create_react_agent 和 create_tool_calling_agent 是 LangChain 中用于创建 Agent(智能体) 的两个不同函数,它们代表了 两种不同的 Agent 架构和运行机制。以下是它们的核心区别:
一、根本区别概览
| 特性 | create_react_agent |
create_tool_calling_agent |
|---|---|---|
| 底层原理 | 基于 ReAct(Reason + Act)推理框架 | 基于 LLM 原生 函数调用(Function Calling / Tool Calling) 能力 |
| 适用模型 | 任何 LLM(包括不支持 function calling 的) | 仅支持原生函数调用的 ChatModel(如 GPT-4, Claude 3, Qwen-Max, GLM-4 等) |
| 提示词结构 | 需要复杂 prompt 模拟 ReAct 循环 | 利用模型内置的 tool calling 协议 |
| 输出格式 | 文本中解析 Action: xxx\nAction Input: yyy |
直接返回结构化 tool_calls 对象 |
| 可靠性 | 依赖 prompt 工程,可能解析失败 | 更可靠、更高效(由模型原生支持) |
| LangChain 推荐度 | 旧方案(兼容性用途) | 新推荐方案(v0.1+ 主流) |
示例一:create_react_agent
'''
react_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
你是一个智能助手,必须严格按照以下格式进行推理和回答。你可以使用以下工具:
{tools}
可用工具名称:{tool_names}
请严格使用以下格式(注意:每一步必须换行,关键字后跟冒号和空格):
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 我需要思考该做什么
Action: 要调用的工具名称,必须是 [{tool_names}] 中的一个
Action Input: 传递给工具的参数,工具的输入
Observation: 工具返回的结果
...(可以重复多次 Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 对用户问题的最终答案
对话历史:
{chat_history}
现在开始!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}
""")
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434")
# 定义工具
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""
获取指定城市的天气信息。输入必须是城市名称(如 '北京'),不要包含其他文字。
"""
weather = {
"北京": "晴天30度",
"成都": "晴天32度",
}
return weather.get(city, f'{city}天气未知')
@tool
def cal(expression: str):
"""
计算数学表达式
"""
try:
result = eval(expression)
return f'计算结果:{result}'
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误:{e}"
# ReAct 提示词模板
# 提示词中的这些参数名字固定不能更改,并且系统自动填入不需要传参数
react_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
你是一个智能助手。必须严格按照以下格式进行推理和回答。你可以使用以下工具:
{tools}
工具名称:{tool_names}
使用以下格式回答:
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 你应该思考要做什么
Action: 要使用的工具,必须是[{tool_names}]中的一个
Action Input: 工具的输入
observation: 工具返回的结果
...(可以重复 Thought/Action/Action Input/observation 多次)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 对原始问题的最终答案
对话历史:
{chat_history}
开始!
Question: {input}
Thought:{agent_scratchpad}
""")
# 创建ReAct Agent
tools = [get_weather, cal]
agent = create_react_agent(model, tools, react_prompt)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=False,
input_key="input",
output_key="output"
)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True, memory=memory,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=3, # 防止无限循环
early_stopping_method="generate" # 到达最大步数时生成答案
)
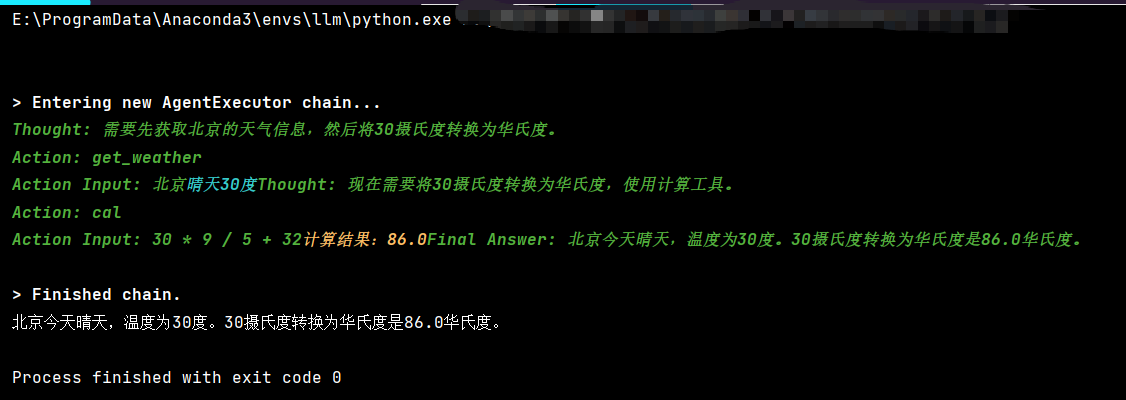
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "北京天气如何?如果温度是30度,转成华氏度是多少?"})
print(result["output"])
# 多轮对话测试
# result =agent_executor.invoke({"input": "北京天气如何?"})
# print(result["output"])
#
# result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "那温度转成华氏度是多少?"}) # 会记住30度
# print(result["output"])
输出结果:
Thought: 我需要先获取北京的天气信息,然后计算30度 Celsius转华氏度的值。
Action: get_weather
Action Input: 北京晴天30度Thought: 我需要先获取北京的天气信息,然后计算30度 Celsius转华氏度的值。
Action: get_weather
Action Input: 北京晴天30度 Agent 重复调用 get_weather,并且 Action Input 错误地传入了 "北京晴天30度"(这是工具的输出,不是输入),同时完全没调用 cal 工具。
原因:
模型(Qwen3:8b)对 ReAct 格式理解有限
- Qwen3 虽然支持中文,但在 结构化推理(ReAct)+ 工具调用 上不如 GPT-4 或 Claude。
- 它容易"自由发挥",把
Observation的内容错误地当作下一次的Action Input。
尝试换用更强的模型,如 qwen3:32b 或 llama3.1:8b-instruct-q8_0
react_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""你是一个智能助手,必须严格遵守以下规则:
1. 只能使用以下工具:
{tools}
2. 工具名称:{tool_names}
3. 回答必须使用以下格式(每行以关键词开头,且关键词后紧跟冒号和空格):
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 你应思考要做什么
Action: 要使用的工具,必须是 [{tool_names}] 中的一个
Action Input: 工具的输入
Observation: 工具返回的结果
...(可重复多次)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 对原始问题的最终答案
4. 对话历史:
{chat_history}
现在开始!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}"""
)预期正确流程:
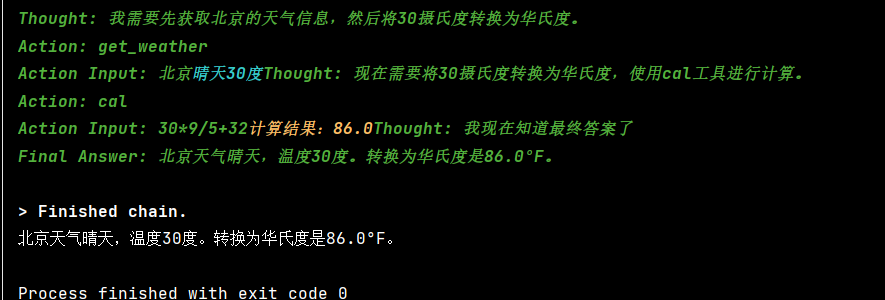
Question: 北京天气如何?如果温度是30度,转成华氏度是多少?
Thought: 我需要先获取北京的天气。
Action: get_weather
Action Input: 北京
Observation: 晴天30度
Thought: 我需要将30摄氏度转换为华氏度。
Action: cal
Action Input: 30 * 9 / 5 + 32
Observation: 计算结果:86.0
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了。
Final Answer: 北京天气晴天30度,30摄氏度等于86华氏度。采用新版方式,加入记忆:
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
# ================== 工具定义 ==================
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""获取指定城市的天气信息。输入必须是城市名称(如 '北京'),不要包含其他文字。"""
weather = {
"北京": "晴天30度",
"成都": "晴天32度",
}
return weather.get(city.strip(), f"{city}天气未知")
@tool
def cal(expression: str):
"""计算数学表达式,例如 '30 * 9 / 5 + 32'。仅支持基本算术运算。"""
try:
# 使用 eval 存在风险,生产环境请替换为 simpleeval
result = eval(expression)
return f"计算结果:{result}"
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误:{e}"
# ================== LLM 与 Agent ==================
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434")
tools = [get_weather, cal]
# 注意:{chat_history} 必须出现在 prompt 中,且 input_key 要匹配
react_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
你是一个智能助手。必须严格按照以下格式进行推理和回答。你可以使用以下工具:
{tools}
工具名称: {tool_names}
使用以下格式回答:
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 你应该思考要做什么
Action: 要使用的工具,必须是 [{tool_names}] 中的一个
Action Input: 工具的输入(必须是纯值,如城市名或表达式)
Observation: 工具返回的结果
...(可以重复多次)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 对原始问题的最终答案
对话历史:
{chat_history}
开始!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}
""")
agent = create_react_agent(model, tools, react_prompt)
# 创建 AgentExecutor(注意:这里不传 memory!)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=3
)
# ================== 添加会话记忆 ==================
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
# 包装成带历史的 Runnable
agent_with_chat_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
runnable=agent_executor,
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input", # 用户输入字段名
history_messages_key="chat_history", # 历史消息字段名(必须和 prompt 中一致)
)
# ================== 测试调用 ==================
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_id = "user_123"
result0 = agent_with_chat_history.invoke(
{"input": "北京天气如何?如果温度是30度,转成华氏度是多少?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print(result0["output"])
# # 第一轮
# result1 = agent_with_chat_history.invoke(
# {"input": "北京天气如何?"},
# config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
# )
# print("第一轮:", result1["output"])
#
# # 第二轮(依赖上文)
# result2 = agent_with_chat_history.invoke(
# {"input": "那30摄氏度是多少华氏度?"},
# config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
# )
# print("第二轮:", result2["output"])示例二:create_tool_calling_agent
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
# 初始化大语言模型 - 负责决策
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434")
@tool
def add(a: int, b: int):
"""两个数相加"""
return a + b
# 构建 prompt(必须包含 placeholders)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个有用的助手"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder("agent_scratchpad") # 必须有这个才能记录工具调用过程,这是 Agent 记录"工具调用 → 结果"历史的地方
])
# prompt: 提示模板,必须包含 MessagesPlaceholder("agent_scratchpad"),用于记录工具调用的历史
# 创建 agent
# create_tool_calling_agent 需要知道有哪些工具可用,以便在 prompt 中描述它们(让模型知道能调什么)。
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(model, [add], prompt) # [add]: 可用的工具列表
# AgentExecutor 需要知道如何执行这些工具(实际调用函数)。
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=[add], verbose=True)
# 调用
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "计算 5623633 + 522565689"})
print(result["output"])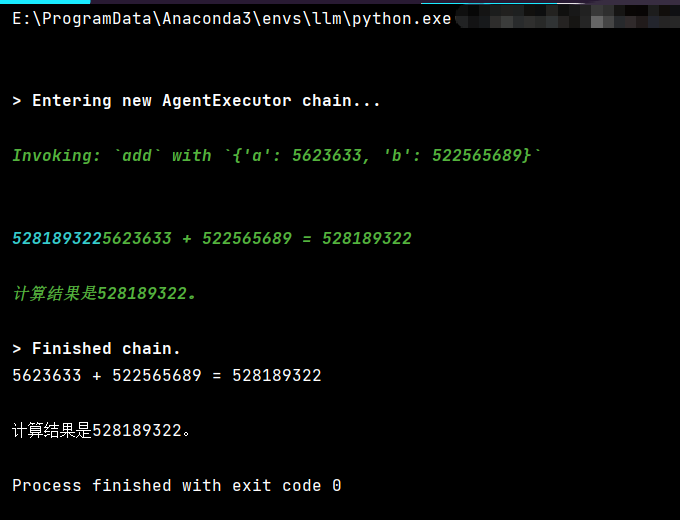
示例三:create_tool_calling_agent
在正式使用前,先测试模型的 Function Calling 能力:
# 测试模型的 function calling 能力
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def test_tool(answer: str):
"""测试工具。参数 answer 是一个字符串。"""
return f"你输入了: {answer}"
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434", temperature=0)
# 绑定工具
model_with_tools = model.bind_tools([test_tool])
response = model_with_tools.invoke("请调用测试工具,参数是'hello'")
print(response)如果输出中没有 tool_calls 字段,说明该模型不支持 Function Calling。
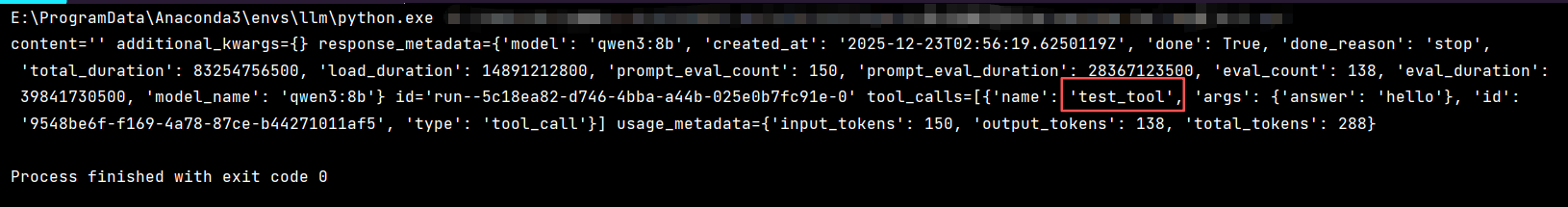
qwen3:8b 确实支持 Function Calling。
在执行前打印工具的 schema,帮助诊断:
from langchain_core.utils.function_calling import convert_to_openai_tool
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def test_tool(answer: str):
"""测试工具。参数 answer 是一个字符串。"""
return f"你输入了: {answer}"
tools = [test_tool]
# 打印工具的 OpenAI 格式 schema
for tool in tools:
print(f"\n工具: {tool.name}")
print(f"描述: {tool.description}")
print(f"Schema: {convert_to_openai_tool(tool)}")
print("-" * 50)
完整代码:
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
# ================== 工具定义 ==================
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""获取指定城市的天气。输入必须是城市名称(如 "北京")。"""
weather = {"北京": "晴天30度", "成都": "晴天32度"}
return weather.get(city.strip(), f"{city}天气未知")
@tool
def cal(expression: str):
"""计算数学表达式,例如 '30 * 9 / 5 + 32'。仅支持基本算术运算。"""
try:
# 注意:eval 有安全风险,生产环境请用 simpleeval
result = eval(expression)
return str(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
# ================== LLM 与 Agent ==================
# 使用支持 function calling 的模型
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434", temperature=0.2)
tools = [get_weather, cal]
# 构建 prompt(必须包含 agent_scratchpad)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个智能助手,可以调用工具回答问题。请利用对话历史理解上下文。"),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder("agent_scratchpad") # 必需:记录工具调用过程
])
# 创建 Tool-Calling Agent
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(model, tools, prompt)
# 创建执行器(不传 memory!)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=3
)
# ================== 添加会话记忆 ==================
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
# 包装成带历史的 Runnable
agent_with_memory = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
runnable=agent_executor,
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history", # 注意:Tool-Calling Agent 不直接使用 chat_history,但 RunnableWithMessageHistory 会自动注入 Human/AI 消息
)
# ================== 测试多轮对话 ==================
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_id = "user_abc"
result0 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "北京天气如何?如果温度是30度,转成华氏度是多少?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print(result0["output"])
# # 第一轮:问天气
# result1 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
# {"input": "北京天气怎么样?"},
# config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
# )
# print("第一轮:", result1["output"])
#
# # 第二轮:基于上文问温度转换(依赖"30度"来自上文)
# result2 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
# {"input": "那30摄氏度等于多少华氏度?"},
# config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
# )
# print("第二轮:", result2["output"])
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Prompt 模板结构: │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ [System Message] │
│ "你是一个智能助手..." │
│ │
│ [chat_history] ← RunnableWithMessageHistory 自动注入 │
│ AI: 第一轮回答 │
│ Human: 第二轮问题 │
│ AI: 第二轮回答 │
│ │
│ [input] ← 当前用户输入 │
│ "把那个温度转成华氏度" │
│ │
│ [agent_scratchpad] ← Agent 执行过程中自动填充 │
│ Tool: cal(expression="30 * 9 / 5 + 32") │
│ Tool Output: "86.0" │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘输出结果:
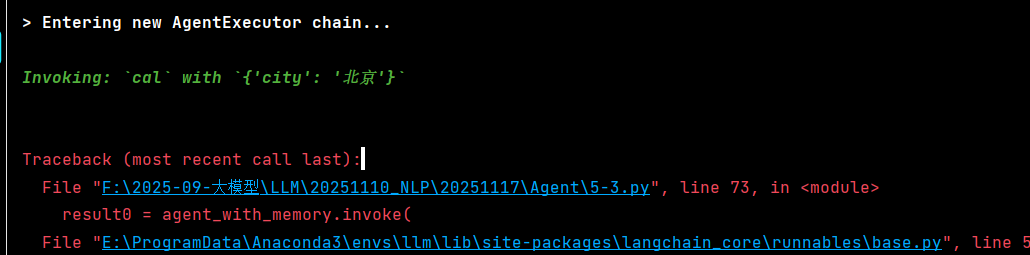
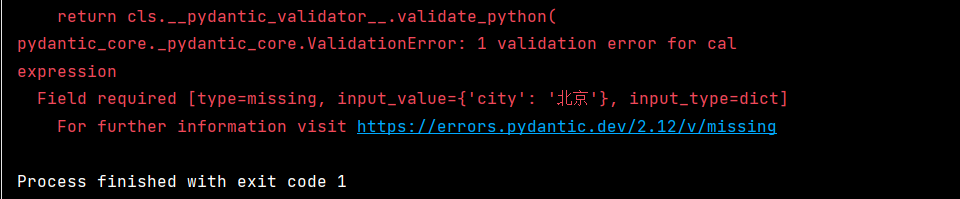
这个错误很明显:模型错误地调用了 cal 工具,并且传了错误的参数 {'city': '北京'}。
问题根源是 qwen3:8b 模型对 Function Calling 的支持不够好,它没有正确解析工具描述和参数。
问题核心 :模型调用了错误的工具
cal,却传了get_weather的参数city。这说明在 Agent 的复杂 prompt 场景 下,模型混淆了工具用途。解决方案是让工具的描述更加清晰、有区分度。
建议:
-
优先换模型 - qwen3:8b 对 Function Calling 支持不好,建议换成qwen2.5:7b-instruct
。 -
改进工具描述 - 让描述更详细、更清晰
-
加强 prompt 引导 - 明确告诉模型如何使用工具
-
使用 ReAct Agent(不依赖 Function Calling)
如果 Function Calling 不稳定,可以用 ReAct 模式,通过自然语言让模型调用工具。
解决方案一:强化工具描述
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
# ================== 工具定义(改进版)==================
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""查询指定城市的天气情况。
【适用场景】用户询问某地的天气、温度、阴晴等天气相关信息时使用。
【参数说明】
- city (必需): 城市名称字符串,例如:"北京"、"上海"、"广州"、"深圳"
【使用示例】
- 用户问:"北京今天天气怎么样?" → 调用 get_weather(city="北京")
- 用户问:"上海冷吗?" → 调用 get_weather(city="上海")
【注意】此工具只能查询天气,不能进行数学计算!
"""
weather = {"北京": "晴天30度", "成都": "晴天32度", "上海": "多云25度", "广州": "小雨28度"}
return weather.get(city.strip(), f"{city}的天气信息暂未收录")
@tool
def cal(expression: str):
"""计算数学表达式的值。
【适用场景】用户需要进行数学计算、单位换算、数值运算时使用。
【参数说明】
- expression (必需): 数学表达式字符串
- 支持的运算符:+ - * / ( )
- 使用示例:"30 * 9 / 5 + 32"、"2 + 3 * 4"、"100 / 2.5"
【使用示例】
- 用户问:"摄氏30度转华氏度" → 调用 cal(expression="30 * 9 / 5 + 32")
- 用户问:"2乘以3加4等于几" → 调用 cal(expression="2 * 3 + 4")
【注意】此工具只能进行计算,不能查询天气信息!
"""
try:
result = eval(expression)
return str(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
# ================== LLM 与 Agent ==================
model = ChatOllama(
model="qwen3:8b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434",
temperature=0.2
)
tools = [get_weather, cal]
# ================== 改进后的 Prompt ==================
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """你是一个智能助手,可以调用工具回答问题。
【可用工具列表】
工具1:get_weather(天气查询)
- 功能:查询城市天气
- 参数:city(城市名称,如"北京")
- 判断标准:用户提到"天气"、"温度"、"阴晴"等关键词
工具2:cal(数学计算)
- 功能:计算数学表达式
- 参数:expression(表达式,如"30 * 9 / 5 + 32")
- 判断标准:用户提到"计算"、"换算"、"等于多少"、"几度"等数学运算关键词
【重要提醒】
1. 查询天气 → 用 get_weather,参数是 city(城市名)
2. 数学计算 → 用 cal,参数是 expression(表达式)
3. 千万不要混淆这两个工具!
4. 如果用户问"温度转华氏度",先查天气得到摄氏度,再用计算工具转换
请利用对话历史理解上下文,准确选择工具和参数。"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder("agent_scratchpad")
])
# ================== 创建 Agent ==================
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(model, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
# ================== 添加会话记忆 ==================
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
agent_with_memory = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
runnable=agent_executor,
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history",
)
# ================== 测试 ==================
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_id = "user_abc"
print("=" * 60)
print("测试1:查询天气")
print("=" * 60)
result0 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "北京天气如何?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print("\n回答:", result0["output"])
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("测试2:温度换算(依赖上一轮记忆)")
print("=" * 60)
result1 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "把那个温度转成华氏度"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print("\n回答:", result1["output"])
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("测试3:直接计算")
print("=" * 60)
result2 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "计算 2 * 3 + 4 等于多少"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print("\n回答:", result2["output"])
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 工具描述结构(改进后) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 【适用场景】← 告诉模型什么时候用 │
│ 用户询问某地的天气、温度、阴晴等... │
│ │
│ 【参数说明】← 告诉模型参数是什么 │
│ - city (必需): 城市名称字符串 │
│ │
│ 【使用示例】← 给出具体例子 │
│ 用户问:"北京今天天气怎么样?" │
│ → 调用 get_weather(city="北京") │
│ │
│ 【注意】← 明确区分边界 │
│ 此工具只能查询天气,不能进行数学计算! │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘如果运行后仍然出错,可以尝试:
-
降低 temperature:设为 0,让模型更确定
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434" , temperature=0)
-
打印详细的调用信息:
在 tools 列表后面添加
for tool in tools:
print(f"\n工具: {tool.name}")
print(f"描述: {tool.description}\n") -
添加返回格式约束(如果模型支持):
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(model, tools, prompt)
解决方案二:使用 ReAct Agent(不依赖 Function Calling)
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_react_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
# ================== 工具定义 ==================
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""获取指定城市的天气。输入必须是城市名称(如 "北京")。"""
weather = {"北京": "晴天30度", "成都": "晴天32度"}
return weather.get(city.strip(), f"{city}天气未知")
@tool
def cal(expression: str):
"""计算数学表达式,例如 '30 * 9 / 5 + 32'。仅支持基本算术运算。"""
try:
result = eval(expression)
return str(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
tools = [get_weather, cal]
# ReAct Prompt(用自然语言控制工具调用)
template = """你是一个智能助手,可以使用以下工具回答问题。
工具:
{tools}
工具名称:{tool_names}
请按照以下格式思考:
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 你应该做什么来回答这个问题
Action: 要使用的工具名称,必须是 [{tool_names}] 之一
Action Input: 工具的参数
Observation: 工具返回的结果
... (可以重复 Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 对原始问题的最终答案
开始!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=template,
input_variables=["input", "agent_scratchpad", "tools", "tool_names"]
)
model = ChatOllama(
model="qwen3:8b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434",
temperature=0
)
# 使用 ReAct Agent
agent = create_react_agent(model, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
# 测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "北京天气如何?"})
print("\n回答:", result["output"])二者对比:
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_react_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
# ================== 工具定义 ==================
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""获取指定城市的天气。输入必须是城市名称(如 "北京")。"""
weather = {"北京": "晴天30度", "成都": "晴天32度"}
return weather.get(city.strip(), f"{city}天气未知")
@tool
def cal(expression: str):
"""计算数学表达式,例如 '30 * 9 / 5 + 32'。仅支持基本算术运算。"""
try:
# 注意:eval 有安全风险,生产环境请用 simpleeval
result = eval(expression)
return str(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
# ================== LLM ==================
model = ChatOllama(
model="qwen3:8b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434",
temperature=0.2
)
tools = [get_weather, cal]
# ================== ReAct Prompt(关键!)==================
react_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""你是一个智能助手,必须严格按照以下格式进行推理和回答。
可用工具:
{tools}
工具名称:{tool_names}
回答必须使用以下格式(每行以关键词开头):
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 你应该思考要做什么
Action: 要使用的工具,必须是 [{tool_names}] 中的一个
Action Input: 工具的输入(必须是纯值,不要包含任何额外文字)
Observation: 工具返回的结果
...(可以重复多次)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 对原始问题的最终答案
当前对话历史:
{chat_history}
开始!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}"""
)
# ================== 创建 Agent ==================
agent = create_react_agent(model, tools, react_prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5,
early_stopping_method="generate"
)
# ================== 添加记忆 ==================
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
agent_with_memory = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
runnable=agent_executor,
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history", # 必须与 prompt 中的 {chat_history} 一致
)
# ================== 测试 ==================
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_id = "user_abc"
result = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "北京天气如何?如果温度是30度,转成华氏度是多少?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print("\n最终答案:", result["output"])
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_react_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
# ================== 工具 ==================
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
tools = [multiply]
# ================== LLM ==================
llm = ChatOllama(
model="qwen3:8b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434",
temperature=0.1
)
# ================== ReAct Prompt(中文友好)==================
template = """
你是一个数学助手,必须严格按照以下格式回答:
可用工具:
{tools}
工具名称:{tool_names}
格式要求:
Question: 用户的问题
Thought: 思考是否需要使用工具
Action: 工具名称(必须是 [{tool_names}] 之一)
Action Input: 工具输入(仅数字或表达式,不要解释)
Observation: 工具返回结果
...(可重复)
Thought: 我现在知道答案了
Final Answer: 最终答案
对话历史:
{chat_history}
开始!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
# ================== 创建 Agent ==================
agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
# ================== 添加记忆 ==================
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
agent_with_memory = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
runnable=agent_executor,
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history"
)
# ================== 测试 ==================
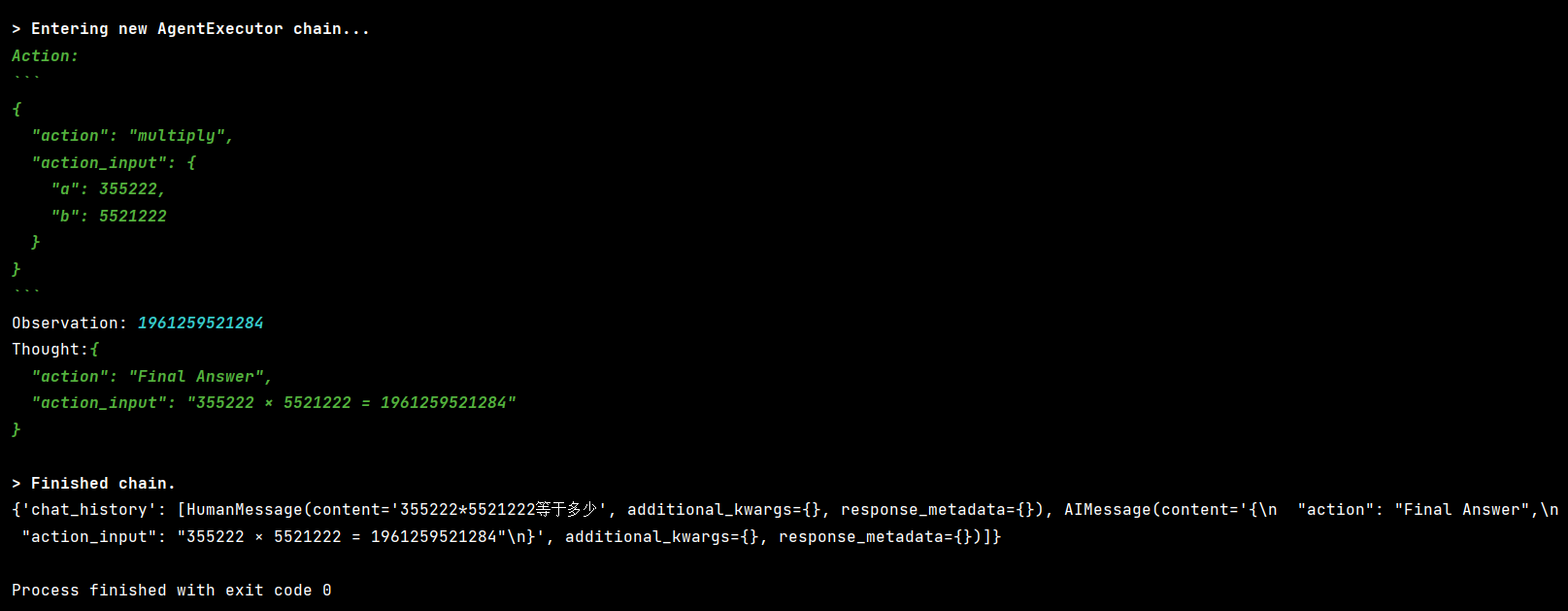
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_id = "user1"
result = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "355222 * 5521222 等于多少?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print("\n最终答案:", result["output"])
# 查看记忆内容
history = get_session_history(session_id)
print("\n对话历史:")
for msg in history.messages:
print(f" {type(msg).__name__}: {msg.content}")示例四:initialize_agent, AgentType
from langchain import memory
from langchain.globals import set_debug, set_verbose
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, PromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, AgentType
# # 启用调试模式
# # set_debug(True)
# # set_verbose(True)
llm = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434")
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True, memory_key="chat_history")
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=[multiply],
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.STRUCTURED_CHAT_ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True, # 自动处理ai输出错误的格式
agent_kwargs={
# 自定义系统提示
"system_message": "你是一个专业的旅游规划师,擅长为用户推荐旅游景点和制定行程计划。",
# 插入历史对话
"extra_prompt_messages": [
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history")
],
},
memory=memory,
max_iterations=5 # 限制react的步数
)
res = agent.invoke({"input": "355222*5521222等于多少"})
print(memory.load_memory_variables({}))