文章目录
IO流
字符流
字符流原理解析
- 创建字符输入流对象
底层::联文件,并创建缓冲区(长度为8192的字节数) - 读取数据
底层:
- 判断缓冲区中是否有数据可以读取
- 缓冲区没有数据:就从文件中获取数据,装到缓冲区中,每次尽可能装满缓冲区
如果文件中也没有数据了,返回-1 - 缓冲区有数据:就从缓冲区中读取
空参的read方法:一次读取一个字节,遇到中文一次读多个字节,把字节解码并转成十进制返回
有参的read方法:把读取字节,解码,强转三步合并了,强转之后的字符放到数组中
flush和close方法
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public void flush() |
将缓冲区中的数据,刷新到本地文件中 |
public void close() |
释放资源/关流 |
文件拷贝代码
java
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File src = new File("E:\\文件练习JAVA嘿嘿嘿");
File dest = new File("E:\\拷贝后的地址");
copydir(src, dest);
}
private static void copydir(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
dest.mkdirs();
File[] files = src.listFiles();
for(File file : files){
if(file.isFile()) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, file.getName()));
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
else {
copydir(file, new File(dest, file.getName()));
}
}
}
}文件加密解密
java
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\111\\哈哈\\4月27日 日报.pdf");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\111\\哈哈\\copy_4月27日 日报.pdf");
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b ^ 2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}修改文件中的数据
java
//1
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {
sb.append((char) ch);
}
fr.close();
System.out.println(sb);
String str = sb.toString();
String[] arrStr = str.split("-");
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(String s : arrStr) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(s);
list.add(i);
}
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("a.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(i == list.size() - 1)
fw.write(list.get(i) + "");
else
fw.write(list.get(i) + "-");
}
fw.close();
}
}
//2
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {
sb.append((char) ch);
}
fr.close();
Integer[] array = Arrays.stream(sb.toString()
.split("-"))
.map(new Function<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
})
.sorted()
.toArray(new IntFunction<Integer[]>() {
@Override
public Integer[] apply(int value) {
return new Integer[value];
}
});
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("a.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(i == array.length - 1)
fw.write(array[i] + "");
else
fw.write(array[i] + "-");
}
fw.close();
}
}缓冲流
字节缓冲流
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream is) |
把基本流包装成高级流,提高读取数据的性能 |
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream os) |
把基本流包装成高级流,提高写出数据的性能 |
原理 :底层自带了长度为8192的缓冲区提高性能
字符缓冲流
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public BufferedReader(Reader r) |
把基本流变成高级流 |
public BufferedWriter(Writer w) |
把基本流变成高级流 |
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public String readLine() |
读取一行数据,如果没有数据可读了,会返回 null |
public void newLine() |
跨平台的换行 |
例题
只能使用三次的程序
java
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
String s = br.readLine();
br.close();
System.out.println(s);
int count = Integer.parseInt(s);
count++;
if(count <= 3){
System.out.println("第" + count + "免费试用~~~");
}
else {
System.out.println("使用结束啦,请充值会员继续使用~~");
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt"));
bw.write(count + "");
bw.close();
}
}转换流
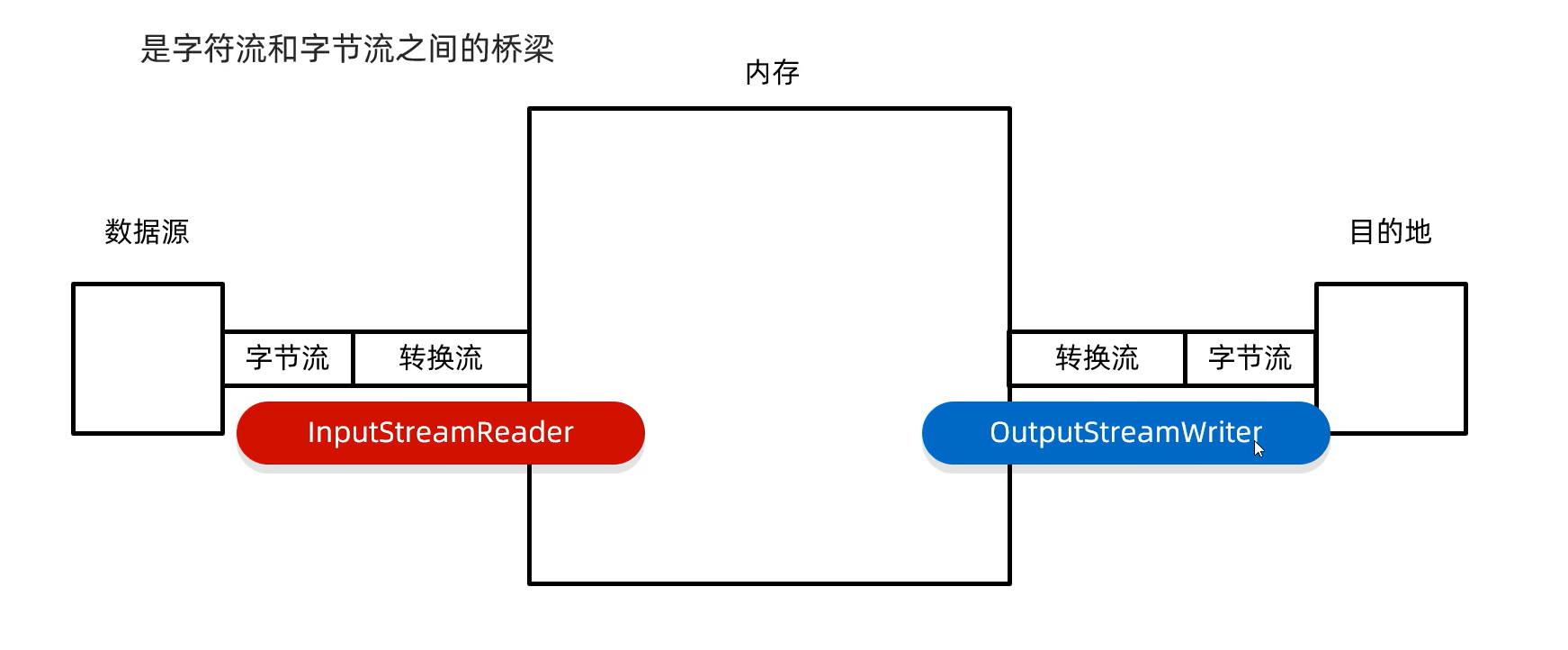
作用1 :指定字符集读写
作用2 :字节流想要使用字符流中的方法
java
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt", Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read())!= -1)
System.out.print((char)ch);
fr.close();
}
}字符转换输入流 :InputStreamReader
字符转换输出流:0utputStreamWriter
序列化流
可以把Java中的对象写到本地文件中
序列化流/对象操作输出流
一、构造方法
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public ObjectOutputStream(0utputStream out) |
把基本流包装成高级流 |
二、成员方法
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public final void writeObject(Object obj) |
把对象序列化(写出)到文件中去 |
java
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Student stu = new Student("xiaodu", 18);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));
oos.writeObject(stu);
oos.close();
}
}使用对象输出流将对象保存到文件时会出现NotserializableException异常
解决方案:需要让Javabean类实现Serializable接口
java
public class Student implements Serializable{}反序列化流
一、构造方法
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) |
把基本流变成高级流 |
|---|
二、成员方法
public Object readObject() |
把序列化到本地文件中的对象,读取到程序中来。 |
|---|
java
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
}
}transient关键字:该关键字标记的成员不参与序列化过程。
序列化流/反序列化流的细节汇总
- 使用序列化流将对象写到文件时,需要让Javabean类实现Serializable接口。
否则,会出现NotSerializableException异常 - 序列化流写到文件中的数据是不能修改的,一旦修改就无法再次读回来了
打印流
分类 :打印流一般是指:PrintStream,PrintWriter两个类
特点1 :打印流只操作文件目的地,不操作数据源
特点2 :特有的写出方法可以实现,数据原样写出
例如 : 打印:97------文件中:97
打印:true------文件中:true
特点3 :特有的写出方法,可以实现自动刷新,自动换行
打印一次数据 = 写出 + 换行 + 刷新
字节打印流
一、构造方法
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public PrintStream(OutputStream/File/String) |
关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
public PrintStream(String fileName, Charset charset) |
指定字符编码 |
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) |
自动刷新 |
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) |
指定字符编码且自动刷新 |
二、成员方法
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public void write(int b) |
常规方法: 将指定的字节写出 |
public void println(Xxx xx) |
特有方法: 打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行 |
public void print(Xxx xx) |
特有方法: 打印任意数据,不换行 |
public void printf(String format, Object... args) |
特有方法: 带有占位符的打印语句,不换行 |
java
public class demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"), true, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
ps.println(97);
ps.println(true);
ps.println("嘿嘿嘿");
ps.close();
}
}字符打印流
一、构造方法
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public PrintWriter(Writer/File/String) |
关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
public PrintWriter(String fileName, Charset charset) |
指定字符编码 |
public PrintWriter(Writer w, boolean autoFlush) |
自动刷新 |
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, Charset charset) |
指定字符编码且自动刷新 |
二、成员方法
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public void write(...) |
常规方法: 规则跟之前一样,写出字节或者字符串 |
public void println(Xxx xx) |
特有方法: 打印任意类型的数据并且换行 |
public void print(Xxx xx) |
特有方法: 打印任意类型的数据,不换行 |
public void printf(String format, Object... args) |
特有方法: 带有占位符的打印语句 |
java
public class demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt"), true);
pw.println(111);
pw.println(222);
pw.println(333);
pw.close();
}
}解压缩流
java
public class demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File src = new File("E:\\aaa.zip");
File dest = new File("E:\\");
unzip(src, dest);
}
private static void unzip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
ZipEntry entry;
while((entry = zip.getNextEntry()) != null) {
if(entry.isDirectory()) {
File file = new File(dest, entry.toString());
file.mkdirs();
}
else {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, entry.toString()));
int b;
while ((b = zip.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
zip.closeEntry();
}
}
zip.close();
}
}压缩流
java
public class ZipStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 源文件路径
File src =new File("E:\\TestCode\\testFile.txt");
// 压缩文件存储路径
File dest =new File("E:\\TestCode");
// 执行文件压缩
toZip(src, dest);
}
private static void toZip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
// 创建压缩输出流
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, "testFile.zip")));
// 创建一个zip文件实体并添加到压缩流中
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(src.getName());
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
// 读取源文件并写入压缩流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
zos.write(b);
}
// 关闭当前zip条目并压缩流
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
}Commons-io
Commons-io是apache开源基金组织提供的一组有关io操作的开源工具包

- 在项目中创建一个文件夹:lib
- 将jar包复制粘贴到lib文件夹
- 右键点击jar包,选择 Add as Library ->点击OK
- 在类中导包使用
常见方法
| FileUtils类(文件/文件夹相关) | 说明 |
|---|---|
static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile) |
复制文件 |
static void copyDirectory(File srcDir, File destDir) |
复制文件夹 |
static void copyDirectoryToDirectory(File srcDir, File destDir) |
复制文件夹 |
static void deleteDirectory(File directory) |
删除文件夹 |
static void cleanDirectory(File directory) |
清空文件夹 |
static String readFileToString(File file, Charset encoding) |
读取文件中的数据变成成字符串 |
static void write(File file, CharSequence data, String encoding) |
写出数据 |
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public static int copy(InputStream input, OutputStream output) |
复制文件 |
public static int copyLarge(Reader input, Writer output) |
复制大文件 |
public static String readLines(Reader input) |
读取数据 |
public static void write(String data, OutputStream output) |
写出数据 |
Hutool工具包
| 相关类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
IoUtil |
流操作工具类 |
FileUtil |
文件读写和操作的工具类 |
FileTypeUtil |
文件类型判断工具类 |
WatchMonitor |
目录、文件监听 |
ClassPathResource |
针对ClassPath中资源的访问封装 |
FileReader |
封装文件读取 |
FileWriter |
封装文件写入 |
多线程
线程是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。
并发和并行
并发:在同一时刻,有多个指令在单个CPU上交替执行
并行:在同一时刻,有多个指令在多个CPU上同时执行
实现方式
-
继承Thread类的方式进行实现
- 自己定义一个类继承Thread
- 重写run方法
- 创建子类的对象,并启动线程
javapublic class demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread t1 = new MyThread(); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(); t1.setName("现成1"); t2.setName("现成2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } public class MyThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println(getName() + "HelloWorld"); } } } -
实现Runnable接口的方式进行实现
- 自己定义一个类实现Runnable接口
- 重写里面的run方法
- 创建自己的类的对象
- 创建一个Thread类的对象,并开启线程
javapublic class demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { myRun mr = new myRun(); Thread t1 = new Thread(mr); Thread t2 = new Thread(mr); t1.setName("现成1"); t2.setName("现成2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } public class myRun implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "HelloWorld"); } } } -
利用Callable接口和Future接口方式实现(可以获取到多线程运行的结果)
-
创建一个类MyCallable实现Callable接口
-
重写ca11(是有返回值的,表示多线程运行的结果)
-
创建MyCa1lable的对象)表示多线程要执行的任务)
-
创建FutureTask的对象(作用管理多线程运行的结果)
-
创建Thread类的对象,并启动(表示线程)
javapublic class demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { MyCallable mc = new MyCallable(); FutureTask<Integer> ft = new FutureTask<>(mc); Thread t1 = new Thread(ft); t1.start(); Integer result = ft.get(); System.out.println(result); } } public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; } }
对比

-
成员方法
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
String getName() |
返回此线程的名称 |
void setName(String name) |
设置线程的名字(构造方法也可以设置名字) |
static Thread currentThread() |
获取当前线程的对象 |
static void sleep(long time) |
让线程休眠指定的时间,单位为毫秒 |
setPriority(int newPriority) |
设置线程的优先级 |
final int getPriority() |
获取线程的优先级 |
final void setDaemon(boolean on) |
设置为守护线程 |
public static void yield() |
出让线程/礼让线程 |
public static void join() |
插入线程/插队线程 |
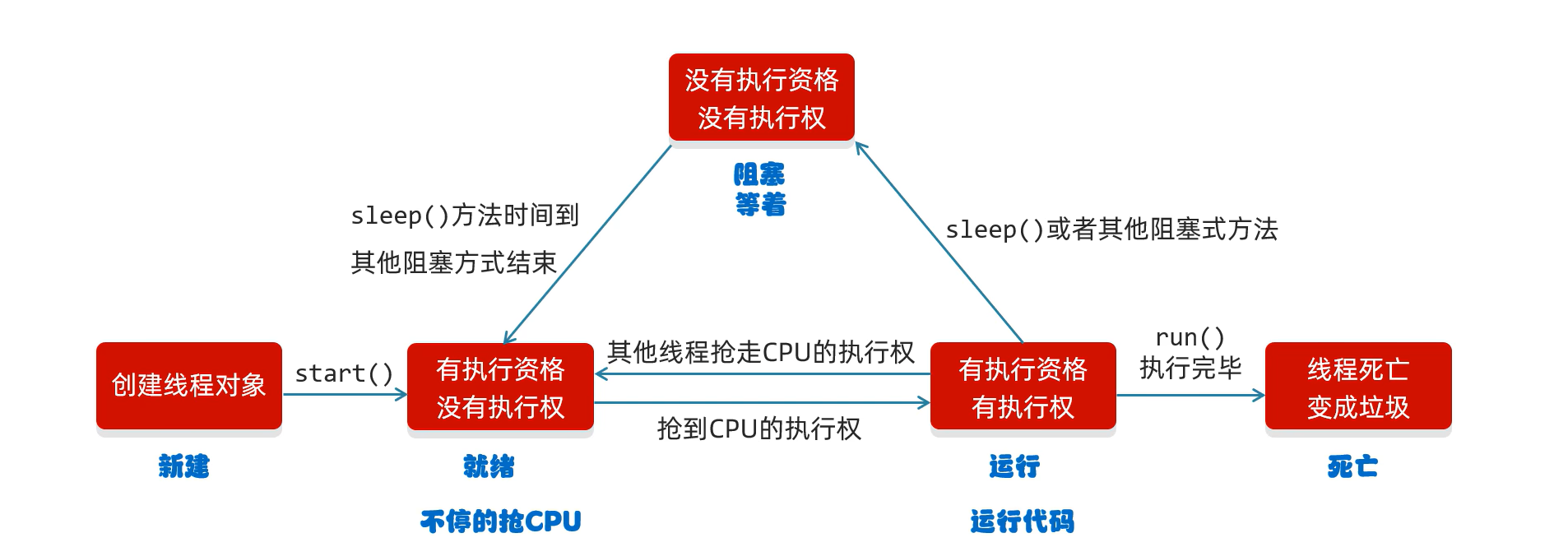
生命周期
同步代码块
格式
java
synchronized{
}特点1:锁默认打开,有一个线程进去了,锁自动关闭
特点2:里面的代码全部执行完毕,线程出来,锁自动打开
java
public class MyThread1 extends Thread{
static int ticket = 0;
static Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (obj) {
if(ticket < 100) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName() + "正在卖" + ticket + "票!!!");
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 t1 = new MyThread1();
MyThread1 t2 = new MyThread1();
t1.setName("111");
t2.setName("222");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}同步方法
就是把synchronized关键字加到方法上
特点1: 同步方法是锁住方法里面所有的代码
特点2:锁对象不能自己指定
非静态:this
静态:当前类的字节码文件对象
java
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
int ticket = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
if(method())
break;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
private synchronized boolean method() throws InterruptedException {
if(ticket == 100)
return true;
else{
Thread.sleep(10);
ticket++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "@" + ticket);
}
return false;
}
}
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable mr = new MyRunnable();
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr);
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr);
Thread t3 = new Thread(mr);
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}Lock锁
虽然我们可以理解同步代码块和同步方法的锁对象问题
但是我们并没有直接看到在哪里加上了锁,在哪里释放了锁
为了更清晰的表达如何加锁和释放锁,JDK5以后提供了一个新的锁对象Lock
Lock实现提供比使用synchronized方法和语句可以获得更广泛的锁定操作
Lock中提供了获得锁和释放锁的方法
void lock():获得锁
void unlock():释放锁
手动上锁、手动释放锁
Lock是接口不能直接实例化,这里采用它的实现类ReentrantLock来实例化
ReentrantLock的构造方法
ReentrantLock():创建一个ReentrantLock的实例
java
public class LockExample {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomething() {
lock.lock(); // 手动上锁
try {
// 访问或修改共享资源的代码
// ...
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 手动释放锁,确保在finally块中执行以处理异常
}
}
}等待唤醒机制(生产者和消费者)
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
void wait() |
当前线程等待,直到被其他线程唤醒 |
void notify() |
随机唤醒单个线程 |
void notifyAll() |
唤醒所有线程 |
已经到底啦!!