文章目录

前言
博主介绍:✌目前全网粉丝4W+,csdn博客专家、Java领域优质创作者,博客之星、阿里云平台优质作者、专注于Java后端技术领域。
涵盖技术内容:Java后端、大数据、算法、分布式微服务、中间件、前端、运维等。
博主所有博客文件目录索引:博客目录索引(持续更新)
CSDN搜索:长路
视频平台:b站-Coder长路
学习引由
我司的代码中包含了RetryUtil.executeWithRetry()重试工具类的操作特来进行梳理学习。
认识重试工具类
我司主要是使用的其中的同步重试比较多:
java
//同步重试
RetryUtil.executeWithRetry(() -> {
//xxx
return null;
}, 3, 200, false);效果:主要是在出现异常的时候进行重试处理,针对比如特殊场景如网络抖动、超时情况会进行使用重试工具类。
完整工具类
完整类源码
java
package com.changlu;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
@author changlu
@description 重试工具类,来源:datax
@date 3/26/2024 11:53 AM
*/
public class RetryUtil {
// private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RetryUtil.class);
private static final long MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND = 256 * 1000;//大约256秒
/**
* 重试次数工具方法.
*
* @param callable 实际逻辑
* @param retryTimes 最大重试次数(>1)
* @param sleepTimeInMilliSecond 运行失败后休眠对应时间再重试
* @param exponential 休眠时间是否指数递增
* @param <T> 返回值类型
* @return 经过重试的callable的执行结果
*/
public static <T> T executeWithRetry(Callable<T> callable,
int retryTimes,
long sleepTimeInMilliSecond,
boolean exponential) throws Exception {
Retry retry = new Retry();
return retry.doRetry(callable, retryTimes, sleepTimeInMilliSecond, exponential, null);
}
/**
* 重试次数工具方法.
*
* @param callable 实际逻辑
* @param retryTimes 最大重试次数(>1)
* @param sleepTimeInMilliSecond 运行失败后休眠对应时间再重试
* @param exponential 休眠时间是否指数递增
* @param <T> 返回值类型
* @param retryExceptionClasss 出现指定的异常类型时才进行重试
* @return 经过重试的callable的执行结果
*/
public static <T> T executeWithRetry(Callable<T> callable,
int retryTimes,
long sleepTimeInMilliSecond,
boolean exponential,
List<Class<?>> retryExceptionClasss) throws Exception {
Retry retry = new Retry();
return retry.doRetry(callable, retryTimes, sleepTimeInMilliSecond, exponential, retryExceptionClasss);
}
/**
* 在外部线程执行并且重试。每次执行需要在timeoutMs内执行完,不然视为失败。
* 执行异步操作的线程池从外部传入,线程池的共享粒度由外部控制。比如,HttpClientUtil共享一个线程池。
* <p/>
* 限制条件:仅仅能够在阻塞的时候interrupt线程
*
* @param callable 实际逻辑
* @param retryTimes 最大重试次数(>1)
* @param sleepTimeInMilliSecond 运行失败后休眠对应时间再重试
* @param exponential 休眠时间是否指数递增
* @param timeoutMs callable执行超时时间,毫秒
* @param executor 执行异步操作的线程池
* @param <T> 返回值类型
* @return 经过重试的callable的执行结果
*/
public static <T> T asyncExecuteWithRetry(Callable<T> callable,
int retryTimes,
long sleepTimeInMilliSecond,
boolean exponential,
long timeoutMs,
ThreadPoolExecutor executor) throws Exception {
Retry retry = new AsyncRetry(timeoutMs, executor);
return retry.doRetry(callable, retryTimes, sleepTimeInMilliSecond, exponential, null);
}
private static class Retry {
public <T> T doRetry(Callable<T> callable, int retryTimes, long sleepTimeInMilliSecond, boolean exponential, List<Class<?>> retryExceptionClasss)
throws Exception {
// 参数校验
if (null == callable) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("系统编程错误, 入参callable不能为空 ! ");
}
//重试次数不能<1
if (retryTimes < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"系统编程错误, 入参retrytime[%d]不能小于1 !", retryTimes));
}
//异常临时存储
Exception saveException = null;
for (int i = 0; i < retryTimes; i++) {
try {
// 执行方法调用
return call(callable);
} catch (Exception e) {
saveException = e;
if (i == 0) {
// LOG.error(String.format("Exception when calling callable, 异常Msg:%s", saveException.getMessage()), saveException);
}
// 如果指定了对应的异常类,则判断当前e是否是多个异常类中的一个,是的话则执行重试,否则直接抛出异常
if (null != retryExceptionClasss && !retryExceptionClasss.isEmpty()) {
boolean needRetry = false;
//若是符合提前设定好的异常,那么进行重试,若是其他异常则直接抛出异常
for (Class<?> eachExceptionClass : retryExceptionClasss) {
if (eachExceptionClass == e.getClass()) {
needRetry = true;
break;
}
}
if (!needRetry) {
throw saveException;
}
}
// 没有执行异常类,表示一旦有异常就会开始走重试逻辑
// 不超过最大重试次数则执行后续重试逻辑(且在提前预定的异常中)
if (i + 1 < retryTimes && sleepTimeInMilliSecond > 0) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 根据入参决定休息多久之后执行重试逻辑,最大不超过MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND
long timeToSleep;
if (exponential) {
//指数级上升重试逻辑沉睡时长
timeToSleep = sleepTimeInMilliSecond * (long) Math.pow(2, i);
if (timeToSleep >= MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND) {
timeToSleep = MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND;
}
} else {
//正常设定沉睡时长
timeToSleep = sleepTimeInMilliSecond;
if (timeToSleep >= MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND) {
timeToSleep = MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND;
}
}
try {
// 当前执行线程沉睡
Thread.sleep(timeToSleep);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
long realTimeSleep = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
// LOG.error(String.format("Exception when calling callable, 即将尝试执行第%s次重试.本次重试计划等待[%s]ms,实际等待[%s]ms, 异常Msg:[%s]",
// i+1, timeToSleep,realTimeSleep, e.getMessage()));
}
}
}
throw saveException;
}
protected <T> T call(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
//执行任务执行器
return callable.call();
}
}
// 直接继承了Retry类
private static class AsyncRetry extends Retry {
private long timeoutMs;//方法超时时长
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;//多增加一个线程池
public AsyncRetry(long timeoutMs, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
this.timeoutMs = timeoutMs;
this.executor = executor;
}
/**
* 使用传入的线程池异步执行任务,并且等待。
* <p/>
* future.get()方法,等待指定的毫秒数。如果任务在超时时间内结束,则正常返回。
* 如果抛异常(可能是执行超时、执行异常、被其他线程cancel或interrupt),都记录日志并且网上抛异常。
* 正常和非正常的情况都会判断任务是否结束,如果没有结束,则cancel任务。cancel参数为true,表示即使
* 任务正在执行,也会interrupt线程。
*
* @param callable
* @param <T>
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected <T> T call(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
// 重写后的call()方法,在执行重试时,直接交由Executor执行,避免了当前线程被阻塞
Future<T> future = executor.submit(callable);
try {
// 在规定时间内获取执行结果
return future.get(timeoutMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 规定时间内没有获取到结果则直接抛出异常
// LOG.warn("Try once failed", e);
throw e;
} finally {
if (!future.isDone()) {
future.cancel(true);
// LOG.warn("Try once task not done, cancel it, active count: " + executor.getActiveCount());
}
}
}
}
}拆解分析
内部类Retry(同步重试)
该类表示的是同步重试类,在这个同步重试类中包含有一个doRetry、call方法。
一个重试方法doRetry需要传递哪些参数呢?
- callable:自定义的带有返回值的回调函数,可抛出异常。
- retryTimes:重试次数。
- sleepTimeInMilliSecond:重试之间的间隔阻塞时间。
- exponential:重试时间是否指数级增长。
- retryExceptionClasss:指定异常集合,若是指明集合那么只有在规定范围中的异常才可重试;若是传null或者集合为空,则任务异常都进行重试。
对于其中的call方法就是执行下callable的回调函数。
java
private static class Retry {
public <T> T doRetry(Callable<T> callable, int retryTimes, long sleepTimeInMilliSecond, boolean exponential, List<Class<?>> retryExceptionClasss)
throws Exception {
// 参数校验
if (null == callable) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("系统编程错误, 入参callable不能为空 ! ");
}
//重试次数不能<1
if (retryTimes < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"系统编程错误, 入参retrytime[%d]不能小于1 !", retryTimes));
}
//异常临时存储
Exception saveException = null;
for (int i = 0; i < retryTimes; i++) {
try {
// 执行方法调用
return call(callable);
} catch (Exception e) {
saveException = e;
if (i == 0) {
// LOG.error(String.format("Exception when calling callable, 异常Msg:%s", saveException.getMessage()), saveException);
}
// 如果指定了对应的异常类,则判断当前e是否是多个异常类中的一个,是的话则执行重试,否则直接抛出异常
if (null != retryExceptionClasss && !retryExceptionClasss.isEmpty()) {
boolean needRetry = false;
//若是符合提前设定好的异常,那么进行重试,若是其他异常则直接抛出异常
for (Class<?> eachExceptionClass : retryExceptionClasss) {
if (eachExceptionClass == e.getClass()) {
needRetry = true;
break;
}
}
if (!needRetry) {
throw saveException;
}
}
// 没有执行异常类,表示一旦有异常就会开始走重试逻辑
// 不超过最大重试次数则执行后续重试逻辑(且在提前预定的异常中)
if (i + 1 < retryTimes && sleepTimeInMilliSecond > 0) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 根据入参决定休息多久之后执行重试逻辑,最大不超过MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND
long timeToSleep;
if (exponential) {
//指数级上升重试逻辑沉睡时长
timeToSleep = sleepTimeInMilliSecond * (long) Math.pow(2, i);
if (timeToSleep >= MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND) {
timeToSleep = MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND;
}
} else {
//正常设定沉睡时长
timeToSleep = sleepTimeInMilliSecond;
if (timeToSleep >= MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND) {
timeToSleep = MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND;
}
}
try {
// 当前执行线程沉睡
Thread.sleep(timeToSleep);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
long realTimeSleep = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
// LOG.error(String.format("Exception when calling callable, 即将尝试执行第%s次重试.本次重试计划等待[%s]ms,实际等待[%s]ms, 异常Msg:[%s]",
// i+1, timeToSleep,realTimeSleep, e.getMessage()));
}
}
}
throw saveException;
}
protected <T> T call(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
//执行任务执行器
return callable.call();
}
}内部类AsyncRetry(异步重试,控制任务执行时间)
AsyncRetry继承了Retry重试方法,那么对于doRetry的逻辑是相同的。
不同点:多增加了两个参数以及重写了call方法。
- 两个参数分别是:①timeoutMs一个方法超时时长(会对方法执行时间有所限制)。②executor传入线程池,后续callable会丢入到线程池中执行,之后通过得到future来控制方法的执行超时时间。
- call方法:实际也是一个同步操作,这里使用get会阻塞住,若是任务执行较长也会在固定时间内超时结束。
java
// 直接继承了Retry类
private static class AsyncRetry extends Retry {
private long timeoutMs;//方法超时时长
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;//多增加一个线程池
public AsyncRetry(long timeoutMs, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
this.timeoutMs = timeoutMs;
this.executor = executor;
}
/**
* 使用传入的线程池异步执行任务,并且等待。
* <p/>
* future.get()方法,等待指定的毫秒数。如果任务在超时时间内结束,则正常返回。
* 如果抛异常(可能是执行超时、执行异常、被其他线程cancel或interrupt),都记录日志并且网上抛异常。
* 正常和非正常的情况都会判断任务是否结束,如果没有结束,则cancel任务。cancel参数为true,表示即使
* 任务正在执行,也会interrupt线程。
*
* @param callable
* @param <T>
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected <T> T call(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
// 重写后的call()方法,在执行重试时,直接交由Executor执行,避免了当前线程被阻塞
Future<T> future = executor.submit(callable);
try {
// 在规定时间内获取执行结果
return future.get(timeoutMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 规定时间内没有获取到结果则直接抛出异常
// LOG.warn("Try once failed", e);
throw e;
} finally {
if (!future.isDone()) {
future.cancel(true);
// LOG.warn("Try once task not done, cancel it, active count: " + executor.getActiveCount());
}
}
}
}基于两个内部类对外封装的工具方法
主要包含三个对外方法:
- executeWithRetry:同步重试,出现任何异常则执行重试操作,重试指定次数,每次重试间隔指定时长。
- executeWithRetry【多传一个异常集合】:同步重试,出现的异常只有在指定集合异常中重试,重试指定次数,每次重试间隔指定时长。
- asyncExecuteWithRetry:异步重试,在同步重试基础上增加了任务超时时间以及可指定线程池来进行处理,对于重试逻辑与同步重试大致相同,不同点就是线程池中提交任务以及控制任务执行时间。
java
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
@author changlu
@description 重试工具类,来源:datax
@date 3/26/2024 11:53 AM
*/
public class RetryUtil {
// private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RetryUtil.class);
private static final long MAX_SLEEP_MILLISECOND = 256 * 1000;//大约256秒
/**
* 重试次数工具方法.
*
* @param callable 实际逻辑
* @param retryTimes 最大重试次数(>1)
* @param sleepTimeInMilliSecond 运行失败后休眠对应时间再重试
* @param exponential 休眠时间是否指数递增
* @param <T> 返回值类型
* @return 经过重试的callable的执行结果
*/
public static <T> T executeWithRetry(Callable<T> callable,
int retryTimes,
long sleepTimeInMilliSecond,
boolean exponential) throws Exception {
Retry retry = new Retry();
return retry.doRetry(callable, retryTimes, sleepTimeInMilliSecond, exponential, null);
}
/**
* 重试次数工具方法.
*
* @param callable 实际逻辑
* @param retryTimes 最大重试次数(>1)
* @param sleepTimeInMilliSecond 运行失败后休眠对应时间再重试
* @param exponential 休眠时间是否指数递增
* @param <T> 返回值类型
* @param retryExceptionClasss 出现指定的异常类型时才进行重试
* @return 经过重试的callable的执行结果
*/
public static <T> T executeWithRetry(Callable<T> callable,
int retryTimes,
long sleepTimeInMilliSecond,
boolean exponential,
List<Class<?>> retryExceptionClasss) throws Exception {
Retry retry = new Retry();
return retry.doRetry(callable, retryTimes, sleepTimeInMilliSecond, exponential, retryExceptionClasss);
}
/**
* 在外部线程执行并且重试。每次执行需要在timeoutMs内执行完,不然视为失败。
* 执行异步操作的线程池从外部传入,线程池的共享粒度由外部控制。比如,HttpClientUtil共享一个线程池。
* <p/>
* 限制条件:仅仅能够在阻塞的时候interrupt线程
*
* @param callable 实际逻辑
* @param retryTimes 最大重试次数(>1)
* @param sleepTimeInMilliSecond 运行失败后休眠对应时间再重试
* @param exponential 休眠时间是否指数递增
* @param timeoutMs callable执行超时时间,毫秒
* @param executor 执行异步操作的线程池
* @param <T> 返回值类型
* @return 经过重试的callable的执行结果
*/
public static <T> T asyncExecuteWithRetry(Callable<T> callable,
int retryTimes,
long sleepTimeInMilliSecond,
boolean exponential,
long timeoutMs,
ThreadPoolExecutor executor) throws Exception {
Retry retry = new AsyncRetry(timeoutMs, executor);
return retry.doRetry(callable, retryTimes, sleepTimeInMilliSecond, exponential, null);
}
}测试demo
由于同步异常重试使用较多,这里给出同步异常重试(所有异常都重试)的demo案例:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//同步重试
RetryUtil.executeWithRetry(() -> {
//随机数来模拟失败异常场景
Random random = new Random();
int randomNumber = random.nextInt(4); // 生成一个0到3的随机整数
if (randomNumber < 2) {
System.out.println("成功处理!random随机数为:" + randomNumber);
}else {
System.out.println("处理失败!random随机数为:" + randomNumber);
throw new RuntimeException("运行失败");
}
return null;
}, 3, 1000, false);
}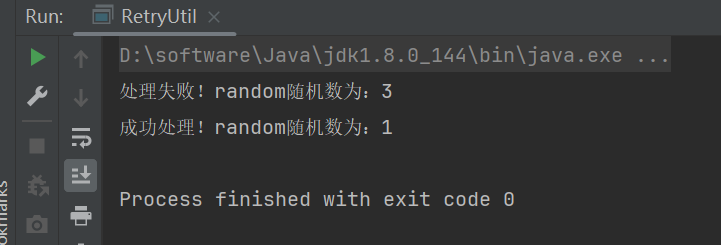
可以看到出现异常的时候,进行了重试。
说明:对于实际情况,选择相应的重试方法,根据具体场景来进行选择。
参考文档
1\]. [Datax之自定义重试工具类RetryUtil](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26323323/article/details/121274075):介绍了Datax中的重试工具类用法 ## 资料获取 大家点赞、收藏、关注、评论啦\~ 精彩专栏推荐订阅:在下方专栏👇🏻 * [长路-文章目录汇总(算法、后端Java、前端、运维技术导航)](https://blog.csdn.net/cl939974883/category_11568291.html?spm=1001.2014.3001.5482):博主所有博客导航索引汇总 * [开源项目Studio-Vue---校园工作室管理系统(含前后台,SpringBoot+Vue)](https://changlu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125295334):博主个人独立项目,包含详细部署上线视频,已开源 * [学习与生活-专栏](https://blog.csdn.net/cl939974883/category_10700595.html):可以了解博主的学习历程 * [算法专栏](https://blog.csdn.net/cl939974883/category_11403550.html?spm=1001.2014.3001.5482):算法收录 更多博客与资料可查看👇🏻获取联系方式👇🏻,🍅文末获取开发资源及更多资源博客获取🍅