虽然单体 Agent 架构对于定义明确的问题可能是有效的,但在面对复杂的多领域任务时,其能力往往受到限 制。多 Agent 协作模式通过将系统构建为由不同专门化 Agent 组成的协作集合来解决这些限制。这种方法基 于任务分解原则,其中高级目标被分解为离散的子问题。然后将每个子问题分配给拥有最适合该任务的特定 工具、数据访问或推理能力的 Agent。
例如,一个复杂的研究查询可能被分解并分配给研究 Agent 进行信息检索、数据分析 Agent 进行统计处理, 以及综合 Agent 生成最终报告。这种系统的效能不仅仅源于劳动分工,而是关键依赖于 Agent 间通信的机 制。这需要标准化的通信协议和共享本体,允许 Agent 交换数据、委托子任务并协调其行动以确保最终输出 的连贯性。
这种分布式架构提供了几个优势,包括增强的模块化、可扩展性和稳健性,因为单个 Agent 的故障不一定会 导致整个系统故障。协作允许产生协同结果,其中多 Agent 系统的集体性能超过集合内任何单个 Agent 的潜 在能力。
多 Agent 协作模式概述
多 Agent 协作模式涉及设计系统,其中多个独立或半独立的 Agent 协同工作以实现共同目标。每个 Agent 通常具有定义的角色、与总体目标一致的特定目标,并且可能访问不同的工具或知识库。此模式的力量在于 这些 Agent 之间的交互和协同作用。
协作可以采取各种形式:
-
**・ 顺序交接:**一个 Agent 完成任务并将其输出传递给另一个 Agent 以进行管道中的下一步(类似于规划 模式,但明确涉及不同的 Agent)。
-
**・ 并行处理:**多个Agent同时处理问题的不同部分,然后它们的结果稍后被组合。
-
**・ 辩论和共识:**多 Agent 协作,其中具有不同观点和信息来源的 Agent 进行讨论以评估选项,最终达成
共识或更明智的决策。
-
**・ 层次结构:**管理者 Agent 可能根据其工具访问或插件能力动态地将任务委托给工作 Agent,并综合其 结果。每个 Agent 还可以处理相关的工具组,而不是单个 Agent 处理所有工具。
-
**・ 专家团队:**在不同领域具有专业知识的Agent(例如,研究员、作家、编辑)协作产生复杂输出。
-
・ 批评者‐审查者:Agent创建初始输出,如计划、草稿或答案。第二组Agent然后批判性地评估此输出 是否符合政策、安全性、合规性、正确性、质量以及与组织目标的一致性。原始创建者或最终 Agent 根据此反馈修订输出。此模式对于代码生成、研究写作、逻辑检查和确保道德一致性特别有效。这种 方法的优势包括增强的稳健性、改进的质量以及减少幻觉或错误的可能性。
多 Agent 系统(见图 1)从根本上包括 Agent 角色和职责的界定、Agent 通过其交换信息的通信渠道的建立, 以及指导其协作努力的任务流或交互协议的制定。
-
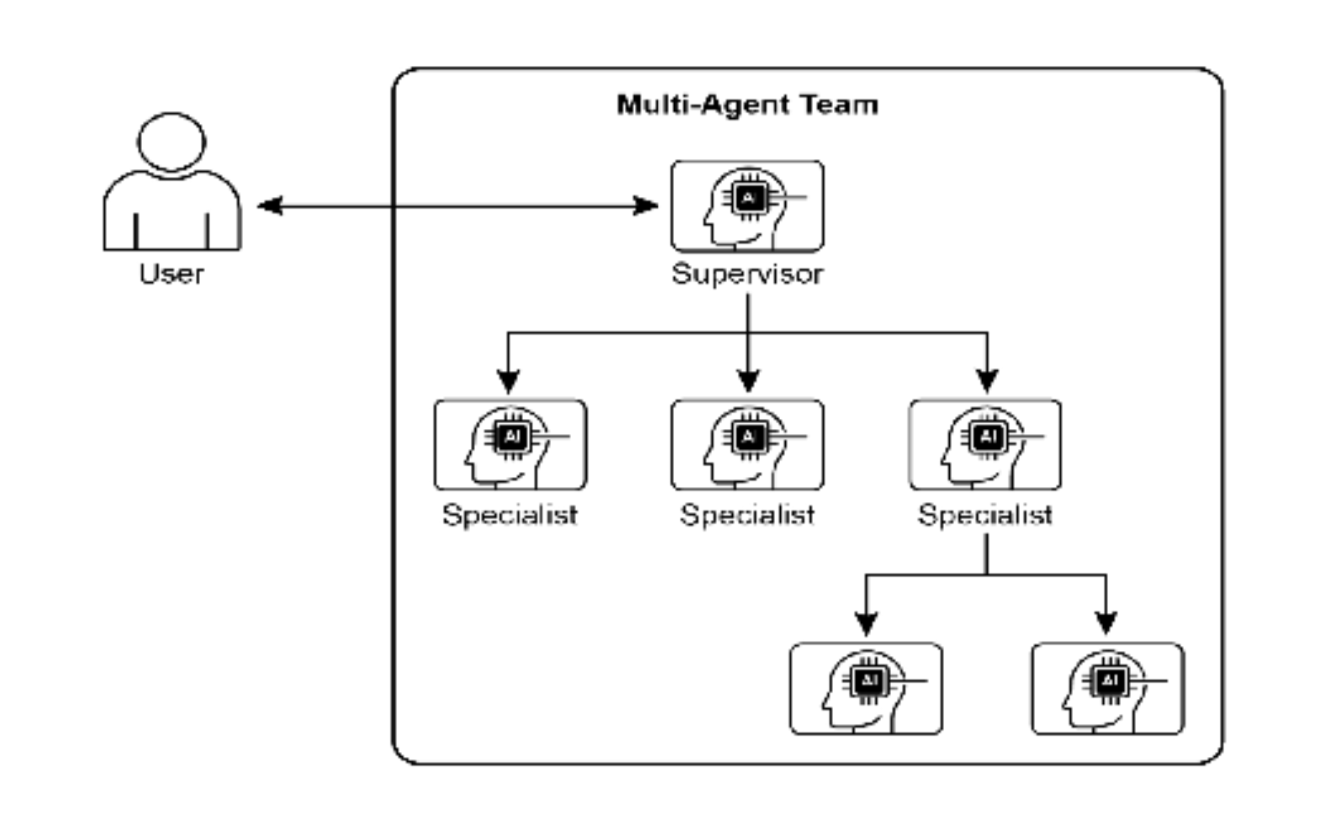
图 1:多 Agent 系统示例
实际应用与用例
多 Agent 协作是一种适用于众多领域的强大模式:
-
・ 复杂研究和分析:一组 Agent 可以协作完成研究项目。一个 Agent 可能专门搜索学术数据库,另一个 总结发现,第三个识别趋势,第四个将信息综合成报告。这反映了人类研究团队可能如何运作。
-
・ 软件开发:想象 Agent 协作构建软件。一个 Agent 可以是需求分析师,另一个是代码生成器,第三个 是测试员,第四个是文档编写者。他们可以在彼此之间传递输出以构建和验证组件。
-
・ 创意内容生成:创建营销活动可能涉及市场研究Agent、文案撰写Agent、图形设计Agent(使用图像 生成工具)和社交媒体调度 Agent,所有这些都在一起工作。
-
・ 财务分析:多 Agent 系统可以分析金融市场。Agent 可能专门获取股票数据、分析新闻情绪、执行技 术分析和生成投资建议。
-
・ 客户支持升级:前线支持Agent可以处理初始查询,在需要时将复杂问题升级给专家Agent(例如,技 术专家或计费专家),展示基于问题复杂性的顺序交接。
-
・ 供应链优化:Agent可以代表供应链中的不同节点(供应商、制造商、分销商)并协作优化库存水平、 物流和调度以响应需求变化或中断。
-
・ 网络分析与修复:自主操作从 Agent 架构中受益匪浅,特别是在故障定位方面。多个 Agent 可以协作 分类和修复问题,建议最佳行动。这些 Agent 还可以与传统机器学习模型和工具集成,利用现有系统, 同时提供生成式 AI 的优势。
界定专门 Agent 并细致编排其相互关系的能力使开发人员能够构建展现增强模块化、可扩展性以及处理单个 集成 Agent 无法解决的复杂性的系统。
多 Agent 协作:探索相互关系和通信结构
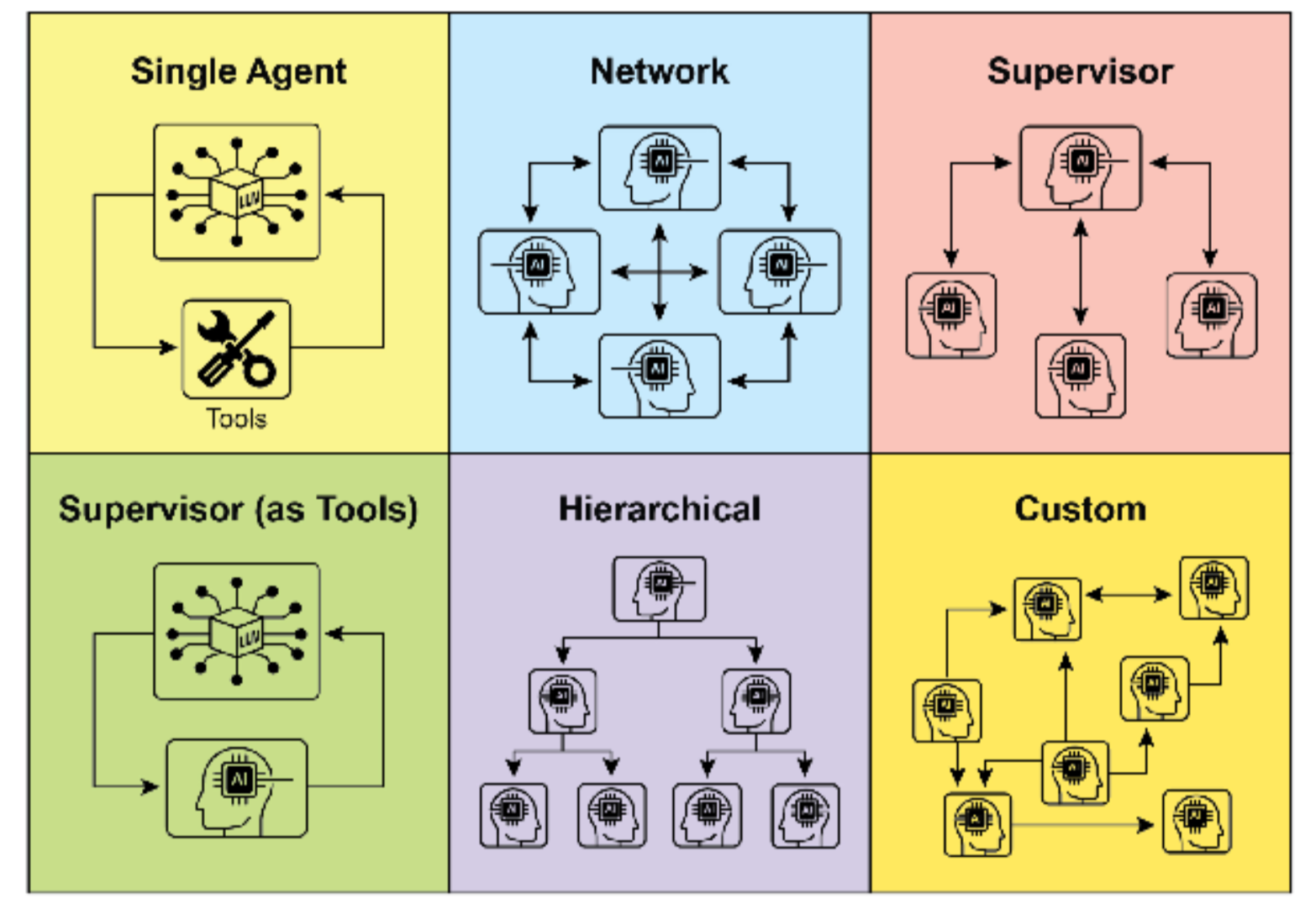
图 2:Agent 以各种方式进行通信和交互
理解 Agent 交互和通信的复杂方式对于设计有效的多 Agent 系统至关重要。如图 2 所示,存在一系列相互关 系和通信模型,从最简单的单 Agent 场景到复杂的、定制设计的协作框架。每个模型都呈现独特的优势和挑 战,影响多 Agent 系统的整体效率、稳健性和适应性。
-
单 Agent:在最基本的层面上,"单 Agent"在没有与其他实体直接交互或通信的情况下自主运行。虽然 此模型易于实现和管理,但其能力固有地受到单个 Agent 范围和资源的限制。它适用于可分解为独立子问题 的任务,每个子问题都可由单个自给自足的 Agent 解决。
-
网络:"网络"模型代表了向协作迈出的重要一步,其中多个 Agent 以去中心化方式直接相互交互。通信 通常以点对点方式进行,允许共享信息、资源甚至任务。此模型促进弹性,因为一个 Agent 的故障不一定会 使整个系统瘫痪。然而,管理通信开销并确保大型非结构化网络中的连贯决策可能具有挑战性。
-
监督者:在"监督者"模型中,专用 Agent("监督者")监督和协调一组下属 Agent 的活动。监督者充当 通信、任务分配和冲突解决的中心枢纽。这种层次结构提供了清晰的权限线,可以简化管理和控制。然而, 它引入了单点故障(监督者),如果监督者被大量下属或复杂任务压倒,可能会成为瓶颈。
-
监督者作为工具:此模型是"监督者"概念的细微扩展,其中监督者的角色不太关乎直接命令和控制,而 更多关乎向其他 Agent 提供资源、指导或分析支持。监督者可能提供工具、数据或计算服务,使其他 Agent 能够更有效地执行其任务,而不必规定其每一个行动。这种方法旨在利用监督者的能力,而不施加严格的自 上而下控制。
-
层次化:"层次化"模型扩展了监督者概念,创建了多层组织结构。这涉及多个监督者级别,高级监督者 监督低级监督者,最终在最低层有一组操作 Agent。此结构非常适合可分解为子问题的复杂问题,每个子问 题由层次结构的特定层管理。它提供了一种结构化的可扩展性和复杂性管理方法,允许在定义的边界内进行 分布式决策。
-
自定义:"自定义"模型代表了多 Agent 系统设计的终极灵活性。它允许创建根据给定问题或应用程序的 特定要求精确定制的独特相互关系和通信结构。这可能涉及结合前述模型元素的混合方法,或从环境的独特 约束和机会中产生的全新设计。自定义模型通常源于需要针对特定性能指标进行优化、处理高度动态的环境 或将特定领域知识纳入系统架构。设计和实现自定义模型通常需要对多 Agent 系统原理有深入理解,并仔细 考虑通信协议、协调机制和涌现行为。
总之,为多 Agent 系统选择相互关系和通信模型是关键的设计决策。每个模型提供不同的优势和劣势,最佳 选择取决于诸如任务复杂性、Agent 数量、期望的自主程度、对稳健性的需求以及可接受的通信开销等因素。 多 Agent 系统的未来进展可能会继续探索和完善这些模型,以及开发协作智能的新范式。
概览
是什么:复杂问题通常超出单个单体基于 LLM 的 Agent 的能力。单个 Agent 可能缺乏解决多方面任务所有 部分所需的多样化专业技能或对特定工具的访问。此限制造成瓶颈,降低系统的整体效率和可扩展性。因此, 处理复杂的多领域目标变得低效,并可能导致不完整或次优的结果。
为什么:多 Agent 协作模式通过创建多个协作 Agent 的系统提供了标准化解决方案。复杂问题被分解为更 小的更易于管理的子问题。然后将每个子问题分配给具有解决它所需的精确工具和能力的专门 Agent。这些 Agent 通过定义的通信协议和交互模型(如顺序交接、并行工作流或层次化委托)协同工作。这种 Agent 化 的分布式方法创造了协同效应,使团队能够实现任何单个 Agent 都无法实现的结果。
经验法则:当任务对于单个 Agent 来说太复杂并且可以分解为需要专业技能或工具的不同子任务时,使用此 模式。它非常适合受益于多样化专业知识、并行处理或具有多个阶段的结构化工作流的问题,例如复杂的研 究和分析、软件开发或创意内容生成。
图 3:多 Agent 设计模式
关键要点
・ 多Agent协作涉及多个Agent协同工作以实现共同目标。
・ 此模式利用专业角色、分布式任务和Agent间通信。
・ 协作可以采取顺序交接、并行处理、辩论或层次结构等形式。
・ 此模式非常适合需要多样化专业知识或多个不同阶段的复杂问题。
代码案例DEMO
根据上面的需求和多Agent 设计模式,我们设计一个多Agent协作系统,每个Agent可以专注于不同的任务,并通过协调器(Coordinator)来分配任务和整合结果。我们将使用以下组件:
-
Coordinator:负责接收用户请求,将任务分解,分配给不同的Agent,并整合结果。
-
Specialist Agents:每个Agent具有特定的能力,例如:
-
ResearchAgent:负责搜索信息
-
AnalysisAgent:负责分析数据
-
CodeAgent:负责编写代码
-
TestAgent:负责测试代码
-
DocumentAgent:负责编写文档
-
每个Agent都可以使用工具,并且我们假设它们都共享同一个LLM,但可以有不同的提示词和工具集。
我们将使用MCP(Model Context Protocol)来让Agent能够使用工具。每个Agent可以注册不同的工具,或者通过MCP服务器访问外部工具。
我们还将使用RAG来为Agent提供相关的知识库,例如代码库、文档等。
步骤:
-
定义Agent接口和基础结构。
-
实现Coordinator,它能够将任务分解,并调用不同的Agent。
-
实现几个具体的Agent,每个Agent都有特定的工具和提示词。
-
使用MCP协议来调用工具。
-
使用RAG来为Agent提供上下文。
多Agent协作系统设计与实现
基于上述用例,我来设计一个完整的Go多Agent协作系统。这个系统将展示复杂的研究分析、软件开发和客户支持等场景。
项目架构
html
multi-agent-system/
├── cmd/
│ ├── coordinator/
│ │ └── main.go
│ ├── agents/
│ │ ├── research/
│ │ ├── coding/
│ │ └── support/
│ └── gateway/
│ └── main.go
├── internal/
│ ├── coordinator/
│ ├── agent/
│ ├── communication/
│ ├── workflow/
│ └── orchestration/
├── pkg/
│ ├── llm/
│ ├── rag/
│ ├── mcp/
│ └── vector/
├── configs/
├── deployments/
└── examples/1. 核心协调器实现
internal/coordinator/engine.go
Go
package coordinator
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"sync"
"time"
"multi-agent-system/internal/agent"
"multi-agent-system/internal/workflow"
"multi-agent-system/pkg/llm"
)
type Orchestrator struct {
agents map[string]*agent.Agent
workflows map[string]*workflow.Workflow
messageBus *MessageBus
taskQueue chan Task
resultStore *ResultStore
coordinatorLLM llm.LLMClient
stateManager *StateManager
metrics *MetricsCollector
mu sync.RWMutex
}
type Task struct {
ID string `json:"id"`
Type TaskType `json:"type"`
Input map[string]interface{} `json:"input"`
Priority int `json:"priority"`
CreatedAt time.Time `json:"created_at"`
Deadline *time.Time `json:"deadline,omitempty"`
Dependencies []string `json:"dependencies,omitempty"`
}
type TaskResult struct {
TaskID string `json:"task_id"`
AgentID string `json:"agent_id"`
Result map[string]interface{} `json:"result"`
Status TaskStatus `json:"status"`
Error string `json:"error,omitempty"`
Duration time.Duration `json:"duration"`
ProducedBy []string `json:"produced_by,omitempty"`
ConsumedBy []string `json:"consumed_by,omitempty"`
}
func NewOrchestrator() *Orchestrator {
return &Orchestrator{
agents: make(map[string]*agent.Agent),
workflows: make(map[string]*workflow.Workflow),
messageBus: NewMessageBus(),
taskQueue: make(chan Task, 1000),
resultStore: NewResultStore(),
stateManager: NewStateManager(),
metrics: NewMetricsCollector(),
}
}
// 注册Agent
func (o *Orchestrator) RegisterAgent(name string, agent *agent.Agent) error {
o.mu.Lock()
defer o.mu.Unlock()
if _, exists := o.agents[name]; exists {
return fmt.Errorf("agent %s already registered", name)
}
o.agents[name] = agent
agent.SetMessageHandler(o.handleAgentMessage)
log.Printf("Agent %s registered with capabilities: %v", name, agent.Capabilities())
return nil
}
// 处理复杂任务分解
func (o *Orchestrator) DecomposeTask(ctx context.Context, userQuery string, workflowType WorkflowType) (*workflow.Workflow, error) {
prompt := fmt.Sprintf(`作为高级任务协调器,请将以下任务分解为可以并行或顺序执行的子任务。
原始任务: %s
工作流类型: %s
请以JSON格式返回任务分解结果:
{
"goal": "总体目标",
"subtasks": [
{
"id": "task_1",
"description": "任务描述",
"agent_type": "适合的Agent类型",
"dependencies": ["依赖的任务ID"],
"expected_output": "预期输出",
"time_estimate": "时间预估",
"parallelizable": true/false
}
],
"constraints": ["约束条件"],
"quality_metrics": ["质量指标"]
}`, userQuery, workflowType)
response, err := o.coordinatorLLM.Generate(prompt, 0.3)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var decomposition TaskDecomposition
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(response), &decomposition); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 创建工作流
wf := workflow.NewWorkflow(userQuery, workflowType)
for _, subtask := range decomposition.Subtasks {
wf.AddTask(workflow.Task{
ID: subtask.ID,
Description: subtask.Description,
AgentType: subtask.AgentType,
Dependencies: subtask.Dependencies,
Priority: subtask.Priority,
})
}
o.workflows[wf.ID] = wf
return wf, nil
}
// 智能任务分配
func (o *Orchestrator) AssignTask(ctx context.Context, task workflow.Task) (string, error) {
// 基于Agent负载、专业能力和历史表现进行分配
candidates := o.findCapableAgents(task.AgentType)
if len(candidates) == 0 {
return "", fmt.Errorf("no capable agent found for task type: %s", task.AgentType)
}
// 使用强化学习或规则引擎选择最佳Agent
selectedAgent := o.selectBestAgent(candidates, task)
// 发送任务
o.taskQueue <- Task{
ID: task.ID,
Type: TaskType(task.AgentType),
Input: map[string]interface{}{"description": task.Description},
Priority: task.Priority,
CreatedAt: time.Now(),
}
return selectedAgent, nil
}
// 处理Agent间通信
func (o *Orchestrator) handleAgentMessage(msg agent.Message) {
o.mu.Lock()
defer o.mu.Unlock()
switch msg.Type {
case agent.MessageTypeTaskComplete:
// 更新任务状态
o.resultStore.Store(msg.TaskID, msg.Data)
// 检查依赖任务是否完成
if o.checkDependencies(msg.TaskID) {
// 触发下游任务
o.triggerDownstreamTasks(msg.TaskID)
}
// 广播结果给感兴趣的Agent
o.broadcastResult(msg.TaskID, msg.Data)
case agent.MessageTypeRequestHelp:
// 寻找可以提供帮助的Agent
helper := o.findHelperAgent(msg.Sender, msg.Data)
if helper != "" {
o.forwardHelpRequest(msg.Sender, helper, msg.Data)
}
case agent.MessageTypeConflict:
// 处理冲突,协调解决方案
o.resolveConflict(msg.Data)
}
}
// 结果整合与验证
func (o *Orchestrator) IntegrateResults(ctx context.Context, workflowID string) (map[string]interface{}, error) {
wf, exists := o.workflows[workflowID]
if !exists {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("workflow not found: %s", workflowID)
}
// 收集所有任务结果
results := make(map[string]interface{})
for _, taskID := range wf.GetTaskIDs() {
result, exists := o.resultStore.Get(taskID)
if exists {
results[taskID] = result
}
}
// 使用LLM进行结果整合和一致性检查
finalResult, err := o.synthesizeResults(ctx, wf.Goal, results)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 质量检查
if err := o.qualityCheck(finalResult, wf.QualityMetrics); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("quality check failed: %v", err)
}
return finalResult, nil
}2. Agent基类与专业Agent
internal/agent/base.go
Go
package agent
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"time"
)
type AgentType string
const (
AgentTypeResearch AgentType = "research"
AgentTypeAnalysis AgentType = "analysis"
AgentTypeCoding AgentType = "coding"
AgentTypeTesting AgentType = "testing"
AgentTypeDocument AgentType = "document"
AgentTypeQA AgentType = "qa"
AgentTypeDeployment AgentType = "deployment"
AgentTypeSupport AgentType = "support"
)
type Agent struct {
ID string
Name string
Type AgentType
Capabilities []Capability
Knowledge *KnowledgeBase
Tools map[string]Tool
LLM LLMClient
State AgentState
Memory *WorkingMemory
MessageChan chan Message
stopChan chan struct{}
}
type Capability struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Description string `json:"description"`
Proficiency float64 `json:"proficiency"` // 0-1的熟练度
Tools []string `json:"tools"`
}
func NewAgent(id, name string, agentType AgentType, llm LLMClient) *Agent {
return &Agent{
ID: id,
Name: name,
Type: agentType,
LLM: llm,
Tools: make(map[string]Tool),
Knowledge: NewKnowledgeBase(),
Memory: NewWorkingMemory(100),
MessageChan: make(chan Message, 100),
stopChan: make(chan struct{}),
State: AgentStateIdle,
}
}
func (a *Agent) Start() {
go a.processMessages()
}
func (a *Agent) ProcessTask(ctx context.Context, task Task) (*TaskResult, error) {
a.State = AgentStateWorking
// 使用思维链(CoT)处理任务
plan, err := a.createExecutionPlan(task)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
results := make(map[string]interface{})
for step, action := range plan.Steps {
result, err := a.executeStep(ctx, action)
if err != nil {
// 错误处理:尝试恢复或请求帮助
if a.canRecover(err) {
result = a.attemptRecovery(ctx, err, action)
} else {
a.requestHelp(task, err)
return nil, err
}
}
results[step] = result
}
// 整合结果
finalResult := a.synthesizeResults(results, task)
// 自我验证
if err := a.selfVerify(finalResult); err != nil {
a.refineResult(ctx, finalResult, err)
}
a.State = AgentStateIdle
return &TaskResult{
TaskID: task.ID,
AgentID: a.ID,
Result: finalResult,
Status: TaskStatusComplete,
}, nil
}
func (a *Agent) createExecutionPlan(task Task) (*ExecutionPlan, error) {
prompt := fmt.Sprintf(`作为%s专家,请为以下任务创建执行计划:
任务: %s
可用工具: %v
知识库: %v
请考虑:
1. 任务分解
2. 工具选择
3. 依赖关系
4. 质量控制步骤
返回JSON格式计划:`, a.Type, task.Description, a.getToolNames(), a.Knowledge.Summary())
response, err := a.LLM.Generate(prompt, 0.2)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var plan ExecutionPlan
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(response), &plan); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &plan, nil
}
// 专业Agent:研究Agent
type ResearchAgent struct {
*Agent
SearchEngine SearchTool
PaperDB DatabaseTool
TrendAnalyzer AnalysisTool
}
func NewResearchAgent(id string, llm LLMClient) *ResearchAgent {
agent := NewAgent(id, "ResearchAgent", AgentTypeResearch, llm)
ra := &ResearchAgent{
Agent: agent,
}
// 添加研究专用工具
ra.Tools["academic_search"] = NewAcademicSearchTool()
ra.Tools["paper_parser"] = NewPaperParserTool()
ra.Tools["citation_analyzer"] = NewCitationAnalyzer()
ra.Tools["trend_detector"] = NewTrendDetectionTool()
ra.Capabilities = []Capability{
{
Name: "学术研究",
Description: "搜索和分析学术论文",
Proficiency: 0.9,
Tools: []string{"academic_search", "paper_parser"},
},
{
Name: "趋势分析",
Description: "识别研究趋势和热点",
Proficiency: 0.85,
Tools: []string{"trend_detector", "citation_analyzer"},
},
}
return ra
}
// 专业Agent:代码生成Agent
type CodingAgent struct {
*Agent
CodeGen CodeGenerationTool
CodeReview CodeReviewTool
TestGen TestGenerationTool
DocGen DocumentationTool
}
func NewCodingAgent(id string, llm LLMClient) *CodingAgent {
agent := NewAgent(id, "CodingAgent", AgentTypeCoding, llm)
ca := &CodingAgent{
Agent: agent,
}
// 添加编程专用工具
ca.Tools["code_generator"] = NewCodeGeneratorTool()
ca.Tools["code_refactor"] = NewRefactoringTool()
ca.Tools["dependency_check"] = NewDependencyAnalyzer()
ca.Tools["security_scan"] = NewSecurityScanner()
ca.Capabilities = []Capability{
{
Name: "代码生成",
Description: "根据需求生成高质量代码",
Proficiency: 0.95,
Tools: []string{"code_generator"},
},
{
Name: "代码审查",
Description: "审查代码质量和最佳实践",
Proficiency: 0.9,
Tools: []string{"code_review", "security_scan"},
},
}
return ca
}
// 专业Agent:客户支持Agent
type SupportAgent struct {
*Agent
KnowledgeBase *RAGRetriever
TicketSystem TicketTool
Escalation EscalationTool
Sentiment SentimentAnalyzer
}
func NewSupportAgent(id string, llm LLMClient) *SupportAgent {
agent := NewAgent(id, "SupportAgent", AgentTypeSupport, llm)
sa := &SupportAgent{
Agent: agent,
}
// 添加支持专用工具
sa.Tools["ticket_manager"] = NewTicketManager()
sa.Tools["faq_retriever"] = NewFAQRetriever()
sa.Tools["troubleshooter"] = NewTroubleshootingGuide()
sa.Tools["escalation"] = NewEscalationManager()
sa.Capabilities = []Capability{
{
Name: "问题诊断",
Description: "快速诊断客户问题",
Proficiency: 0.88,
Tools: []string{"troubleshooter", "faq_retriever"},
},
{
Name: "升级管理",
Description: "管理问题升级流程",
Proficiency: 0.92,
Tools: []string{"escalation", "ticket_manager"},
},
}
return sa
}3. 工作流定义与执行
internal/workflow/manager.go
Go
package workflow
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"multi-agent-system/internal/agent"
)
type WorkflowType string
const (
WorkflowTypeResearch WorkflowType = "research"
WorkflowTypeDevelopment WorkflowType = "development"
WorkflowTypeSupport WorkflowType = "support"
WorkflowTypeAnalysis WorkflowType = "analysis"
)
type Workflow struct {
ID string
Name string
Type WorkflowType
Goal string
Tasks []Task
Dependencies map[string][]string
State WorkflowState
CreatedAt time.Time
StartedAt *time.Time
CompletedAt *time.Time
QualityMetrics []QualityMetric
Participants []string
}
type Task struct {
ID string
Description string
AgentType agent.AgentType
Dependencies []string
Priority int
Timeout time.Duration
RetryPolicy RetryPolicy
InputSchema map[string]interface{}
OutputSchema map[string]interface{}
}
type RetryPolicy struct {
MaxAttempts int
Backoff time.Duration
Conditions []string
}
// 预定义工作流模板
var WorkflowTemplates = map[WorkflowType]Workflow{
WorkflowTypeResearch: {
Name: "学术研究工作流",
Type: WorkflowTypeResearch,
Tasks: []Task{
{
ID: "literature_review",
Description: "文献综述:搜索相关学术论文",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeResearch,
Priority: 1,
OutputSchema: map[string]interface{}{
"papers": "[]Paper",
"key_findings": "string",
},
},
{
ID: "trend_analysis",
Description: "趋势分析:识别研究热点和方向",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeAnalysis,
Dependencies: []string{"literature_review"},
Priority: 2,
},
{
ID: "gap_identification",
Description: "研究缺口识别",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeAnalysis,
Dependencies: []string{"trend_analysis"},
Priority: 3,
},
{
ID: "report_synthesis",
Description: "研究报告合成",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeDocument,
Dependencies: []string{"gap_identification"},
Priority: 4,
},
},
},
WorkflowTypeDevelopment: {
Name: "软件开发工作流",
Type: WorkflowTypeDevelopment,
Tasks: []Task{
{
ID: "requirements_analysis",
Description: "需求分析和规格制定",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeAnalysis,
Priority: 1,
},
{
ID: "architecture_design",
Description: "系统架构设计",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeAnalysis,
Dependencies: []string{"requirements_analysis"},
Priority: 2,
},
{
ID: "code_implementation",
Description: "代码实现",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeCoding,
Dependencies: []string{"architecture_design"},
Priority: 3,
},
{
ID: "unit_testing",
Description: "单元测试编写",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeTesting,
Dependencies: []string{"code_implementation"},
Priority: 4,
},
{
ID: "integration_testing",
Description: "集成测试",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeTesting,
Dependencies: []string{"unit_testing"},
Priority: 5,
},
{
ID: "documentation",
Description: "代码文档编写",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeDocument,
Dependencies: []string{"integration_testing"},
Priority: 6,
},
},
},
WorkflowTypeSupport: {
Name: "客户支持升级工作流",
Type: WorkflowTypeSupport,
Tasks: []Task{
{
ID: "initial_triage",
Description: "初始分流:识别问题类型和紧急程度",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeSupport,
Priority: 1,
Timeout: 5 * time.Minute,
},
{
ID: "basic_troubleshooting",
Description: "基础故障排除",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeSupport,
Dependencies: []string{"initial_triage"},
Priority: 2,
Timeout: 10 * time.Minute,
},
{
ID: "advanced_diagnosis",
Description: "高级诊断(如果需要)",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeSupport,
Dependencies: []string{"basic_troubleshooting"},
Priority: 3,
Conditions: []string{"issue_complexity > 0.7"},
},
{
ID: "escalation_to_expert",
Description: "升级给专家",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeSupport,
Dependencies: []string{"advanced_diagnosis"},
Priority: 4,
Conditions: []string{"resolution_attempts >= 2"},
},
{
ID: "solution_verification",
Description: "解决方案验证",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeQA,
Dependencies: []string{"escalation_to_expert"},
Priority: 5,
},
{
ID: "knowledge_base_update",
Description: "更新知识库",
AgentType: agent.AgentTypeDocument,
Dependencies: []string{"solution_verification"},
Priority: 6,
},
},
},
}
// 动态创建工作流
func CreateDynamicWorkflow(goal string, workflowType WorkflowType, constraints []Constraint) (*Workflow, error) {
baseTemplate, exists := WorkflowTemplates[workflowType]
if !exists {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown workflow type: %s", workflowType)
}
// 根据约束调整工作流
wf := &Workflow{
ID: generateWorkflowID(),
Name: baseTemplate.Name,
Type: workflowType,
Goal: goal,
Tasks: make([]Task, len(baseTemplate.Tasks)),
Dependencies: make(map[string][]string),
State: WorkflowStateCreated,
CreatedAt: time.Now(),
QualityMetrics: baseTemplate.QualityMetrics,
}
// 复制并调整任务
for i, task := range baseTemplate.Tasks {
adjustedTask := task
// 根据约束调整任务参数
for _, constraint := range constraints {
if constraint.AppliesTo(task.ID) {
adjustedTask = constraint.Apply(adjustedTask)
}
}
wf.Tasks[i] = adjustedTask
if len(adjustedTask.Dependencies) > 0 {
wf.Dependencies[adjustedTask.ID] = adjustedTask.Dependencies
}
}
return wf, nil
}4. Agent间通信协议
internal/communication/bus.go
Go
package communication
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"sync"
"time"
"multi-agent-system/internal/agent"
)
type MessageType string
const (
MessageTypeTaskRequest MessageType = "task_request"
MessageTypeTaskResult MessageType = "task_result"
MessageTypeQuery MessageType = "query"
MessageTypeResponse MessageType = "response"
MessageTypeNotification MessageType = "notification"
MessageTypeError MessageType = "error"
MessageTypeHelpRequest MessageType = "help_request"
MessageTypeHelpResponse MessageType = "help_response"
)
type Message struct {
ID string `json:"id"`
Type MessageType `json:"type"`
Sender string `json:"sender"`
Recipient string `json:"recipient"`
Timestamp time.Time `json:"timestamp"`
Payload map[string]interface{} `json:"payload"`
Priority int `json:"priority"`
TTL time.Duration `json:"ttl"`
CorrelationID string `json:"correlation_id,omitempty"`
}
type MessageBus struct {
channels map[string]chan Message
subscriptions map[string][]string // agentID -> []channelNames
mu sync.RWMutex
messageStore MessageStore
router *MessageRouter
}
func NewMessageBus() *MessageBus {
return &MessageBus{
channels: make(map[string]chan Message),
subscriptions: make(map[string][]string),
messageStore: NewMessageStore(),
router: NewMessageRouter(),
}
}
// 发布消息
func (b *MessageBus) Publish(channel string, msg Message) error {
b.mu.Lock()
ch, exists := b.channels[channel]
if !exists {
ch = make(chan Message, 1000)
b.channels[channel] = ch
}
b.mu.Unlock()
// 存储消息
b.messageStore.Store(msg)
// 路由消息
recipients := b.router.Route(msg)
for _, recipient := range recipients {
select {
case ch <- msg:
log.Printf("Message %s published to %s", msg.ID, channel)
default:
log.Printf("Channel %s is full, dropping message", channel)
}
}
return nil
}
// 订阅消息
func (b *MessageBus) Subscribe(agentID, channel string) (<-chan Message, error) {
b.mu.Lock()
defer b.mu.Unlock()
ch, exists := b.channels[channel]
if !exists {
ch = make(chan Message, 1000)
b.channels[channel] = ch
}
b.subscriptions[agentID] = append(b.subscriptions[agentID], channel)
return ch, nil
}
// 请求-响应模式
func (b *MessageBus) Request(ctx context.Context, req Message, timeout time.Duration) (*Message, error) {
// 生成响应通道
responseChannel := fmt.Sprintf("response_%s", req.ID)
responseCh, err := b.Subscribe(req.Sender, responseChannel)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer b.Unsubscribe(req.Sender, responseChannel)
// 发送请求
req.CorrelationID = req.ID
if err := b.Publish(req.Recipient, req); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 等待响应
select {
case resp := <-responseCh:
if resp.CorrelationID == req.ID {
return &resp, nil
}
case <-time.After(timeout):
return nil, fmt.Errorf("request timeout after %v", timeout)
case <-ctx.Done():
return nil, ctx.Err()
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no response received")
}
// Agent协作模式
func (b *MessageBus) Collaborate(ctx context.Context, agents []string, task Task) (map[string]interface{}, error) {
// 广播任务给所有相关Agent
responses := make(map[string]interface{})
var wg sync.WaitGroup
var mu sync.Mutex
for _, agentID := range agents {
wg.Add(1)
go func(aid string) {
defer wg.Done()
req := Message{
ID: generateMessageID(),
Type: MessageTypeTaskRequest,
Sender: "coordinator",
Recipient: aid,
Payload: map[string]interface{}{
"task": task,
},
}
resp, err := b.Request(ctx, req, 30*time.Second)
if err == nil {
mu.Lock()
responses[aid] = resp.Payload["result"]
mu.Unlock()
}
}(agentID)
}
wg.Wait()
// 整合所有响应
return b.integrateCollaborativeResponses(responses)
}
// 黑板模式实现
type Blackboard struct {
data map[string]interface{}
subscribers map[string]func(key string, value interface{})
mu sync.RWMutex
}
func NewBlackboard() *Blackboard {
return &Blackboard{
data: make(map[string]interface{}),
subscribers: make(map[string]func(key string, value interface{})),
}
}
func (bb *Blackboard) Post(key string, value interface{}) {
bb.mu.Lock()
bb.data[key] = value
bb.mu.Unlock()
// 通知订阅者
for _, callback := range bb.subscribers {
go callback(key, value)
}
}
func (bb *Blackboard) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
bb.mu.RLock()
defer bb.mu.RUnlock()
value, exists := bb.data[key]
return value, exists
}
// Agent通过黑板进行间接通信
func (bb *Blackboard) Subscribe(agentID string, callback func(key string, value interface{})) {
bb.mu.Lock()
bb.subscribers[agentID] = callback
bb.mu.Unlock()
}5. 完整的用例实现
examples/research_workflow.go
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"time"
"multi-agent-system/internal/coordinator"
"multi-agent-system/internal/agent"
"multi-agent-system/pkg/llm"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// 初始化协调器
orch := coordinator.NewOrchestrator()
// 初始化LLM客户端
openai, err := llm.NewOpenAIClient("gpt-4")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 创建各种专业Agent
researchAgent := agent.NewResearchAgent("research-1", openai)
analysisAgent := agent.NewAnalysisAgent("analysis-1", openai)
codingAgent := agent.NewCodingAgent("coding-1", openai)
testingAgent := agent.NewTestingAgent("testing-1", openai)
documentAgent := agent.NewDocumentAgent("doc-1", openai)
// 注册Agent
orch.RegisterAgent("research", researchAgent)
orch.RegisterAgent("analysis", analysisAgent)
orch.RegisterAgent("coding", codingAgent)
orch.RegisterAgent("testing", testingAgent)
orch.RegisterAgent("document", documentAgent)
// 启动所有Agent
researchAgent.Start()
analysisAgent.Start()
codingAgent.Start()
testingAgent.Start()
documentAgent.Start()
// 用例1:复杂研究和分析
log.Println("=== 用例1: 复杂研究和分析 ===")
researchGoal := "研究当前人工智能在医疗诊断领域的最新进展,识别关键技术突破和未来趋势"
executeResearchWorkflow(ctx, orch, researchGoal)
// 用例2:软件开发
log.Println("\n=== 用例2: 软件开发 ===")
devGoal := "开发一个基于Go的分布式任务调度系统,支持优先级队列和故障恢复"
executeDevelopmentWorkflow(ctx, orch, devGoal)
// 用例3:客户支持升级
log.Println("\n=== 用例3: 客户支持升级 ===")
supportIssue := "用户报告API响应缓慢,错误率上升"
executeSupportWorkflow(ctx, orch, supportIssue)
}
func executeResearchWorkflow(ctx context.Context, orch *coordinator.Orchestrator, goal string) {
// 分解研究任务
workflow, err := orch.DecomposeTask(ctx, goal, coordinator.WorkflowTypeResearch)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Failed to decompose task: %v", err)
return
}
log.Printf("研究工作流创建: %s", workflow.ID)
log.Printf("任务数量: %d", len(workflow.Tasks))
// 执行工作流
results, err := orch.ExecuteWorkflow(ctx, workflow.ID)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("工作流执行失败: %v", err)
return
}
// 输出结果
fmt.Println("\n=== 研究结果 ===")
for taskID, result := range results {
if data, ok := result.(map[string]interface{}); ok {
if summary, ok := data["summary"].(string); ok {
fmt.Printf("任务 %s:\n%s\n\n", taskID, summary)
}
}
}
// 生成最终报告
finalReport, err := orch.IntegrateResults(ctx, workflow.ID)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("结果整合失败: %v", err)
return
}
// 保存报告
saveResearchReport(finalReport)
}
func executeDevelopmentWorkflow(ctx context.Context, orch *coordinator.Orchestrator, goal string) {
// 创建开发工作流
workflow, err := coordinator.CreateDynamicWorkflow(
goal,
coordinator.WorkflowTypeDevelopment,
[]coordinator.Constraint{
{
Type: "time",
Value: "2小时",
AppliesTo: func(taskID string) bool {
return taskID == "code_implementation" || taskID == "unit_testing"
},
Apply: func(task coordinator.Task) coordinator.Task {
task.Timeout = 2 * time.Hour
return task
},
},
},
)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("创建工作流失败: %v", err)
return
}
// 注册工作流
orch.RegisterWorkflow(workflow)
// 执行工作流
results := make(chan coordinator.TaskResult, 10)
go orch.ExecuteWorkflowWithProgress(ctx, workflow.ID, results)
// 监控进度
for result := range results {
log.Printf("任务完成: %s by %s, 状态: %s",
result.TaskID, result.AgentID, result.Status)
if result.Error != "" {
log.Printf("错误: %s", result.Error)
}
// 如果是代码实现任务,可以立即进行代码审查
if result.TaskID == "code_implementation" && result.Status == coordinator.TaskStatusComplete {
triggerCodeReview(ctx, orch, result.Result)
}
}
// 获取最终产物
artifacts, err := orch.GetWorkflowArtifacts(workflow.ID)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("获取产物失败: %v", err)
return
}
// 保存代码、测试和文档
saveDevelopmentArtifacts(artifacts)
}
func executeSupportWorkflow(ctx context.Context, orch *coordinator.Orchestrator, issue string) {
// 创建支持工单
ticket := coordinator.SupportTicket{
ID: generateTicketID(),
Description: issue,
Priority: coordinator.PriorityHigh,
CreatedAt: time.Now(),
Status: coordinator.TicketStatusOpen,
}
// 分配支持Agent
agentID, err := orch.AssignSupportTicket(ticket)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("分配工单失败: %v", err)
return
}
log.Printf("工单 %s 分配给 Agent: %s", ticket.ID, agentID)
// 监控处理过程
updates := make(chan coordinator.TicketUpdate, 10)
orch.SubscribeToTicketUpdates(ticket.ID, updates)
for update := range updates {
log.Printf("工单更新: %s - %s", update.Stage, update.Message)
// 如果问题复杂,触发升级
if update.Stage == "advanced_diagnosis" && update.Data["complexity"].(float64) > 0.7 {
log.Println("问题复杂,触发升级流程")
orch.EscalateTicket(ticket.ID, coordinator.EscalationReasonComplexIssue)
}
// 如果解决,更新知识库
if update.Stage == "solution_verification" && update.Data["verified"].(bool) {
solution := update.Data["solution"].(string)
updateKnowledgeBase(ticket.Description, solution)
}
if update.Stage == "resolved" {
log.Printf("工单 %s 已解决", ticket.ID)
close(updates)
break
}
}
}
// 保存研究报告
func saveResearchReport(report map[string]interface{}) {
data, err := json.MarshalIndent(report, "", " ")
if err != nil {
log.Printf("序列化报告失败: %v", err)
return
}
filename := fmt.Sprintf("research_report_%d.json", time.Now().Unix())
if err := os.WriteFile(filename, data, 0644); err != nil {
log.Printf("保存报告失败: %v", err)
return
}
log.Printf("研究报告已保存到: %s", filename)
}6. 配置与部署
configs/agent_config.yaml
Go
agents:
research:
count: 2
capabilities:
- academic_search
- trend_analysis
- paper_summarization
llm_model: "gpt-4"
knowledge_base: "./data/research_papers"
analysis:
count: 2
capabilities:
- data_analysis
- pattern_recognition
- insight_generation
llm_model: "claude-3"
coding:
count: 3
capabilities:
- code_generation
- code_review
- refactoring
llm_model: "gpt-4"
language_specialties:
- go
- python
- javascript
testing:
count: 2
capabilities:
- test_generation
- bug_detection
- performance_testing
llm_model: "gpt-4"
support:
count: 4
capabilities:
- troubleshooting
- escalation_management
- knowledge_base_maintenance
llm_model: "gpt-3.5-turbo"
shift_schedule: "24/7"
coordinator:
llm_model: "gpt-4"
max_concurrent_workflows: 10
task_timeout: "30m"
retry_policy:
max_attempts: 3
backoff: "10s"
communication:
message_bus:
type: "redis"
address: "localhost:6379"
blackboard:
enabled: true
persistence: true
monitoring:
prometheus:
enabled: true
port: 9090
logging:
level: "info"
format: "json"
rag:
vector_store:
type: "qdrant"
address: "localhost:6334"
collection_prefix: "agent_knowledge"
embedding_model: "text-embedding-ada-002"deployments/docker-compose.yml
html
version: '3.8'
services:
coordinator:
build: ./cmd/coordinator
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- REDIS_HOST=redis
- QDRANT_HOST=qdrant
- OPENAI_API_KEY=${OPENAI_API_KEY}
depends_on:
- redis
- qdrant
volumes:
- ./configs:/app/configs
- ./data:/app/data
research-agent:
build: ./cmd/agents/research
scale: 2
environment:
- COORDINATOR_HOST=coordinator
- LLM_MODEL=gpt-4
depends_on:
- coordinator
coding-agent:
build: ./cmd/agents/coding
scale: 3
environment:
- COORDINATOR_HOST=coordinator
- LLM_MODEL=gpt-4
depends_on:
- coordinator
support-agent:
build: ./cmd/agents/support
scale: 4
environment:
- COORDINATOR_HOST=coordinator
- LLM_MODEL=gpt-3.5-turbo
depends_on:
- coordinator
gateway:
build: ./cmd/gateway
ports:
- "80:8080"
- "443:8443"
environment:
- COORDINATOR_HOST=coordinator
depends_on:
- coordinator
redis:
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- "6379:6379"
volumes:
- redis-data:/data
qdrant:
image: qdrant/qdrant
ports:
- "6333:6333"
- "6334:6334"
volumes:
- qdrant-data:/qdrant/storage
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus
ports:
- "9090:9090"
volumes:
- ./monitoring/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin
volumes:
- grafana-data:/var/lib/grafana
volumes:
redis-data:
qdrant-data:
grafana-data:7. 监控与可观测性
internal/monitoring/collector.go
Go
package monitoring
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus/promauto"
)
type MetricsCollector struct {
tasksProcessed prometheus.CounterVec
taskDuration prometheus.HistogramVec
agentUtilization prometheus.GaugeVec
workflowSuccess prometheus.CounterVec
messagesExchanged prometheus.CounterVec
errorRate prometheus.GaugeVec
resourceUsage prometheus.GaugeVec
}
func NewMetricsCollector() *MetricsCollector {
return &MetricsCollector{
tasksProcessed: *promauto.NewCounterVec(
prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "agent_tasks_processed_total",
Help: "Total number of tasks processed by agents",
},
[]string{"agent_type", "task_type", "status"},
),
taskDuration: *promauto.NewHistogramVec(
prometheus.HistogramOpts{
Name: "agent_task_duration_seconds",
Help: "Duration of agent tasks in seconds",
Buckets: prometheus.DefBuckets,
},
[]string{"agent_type", "task_type"},
),
agentUtilization: *promauto.NewGaugeVec(
prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Name: "agent_utilization_ratio",
Help: "Agent utilization ratio (0-1)",
},
[]string{"agent_id", "agent_type"},
),
workflowSuccess: *promauto.NewCounterVec(
prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "workflow_success_total",
Help: "Total number of successful workflows",
},
[]string{"workflow_type", "complexity"},
),
messagesExchanged: *promauto.NewCounterVec(
prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "agent_messages_exchanged_total",
Help: "Total number of messages exchanged between agents",
},
[]string{"message_type", "direction"},
),
errorRate: *promauto.NewGaugeVec(
prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Name: "agent_error_rate",
Help: "Error rate of agent operations",
},
[]string{"agent_type", "error_type"},
),
resourceUsage: *promauto.NewGaugeVec(
prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Name: "agent_resource_usage",
Help: "Resource usage by agents",
},
[]string{"agent_id", "resource_type"},
),
}
}
func (mc *MetricsCollector) RecordTaskCompletion(agentType, taskType string, status TaskStatus, duration time.Duration) {
mc.tasksProcessed.WithLabelValues(agentType, taskType, string(status)).Inc()
mc.taskDuration.WithLabelValues(agentType, taskType).Observe(duration.Seconds())
}
func (mc *MetricsCollector) RecordAgentUtilization(agentID, agentType string, utilization float64) {
mc.agentUtilization.WithLabelValues(agentID, agentType).Set(utilization)
}
func (mc *MetricsCollector) RecordWorkflowCompletion(workflowType string, complexity int, success bool) {
if success {
mc.workflowSuccess.WithLabelValues(workflowType, fmt.Sprintf("%d", complexity)).Inc()
}
}
// 实时监控仪表板
type Dashboard struct {
metrics *MetricsCollector
alerts []Alert
trends map[string]Trend
performance *PerformanceAnalyzer
}
func NewDashboard() *Dashboard {
return &Dashboard{
metrics: NewMetricsCollector(),
alerts: make([]Alert, 0),
trends: make(map[string]Trend),
performance: NewPerformanceAnalyzer(),
}
}
func (d *Dashboard) MonitorSystem(ctx context.Context) {
ticker := time.NewTicker(30 * time.Second)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-ticker.C:
d.collectMetrics()
d.checkAlerts()
d.updateTrends()
d.analyzePerformance()
case <-ctx.Done():
return
}
}
}
func (d *Dashboard) collectMetrics() {
// 收集各种系统指标
metrics := map[string]interface{}{
"agent_count": getActiveAgentCount(),
"workflow_count": getActiveWorkflowCount(),
"queue_size": getTaskQueueSize(),
"avg_response_time": getAverageResponseTime(),
"success_rate": getSuccessRate(),
"collaboration_rate": getCollaborationRate(),
"knowledge_base_size": getKnowledgeBaseSize(),
}
d.recordMetrics(metrics)
}
func (d *Dashboard) checkAlerts() {
// 检查系统健康状况
alerts := []Alert{
d.checkAgentHealth(),
d.checkWorkflowProgress(),
d.checkResourceUsage(),
d.checkErrorRates(),
d.checkLatency(),
}
for _, alert := range alerts {
if alert.Severity >= AlertSeverityWarning {
d.notifyAlert(alert)
}
}
}总结
这个多Agent协作系统提供了:
-
模块化设计:每个Agent专注于特定领域,通过协调器协同工作
-
灵活的通信模式:支持直接通信、黑板模式、发布-订阅等
-
智能任务分配:基于Agent能力和负载的动态分配
-
容错机制:支持错误恢复、重试和升级
-
完整的工作流:预定义模板和动态创建工作流
-
全面的监控:实时监控、警报和性能分析
-
可扩展架构:易于添加新的Agent类型和工作流
系统可以应用于:
-
复杂研究项目
-
软件开发生命周期
-
客户支持和服务台
-
供应链优化
-
金融分析
-
网络运维和故障排除
通过结合MCP、LLM和RAG技术,这个系统展示了现代AI Agent在实际业务场景中的应用潜力。
本文探讨了多 Agent 协作模式,展示了在系统内编排多个专门 Agent 的好处。我们研究了各种协作模型,强 调该模式在跨不同领域解决复杂多方面问题中的关键作用。理解 Agent 协作自然会引出对其与外部环境交互 的探究。
参考文献
1、Multi‐AgentCollaborationMechanisms:ASurveyofLLMs,https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.06322
2、Multi‐AgentSystem---ThePowerofCollaboration,https://aravindakumar.medium.com/introdu
cing‐multi‐agent‐frameworks‐the‐power‐of‐collaboration‐e9db31bba1b6