第九章 WebSocket

WebSocket 是一种在单个 TCP 连接上实现全双工通信的协议,允许客户端和服务器之间实时、双向地传输数据。相比传统的 HTTP 请求-响应模式,WebSocket 在建立连接后可以持续通信,无需反复建立连接,大大降低了延迟和开销。
main.py
py
import logging
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import (
Depends,
FastAPI,
WebSocket,
WebSocketException,
status,
)
from fastapi.websockets import WebSocketDisconnect
from app.chat import router as chat_router
from app.exclusive_chatroom import (
router as exclusive_chatroom_router,
)
from app.security import get_username_from_token
from app.security import router as security_router
app = FastAPI()
app.include_router(security_router)
app.include_router(exclusive_chatroom_router)
# 注册聊天路由
app.include_router(chat_router)
logger = logging.getLogger("uvicorn")端点创建
py
# 装饰器将函数注册为WebSocket端点
@app.websocket("/ws")
async def ws_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):
# 接受客户端的WebSocket握手请求
await websocket.accept()
# 向客户端发送欢迎消息
await websocket.send_text(
"欢迎"
)
try:
# 使用无限循环保持活跃
while True:
# 异步接受消息 阻塞直到有消息到达
data = await websocket.receive_text()
logger.info(f"Message received: {data}")
# 发送确认消息
await websocket.send_text("Message received!")
# 当收到"disconnect"消息时,主动关闭连接
if data == "disconnect":
logger.warn("Disconnecting...")
# 关闭连接
return await websocket.close(
# 使用标准WebSocket关闭码1000表示正常关闭
code=status.WS_1000_NORMAL_CLOSURE,
reason="Disconnecting...",
)
# 在客户端发送不好的内容时断开连接
if "bad message" in data:
raise WebSocketException(
code=status.WS_1008_POLICY_VIOLATION,
reason="Inappropriate message",
)
# 捕获WebSocket断开异常
except WebSocketDisconnect:
logger.warning(
"客户断开连接"
)
py
# 在服务端运行这个代码即可进行体验
import asyncio
import websockets
SERVER = "ws://服务器地址:8000/ws"
async def main():
async with websockets.connect(SERVER) as ws:
print(f"已连接到 {SERVER}")
async def recv_loop():
async for msg in ws:
print("服务器消息:", msg)
async def send_loop():
while True:
text = input("输入要发送的内容(exit 退出): ")
if text == "exit":
await ws.close()
break
await ws.send(text)
await asyncio.gather(recv_loop(), send_loop())
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())实现聊天功能
WebSocket连接管理器
连接管理器的作用是跟踪打开的WebSocket连接并向活跃连接广播消息。
python
# ConnectionManage.py
import asyncio
from fastapi import WebSocket
# 通常使用单例模式
class ConnectionManager:
def __init__(self):
# :维护活跃连接列表作为共享状态
self.active_connections: list[WebSocket] = []
async def connect(self, websocket: WebSocket):
# 接受WebSocket握手
await websocket.accept()
# 添加到活跃连接列表
self.active_connections.append(websocket)
# 同步的断开连接方法
def disconnect(self, websocket: WebSocket):
self.active_connections.remove(websocket)
# 向指定用户的连接发送消息
async def send_personal_message(
self, message: dict, websocket: WebSocket
):
# 使用send_json()自动序列化字典为JSON字符串
await websocket.send_json(message)
# 广播消息
async def broadcast(
self, message: dict, exclude: WebSocket = None
):
tasks = [
connection.send_json(message)
for connection in self.active_connections
if connection != exclude
]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)聊天端点
py
# chat.py
import logging
from fastapi import APIRouter, Request, WebSocket, WebSocketDisconnect
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
from app.templating import templates
from app.ws_manager import ConnectionManager
# 获取一个全局连接管理器示例
conn_manager = ConnectionManager()
logger = logging.getLogger("uvicorn")
router = APIRouter()
@router.websocket("/chatroom/{username}")
async def chatroom_endpoint(
websocket: WebSocket, username: str
):
# 注册新连接
await conn_manager.connect(websocket)
# 向其他用户广播新用户加入消息
await conn_manager.broadcast(
{
"sender": "system",
"message": f"{username} joined the chat",
},
# 排除新加入用户,避免看到自己的加入消息
exclude=websocket,
)
logger.info(f"{username} joined the chat")
try:
while True:
# 接收消息
data = await websocket.receive_text()
# 向其他所有用户广播消息
await conn_manager.broadcast(
{"sender": username, "message": data},
exclude=websocket,
)
# 消息回显只发给自己
await conn_manager.send_personal_message(
{"sender": "You", "message": data},
websocket,
)
logger.info(
f"{username} says: {data}"
)
except WebSocketDisconnect:
# 连接断开时的清理工作
conn_manager.disconnect(websocket) # 从连接池移除
# 通知其他用户该用户离开
await conn_manager.broadcast(
{
"sender": "system",
"message": f"{username} "
"left the chat",
}
)
logger.info(f"{username} left the chat")
@router.get("/chatroom/{username}")
async def chatroom_page_endpoint(
request: Request, username: str
) -> HTMLResponse:
return templates.TemplateResponse(
request=request,
# 模板文件名
name="chatroom.html",
# 传递用户名到模板
context={"username": username},
)前端页面
py
# templating.py
# 创建一个模板引擎实例,用于渲染 HTML 页面
from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates
templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")假设用户访问 http://服务器地址:8000/chatroom/alice
浏览器 → GET /chatroom/alice
↓
chat.py 中的 chatroom_page_endpoint(username="alice") 被调用
↓
templates.TemplateResponse(
name="chatroom.html",
context={"username": "alice"}
)
↓
读取 templates/chatroom.html 文件
↓
把模板中的 {{ username }} 替换为 "alice"
↓
返回渲染后的 HTML 给浏览器
↓
浏览器显示聊天页面,页面中的 JavaScript 看到:
var client_id = "alice";
var ws = new WebSocket(`ws://服务器地址:8000/chatroom/alice`);
html
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Chat</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>WebSocket Chat</h1>
<h2>Your ID: <span id="ws-id"></span></h2>
<form action="" onsubmit="sendMessage(event)">
<input
type="text"
id="messageText"
autocomplete="off"
/>
<button>Send</button>
</form>
<ul id="messages"></ul>
<script>
var client_id = "{{ username }}";
document.querySelector("#ws-id").textContent =
client_id;
var ws = new WebSocket(
`ws://服务器地址:8000/chatroom/${client_id}`
);
ws.onmessage = function (event) {
var messages =
document.getElementById("messages");
var message = document.createElement("li");
var data = JSON.parse(event.data);
if (data.sender == "You") {
data_message =
"You wrote: \n" + data.message;
message.style.textAlign = "right";
message.style.color = "blue";
message.style.listStyle = "none";
} else if (data.sender == "system") {
data_message = data.message;
message.style.textAlign = "center";
message.style.color = "red";
message.style.listStyle = "none";
} else {
data_message =
data.sender + ":\n" + data.message;
message.style.textAlign = "left";
message.style.color = "green";
message.style.listStyle = "none";
}
var content =
document.createTextNode(data_message);
message.appendChild(content);
messages.appendChild(message);
};
function sendMessage(event) {
var input =
document.getElementById("messageText");
ws.send(input.value);
input.value = "";
event.preventDefault();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>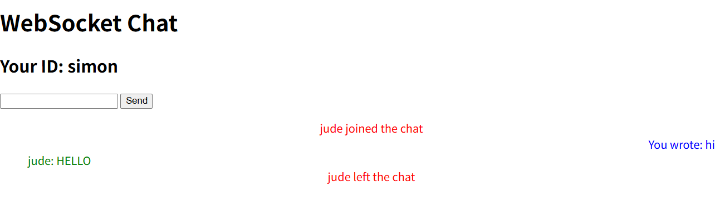
用户B的WebSocket 用户A的WebSocket ConnectionManager chat.py 用户B浏览器 用户A浏览器 用户B的WebSocket 用户A的WebSocket ConnectionManager chat.py 用户B浏览器 用户A浏览器 1. 用户A登录(打开页面) 2. 用户B登录(打开页面) 3. 用户A发送消息 4. 用户B发送消息 5. 用户A退出登录(关闭页面) GET /chatroom/alice 返回 chatroom.html (username=alice) WebSocket 连接 /chatroom/alice connect(websocket_A) accept() 接受连接 active_connections.append(websocket_A) broadcast("alice joined", exclude=websocket_A) send_json("alice joined") GET /chatroom/bob 返回 chatroom.html (username=bob) WebSocket 连接 /chatroom/bob connect(websocket_B) accept() 接受连接 active_connections.append(websocket_B) broadcast("bob joined", exclude=websocket_B) send_json("bob joined") send("hello") broadcast({sender:"alice", message:"hello"}, exclude=websocket_A) send_json({sender:"alice", message:"hello"}) send_personal_message({sender:"You", message:"hello"}, websocket_A) send_json({sender:"You", message:"hello"}) 显示"alice: hello"(绿色,左对齐) 显示"You wrote: hello"(蓝色,右对齐) send("hi alice") broadcast({sender:"bob", message:"hi alice"}, exclude=websocket_B) send_json({sender:"bob", message:"hi alice"}) send_personal_message({sender:"You", message:"hi alice"}, websocket_B) send_json({sender:"You", message:"hi alice"}) 显示"bob: hi alice"(绿色,左对齐) 显示"You wrote: hi alice"(蓝色,右对齐) WebSocketDisconnect disconnect(websocket_A) active_connections.remove(websocket_A) broadcast("alice left the chat") send_json("alice left the chat") 显示"alice left the chat"(红色,居中)
性能测试
建立一个 WebSocket 负载测试脚本,用于模拟多个客户端同时连接到 FastAPI 服务器的 WebSocket 端点,并测试服务器在并发连接下的行为。核心功能是启动一个服务器进程,同时创建多个异步客户端连接,最后优雅关闭。
py
import asyncio
import multiprocessing
import uvicorn
from websockets import connect
from app.main import app
# 在独立进程中启动 FastAPI 服务器
def run_server():
uvicorn.run(app)
# 模拟单个客户端行为
async def connect_client(
n: int, n_messages: int = 3
):
# 连接到专属 WebSocket 端点
async with connect(
f"ws://localhost:8000/chatroom/user{n}",
) as client:
for _ in range(n_messages):
await client.send(
f"Hello World from user{n}"
)
await asyncio.sleep(n * 0.1)
await asyncio.sleep(2)
async def main(n_clients: int = 10):
# 启动服务器进程
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_server)
p.start()
# 等待服务器启动
await asyncio.sleep(1)
connections = [
connect_client(n) for n in range(n_clients)
]
await asyncio.gather(*connections)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
p.terminate()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())客户端(0-9) 服务器子进程 主进程 客户端(0-9) 服务器子进程 主进程 每个客户端: 启动进程(p.start()) 等待1秒(确保服务启动) 并发创建10个连接 同时连接/chatroom/user{n} 发送3条消息(间隔n*0.1秒) 保持连接2秒后断开 等待所有客户端完成 额外等待1秒 终止进程(p.terminate())
OAuth2 加密
py
# main.py
@app.websocket("/secured-ws")
async def secured_websocket(
websocket: WebSocket,
username: Annotated[
get_username_from_token, Depends()
],
):
await websocket.accept()
await websocket.send_text(f"Welcome {username}!")
async for data in websocket.iter_text():
await websocket.send_text(
f"You wrote: {data}"
)
py
# ws_password_bearer.py
# 实现了一个 WebSocket 专用的 OAuth2 Bearer Token 认证器
from fastapi import (
WebSocket,
WebSocketException,
status,
)
from fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer
class OAuth2WebSocketPasswordBearer(
# 通过继承复用父类逻辑 通过重写 __call__ 适配 WebSocket
OAuth2PasswordBearer
):
async def __call__(
self, websocket: WebSocket
) -> str:
# 获取认证头
authorization: str = websocket.headers.get(
"authorization"
)
# 缺失认证处理
if not authorization:
raise WebSocketException(
code=status.WS_1008_POLICY_VIOLATION,
reason="Not authenticated",
)
# 解析 Bearer Token
scheme, param = authorization.split()
if scheme.lower() != "bearer":
raise WebSocketException(
code=status.WS_1008_POLICY_VIOLATION,
reason="Invalid authentication credentials",
)
return param常用命令
PowerShell
Test-NetConnection x.x.x.x -Port 8000测试本地计算机是否能与目标 IP 地址的 TCP 端口 8000 建立连接,常用于排查网络连通性或服务是否监听的问题
Linux
curl -v http://x.x.x.x