3. Tinystories 数据集上训练
3.1. 阅读分析题目要求
这个题目有两个要求
- a. vocab size 最大 10,000,确保将 speicial token
"<|endoftext|>"加入到 vocabulary。 资源要求 :训练时长 ≤ 30 minutes (no GPUs), 占用内存 ≤ 30GB RAM
Tips:如果要在 2 分钟内完成训练,可以考虑多线程处理 pretokenize。 - b. "tokenizer 训练过程中哪一部分最耗时?"
按照作业要求,我将分三步来完成:
-
编写训练脚本:包含加载数据、训练、保存模型、统计时间和内存。
-
运行并分析性能 (Profiling):回答瓶颈在哪里。
-
检查结果:找出最长的 Token。
3.2 逐步实现
-
查看训练数据
训练前,可以用 head 命令查看下训练数据,确认数据与之前测试的类型基本一致。
-
代码关键实现分析
-
获取项目根路径
为了正确方便读写文件,工程中通常首先获取项目根路径。sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(file), "..")))
-
获取进程运行时的内存
def get_memory_usage_mb():
"""Get current process memory usage in MB"""
process = psutil.Process(os.getpid())
return process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 -
将训练获得的 vocabulary 和 merges 规则写入磁盘进行持久化。
vocabulary 结构是 Dict,所以保存为 json格式,并且为了人类阅读,将bytesdecode为字符串保存在vocab.json中,无法解码的保留repr形式。def save_vocab_and_merges(vocab, merges, output_dir="results"):
"""Save vocabulary and merges to disk"""
Path(output_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)# Save vocab.json vocab_str = {} for idx, token_bytes in vocab.items(): try: vocab_str[idx] = token_bytes.decode('utf-8') except UnicodeDecodeError: vocab_str[idx] = str(token_bytes) with open(f"{output_dir}/vocab.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: json.dump(vocab_str, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2) # Save merges.txt with open(f"{output_dir}/merges.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: for p1, p2 in merges: f.write(f"{p1.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')} {p2.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')}\n") print(f"Artifacts saved to {output_dir}/") -
定义训练 & 打印统计信息
def run_training(input_path, vocab_size, special_tokens, output_dir):
# record the initial memory usage before training print(f"Initial Memory: {get_memory_usage_mb():.2f} MB") # Initialize the BPE trainer trainer = BPETrainer_Optimized() # start training and record the time and memory usage start_time = time.time() print(f"Starting training on {input_path}...") vocab, merges = trainer.train( input_path=input_path, vocab_size=vocab_size, special_tokens=special_tokens ) end_time = time.time() duration = end_time - start_time peak_memory = get_memory_usage_mb() print("-" * 30) print(f"Training Complete.") print(f"Time Taken: {duration:.2f} seconds ({duration/60:.2f} minutes)") print(f"Final Memory: {peak_memory:.2f} MB") print("-" * 30) save_vocab_and_merges(vocab, merges, output_dir) # Output Statistics information print("\n=== Statistics (Problem b) ===") # 1. Longest token longest_token_bytes = max(vocab.values(), key=len) try: longest_token_str = longest_token_bytes.decode('utf-8') except: longest_token_str = str(longest_token_bytes) print(f"Longest Token: {longest_token_str!r}") print(f"Length in bytes: {len(longest_token_bytes)}") # 2. Most frequent token (approximate, based on merge priority if we tracked it, # but here we can just say the last merged token was the most frequent *at that step*) # The assignment asks for "most frequent token in the dataset"? # Usually BPE doesn't keep full frequency counts of final vocab unless we re-tokenize. # We will just print the last merge which represents the most frequent pair remaining. print(f"Total Merges: {len(merges)}")
3.3 运行训练脚本
-
执行如下命令
uv run python scripts/train_bpe_tinystories.py
--input_path data/TinyStoriesV2-GPT4-train.txt
--vocab_size 10000
--profile
控制台可以看到如下输出
Enabling cProfile...
Initial Memory: 23.41 MB
Starting training on data/TinyStoriesV2-GPT4-train.txt...
Starting BPE training (Optimized)...
Merge 0/9743: (b' ', b't')
Merge 100/9743: (b'ri', b'end')
...
Merge 9600/9743: (b' pain', b'ful')
Merge 9700/9743: (b'St', b'ill')
------------------------------
Training Complete.
Time Taken: 731.09 seconds (12.18 minutes)
Final Memory: 96.74 MB
------------------------------
Artifacts saved to tinystories_tokenizer/
=== Statistics (Problem b) ===
Longest Token: ' accomplishment'
Length in bytes: 15
Total Merges: 9743
Profiling data saved to training.prof
Use 'snakeviz training.prof' to visualize.3.4 检查确认
-
0,255\] 为 256 个字符。
输出258: "256": "<|endoftext|>",确认 "<|endoftext|>" 加入到 vocabulary, idx 为 256,符合预期。
文件不大也可以打开查看。 -
257:\]: 训练完成得到的 vocabulary。
由于 toml 文件中没有 snakeviz,我们需要单独安装 snakeviz,
-
安装 snakeviz (如果还没安装)
uv pip install snakeviz
-
启动可视化服务器
uv run snakeviz training.prof
然后浏览器打开
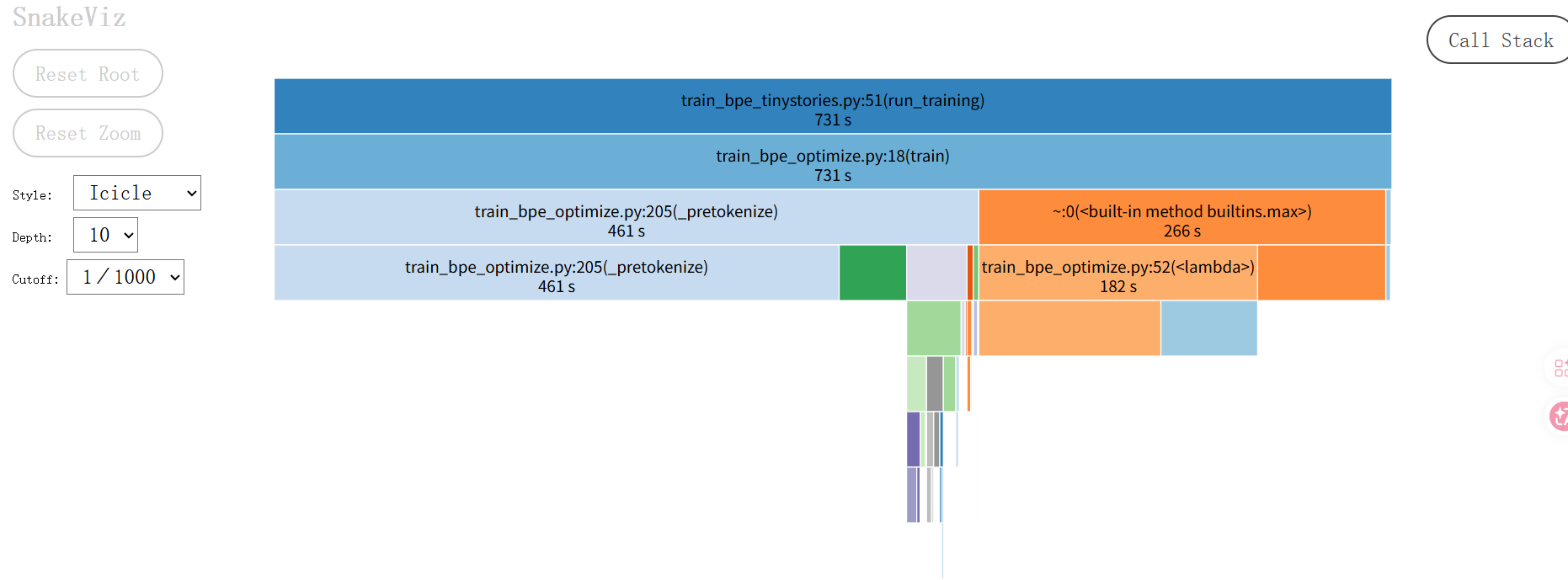
如果本地不方便,可以使用 python 内置的 pstats 查看文本报告
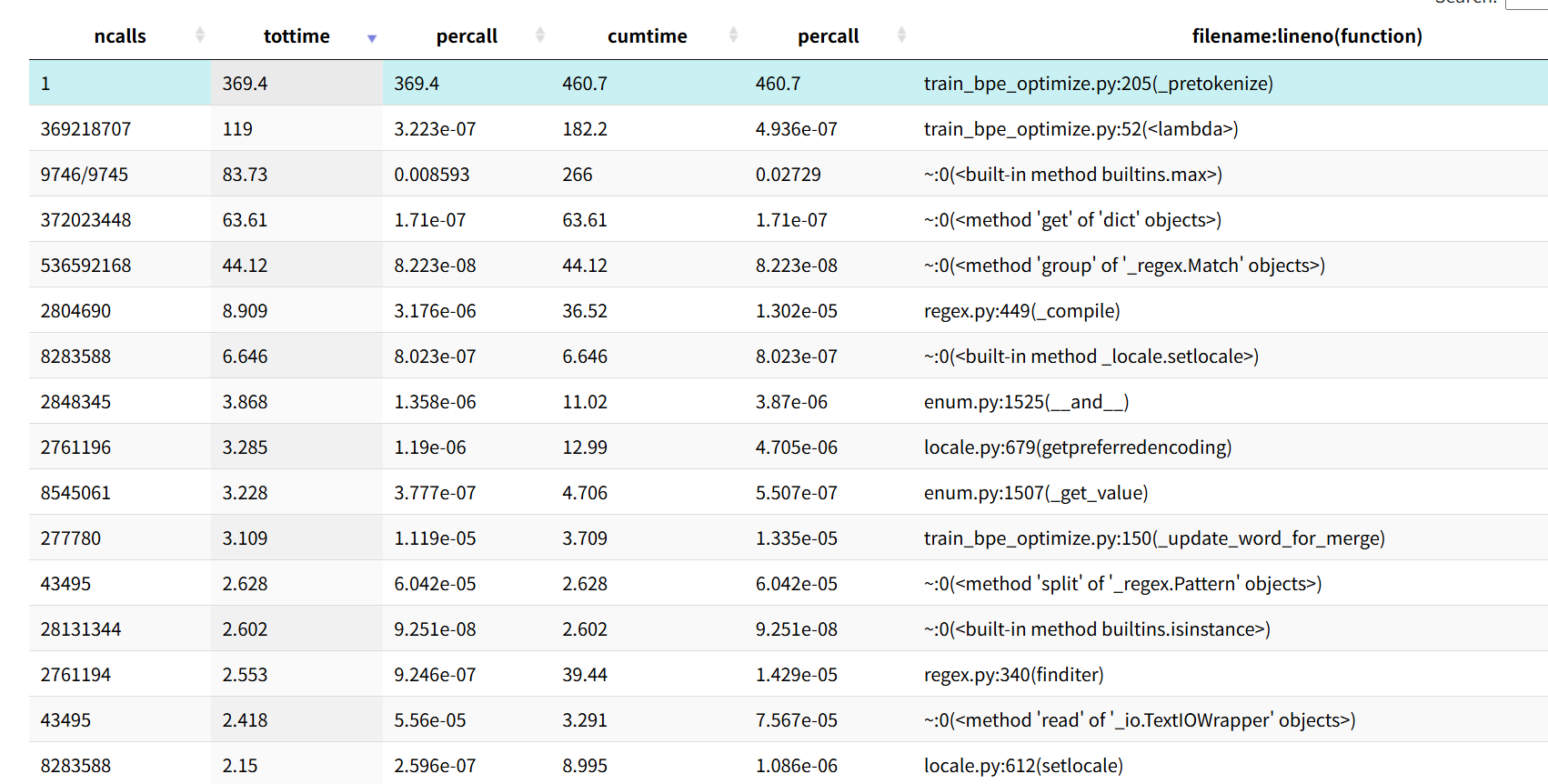
# 查看累计耗时(cumulative)排名前 10 的函数
uv run python -c "import pstats; p = pstats.Stats('training.prof'); p.sort_stats('cumulative').print_stats(10)" 耗时最长的前10
1368017311 function calls (1368017210 primitive calls) in 731.144 seconds
Ordered by: cumulative time
List reduced from 251 to 10 due to restriction <10>
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
1 0.029 0.029 731.144 731.144 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/scripts/train_bpe_tinystories.py:51(run_training)
1 0.372 0.372 731.066 731.066 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/cs336_basics/train_bpe_optimize.py:18(train)
1 369.361 369.361 460.691 460.691 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/cs336_basics/train_bpe_optimize.py:205(_pretokenize)
9746/9745 83.735 0.009 265.975 0.027 {built-in method builtins.max}
369218707 118.986 0.000 182.240 0.000 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/cs336_basics/train_bpe_optimize.py:52(<lambda>)
372023448 63.614 0.000 63.614 0.000 {method 'get' of 'dict' objects}
536592168 44.123 0.000 44.123 0.000 {method 'group' of '_regex.Match' objects}
2761194 2.553 0.000 39.444 0.000 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/regex/regex.py:340(finditer)
2804690 8.909 0.000 36.517 0.000 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/regex/regex.py:449(_compile)
2761196 3.285 0.000 12.991 0.000 /home/fdq/.local/share/uv/python/cpython-3.11.12-linux-x86_64-gnu/lib/python3.11/locale.py:679(getpreferredencoding)根据 Profiling (性能分析) 结果揭示了程序的运行状况!这对于回答作业中的问题 (b) 以及后续优化至关重要。
1. 深度分析 Profiling 结果
根据 pstats 文本和 snakeviz 可视化页面,我们可以清晰地得出结论:
瓶颈一:Pre-tokenization (最耗时)
- 原因 1:这是单线程运行的。Python 的正则引擎虽然快,但要处理的是几 GB 的文本数据。一个 CPU 核心逐字逐句地扫描、匹配、计数,必然是慢的。
- 证据 :
_pretokenize函数占据了 460.69 秒 (约占总时间的 63%)。 - 作业提示 :这就是为什么作业 Hint 提到 "using multiprocessing during pretokenization"。
- 原因 2:正则匹配耗时
- 证据:finditer 和 _compile 以及 group 方法被调用了数百万次,占用了大量时间。我是在循环外编译的,
瓶颈二:寻找最佳 Pair (max 操作)
-
证据 :
builtins.max耗时 265.97 秒。 -
细节分析:
-
调用了
max约 1 万次(每次合并一次)。 -
但关键在于那个
lambda函数被调用了 3.69 亿次! -
369218707 ... <lambda>和372023448 ... {method 'get' of 'dict' objects}。 -
罪魁祸首
找到这行代码
max(pair_counts, key=lambda x: (pair_counts[x], pair_strings.get(x, (b'', b''))))当pair 频次相同时,为了打破平局(Tie-breaking),再按 pair 的字典序排序,对于字典里的每一个 Pair,都调用了一次 pair_strings.get(x)。这在 3.69 亿次调用下,带来了巨大的累积开销 (约 63秒花在 get 上,118秒花在 lambda 本身逻辑上)。
2. 回答作业问题 (b)
(b) Profile your code. What part of the tokenizer training process takes the most time?
中文: "性能分析显示,预分词 (pre-tokenization) 步骤 是最耗时的部分,约占总运行时间的 63% (460秒),这是由于单线程正则处理大量语料造成的。第二大的瓶颈是合并循环中的 max 操作 (265秒),主要是因为在处理平局的 lambda 函数中频繁进行字典查找 (pair_strings.get) 带来的开销。
" 英文回答: "The profiling results indicate that the pre-tokenization step is the most time-consuming part, accounting for approximately 63% of the total runtime (460s) due to the single-threaded regex processing of the large corpus. The second largest bottleneck is the max operation in the merge loop (265s), specifically caused by the overhead of dictionary lookups (pair_strings.get) inside the tie-breaking lambda function."
3. (可选但推荐) 冲击 "2分钟" 目标:代码优化
虽然现在的 12 分钟已经远低于作业要求的 30 分钟,但如果想体验一下极致优化的快感(以及满足 Hint 里的 2 分钟目标),需要做两件事:
第一步:优化 max 的 Tie-breaking (极速修正)
这个只需要修改一行代码,我就先做了,结果翻车了。。。。
在 max 里做这种复杂的 get 查找太慢了。我们可以利用 Python 元组比较的特性,直接比较 pair 本身(它是 int tuple,比如 (12, 34)),这比查字典找 bytes 快得多。
修改 train_bpe_optimize.py 中的这一行:
# 原来的代码 (慢)
# merge_pair = max(pair_counts, key=lambda x: (pair_counts[x], pair_strings.get(x, (b'', b''))))
# 修改后的代码 (快)
# 解释:如果频率一样,Python 会自动比较 key 本身 (id_1, id_2)。
# 这种比较是 C 语言层面的,极快,且结果是确定的。
merge_pair = max(pair_counts, key=lambda x: (pair_counts[x], x))profiling 结果:
List reduced from 251 to 10 due to restriction <10>
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
1 0.029 0.029 713.010 713.010 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/scripts/train_bpe_tinystories.py:51(run_training)
1 0.355 0.355 712.921 712.921 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/cs336_basics/train_bpe_optimize.py:18(train)
1 364.844 364.844 452.898 452.898 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/cs336_basics/train_bpe_optimize.py:205(_pretokenize)
9746/9745 83.417 0.009 255.732 0.026 {built-in method builtins.max}
369218707 114.033 0.000 172.315 0.000 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/cs336_basics/train_bpe_optimize.py:52(<lambda>)
372023448 58.602 0.000 58.602 0.000 {method 'get' of 'dict' objects}
536592168 44.608 0.000 44.608 0.000 {method 'group' of '_regex.Match' objects}
2761194 2.350 0.000 35.984 0.000 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/regex/regex.py:340(finditer)
2804690 8.114 0.000 33.361 0.000 /home/fdq/cources/cs336/assignment1-basics/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/regex/regex.py:449(_compile)
2761196 3.020 0.000 11.858 0.000 /home/fdq/.local/share/uv/python/cpython-3.11.12-linux-x86_64-gnu/lib/python3.11/locale.py:679(getpreferredencoding)但是,我修改了之后并没有改善,而且从 profiling 看,还在调用 dict.get,改动没有生效????我打算暂时放过这里,把经历放在 pretokenize 的多进程上,这是assignment 的建议。
接下来我把重点放在使用 multiprocessing 实现 pretokenize上。