Taro项目架构搭建与页面实现技术总结
1. 核心概念阐述
1.1 Taro框架基本原理
Taro是一个多端统一开发框架,其核心原理是通过编译转换,将一套基于React/Vue的代码编译为不同平台(微信小程序、H5、App等)的可执行代码。Taro的跨端开发机制主要包括:
- 编译时转换:通过编译工具将React/Vue组件转换为各平台原生组件
- 运行时适配:提供统一的API适配层,处理各平台API的差异
- 组件库兼容:提供跨平台兼容的组件库,确保组件在不同平台的一致性
1.2 Taro框架特性优势
Taro框架具有以下显著优势:
- 一套代码多端运行:支持微信小程序、H5、App(React Native)、支付宝小程序、百度小程序等多个平台
- 组件化开发:采用React/Vue组件化开发模式,提高代码复用率和开发效率
- TypeScript支持:原生支持TypeScript,提供类型安全和更好的开发体验
- 生态丰富:拥有丰富的组件库和插件支持,社区活跃
- 性能优化:提供了多种性能优化方案,如组件懒加载、代码分割等
1.3 Taro框架适用场景
Taro框架适合以下场景:
- 需要跨平台开发的应用:如同时需要支持微信小程序、H5、App的电商应用
- 已有React/Vue技术栈的团队:可以快速迁移到Taro框架,减少学习成本
- 需要快速迭代的项目:一套代码多端运行,减少维护成本,提高迭代效率
- 对性能有一定要求的应用:Taro提供了多种性能优化方案,可以满足大多数应用的性能需求
2. 项目架构搭建
2.1 开发环境配置
搭建Taro开发环境需要以下步骤:
-
安装Node.js:确保Node.js版本≥16.0.0
-
安装Taro CLI :使用npm全局安装Taro CLI
bashnpm install -g @tarojs/cli -
安装依赖 :进入项目目录,安装项目依赖
bashnpm install -
配置编辑器:推荐使用VS Code,并安装相关插件如TypeScript、ESLint等
2.2 项目初始化
使用Taro CLI初始化项目:
bash
npx taro init my-taro-project初始化过程中需要选择:
- 框架:React或Vue
- 语言:TypeScript或JavaScript
- CSS预处理器:Sass、Less或Stylus
- 模板:默认模板或自定义模板
2.3 目录结构解析
Taro项目的典型目录结构如下:
my-taro-project/
├── config/ # 配置目录
│ ├── dev.js # 开发环境配置
│ ├── index.js # 主配置文件
│ └── prod.js # 生产环境配置
├── src/ # 源代码目录
│ ├── components/ # 公共组件
│ ├── pages/ # 页面组件
│ ├── utils/ # 工具函数
│ ├── services/ # API服务
│ ├── app.tsx # 应用入口组件
│ ├── app.config.ts # 应用配置
│ └── app.scss # 全局样式
├── package.json # 项目配置
├── tsconfig.json # TypeScript配置
└── .gitignore # Git忽略文件2.4 基础配置优化
2.4.1 配置文件说明
config/index.js是Taro项目的主配置文件,主要配置项包括:
projectName:项目名称designWidth:设计稿宽度deviceRatio:设备像素比sourceRoot:源代码目录outputRoot:输出目录plugins:插件配置framework:使用的框架(react或vue)compiler:使用的编译器(vite或webpack)
2.4.2 优化建议
- 设计稿适配 :根据设计稿设置
designWidth,如375或750 - 插件配置 :根据需要配置插件,如
@tarojs/plugin-html用于H5支持 - CSS预处理器:选择适合团队的CSS预处理器,推荐使用Sass
- TypeScript配置:优化TypeScript配置,提高类型检查的准确性和开发体验
3. 页面实现详解
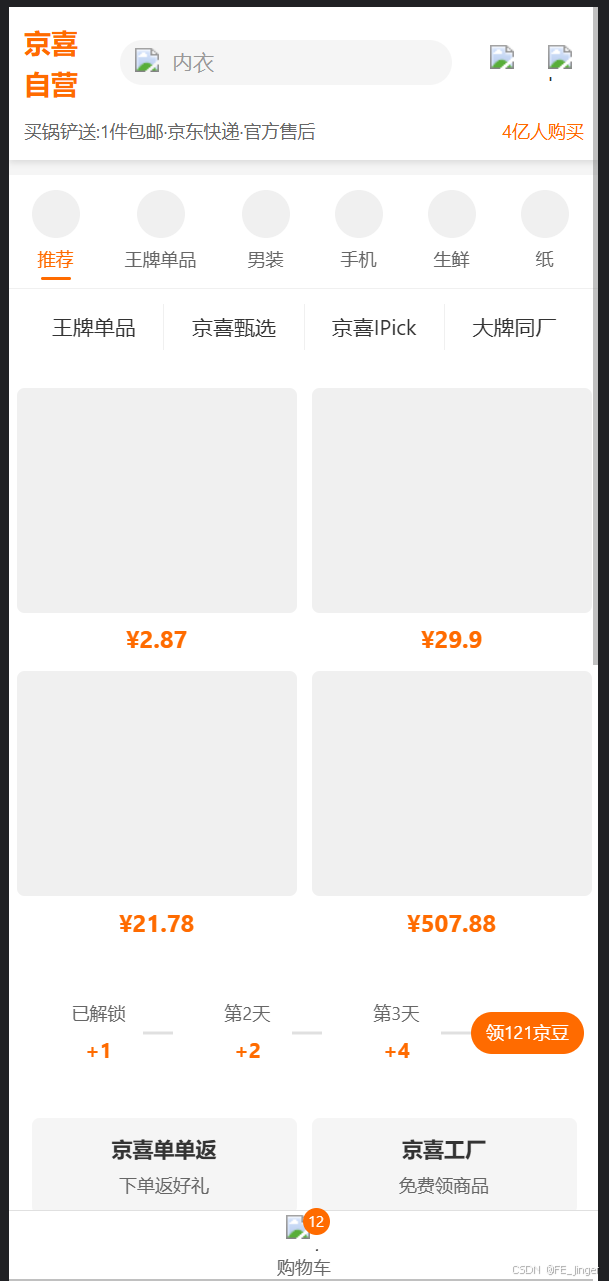
以京东京喜移动端应用的首页为例,详细阐述页面实现过程:
3.1 需求分析
首页需要实现以下功能:
- 头部导航(Logo、搜索框、用户图标)
- 分类标签(推荐、王牌单品、男装、手机等)
- 产品网格展示
- 促销活动展示
- 优惠券展示
- 特色产品展示
- 底部操作栏(购物车图标和数量)
3.2 UI组件设计
将页面拆分为以下组件:
| 组件名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| Header | 头部导航组件 |
| CategoryTabs | 分类标签组件 |
| ProductGrid | 产品网格组件 |
| PromotionSection | 促销活动组件 |
| CouponSection | 优惠券组件 |
| FeaturedProducts | 特色产品组件 |
| BottomBar | 底部操作栏组件 |
3.3 组件实现示例
3.3.1 Header组件
tsx
import React from 'react'
import { View, Text, Image, Input } from '@tarojs/components'
import './index.scss'
interface HeaderProps {
onSearch?: (keyword: string) => void
}
const Header: React.FC<HeaderProps> = ({ onSearch }) => {
const handleSearch = (e: any) => {
if (onSearch) {
onSearch(e.detail.value)
}
}
return (
<View className="header">
<View className="header-top">
<View className="logo">
<Text className="logo-text">京喜自营</Text>
</View>
<View className="search-bar">
<Image className="search-icon" src="https://img11.360buyimg.com/imagetools/jfs/t1/117566/28/28732/2841/631c0d3dE12e915a9/4c250a5d7250dd2b.png" />
<Input
className="search-input"
placeholder="内衣"
placeholderClass="search-placeholder"
onInput={handleSearch}
/>
</View>
<View className="header-icons">
<Image className="icon" src="https://img12.360buyimg.com/imagetools/jfs/t1/212445/34/1963/2557/631c0d3eE1c52f3f9/1a2b3c4d5e6f7g8h.png" />
<Image className="icon" src="https://img13.360buyimg.com/imagetools/jfs/t1/187654/22/2012/2341/631c0d3fE7a8b9c0d/8e7d6c5b4a3f2e1d.png" />
</View>
</View>
<View className="header-subtitle">
<Text className="subtitle-text">买锅铲送:1件包邮·京东快递·官方售后</Text>
<Text className="subtitle-link">4亿人购买</Text>
</View>
</View>
)
}
export default Header3.4 状态管理实现
采用React Context API进行状态管理:
tsx
// src/context/appContext.ts
import React, { createContext, useState, useContext, ReactNode } from 'react'
interface AppContextType {
cartCount: number
setCartCount: (count: number) => void
userInfo: any
setUserInfo: (info: any) => void
}
const AppContext = createContext<AppContextType | undefined>(undefined)
export const AppProvider: React.FC<{ children: ReactNode }> = ({ children }) => {
const [cartCount, setCartCount] = useState(0)
const [userInfo, setUserInfo] = useState(null)
return (
<AppContext.Provider value={{ cartCount, setCartCount, userInfo, setUserInfo }}>
{children}
</AppContext.Provider>
)
}
export const useAppContext = () => {
const context = useContext(AppContext)
if (context === undefined) {
throw new Error('useAppContext must be used within an AppProvider')
}
return context
}3.5 API数据交互
tsx
// src/services/api.ts
import Taro from '@tarojs/taro'
export const fetchProducts = async (params: any) => {
try {
const res = await Taro.request({
url: 'https://api.example.com/products',
method: 'GET',
data: params
})
return res.data
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to fetch products:', error)
throw error
}
}
export const fetchPromotions = async () => {
try {
const res = await Taro.request({
url: 'https://api.example.com/promotions',
method: 'GET'
})
return res.data
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to fetch promotions:', error)
throw error
}
}3.6 页面整合
tsx
// src/pages/index/index.tsx
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react'
import { View, ScrollView } from '@tarojs/components'
import './index.scss'
import Header from '../../components/Header'
import CategoryTabs from '../../components/CategoryTabs'
import ProductGrid from '../../components/ProductGrid'
import PromotionSection from '../../components/PromotionSection'
import CouponSection from '../../components/CouponSection'
import FeaturedProducts from '../../components/FeaturedProducts'
import BottomBar from '../../components/BottomBar'
import { fetchProducts, fetchPromotions } from '../../services/api'
import { useAppContext } from '../../context/appContext'
const Index: React.FC = () => {
const { cartCount } = useAppContext()
const [products, setProducts] = useState<any[]>([])
const [promotions, setPromotions] = useState<any[]>([])
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
useEffect(() => {
loadData()
}, [])
const loadData = async () => {
setLoading(true)
try {
const [productsData, promotionsData] = await Promise.all([
fetchProducts({ page: 1, limit: 10 }),
fetchPromotions()
])
setProducts(productsData)
setPromotions(promotionsData)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to load data:', error)
} finally {
setLoading(false)
}
}
return (
<View className="index-container">
<Header />
<ScrollView className="content-wrapper">
<CategoryTabs />
<ProductGrid products={products} loading={loading} />
<PromotionSection promotions={promotions} />
<CouponSection />
<FeaturedProducts />
</ScrollView>
<BottomBar cartCount={cartCount} />
</View>
)
}
export default Index4. 关键技术点分析
4.1 组件通信
Taro组件通信主要有以下几种方式:
- Props传递:父组件通过props向子组件传递数据和回调函数
- 事件总线:使用事件机制进行组件间通信,适合跨层级组件通信
- Context API:React内置的上下文机制,适合共享全局状态
- 状态管理库:如Redux、MobX,适合复杂应用的状态管理
4.2 状态管理方案
4.2.1 Redux
Redux是Taro项目中常用的状态管理方案,适合大型应用:
bash
# 安装依赖
npm install redux react-redux @tarojs/redux @tarojs/redux-h5配置Redux:
tsx
// src/store/index.ts
import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import { createLogger } from 'redux-logger'
import cartReducer from './reducers/cart'
import userReducer from './reducers/user'
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
cart: cartReducer,
user: userReducer
})
const middleware = [thunk]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
middleware.push(createLogger())
}
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(...middleware))
export default store4.2.2 MobX
MobX是另一种状态管理方案,采用响应式设计,学习成本较低:
bash
# 安装依赖
npm install mobx mobx-react-lite4.3 性能优化策略
- 组件懒加载 :使用Taro的
lazyLoad配置或React的React.lazy实现组件按需加载 - 代码分割:使用Webpack或Vite的代码分割功能,减少初始加载体积
- 图片优化:使用合适的图片格式和尺寸,实现图片懒加载
- 避免不必要的渲染 :使用
shouldComponentUpdate或React.memo优化组件渲染 - 减少setState调用:合并多个setState调用,减少重渲染次数
- 使用虚拟列表:对于长列表,使用虚拟列表减少DOM节点数量
4.4 跨端兼容性处理
-
条件编译:使用Taro的条件编译功能,针对不同平台编写特定代码
tsx{/* #ifdef H5 */} <View className="h5-specific">H5特定内容</View> {/* #endif */} {/* #ifdef MP-WEIXIN */} <View className="wechat-specific">微信小程序特定内容</View> {/* #endif */} -
API适配:使用Taro提供的统一API,避免直接调用平台特定API
-
组件适配:使用Taro组件库提供的跨平台组件,避免使用平台特定组件
-
样式适配:使用Taro的样式转换功能,处理不同平台的样式差异
4.5 调试技巧
- 小程序调试:使用微信开发者工具进行调试,查看控制台输出和网络请求
- H5调试:使用Chrome DevTools进行调试,查看组件结构和状态
- App调试:使用React Native调试工具或Chrome DevTools进行调试
- 日志输出 :使用Taro的
console.log或调试工具进行日志输出 - 断点调试:在编辑器中设置断点,进行代码调试
5. 实际应用场景说明
5.1 电商应用场景
以京东京喜应用为例,说明Taro在不同端的适配方案:
5.1.1 微信小程序适配
- 使用微信小程序的原生组件和API,确保性能最优
- 处理微信小程序的尺寸单位转换(rpx)
- 适配微信小程序的导航栏和底部TabBar
- 处理微信小程序的授权和登录流程
5.1.2 H5适配
- 使用Taro的H5插件,处理路由和组件适配
- 适配不同浏览器的兼容性问题
- 处理H5的响应式设计,适配不同屏幕尺寸
- 优化H5的性能,减少初始加载时间
5.1.3 App适配
- 使用React Native或Flutter实现App端
- 处理原生组件和Taro组件的混合使用
- 适配不同系统(iOS、Android)的差异
- 优化App的启动速度和运行性能
5.2 最佳实践
- 组件设计:设计通用组件时,考虑跨端兼容性,避免使用平台特定功能
- 样式编写:使用相对单位(rpx),避免使用固定像素值
- API调用:使用Taro提供的统一API,减少平台特定代码
- 性能优化:针对不同平台进行针对性优化,如小程序的包体积优化
- 测试策略:在不同平台进行充分测试,确保功能正常
6. 总结与展望
6.1 项目开发总结
通过Taro项目的开发实践,我们可以总结以下经验教训:
- 技术选型:根据项目需求和团队技术栈选择合适的框架和工具
- 项目架构:设计清晰的项目架构,便于维护和扩展
- 组件设计:设计可复用的组件,提高开发效率和代码质量
- 性能优化:注重性能优化,提供良好的用户体验
- 跨端适配:充分考虑不同平台的差异,确保应用在各平台正常运行
- 测试调试:建立完善的测试和调试流程,确保代码质量
6.2 Taro框架优势
Taro框架具有以下显著优势:
- 跨平台开发:一套代码多端运行,减少开发和维护成本
- 技术栈友好:支持React/Vue技术栈,学习成本低
- 生态成熟:拥有丰富的组件库和插件支持
- 社区活跃:社区贡献活跃,问题解决及时
- 性能优化:提供了多种性能优化方案
6.3 未来发展趋势
Taro框架的未来发展趋势:
- 更好的跨平台支持:支持更多平台,如鸿蒙OS、快手小程序等
- 性能优化:进一步优化各平台的性能,提供更好的用户体验
- 开发体验提升:优化开发工具链,提供更好的开发体验
- 生态完善:丰富组件库和插件,支持更多业务场景
- 与现代前端技术结合:支持React 18、Vue 3等现代前端技术
6.4 应用前景
Taro框架在未来的应用前景广阔:
- 电商应用:适合需要跨平台的电商应用,如京东京喜、拼多多等
- 生活服务应用:如外卖、出行等需要多端支持的应用
- 企业内部应用:适合企业内部的管理系统,需要跨平台支持
- 教育应用:如在线教育平台,需要支持多种设备
- 社交应用:适合需要跨平台的社交应用
7. 总结
Taro框架为跨平台开发提供了一种高效的解决方案,通过一套代码多端运行,减少了开发和维护成本。在实际项目开发中,需要充分考虑跨平台兼容性、性能优化和用户体验,选择合适的技术栈和工具,设计清晰的项目架构和组件结构。
随着Taro框架的不断发展和完善,其在跨平台开发领域的应用前景将更加广阔,为前端开发者提供更多的选择和更好的开发体验。
作者:SOLO Coder