前文提要:还有比ollama更傻瓜式的大模型本地部署方式吗 ?
1.function calling 底层工作原理
大模型重塑了我们与软件应用的交互方式, 其中最重要的特性就是 function calling 。
一种利用结构化输入/输出在LLM和编程应用之间建立桥梁的方式。
不管是当前火热的AI-agent还是MCP,了解function calling底层工作原理都至关重要,特别是request和response payload。
回顾上文我们与qwen大模型的对话:
what is the temperature in the capital of china today?
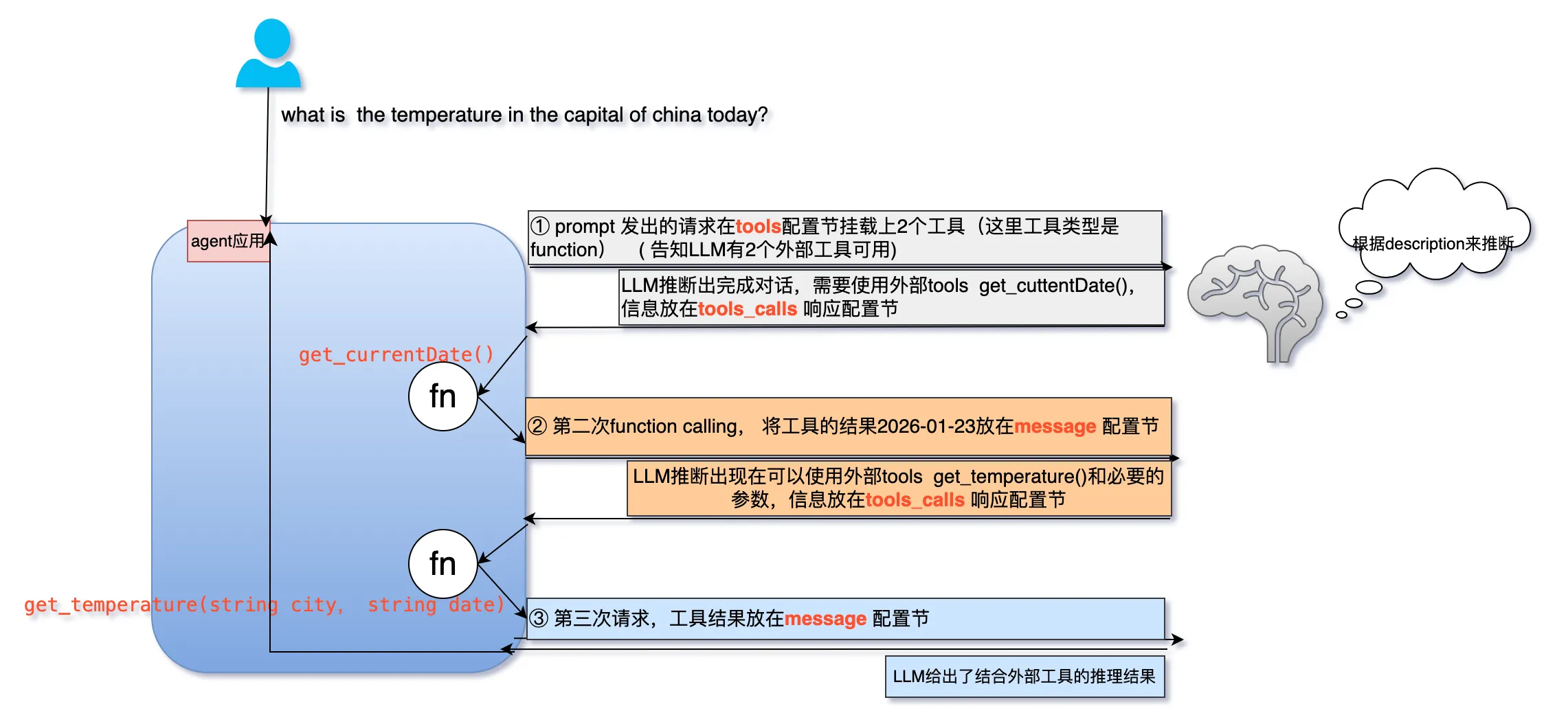
一个由LLM驱动的应用, 回答这个问题,应用与LLM经历了三次对话。
① 第一次请求payload:
- message:标准的历史对话, 提供上下文context
- tools:一系列的工具函数定义, 提供给LLM来选择
LLM的响应payload:
tool_calls.function.name: LLM选中的工具函数get_currentDatetool_calls.id: 由LLM为这个函数指定的id,后面会用到
② 第二次request:
messages.role.assistant: 告诉LLM我们这次请求包含了上次function calling的结果messages.role.tool: 上次function calling执行的结果2026-01-24
LLM的响应payload:
如第一次类似:
本例也有tool_calls:包含LLM选中的函数get_temperature() 和所有的参数beijing 2026-01-24。
③ 应用最后一次请求,包含所有信息
LLM推理认为不再需要外部工具,不再返回tool_calls,给出结合外部工具的对话结果。
从三次请求对话来看, LLM在三次对话的响应中体现了它的思考和逻辑步骤,应用持续被LLM引导做出行动,同时LLM也持续对应用的行为做出进一步观察和思考。
2. agent的实现原理
大模型是 AI 的大脑,其核心是理解自然语言,并做出回应,(文本)大模型本身只能接收一段文本,然后输出一段文本。
而当你希望大模型能使用一些工具自行获取所需的信息、执行一些动作,就需要使用 Tool 来实现了,拥有了 Tool 的大模型就像是拥有了手脚,可以和当下已有的 IT 基础设施进行交互。
RAG给LLM装上实时知识外挂, 通过将信息检索与文本生成结合,让模型能引用外部权威信息生成回答,既保证了时效性,又提升了准确性。
字节开源的Eino标榜的优势在于:
-
LangChain,LlamaIndex等主流框架虽然起源自python强大的AI生态,但是也继承了python"弱类型检查"和"长期维护成本高"的诟病。 Eino作为golang下的开源agent开发框架,规避了这一问题。
-
另一方面, 借助字节系在agent领域的工程化实践,Eino既封装了领域内不变的通用核心和最佳实践,也能敏捷的反映业内技术动向。
Eino框架结构图:
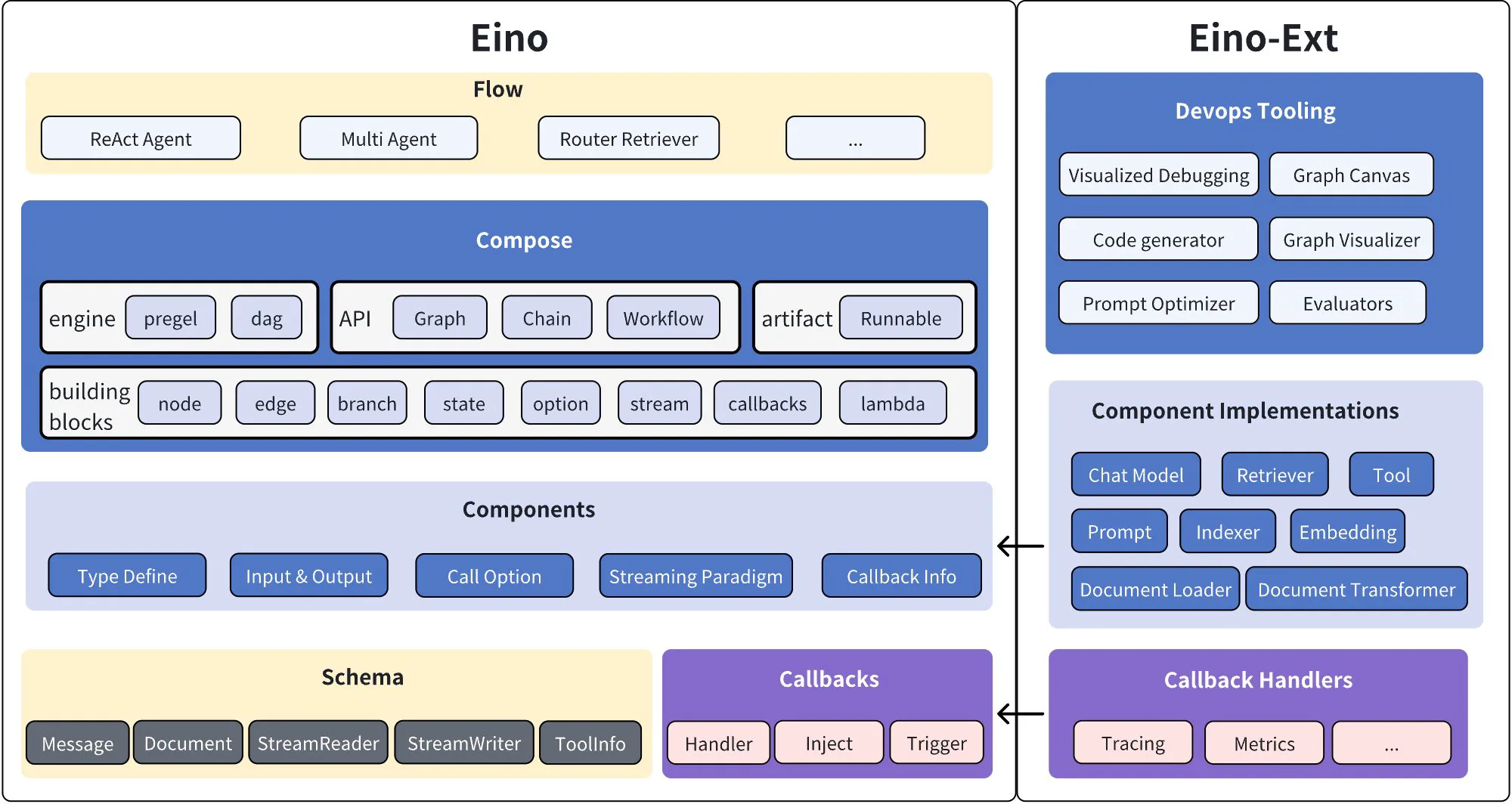
Eino 有三大稳定内核: compose编排、components组件,common公共库。
组件一抹多,是原子能力的最小单位, 编排对这些组件进行组合、串连。
3. 中国首都今天的天气怎么样? 我母鸡啊
我们使用Eino框架来实现本文的题目:
what is the temperature in the capital of china today。
按照我们的分析,
从LLM的视角,要回答这个问题,经历了"思考-行动-观察-思考" 循环, 这是一个ReAct模式的agent。
下面基于阿里百炼千问大模型,实现了天气对话,请自行从阿里百炼平台申请的apiKey替换到54行。
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/qwen"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
// what is the temperature in the capital of china today
type weatherReqParam struct {
City string `json:"city" jsonschema:"description=the name of the city"`
Date string `json:"date" jsonschema:"description=the date in the format of YYYY-MM-DD"`
}
func GetTemperatureFunc(_ context.Context, p weatherReqParam) (float64, error) {
// 这里直接mock一个温度值,实际应用中应该替换为真实的API调用
return 32, nil
}
func GetCurrentDateFunc(_ context.Context, _ struct{}) (string, error) {
return time.Now().Format("2006-01-02"), nil
}
func of[T any](t T) *T {
return &t
}
func main() {
getDateTool, err := utils.InferTool("get_currentDate", "Get the current date", GetCurrentDateFunc)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
getTemperatureTool, err := utils.InferTool("get_temperature", "Get the temperature in the capital of the city", GetTemperatureFunc)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 初始化 tools
weatherTools := []tool.BaseTool{
getDateTool,
getTemperatureTool,
}
apiKey := os.Getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY")
apiKey = "{}" // 在阿里百炼平台申请签名
modelName := os.Getenv("MODEL_NAME")
modelName = "qwen3-max"
chatModel, err := qwen.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &qwen.ChatModelConfig{
BaseURL: "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
APIKey: apiKey,
Timeout: 0,
Model: modelName,
MaxTokens: of(2048),
Temperature: of(float32(0.7)),
TopP: of(float32(0.7)),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("NewChatModel of qwen failed, err=%v", err)
}
var ctx = context.Background()
// 获取工具信息并绑定到 ChatModel
toolInfos := make([]*schema.ToolInfo, 0, len(weatherTools))
for _, tool := range weatherTools {
info, err := tool.Info(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
toolInfos = append(toolInfos, info)
}
err = chatModel.BindTools(toolInfos)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 创建 tools 节点
weatherToolsNode, err := compose.NewToolNode(context.Background(), &compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: weatherTools,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 构建基于 Graph 的 Agent,实现 ReAct 模式(自动执行工具并生成自然语言回复)
// 定义状态,用于保存对话历史
type appState struct {
messages []*schema.Message
}
graph := compose.NewGraph[[]*schema.Message, *schema.Message](
compose.WithGenLocalState(func(ctx context.Context) *appState {
return &appState{}
}),
)
// 添加 ChatModel 节点
err = graph.AddChatModelNode("qwen_chat_model", chatModel,
compose.WithStatePreHandler(func(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message, state *appState) ([]*schema.Message, error) {
// 如果是第一次进入(从 Start),将输入(用户问题)添加到历史
if len(state.messages) == 0 {
state.messages = append(state.messages, input...)
}
// 始终将完整的历史记录作为 ChatModel 的输入
return state.messages, nil
}),
compose.WithStatePostHandler(func(ctx context.Context, output *schema.Message, state *appState) (*schema.Message, error) {
// 将 ChatModel 的输出(可能是工具调用或最终回复)添加到历史
state.messages = append(state.messages, output)
return output, nil
}),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 添加 Tools 节点
err = graph.AddToolsNode("agent_tools", weatherToolsNode,
compose.WithStatePostHandler(func(ctx context.Context, output []*schema.Message, state *appState) ([]*schema.Message, error) {
// 将工具执行结果添加到历史
state.messages = append(state.messages, output...)
return output, nil
}),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 添加边和分支
_ = graph.AddEdge(compose.START, "qwen_chat_model")
// 如果有工具调用,流转到 tools;否则结束
_ = graph.AddBranch("qwen_chat_model", compose.NewGraphBranch(func(ctx context.Context, msg *schema.Message) (string, error) {
if len(msg.ToolCalls) > 0 {
return "agent_tools", nil
}
return compose.END, nil
}, map[string]bool{"agent_tools": true, compose.END: true}))
// 工具执行完后,回流到 chat_model 生成回复
_ = graph.AddEdge("agent_tools", "qwen_chat_model")
// 编译运行
agent, err := graph.Compile(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 运行示例
resp, err := agent.Invoke(ctx, []*schema.Message{
{
Role: schema.User,
Content: "what is the temperature in the capital of china today? please answer in a humam like way.",
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 输出结果
fmt.Println(resp.Content)
}一开始我参照的官网的chain编排Eino组件,但是得到的结果是数字"32", 并不是LLM对话的类人语言。
使用Trae的编码agent,20s就帮我改成了Graph形式的正确编码, 输出:
The temperature in Beijing, the capital of China, today (January 28, 2026) is a warm 32°C! That's quite hot for this time of year---make sure to stay hydrated and cool if you're out and about!本例实际也可以使用
Chain来完成,chain是一种特殊的、简化的graph,chain不能回头,本例需要手动串起来,Chain更适合确定性的编排。
Graph就像一个自动化的流水线(loop),工人是 chat_model 和 tools :
本例的Graph图如下,读者可以结合源代码理解。
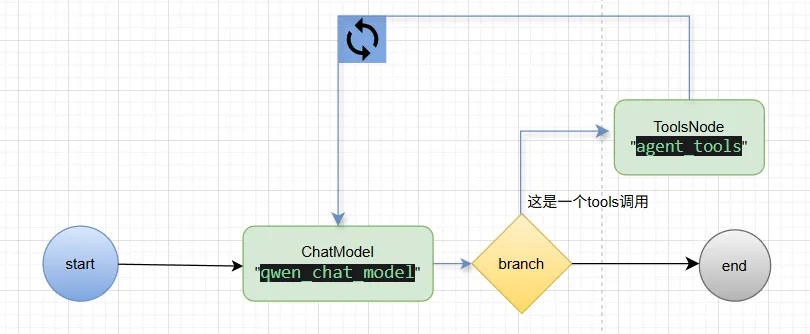
- START -> chat_model
- ChatModel 拿到用户问题,思考后说:"我需要查日期。"(输出包含 ToolCall)
- chat_model -> tools (由 Branch 判断)
- Tools 听到指令,去查日期,得到 "2026-01-24"。
- tools -> chat_model (由 AddEdge 强制流转)
- ChatModel 再次被唤醒。这次它的输入包含了之前的历史(用户问题 + 刚才的 ToolCall + 刚才的结果)。
- 它再次思考:"我知道日期了,现在我要查北京的温度。"(输出包含 ToolCall)
- chat_model -> tools (再次循环)
- Tools 去查温度,得到 "32度"。
- tools -> chat_model (再次循环)
- ChatModel 再次被唤醒。现在的输入更丰富了(所有历史)。
- 它再次思考:"日期有了,温度也有了,我可以直接回答用户了。"(输出 不包含 ToolCall)
- chat_model -> END (由 Branch 判断)
- 循环结束。
最后我们重温全文,function calling(function tools)在agent中的作用:
在由LLM驱动的agent应用中,function calling(function tools)作为LLM的手脚,让LLM具备使用工具从外部获取最新信息并指导应用行为的能力,这一过程由结构化的输入输出参数来传递。