git介绍
客户端并不只提取最新版本的文件,而是把原始的代码仓库完整地克隆下来。
优点:
a.由于任何人每次提取操作,实际上都是一次对代码仓库的完整备份,因此近乎所有的操作都可以在本地执行,速度就是相当的快,并且可以在网络断开的时候操作仍然不受影响,可以频繁的进行提交更新,等到有网络的时候再上传到远程的仓库就可以了。
b.git的分支模型,相当的轻量级,被称为"必杀技"。
(git仓库在创建好之后是没有分支模型的,当开发人员把仓库克隆下来以后,在本地进行提交代码执行提交commit命令的同时,它会给你创建一个默认分支为主分支的master分支) (master主分支,用来存放一已经开发完整的代码,用来存放在主分支上)
缺点:
a.每个开发人员都拥有所有的代码,不利于核心代码的保密(如果有重要代码需要保密,则不建议使用git)
我的开发想从git服务器里面下载代码,就从我这里(git服务器)克隆代码到自己的服务器里面去。
分支
比如说:我的项目微信小程序'佳农物流生鲜店'我的1.0是主分支
git操作流程
1.先将代码放到工作区(目录)里面,
2.通过add添加到版本库的stage暂存区里面,
3.通过commit添加到版本库的某个分支(或者master分支),
4.代码都没有用任何问题,push传到远程仓库。
第一次提交会生成master分支并提交到master分支 HEAD指针会指向master分支,
同时commit会生成一个版本号叫做commit id。通过commit id进项版本回退。
1.部署git与准备
环境:
git-server 192.168.9.134 充当服务器
client 192.168.9.135
安装:所有机器都安装
root@git-server \~\]# yum install -y git \[root@git-server \~\]# git --version git version 2.31.1 准备: 因为Git是分布式版本控制系统,所以,每个客户端机器都必须自报家门:你的名字和Email地址。 注意git config命令的--global参数,用了这个参数,表示你这台机器上所有的Git仓库都会使用这个配置。
必须要添加账户
在客户端上部署:
开始:所有的机器都添加,只要邮箱和用户不一样就可以。
git config --global user.email "336699369@163.com" ----设置邮箱
git config --global user.name "liu" ----加添用户
2.git的使用
创建版本库:
服务端
1.创建一个空目录**:**在中心服务器上创建
[root@git-server ~]# mkdir /git-test 在/目录下创建目录叫git-test目录
[root@git-server ~]# useradd git #创建一个git用户用来运行git
[root@git-server ~]# passwd git #给用户设置密码
[root@git-server ~]# cd /git-test/
[root@git-server git-test]# chown -R git.git /git-test/ 2.通过git init命令把这个目录变成Git可以管理的仓库:
创建裸库: 适用与作为远程中心仓库使用
创建裸库才可以从别处push(传)代码过来,使用--bare参数------裸创建一裸库:
每次创建裸库都需要chown修改权限
[root@git-server git-test]# git init --bare testgit #创建一个库
Initialized empty Git repository in /git-test/testgit/
[root@git-server ~]# chown git.git /git-test -R #修改权限
2.仓库创建完成后查看库目录:
[root@git-server git-test]# cd testgit/
[root@git-server testgit]# ls
branches config description HEAD hooks info objects refs客户端
1.克隆仓库
1.配置免密登录
[root@client ~]# ssh-keygen #生成秘钥
[root@client ~]# ssh-copy-id -i git@192.168.9.134 #将秘钥传输到git服务器中的git用户
2.克隆git仓库
[root@client ~]# git clone git@192.168.9.134:/git-test/testgit/
Cloning into 'testgit'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.
[root@client ~]# ls #查看仓库已经克隆下来了
anaconda-ks.cfg testgit
2.不配置免密
[root@localhost ~]# git clone git@192.168.9.134:/git-server/jdsc
正克隆到 'jdsc'...
The authenticity of host '192.168.9.134 (192.168.9.236)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:mFXPZmvs5HKnE+VxqSY85VzcX/KF33UTgiAPeXGjVys.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:8e:93:5c:a8:05:00:56:36:a9:1d:98:f1:fe:3d:bd:2a.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.9.134' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
git@192.168.9.236's password:
warning: 您似乎克隆了一个空版本库。
[root@localhost ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg jdsc2.创建文件模拟代码提交到仓库
1.在testgit目录下创建一个测试文件test.txt
[root@client ~]# cd testgit/
[root@client testgit]# vi test.txt #随便写点东西
2.把文件添加到暂存区:使用 "git add" 建立跟踪
[root@client testgit]# git add test.txt #创建完查看git status查看stage(暂存区状态)状态
注: 这里可以使用 git add * 或者 git add -A
提交完之后使用git status查看stage(暂存区状态)状态
3.提交文件到本地仓库分支:
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "test1"
注:在第一次在使用commit命令时,创建第一个分支也就是master分支
[master (root-commit) 2b51ff9] test1
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 test.txt
-m:描述 这是第一个实验
4.查看git状态:
[root@client testgit]# git status
# On branch master #分支位于master
假设文件(代码)不行,需要修改
假设文件(代码)不行,需要修改
假设文件(代码)不行,需要修改
5.修改文件后再此查看状态:
[root@client testgit]# echo '336699' >> test.txt
[root@client testgit]# git status
# 位于分支 master
# 尚未暂存以备提交的变更:
# (使用 "git add <file>..." 更新要提交的内容)
# (使用 "git checkout -- <file>..." 丢弃工作区的改动)
#
# 修改(modified): readme.txt
#
修改尚未加入提交(使用 "git add" 和/或 "git commit " )
这个地方说明修改修改完之后需要重新add 提交 commit提交才可以
6.先add
[root@client testgit]# git add -A #先更新一下
8.再次提交commit:
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "add2" test.txt #第二次提交
[master 73bf688] add2
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
[root@client testgit]# git status
# On branch master
nothing to commit, working directory clean3.版本回退
已经提交了不合适的修改到版本库时,想要撤销本次提交,使用版本回退,不过前提是没有推送到远程库。
查看现在的版本:
[root@client testgit]# git log
显示的哪个版本在第一个就是当前使用的版本。 版本回退(切换):
在Git中,上一个版本就HEAD^,上上一个版本就是HEAD^^,当然往上100个版本写100个^比较容易数不过来,所以写成HEAD~100(一般使用id号来恢复) 回到上一个版本
[root@client testgit]# git reset --hard HEAD^
HEAD is now at 0126755 test1
2.回到指定的版本(根据版本号):
[root@client testgit]# git reset --hard dd66ff
HEAD is now at dd66ff9 add2
==========================================================
注:消失的ID号:
回到早期的版本后再查看git log会发现最近的版本消失,可以使用reflog查看消失的版本ID,用于回退到消失的版本
[root@vm20 gittest]# git reflog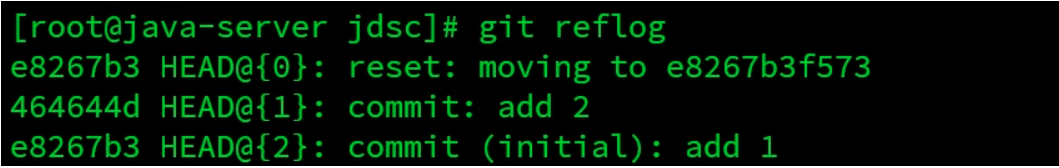
如果我想回到add2

就指向add2的id号
3.删除文件
从工作区删除test.txt,并且从版本库一起删除
从工作区删除
[root@client testgit]# rm -rf test. txt
从暂存区移除:
git rm --cached test.txt
从版本库删除:
[root@client testgit]# git rm test.txt
rm 'test.txt'
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "delete test.txt" #更新一下
[master cebc081] 删除文件test.txt
1 file changed, 3 deletions(-)
delete mode 100644 test.txt4.将代码上传到仓库的master分支
[root@client testgit]# vi a.txt #创建一个新文件
[root@client testgit]# git add a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "add"
[root@client testgit]# git push origin master #上传到远程仓库master分支
Counting objects: 11, done.
Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
Writing objects: 100% (11/11), 828 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 11 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To git@192.168.246.214:/git-test/testgit/
* [new branch] master -> master测试:
在客户端将仓库删除掉然后在克隆下来查看仓库中是否有文件
[root@git-client ~]# rm -rf testgit/
[root@client ~]# git clone git@192.168.246.214:/git-test/testgit/
Cloning into 'testgit'...
remote: Counting objects: 11, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Total 11 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (11/11), done.
[root@client ~]# cd testgit/
[root@client testgit]# ls
a.txt
[root@client testgit]# cat a.txt
hello world5.创建分支并合并分支
每次提交,Git都把它们串成一条时间线,这条时间线就是一个分支。截止到目前,只有一条时间线,在Git里,这个分支叫主分支,即
master分支。HEAD是指向master,所以,HEAD指向的就是当前分支。
在客户端操作:
[root@client ~]# git clone git@192.168.246.214:/git-test/testgit/
[root@client testgit]# git status
# On branch master #当前所在为master分支
#
# Initial commit
#
nothing to commit (create/copy files and use "git add" to track)
创建分支:
[root@client testgit]# git branch dev #创建分支。
[root@client testgit]# git branch #查看分支。*在哪里就表示当前是哪个分支
dev
* master
切换分支:
[root@client testgit]# git checkout dev
Switched to branch 'dev'
[root@client testgit]# git branch
* dev
master
在dev分支创建一个文件;
[root@client testgit]# vi test.txt
[root@client testgit]# git add test.txt
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "add dev"
[dev f855bdf] add dev
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 test.txt
现在,dev分支的工作完成,我们就可以切换回master分支:
[root@client testgit]# git checkout master
Switched to branch 'master'切换回
master分支后,再查看一个test.txt文件,刚才添加的内容不见了!因为那个提交是在dev分支上,而master分支此刻的提交点并没有变:
[root@client testgit]# ls
a.txt现在,我们把
dev分支的工作成果合并到master分支上(一定是从侧分支合并到主分支上面)
[root@client testgit]# git merge dev
Updating 40833e0..f855bdf
Fast-forward
test.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 test.txt
[root@client testgit]# ls
a.txt test.txt
现在已经将dev分支的内容合并到master上。确认没有问题上传到远程仓库:
[root@client testgit]# git push origin master
git merge命令用于合并指定分支到当前分支。合并后,再查看test.txt的内容,就可以看到,和dev分支的最新提交是完全一样的。合并完成后,就可以放心地删除
dev分支了:
[root@client testgit]# git branch -d dev
Deleted branch dev (was f855bdf).删除后,查看
branch,就只剩下master分支了:
[root@client testgit]# git branch
* master6.git标签
Git 标签(Tag)用于给仓库中的特定提交点加上标记,通常用于发布版本(如 v1.0, v2.0)。比如说,我们想为我们的 tmsc 项目发布一个 "1.0" 版本,可以用 **git tag -a v1.0** 命令给最新一次提交打上(HEAD) "v1.0" 的标签。
-a 选项意为"创建一个带注解的标签",不用 -a 选项也可以执行的,但不会记录这标签是啥时候打的,谁打的。推荐一直创建带注解的标签。
tag是git版本库的一个标记,指向某个commit的指针。
[root@client ~]# git clone git@192.168.9.134:/git-test/testgit
[root@client ~]# cd testgit/
[root@client testgit]# touch a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git add a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "add 1"
[master 61a232c] add 1
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git tag -a v1.0 -m "add 1"
[root@client testgit]# git tag
v1.0
[root@client testgit]# echo 12321323 >> a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git add a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git commit -m "add 2"
[master a5324a3] add 2
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
[root@client testgit]# git tag -a "v1.1" -m "指定commit id"
[root@client testgit]# git tag
v1.0
v1.1
[root@client testgit]# git show v1.1 #查看标签的详情
tag v1.1
Tagger: jack <jack@163.com>
Date: Sat Aug 31 17:01:41 2024 +0800
第二次修改内容并提交
commit a5324a3a0da23ffc878f0a69b7dcca2a0dec6002
Author: jack <jack@163.com>
Date: Sat Aug 31 17:01:24 2024 +0800
add 2
diff --git a/a.txt b/a.txt
index e69de29..59be678 100644
--- a/a.txt
+++ b/a.txt
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+12321323
[root@client testgit]# git push origin v1.0 #推送标签到远程仓库
Counting objects: 5, done.
Delta compression using up to 2 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 358 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 2 (delta 0)
To git@192.168.209.168:/git-test/didipm
* [new tag] v1.0 -> v1.0
#git push origin --tags # 推送所有标签
[root@client testgit]# git tag -d v1.0 #删除本地标签
Deleted tag 'v1.0' (was 00265b7)
[root@localhost testgit]# git tag -d v1.1
Deleted tag 'v1.1' (was 4616fef)
测试:
[root@client ~]# rm -rf testgit/
[root@client ~]# git clone git@192.168.9.134:/git-test/testgit
Cloning into 'didipm'...
remote: Counting objects: 18, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (11/11), done.
remote: Total 18 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (18/18), 24.41 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done.
[root@client ~]# cd testgit/
[root@client testgit]# ls
[root@client testgit]# git tag
v1.0
v1.1
[root@client testgit]# git checkout v1.0 #切换标签
Note: checking out 'v1.0'.
You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental
changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this
state without impacting any branches by performing another checkout.
If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may
do so (now or later) by using -b with the checkout command again. Example:
git checkout -b new_branch_name
HEAD is now at 61a232c... add 1
[root@client testgit]# ls
a.txt
[root@client testgit]# cat a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git checkout v1.1
Previous HEAD position was 61a232c... add 1
HEAD is now at a5324a3... add 2
[root@client testgit]# cat a.txt
12321323
指定标签进行版本回退,做为一个新的branch继续增加功能
[root@client testgit]# git tag
v1.0
v1.1
v1.2
[root@client testgit]# git reset --hard v1.0
HEAD is now at 61a232c add 1
[root@client testgit]# cat a.txt
[root@client testgit]# echo hangzhou >> a.txt
[root@client testgit]# git add a.txt
[root@client testgit# git commit -m "hangzhou"
[detached HEAD b2fa719] hangzhou
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
[root@client testgit]# git tag -a "v1.0.1" -m "b2fa719"
[root@client testgit]# git tag
v1.0
v1.0.1
v1.1
v1.2
[root@client testgit]# git push origin v1.0.1
Counting objects: 6, done.
Delta compression using up to 2 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 350 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To git@192.168.209.168:/git-test/didipm
* [new tag] v1.0.1 -> v1.0.1
删除远程仓库上的标签
[root@client testgit]# git push --delete origin v1.0
To git@192.168.209.168:/git-test/didipm
- [deleted] v1.0