= ARGV[2] and redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], lastThreadId) ~= false then " +
" ttl = tonumber(redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], lastThreadId)) - tonumber(ARGV[4]); " +
"else " +
" ttl = redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]); " +
"end; " +
"local timeout = ttl + tonumber(ARGV[3]) + tonumber(ARGV[4]); " +
"if redis.call('zadd', KEYS[3], timeout, ARGV[2]) == 1 then " +
" redis.call('rpush', KEYS[2], ARGV[2]); " +
"end; " +
"return ttl;",
Arrays.asList(this.getRawName(), this.threadsQueueName, this.timeoutSetName),
new Object[]{unit.toMillis(leaseTime), this.getLockName(threadId), wait, currentTime}
);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}这里有俩段lua脚本,第一段对应的是无参的tryLock()方法,进行一次快速尝试,如果获取不到锁直接返回。第二段对应的是tryLock(waitTime)/lock这俩个阻塞等锁的方法。这里我们重点看第二段lua脚本,第一个lua脚本和第二个类似:
java
--循环的判断是否有waitTime已经超过的节点,如果有就剔除掉,防止占用着队列
while true do
--查询等待队列头节点是什么
local firstThreadId2 = redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], 0);
--如果等待队列为空则跳出循环
if firstThreadId2 == false then
break;
end;
--不为空,判断一下是否超过了超时时间,如果是就删除掉,没有就跳出循环
local timeout = redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], firstThreadId2);
if timeout ~= false and tonumber(timeout) <= tonumber(ARGV[4]) then
redis.call('zrem', KEYS[3], firstThreadId2);
redis.call('lpop', KEYS[2]);
else
break;
end;
end;
--判断一下锁是否没有被其他线程持有并且等待队列不存在(等待队列为空)或者对头是此线程,如果是则进入抢锁。
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) and ((redis.call('exists', KEYS[2]) == 0) or (redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], 0) == ARGV[2])) then
--将自己从队列移除
redis.call('lpop', KEYS[2]);
redis.call('zrem', KEYS[3], ARGV[2]);
local keys = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[3], 0, -1);
--循环整个队列,更新所有节点的超时时间(减少等待预算)
for i = 1, #keys, 1 do
redis.call('zincrby', KEYS[3], -tonumber(ARGV[3]), keys[i]);
end;
--真正的加锁逻辑,加锁后直接返回。
redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
--返回nil说明抢锁成功
return nil;
end;
--前面判断为false,说明锁被持有了,判断一下锁是否被本线程持有,如果是重入加1并返回
if redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1 then
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
--走到这里说明锁被其他人持有了,此时判断一下本线程是否已经在排队了
local timeout = redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], ARGV[2]);
if timeout ~= false then
--如果在排队了,则返回锁的剩余持有时间
local ttl = redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);
return math.max(0, ttl);
end;
--走到这里说明没有入队,先查看一下队尾节点
local lastThreadId = redis.call('lindex', KEYS[2], -1);
local ttl;
--如果队尾节点存在(锁被持有,有线程等待抢锁)则ttl是钱一个人的超时时间-当前时间。
if lastThreadId ~= false and lastThreadId ~= ARGV[2] and redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], lastThreadId) ~= false then
ttl = tonumber(redis.call('zscore', KEYS[3], lastThreadId)) - tonumber(ARGV[4]);
else
--如果队尾节点不存在(锁被持有,且没有线程等待抢锁)则ttl就是锁的过期时间
ttl = redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);
end;
local timeout = ttl + tonumber(ARGV[3]) + tonumber(ARGV[4]);
--然后入队,将计算好的超时时间放入Zset,并将本线程放入队尾。
if redis.call('zadd', KEYS[3], timeout, ARGV[2]) == 1 then
redis.call('rpush', KEYS[2], ARGV[2]);
end;
--返回告诉客户端,还需要时间为ttl,使用Semaphore去阻塞。(唤醒过程和前文提到过的一样)
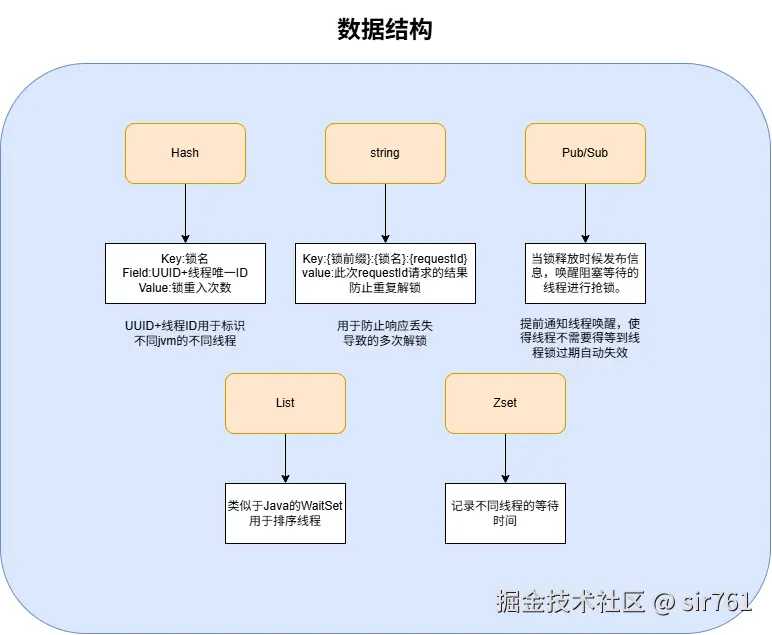
return ttl;此过程中用到了Zset,List,我们直到List用于存放资源争抢者,那Zset又是干嘛的?
List 虽然能完美实现 FIFO(先进先出),但它有2个致命弱点:
- 不好判断过期时间:List 只能告诉你谁排第一,但不能告诉你他还是不是活的(有没有超时),如果非要利用List存储过期时间就得通过value去分割,不仅需要占用cpu资源而且不好判断如何分割,万一用户命名不规范导致分割错误,此时需要Zset,它存储了每个人的"死亡时间",用来在每次操作前清理 List 里的僵尸节点。member是uuid+线程id,score是过期时间
- 不好判断是否当前线程在队列中:List需要O(n)判断,时间慢,通过Zset的dict数据结构O(1)判断。
此外,由于每一个节点有可能是lock()这种无等待时间,会阻塞到一直获取锁,在Zset中难道我们要将Zset的过期分数设置很大或者设置为-1代表没有过期时间吗?那如果客户端宕机了,该节点不就占用这个Zset和list的节点,且谁也清除不掉,导致内存泄露。且轮到它作为头节点时候,又不会抢锁,导致全部都在死等。
旧版本的redisson是默认给5秒过期时间,每次5秒后就刷新一下,如果客户端宕机了就不会刷新,这个节点会被清除掉。但是当竞争激烈的时候5秒获取不到锁时候大量的线程醒过来同时去更新过期时间,这个惊群效应会导致性能急剧下降,后续新版本改为了5分钟。
如图,比起非公平锁多了俩个数据结构
若有错误欢迎指出,将及时改正。