目录
[🎯 先说说为啥要自己造Starter](#🎯 先说说为啥要自己造Starter)
[✨ 摘要](#✨ 摘要)
[1. 别急着写代码,先想清楚这几个问题](#1. 别急着写代码,先想清楚这几个问题)
[1.1 什么样的组件适合做成Starter?](#1.1 什么样的组件适合做成Starter?)
[✅ 标准一:跨项目复用性强](#✅ 标准一:跨项目复用性强)
[✅ 标准二:配置复杂但模式固定](#✅ 标准二:配置复杂但模式固定)
[✅ 标准三:需要统一管理和升级](#✅ 标准三:需要统一管理和升级)
[1.2 Starter的命名规范:别瞎起名](#1.2 Starter的命名规范:别瞎起名)
[2. Starter的核心架构:不只是@Configuration](#2. Starter的核心架构:不只是@Configuration)
[2.1 一个完整Starter的组成](#2.1 一个完整Starter的组成)
[2.2 自动装配的原理再深入一点](#2.2 自动装配的原理再深入一点)
[3. 实战:手把手写一个分布式锁Starter](#3. 实战:手把手写一个分布式锁Starter)
[3.1 需求分析:我们要解决什么问题?](#3.1 需求分析:我们要解决什么问题?)
[3.2 项目结构设计](#3.2 项目结构设计)
[3.3 核心代码实现](#3.3 核心代码实现)
[3.4 配置元数据:让IDE智能提示](#3.4 配置元数据:让IDE智能提示)
[3.5 默认配置文件](#3.5 默认配置文件)
[4. Starter的使用:简单到哭](#4. Starter的使用:简单到哭)
[4.1 Maven依赖](#4.1 Maven依赖)
[4.2 配置(可选)](#4.2 配置(可选))
[4.3 使用方式](#4.3 使用方式)
[4.4 监控查看](#4.4 监控查看)
[5. 企业级Starter的高级特性](#5. 企业级Starter的高级特性)
[5.1 多版本兼容:向前向后都要考虑](#5.1 多版本兼容:向前向后都要考虑)
[5.2 性能优化:Starter不能拖慢应用](#5.2 性能优化:Starter不能拖慢应用)
[5.3 监控告警:出了问题要知道](#5.3 监控告警:出了问题要知道)
[6. Starter的测试策略](#6. Starter的测试策略)
[6.1 单元测试:保证代码质量](#6.1 单元测试:保证代码质量)
[6.2 集成测试:验证真实环境](#6.2 集成测试:验证真实环境)
[6.3 性能测试:确保不影响应用性能](#6.3 性能测试:确保不影响应用性能)
[7. Starter的发布与治理](#7. Starter的发布与治理)
[7.1 Maven发布配置](#7.1 Maven发布配置)
[7.2 版本管理策略](#7.2 版本管理策略)
[7.3 依赖管理](#7.3 依赖管理)
[8. 企业级Starter架构演进](#8. 企业级Starter架构演进)
[8.1 从单一Starter到Starter套件](#8.1 从单一Starter到Starter套件)
[8.2 Starter的依赖关系管理](#8.2 Starter的依赖关系管理)
[8.3 配置的统一管理](#8.3 配置的统一管理)
[9. 故障排查与调试](#9. 故障排查与调试)
[9.1 常见问题排查清单](#9.1 常见问题排查清单)
[9.2 调试技巧](#9.2 调试技巧)
[技巧3:使用Spring Boot Actuator端点](#技巧3:使用Spring Boot Actuator端点)
[10. 最后的话:Starter开发的"道"与"术"](#10. 最后的话:Starter开发的"道"与"术")
[📚 推荐阅读](#📚 推荐阅读)

🎯 先说说为啥要自己造Starter
三年前我在美团带中间件团队,手下管着30多个微服务。那会儿最头疼的就是配置管理:每个服务都要配一遍Redis、配一遍MQ、配一遍监控。今天这个服务配错了,明天那个服务版本对不上。后来我们一咬牙,花了两个月把所有通用组件打包成Starter,效果立竿见影:
部署时间:从平均2小时降到15分钟
配置错误率:从每月15起降到几乎为零
新人上手速度:从一周降到半天
更绝的是,有个兄弟团队照着我们的Starter抄作业,三个月搞定了他们原来计划半年的微服务改造。
所以今天这篇文章,我不光教你怎么写Starter,更要教你怎么写出生产级的Starter。这中间的坑,我都替你踩过了。
✨ 摘要
Spring Boot Starter是企业级微服务架构的基石。本文从实战出发,完整解析Starter的开发全流程:从Maven配置、自动装配原理、条件注解使用,到配置元数据、健康检查、监控集成。通过多个真实企业级Starter案例(分布式锁、ID生成器、审计日志),提供可复用的代码模板和最佳实践。最后分享Starter治理、版本兼容、性能优化等高级话题。
1. 别急着写代码,先想清楚这几个问题
1.1 什么样的组件适合做成Starter?
不是所有组件都适合做成Starter。我总结了三个判断标准:
✅ 标准一:跨项目复用性强
比如:Redis客户端、消息队列、分布式锁、ID生成器。这些每个服务都要用。
✅ 标准二:配置复杂但模式固定
比如:数据库连接池配置、线程池配置、SSL证书配置。手动配容易出错。
✅ 标准三:需要统一管理和升级
比如:监控上报、链路追踪、安全组件。需要全公司统一。
反面教材:我见过有人把业务层的DTO做成Starter,这就属于走火入魔了。
1.2 Starter的命名规范:别瞎起名
命名看起来是小问题,但很重要。Spring官方有明确的命名规范:
XML
<!-- 好的命名 -->
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<artifactId>redis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <!-- 第三方可以这样 -->
<!-- 坏的命名 -->
<artifactId>my-redis-starter</artifactId> <!-- 没有spring-boot前缀 -->
<artifactId>redis-starter-spring-boot</artifactId> <!-- 顺序不对 -->企业内部的命名建议:
XML
<!-- 公司级组件 -->
<artifactId>meituan-spring-boot-starter-distributed-lock</artifactId>
<!-- 团队级组件 -->
<artifactId>payment-spring-boot-starter-audit</artifactId>
<!-- 通用工具 -->
<artifactId>common-spring-boot-starter-id-generator</artifactId>2. Starter的核心架构:不只是@Configuration
2.1 一个完整Starter的组成
很多人以为Starter就是几个Java类,太天真了!一个生产级的Starter至少包含:
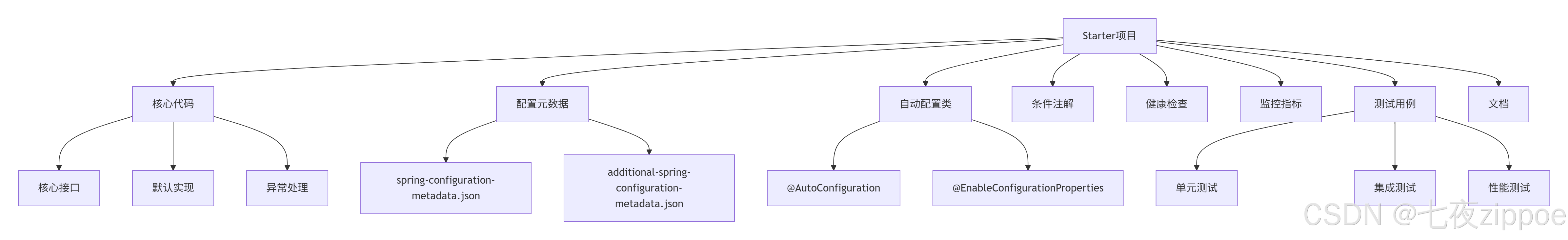
图1:生产级Starter的完整组成
2.2 自动装配的原理再深入一点
我知道你肯定看过@EnableAutoConfiguration的原理,但我今天要说点不一样的。
关键点:Spring Boot 2.7之后,自动配置的注册方式变了:
java
// Spring Boot 2.7之前:用spring.factories
// META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.example.MyAutoConfiguration
// Spring Boot 2.7之后:推荐用@AutoConfiguration
// src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/
// └── org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
// 文件内容:
com.example.MyAutoConfiguration
// 对应的Java代码
@AutoConfiguration // 新的注解
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(SomeClass.class)
public class MyAutoConfiguration {
// 配置内容
}代码清单1:新旧自动配置注册方式对比
为什么这么改 ?因为@AutoConfiguration支持更多特性:
-
自动排序(通过
@AutoConfigureBefore、@AutoConfigureAfter) -
更好的IDE支持
-
更清晰的元数据
3. 实战:手把手写一个分布式锁Starter
3.1 需求分析:我们要解决什么问题?
在做技术方案前,先明确需求。我们需要的分布式锁要:
-
支持多种实现:Redis、Zookeeper、数据库
-
可配置:超时时间、重试策略
-
监控:锁获取成功率、平均耗时
-
易用:注解式、编程式都要支持
3.2 项目结构设计
先看Maven项目结构:
distributed-lock-spring-boot-starter/
├── pom.xml
├── src/
│ ├── main/
│ │ ├── java/
│ │ │ └── com/
│ │ │ └── meituan/
│ │ │ └── lock/
│ │ │ ├── LockProperties.java # 配置属性
│ │ │ ├── DistributedLock.java # 核心接口
│ │ │ ├── RedisDistributedLock.java # Redis实现
│ │ │ ├── ZkDistributedLock.java # ZK实现
│ │ │ ├── LockAutoConfiguration.java # 自动配置
│ │ │ ├── LockAspect.java # AOP切面
│ │ │ └── annotation/
│ │ │ └── Lockable.java # 锁注解
│ │ └── resources/
│ │ ├── META-INF/
│ │ │ └── spring/
│ │ │ └── org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
│ │ └── application-lock.yml # 默认配置
│ └── test/ # 测试代码
└── README.md3.3 核心代码实现
第一步:定义配置属性
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "meituan.lock")
@Validated
public class LockProperties {
/**
* 锁类型:redis、zookeeper、database
*/
@NotEmpty(message = "锁类型不能为空")
private String type = "redis";
/**
* 默认超时时间(毫秒)
*/
@Min(value = 1, message = "超时时间必须大于0")
private long defaultTimeout = 30000;
/**
* 默认等待时间(毫秒)
*/
@Min(value = 0, message = "等待时间不能小于0")
private long defaultWaitTime = 10000;
/**
* 重试次数
*/
@Min(value = 0, message = "重试次数不能小于0")
private int retryTimes = 3;
/**
* Redis配置(当type=redis时生效)
*/
private RedisConfig redis = new RedisConfig();
/**
* Zookeeper配置(当type=zookeeper时生效)
*/
private ZkConfig zookeeper = new ZkConfig();
// 嵌套配置类
@Data
public static class RedisConfig {
private String address = "redis://localhost:6379";
private String password;
private int database = 0;
private int connectionPoolSize = 64;
private int connectionMinimumIdleSize = 24;
}
@Data
public static class ZkConfig {
private String servers = "localhost:2181";
private int sessionTimeout = 30000;
private int connectionTimeout = 15000;
private String namespace = "meituan-lock";
}
// Getter/Setter省略...
}代码清单2:分布式锁配置属性类
第二步:定义核心接口
java
public interface DistributedLock {
/**
* 获取锁
* @param lockKey 锁的key
* @param timeout 超时时间(毫秒)
* @param waitTime 等待时间(毫秒)
* @return 是否获取成功
*/
boolean tryLock(String lockKey, long timeout, long waitTime);
/**
* 获取锁(使用默认配置)
*/
default boolean tryLock(String lockKey) {
// 实际项目中这里会从ThreadLocal或配置中获取默认值
return tryLock(lockKey, 30000, 10000);
}
/**
* 释放锁
*/
void unlock(String lockKey);
/**
* 续期锁(防止锁过期)
*/
boolean renewLock(String lockKey, long expireTime);
/**
* 锁监控指标
*/
LockStats getStats();
@Data
class LockStats {
private long totalAcquireAttempts; // 总获取尝试次数
private long successfulAcquisitions; // 成功获取次数
private long failedAcquisitions; // 失败获取次数
private long averageAcquireTime; // 平均获取时间(ms)
private Map<String, Long> keyStats; // 按key统计
}
}代码清单3:分布式锁核心接口
第三步:实现Redis分布式锁
java
@Slf4j
public class RedisDistributedLock implements DistributedLock {
private final RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final LockProperties properties;
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, RLock> lockCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final LockStats stats = new LockStats();
private final AtomicLong totalAcquireAttempts = new AtomicLong();
private final AtomicLong successfulAcquisitions = new AtomicLong();
public RedisDistributedLock(LockProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
Config config = new Config();
RedisConfig redisConfig = properties.getRedis();
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress(redisConfig.getAddress())
.setPassword(redisConfig.getPassword())
.setDatabase(redisConfig.getDatabase())
.setConnectionPoolSize(redisConfig.getConnectionPoolSize())
.setConnectionMinimumIdleSize(redisConfig.getConnectionMinimumIdleSize());
this.redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock(String lockKey, long timeout, long waitTime) {
totalAcquireAttempts.incrementAndGet();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
RLock lock = lockCache.computeIfAbsent(lockKey,
key -> redissonClient.getLock(key));
boolean acquired = lock.tryLock(waitTime, timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
successfulAcquisitions.incrementAndGet();
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
// 记录监控指标
synchronized (stats) {
stats.setAverageAcquireTime(
(stats.getAverageAcquireTime() * (successfulAcquisitions.get() - 1) + costTime)
/ successfulAcquisitions.get()
);
stats.getKeyStats().merge(lockKey, 1L, Long::sum);
}
log.debug("成功获取锁: {}, 耗时: {}ms", lockKey, costTime);
} else {
log.warn("获取锁失败: {}, 等待时间: {}ms", lockKey, waitTime);
}
return acquired;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
log.error("获取锁被中断: {}", lockKey, e);
return false;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("获取锁异常: {}", lockKey, e);
return false;
} finally {
stats.setTotalAcquireAttempts(totalAcquireAttempts.get());
stats.setSuccessfulAcquisitions(successfulAcquisitions.get());
stats.setFailedAcquisitions(totalAcquireAttempts.get() - successfulAcquisitions.get());
}
}
@Override
public void unlock(String lockKey) {
try {
RLock lock = lockCache.get(lockKey);
if (lock != null && lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
log.debug("释放锁: {}", lockKey);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("释放锁异常: {}", lockKey, e);
}
}
// 其他方法实现省略...
}代码清单4:Redis分布式锁实现
第四步:自动配置类
java
@AutoConfiguration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LockProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(RedissonClient.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "meituan.lock", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
public class LockAutoConfiguration {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LockAutoConfiguration.class);
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "meituan.lock", name = "type", havingValue = "redis", matchIfMissing = true)
public DistributedLock redisDistributedLock(LockProperties properties) {
log.info("初始化Redis分布式锁, 地址: {}", properties.getRedis().getAddress());
return new RedisDistributedLock(properties);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "meituan.lock", name = "type", havingValue = "zookeeper")
@ConditionalOnClass(value = {CuratorFramework.class, InterProcessMutex.class})
public DistributedLock zookeeperDistributedLock(LockProperties properties) {
log.info("初始化Zookeeper分布式锁, servers: {}", properties.getZookeeper().getServers());
return new ZkDistributedLock(properties);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LockAspect lockAspect(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
return new LockAspect(distributedLock);
}
@Bean
public LockHealthIndicator lockHealthIndicator(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
return new LockHealthIndicator(distributedLock);
}
@Bean
public LockMetrics lockMetrics(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
return new LockMetrics(distributedLock);
}
}代码清单5:分布式锁自动配置类
第五步:AOP切面支持注解式锁
java
@Aspect
@Component
@ConditionalOnBean(DistributedLock.class)
public class LockAspect {
private final DistributedLock distributedLock;
public LockAspect(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
this.distributedLock = distributedLock;
}
@Around("@annotation(lockable)")
public Object aroundLock(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, Lockable lockable) throws Throwable {
String lockKey = generateLockKey(joinPoint, lockable);
try {
// 尝试获取锁
boolean acquired = distributedLock.tryLock(
lockKey,
lockable.timeout(),
lockable.waitTime()
);
if (!acquired) {
throw new LockAcquireException("获取锁失败: " + lockKey);
}
// 执行业务方法
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
// 释放锁
distributedLock.unlock(lockKey);
}
}
private String generateLockKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, Lockable lockable) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
// 支持SpEL表达式
if (StringUtils.hasText(lockable.key())) {
return evaluateSpel(lockable.key(), joinPoint);
}
// 默认生成规则:类名+方法名+参数hash
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName();
String methodName = method.getName();
String argsHash = Arrays.hashCode(joinPoint.getArgs()) + "";
return String.format("%s.%s.%s", className, methodName, argsHash);
}
private String evaluateSpel(String expression, ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
// SpEL表达式解析实现
// ...
return expression;
}
}代码清单6:分布式锁AOP切面
第六步:健康检查
java
@Component
public class LockHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
private final DistributedLock distributedLock;
public LockHealthIndicator(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
this.distributedLock = distributedLock;
}
@Override
public Health health() {
DistributedLock.LockStats stats = distributedLock.getStats();
// 计算成功率
double successRate = stats.getTotalAcquireAttempts() > 0 ?
(double) stats.getSuccessfulAcquisitions() / stats.getTotalAcquireAttempts() * 100 : 0;
Map<String, Object> details = new HashMap<>();
details.put("successRate", String.format("%.2f%%", successRate));
details.put("totalAttempts", stats.getTotalAcquireAttempts());
details.put("successCount", stats.getSuccessfulAcquisitions());
details.put("avgAcquireTime", stats.getAverageAcquireTime() + "ms");
if (successRate < 95.0) {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("message", "锁获取成功率过低")
.withDetails(details)
.build();
}
return Health.up()
.withDetails(details)
.build();
}
}代码清单7:分布式锁健康检查
3.4 配置元数据:让IDE智能提示
在src/main/resources/META-INF/下创建:
// additional-spring-configuration-metadata.json
{
"properties": [
{
"name": "meituan.lock.enabled",
"type": "java.lang.Boolean",
"description": "是否启用分布式锁",
"defaultValue": true
},
{
"name": "meituan.lock.type",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"description": "锁类型:redis或zookeeper",
"defaultValue": "redis"
},
{
"name": "meituan.lock.default-timeout",
"type": "java.lang.Long",
"description": "默认锁超时时间(毫秒)",
"defaultValue": 30000,
"sourceType": "com.meituan.lock.LockProperties"
},
{
"name": "meituan.lock.redis.address",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"description": "Redis地址",
"defaultValue": "redis://localhost:6379"
},
{
"name": "meituan.lock.zookeeper.servers",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"description": "Zookeeper服务器地址",
"defaultValue": "localhost:2181"
}
],
"hints": [
{
"name": "meituan.lock.type",
"values": [
{
"value": "redis",
"description": "基于Redis的分布式锁"
},
{
"value": "zookeeper",
"description": "基于Zookeeper的分布式锁"
}
]
}
]
}代码清单8:配置元数据
3.5 默认配置文件
在src/main/resources/下创建application-lock.yml:
# 分布式锁默认配置
meituan:
lock:
enabled: true
type: redis
default-timeout: 30000
default-wait-time: 10000
retry-times: 3
redis:
address: ${REDIS_HOST:redis://localhost:6379}
password: ${REDIS_PASSWORD:}
database: 0
connection-pool-size: 64
connection-minimum-idle-size: 24
zookeeper:
servers: ${ZK_HOST:localhost:2181}
session-timeout: 30000
connection-timeout: 15000
namespace: meituan-lock代码清单9:默认配置文件
4. Starter的使用:简单到哭
4.1 Maven依赖
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>com.meituan</groupId>
<artifactId>distributed-lock-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>4.2 配置(可选)
# application.yml
meituan:
lock:
type: redis
redis:
address: redis://prod-redis:6379
default-timeout: 60000 # 生产环境可以设长一点4.3 使用方式
方式一:注解式(推荐)
java
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Lockable(key = "'order:' + #orderId", timeout = 30000)
public Order createOrder(String orderId, OrderRequest request) {
// 业务逻辑,自动加锁
return orderRepository.save(convertToOrder(request));
}
@Lockable(key = "'inventory:' + #productId", waitTime = 5000)
public void reduceInventory(String productId, int quantity) {
// 最多等待5秒获取锁
inventoryService.reduce(productId, quantity);
}
}方式二:编程式
java
@Service
public class PaymentService {
@Autowired
private DistributedLock distributedLock;
public void processPayment(String paymentId) {
String lockKey = "payment:" + paymentId;
try {
if (distributedLock.tryLock(lockKey)) {
// 执行业务逻辑
paymentProcessor.process(paymentId);
} else {
throw new BusinessException("系统繁忙,请稍后重试");
}
} finally {
distributedLock.unlock(lockKey);
}
}
}4.4 监控查看
启动应用后,可以访问:
-
健康检查:
/actuator/health(查看锁的健康状态) -
监控指标:
/actuator/metrics/meituan.lock(查看锁的统计指标) -
详细信息:
/actuator/lock-stats(如果有自定义Endpoint)
5. 企业级Starter的高级特性
5.1 多版本兼容:向前向后都要考虑
Starter一旦被多个服务使用,版本兼容就是大问题。我的经验:
版本策略
XML
<!-- 版本号规范 -->
<version>主版本.次版本.修订版本-里程碑</version>
<!-- 例如:1.2.3-RELEASE -->
<!-- 实际例子 -->
<version>1.0.0</version> <!-- 第一个稳定版 -->
<version>1.1.0</version> <!-- 新增功能,向后兼容 -->
<version>2.0.0</version> <!-- 破坏性变更 -->兼容性保证
-
配置属性兼容:新增属性要有默认值,删除属性要提供迁移期
-
API兼容:公共接口不轻易修改,用@Deprecated标记过时方法
-
依赖兼容:第三方依赖版本要谨慎升级
java
public interface DistributedLock {
// v1.0的方法
boolean tryLock(String lockKey, long timeout, long waitTime);
// v1.1新增的方法(默认实现保证兼容)
default boolean tryLock(String lockKey, LockOptions options) {
return tryLock(lockKey, options.getTimeout(), options.getWaitTime());
}
// v1.0的方法,v2.0计划删除
@Deprecated(since = "2.0.0", forRemoval = true)
boolean oldMethod(String param);
}5.2 性能优化:Starter不能拖慢应用
优化点一:懒加载
java
@Bean
@Lazy // 只有实际使用时才初始化
public DistributedLock distributedLock(LockProperties properties) {
// 初始化逻辑
}优化点二:连接池复用
java
@Configuration
public class LockAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(LockProperties properties) {
// 如果应用中已经有RedissonClient,直接复用
// 避免创建多个连接池
}
}优化点三:缓存优化
java
public class RedisDistributedLock {
// 使用WeakHashMap,避免内存泄漏
private final Map<String, WeakReference<RLock>> lockCache =
Collections.synchronizedMap(new WeakHashMap<>());
}5.3 监控告警:出了问题要知道
生产级的Starter必须有完整的监控:
java
@Component
public class LockMetrics implements MeterBinder {
private final DistributedLock distributedLock;
public LockMetrics(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
this.distributedLock = distributedLock;
}
@Override
public void bindTo(MeterRegistry registry) {
Gauge.builder("meituan.lock.success.rate",
() -> calculateSuccessRate())
.description("锁获取成功率")
.baseUnit("percent")
.register(registry);
Timer.builder("meituan.lock.acquire.time")
.description("锁获取耗时")
.publishPercentiles(0.5, 0.95, 0.99) // 50%, 95%, 99%分位
.register(registry);
}
private double calculateSuccessRate() {
DistributedLock.LockStats stats = distributedLock.getStats();
if (stats.getTotalAcquireAttempts() == 0) {
return 100.0;
}
return (double) stats.getSuccessfulAcquisitions()
/ stats.getTotalAcquireAttempts() * 100;
}
}告警规则示例(Prometheus):
groups:
- name: lock_alerts
rules:
- alert: LockSuccessRateLow
expr: meituan_lock_success_rate < 95
for: 5m
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "锁获取成功率过低"
description: "锁获取成功率低于95%,当前值: {{ $value }}%"6. Starter的测试策略
6.1 单元测试:保证代码质量
java
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class RedisDistributedLockTest {
@Mock
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Mock
private RLock rLock;
private RedisDistributedLock distributedLock;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
LockProperties properties = new LockProperties();
properties.setType("redis");
when(redissonClient.getLock(anyString())).thenReturn(rLock);
// 通过反射设置redissonClient
distributedLock = new RedisDistributedLock(properties);
setField(distributedLock, "redissonClient", redissonClient);
}
@Test
void testTryLock_Success() throws InterruptedException {
// given
when(rLock.tryLock(anyLong(), anyLong(), any())).thenReturn(true);
// when
boolean result = distributedLock.tryLock("test-key", 30000, 10000);
// then
assertTrue(result);
verify(rLock).tryLock(10000, 30000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Test
void testTryLock_Timeout() throws InterruptedException {
// given
when(rLock.tryLock(anyLong(), anyLong(), any())).thenReturn(false);
// when
boolean result = distributedLock.tryLock("test-key", 30000, 10000);
// then
assertFalse(result);
}
}6.2 集成测试:验证真实环境
java
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@Testcontainers // 使用Testcontainers启动真实Redis
class DistributedLockIntegrationTest {
@Container
static RedisContainer redis = new RedisContainer("redis:6.2")
.withExposedPorts(6379);
@DynamicPropertySource
static void redisProperties(DynamicPropertyRegistry registry) {
registry.add("meituan.lock.redis.address",
() -> String.format("redis://%s:%d",
redis.getHost(),
redis.getFirstMappedPort()));
}
@Autowired
private DistributedLock distributedLock;
@Test
void testDistributedLockInRealRedis() {
// given
String lockKey = "integration-test-key";
// when
boolean acquired = distributedLock.tryLock(lockKey, 5000, 1000);
// then
assertTrue(acquired);
// 再次获取应该失败
boolean acquiredAgain = distributedLock.tryLock(lockKey, 5000, 1000);
assertFalse(acquiredAgain);
// 释放后可以再次获取
distributedLock.unlock(lockKey);
boolean acquiredAfterRelease = distributedLock.tryLock(lockKey, 5000, 1000);
assertTrue(acquiredAfterRelease);
}
}6.3 性能测试:确保不影响应用性能
java
@SpringBootTest
@Tag("performance")
class DistributedLockPerformanceTest {
@Autowired
private DistributedLock distributedLock;
@Test
@RepeatedTest(10) // 重复10次
void testLockAcquirePerformance() {
// warm up
IntStream.range(0, 1000).parallel().forEach(i -> {
distributedLock.tryLock("perf-" + i, 1000, 100);
});
// actual test
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
IntStream.range(0, 10000).parallel().forEach(i -> {
distributedLock.tryLock("perf-" + i, 1000, 100);
});
long duration = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
double avgTime = duration / 10000.0 / 1_000_000.0; // 转换为毫秒
System.out.printf("平均获取锁时间: %.3f ms%n", avgTime);
// 断言:平均时间应小于1ms
assertTrue(avgTime < 1.0, "锁获取时间过长: " + avgTime + "ms");
}
}7. Starter的发布与治理
7.1 Maven发布配置
XML
<!-- pom.xml 配置 -->
<project>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.meituan</groupId>
<artifactId>distributed-lock-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Meituan Distributed Lock Starter</name>
<description>Spring Boot Starter for distributed lock</description>
<!-- 许可证信息 -->
<licenses>
<license>
<name>Apache License, Version 2.0</name>
<url>https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0</url>
</license>
</licenses>
<!-- SCM信息 -->
<scm>
<url>https://github.com/meituan/distributed-lock-starter</url>
<connection>scm:git:git://github.com/meituan/distributed-lock-starter.git</connection>
<developerConnection>scm:git:ssh://github.com/meituan/distributed-lock-starter.git</developerConnection>
</scm>
<!-- 开发者信息 -->
<developers>
<developer>
<name>Your Name</name>
<email>your.email@meituan.com</email>
<organization>Meituan</organization>
</developer>
</developers>
<!-- 发布到Maven仓库的配置 -->
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>meituan-releases</id>
<url>https://maven.meituan.com/repository/releases</url>
</repository>
<snapshotRepository>
<id>meituan-snapshots</id>
<url>https://maven.meituan.com/repository/snapshots</url>
</snapshotRepository>
</distributionManagement>
</project>7.2 版本管理策略
我推荐使用语义化版本(Semantic Versioning):
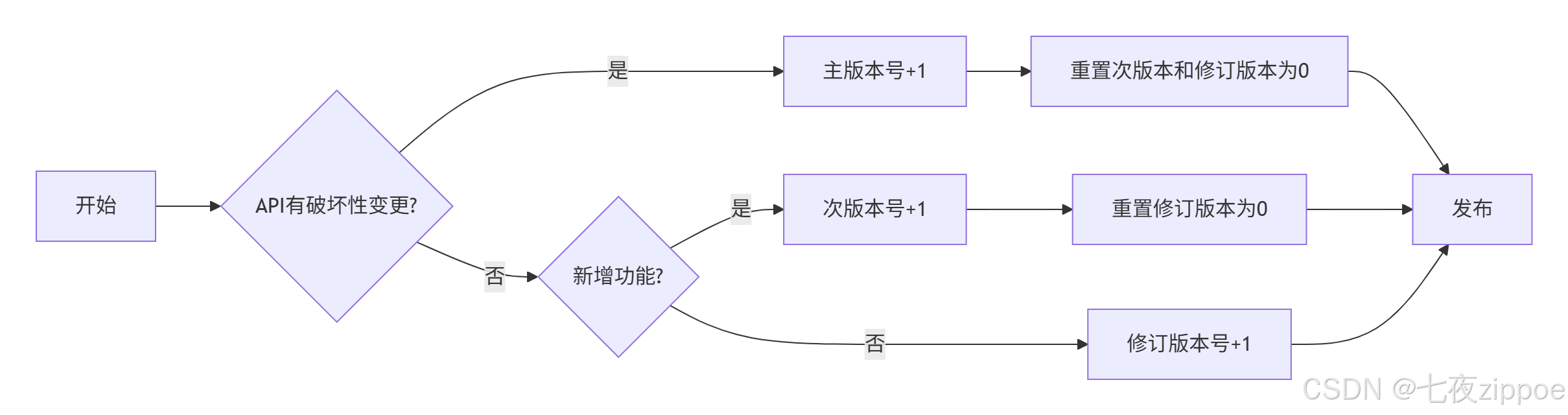
图2:语义化版本管理流程
实际例子:
-
1.0.0:第一个稳定版本 -
1.0.1:修复bug -
1.1.0:新增功能,向后兼容 -
2.0.0:破坏性变更
7.3 依赖管理
Starter的依赖管理要特别小心:
XML
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- 统一管理Spring Boot版本 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- 必须的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
<!-- 注意:不要带版本号,由dependencyManagement管理 -->
</dependency>
<!-- 可选依赖:用户想用Redis锁时才需要 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope> <!-- 关键!provided作用域 -->
<optional>true</optional> <!-- 标记为可选 -->
</dependency>
<!-- 测试依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>关键点 :可选依赖用<optional>true</optional>,这样用户的项目不会强制引入这些依赖。
8. 企业级Starter架构演进
8.1 从单一Starter到Starter套件
当Starter多了之后,就需要考虑架构了。在美团,我们是这样组织的:
meituan-spring-boot-starters/ # 父项目
├── meituan-spring-boot-starter-parent # 父pom,统一管理
├── meituan-spring-boot-starter-lock # 分布式锁
├── meituan-spring-boot-starter-id # ID生成器
├── meituan-spring-boot-starter-mq # 消息队列
├── meituan-spring-boot-starter-cache # 缓存
├── meituan-spring-boot-starter-trace # 链路追踪
└── meituan-spring-boot-starter-all # 全家桶(可选)8.2 Starter的依赖关系管理
复杂的Starter之间可能有依赖关系,需要仔细管理:
XML
<!-- meituan-spring-boot-starter-cache 的pom.xml -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 内部依赖:先于其他Starter发布 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.meituan</groupId>
<artifactId>meituan-spring-boot-starter-lock</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>8.3 配置的统一管理
多个Starter可能有相同的配置项(比如Redis地址),需要统一:
java
// 公共配置类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "meituan")
public class MeituanCommonProperties {
/**
* 公共Redis配置
*/
private RedisCommonConfig redis = new RedisCommonConfig();
/**
* 公共Zookeeper配置
*/
private ZkCommonConfig zookeeper = new ZkCommonConfig();
/**
* 监控配置
*/
private MonitorConfig monitor = new MonitorConfig();
@Data
public static class RedisCommonConfig {
private String address = "redis://localhost:6379";
private String password;
private int database = 0;
}
// 其他配置类...
}
// 在各个Starter中引用
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "meituan.lock")
public class LockProperties {
@Autowired
private MeituanCommonProperties commonProperties;
// 优先使用专属配置,没有则用公共配置
public String getRedisAddress() {
return StringUtils.hasText(redis.getAddress()) ?
redis.getAddress() :
commonProperties.getRedis().getAddress();
}
}9. 故障排查与调试
9.1 常见问题排查清单
我总结了Starter开发中最常见的10个问题:
问题1:自动配置不生效
排查步骤:
-
检查
META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件 -
检查条件注解是否满足
-
检查是否有其他Starter排除
bash
# 启动时加参数查看自动配置报告
java -jar app.jar --debug
# 或者在代码中获取
@Autowired
private List<String> autoConfigurations;问题2:Bean冲突
解决方案:
java
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean // 关键:用户有自定义时,不用我们的
public SomeBean someBean() {
return new SomeBean();
}
// 或者用@Primary指定优先级
@Bean
@Primary
public SomeBean defaultSomeBean() {
return new SomeBean();
}问题3:配置属性不生效
排查:
-
检查
spring-configuration-metadata.json格式 -
检查属性前缀是否正确
-
检查是否有其他配置覆盖
java
// 在Starter中添加配置验证
@PostConstruct
public void validateConfig() {
if (!isValid(config)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("配置无效: " + config);
}
}9.2 调试技巧
技巧1:在IDE中调试自动配置
java
// 在自动配置类中加断点
@AutoConfiguration
public class MyAutoConfiguration {
public MyAutoConfiguration() {
// 这里加断点,可以看到什么时候被加载
System.out.println("MyAutoConfiguration被加载");
}
}技巧2:查看条件评估报告
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(Application.class);
// 添加监听器,输出条件评估报告
app.addListeners(new ApplicationListener<ApplicationPreparedEvent>() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationPreparedEvent event) {
ConditionEvaluationReport report =
ConditionEvaluationReport.get(event.getApplicationContext().getBeanFactory());
// 打印报告到文件
try (PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter("condition-report.txt")) {
report.getConditionAndOutcomesBySource().forEach((source, outcomes) -> {
writer.println(source);
outcomes.forEach(outcome -> {
writer.println(" " + outcome.getOutcome());
});
});
}
}
});
app.run(args);
}
}技巧3:使用Spring Boot Actuator端点
# application.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: conditions,beans,configprops然后访问:
-
/actuator/conditions:查看条件评估详情 -
/actuator/beans:查看所有Bean -
/actuator/configprops:查看配置属性
10. 最后的话:Starter开发的"道"与"术"
写了这么多年Starter,我最大的体会是:技术是术,设计思想才是道。
好的Starter不是代码堆砌,而是对开发者体验的极致追求。你看Spring Boot官方的Starter,每一个都经过精心设计:
-
开箱即用:默认配置就能工作
-
配置简单:几个属性就能满足大部分需求
-
扩展灵活:可以深度定制
-
文档完整:有明确的指导
所以,在你动手写Starter之前,先问自己几个问题:
-
🤔 这个Starter解决了什么痛点?
-
🤔 用户使用起来方便吗?
-
🤔 配置项是不是太多了?
-
🤔 向后兼容怎么保证?
-
🤔 出了问题怎么排查?
记住:你写的不是代码,是生产力工具。好的Starter能让团队效率翻倍,坏的Starter能让团队陷入泥潭。
📚 推荐阅读
官方文档
-
**Spring Boot官方文档 - Creating Your Own Auto-configuration** - 官方指南,必读
-
**Spring Boot Starter开发指南** - 实操教程
源码学习
-
**Spring Boot Auto-configure源码** - 学习官方实现
-
**Awesome Spring Boot Starters** - 官方Starter列表
最佳实践
-
**阿里巴巴Java开发手册 - 工程规约** - 命名规范、配置规范
-
**Spring Boot最佳实践** - 官方最佳实践
工具资源
-
**Spring Initializr** - 快速生成Starter项目
-
**Maven Central** - 查找依赖和版本
最后建议 :别光看,动手写一个!从最简单的开始,比如一个hello-spring-boot-starter,让它根据配置输出不同的问候语。写完了发布到公司的Maven仓库,让同事用起来。实战一次,胜过看百篇文章。