
Conference:International Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB)
CCF level:CCF A
Categories:Database/Data Mining/Content Retrieval
Year:2023
Num:8
1
Title:
FlexChain: An Elastic Disaggregated Blockchain
FlexChain:一个弹性的分解区块链
Authors:****

Abstract:****
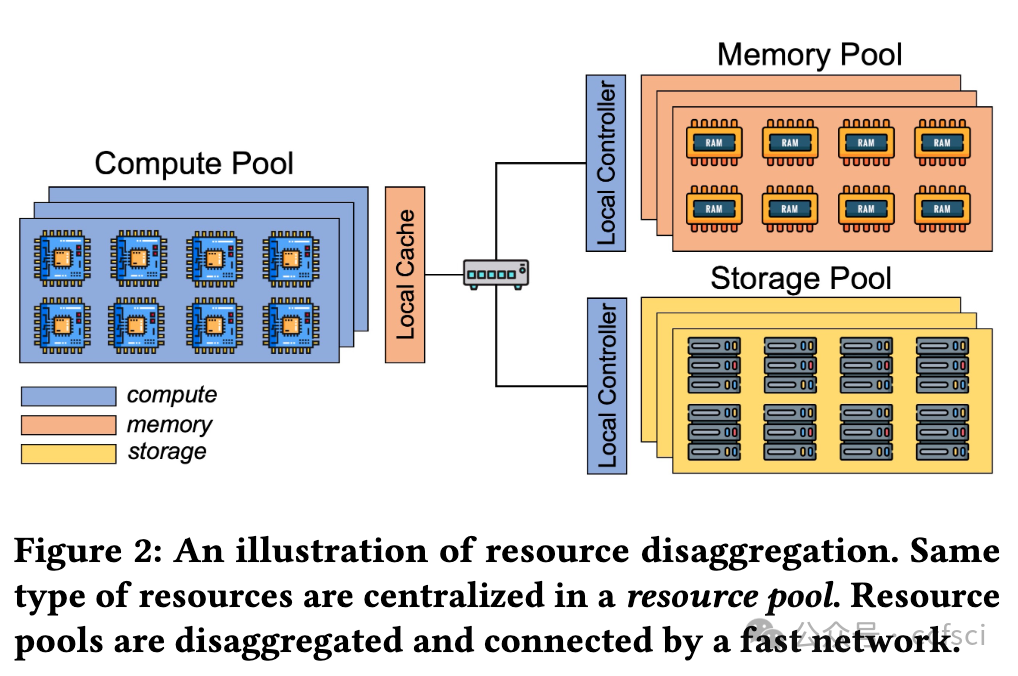
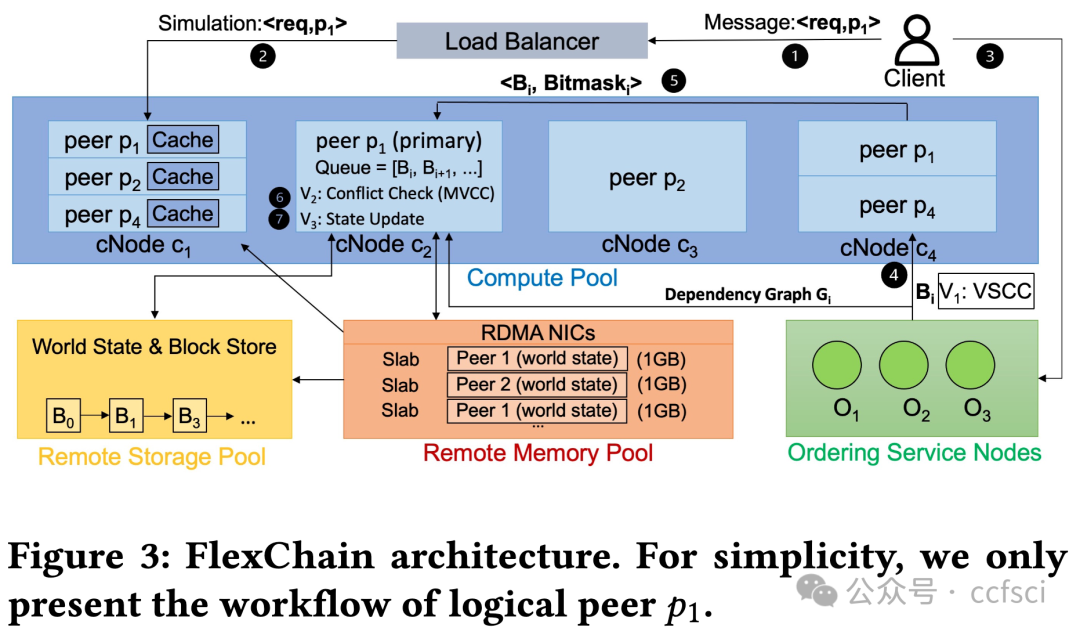
While permissioned blockchains enable a family of data center applications, existing systems suffer from imbalanced loads across compute and memory, exacerbating the underutilization of cloud resources. This paper presents FlexChain, a novel permissioned blockchain system that addresses this challenge by physically disaggregating CPUs, DRAM, and storage devices to process different blockchain workloads efficiently. Disaggregation allows blockchain service providers to upgrade and expand hardware resources independently to support a wide range of smart contracts with diverse CPU and memory demands. Moreover, it ensures efficient resource utilization and hence prevents resource fragmentation in a data center. We have explored the design of XOV blockchain systems in a disaggregated fashion and developed a tiered key-value store that can elastically scale its memory and storage. Our design significantly speeds up the execution stage. We have also leveraged several techniques to parallelize the validation stage in FlexChain to further improve the overall blockchain performance. Our evaluation results show that FlexChain can provide independent compute and memory scalability, while incurring at most 12.8% disaggregation overhead. FlexChain achieves almost identical throughput as the state-of-the-art distributed approaches with significantly lower memory and CPU consumption for compute-intensive and memory-intensive workloads respectively.
虽然许可区块链支持一系列数据中心应用,但现有系统存在计算和内存负载不平衡的问题,加剧了云资源利用率不足的问题。本文介绍的 FlexChain 是一种新型许可区块链系统,它通过物理分解 CPU、DRAM 和存储设备来高效处理不同的区块链工作负载,从而解决了这一难题。分解允许区块链服务提供商独立升级和扩展硬件资源,以支持各种对 CPU 和内存有不同需求的智能合约。此外,它还能确保资源的高效利用,从而防止数据中心的资源碎片化。我们探索了以分解方式设计 XOV 区块链系统,并开发了一种可弹性扩展内存和存储的分层键值存储。我们的设计大大加快了执行阶段的速度。我们还利用多种技术对 FlexChain 中的验证阶段进行并行化,以进一步提高区块链的整体性能。我们的评估结果表明,FlexChain 可以提供独立的计算和内存可扩展性,同时产生最多 12.8% 的分解开销。对于计算密集型和内存密集型工作负载,FlexChain 的吞吐量几乎与最先进的分布式方法相同,而内存和 CPU 消耗却分别显著降低。
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p23-wu.pdf
2
Title:
Privacy-preserving cooperative online matching over spatial crowdsourcing platforms
空间众包平台上的隐私保护合作的在线匹配
Authors:****

Abstract:****
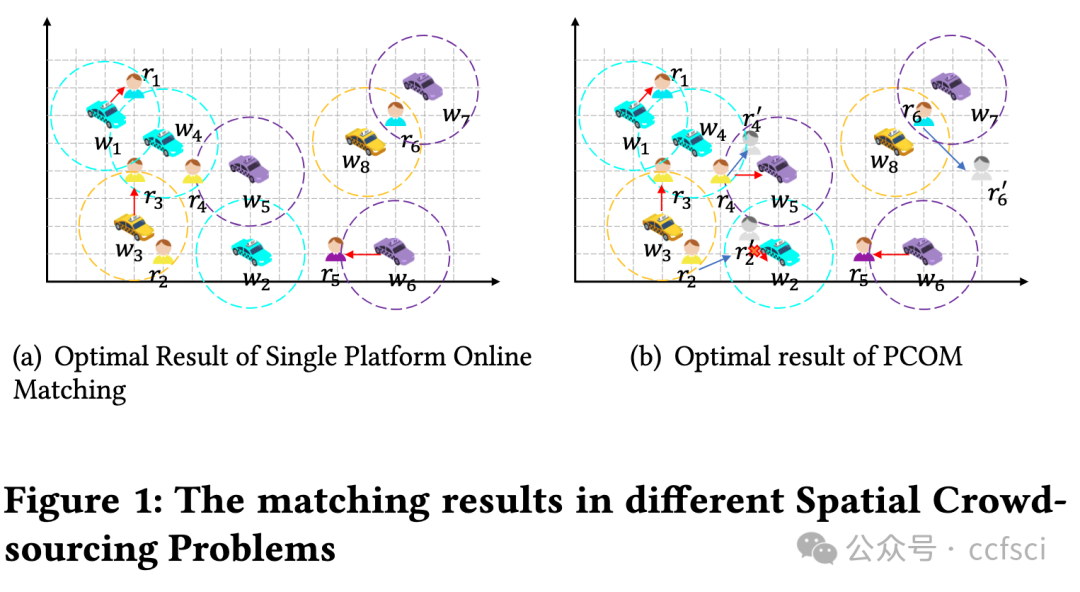
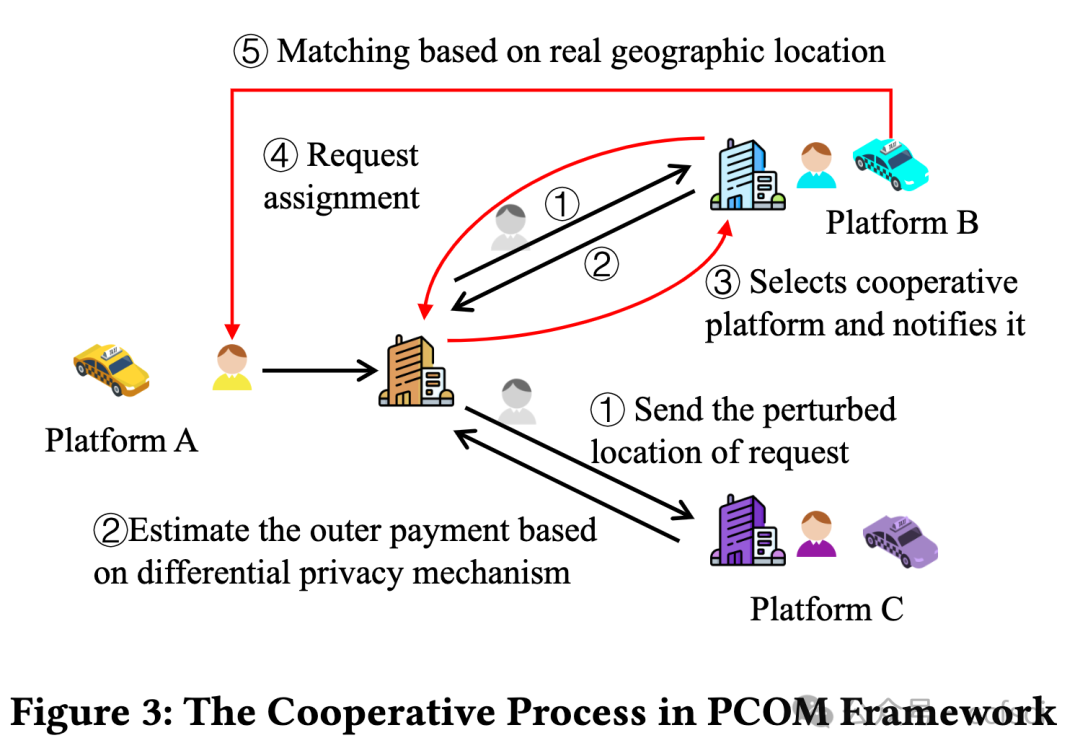
With the continuous development of spatial crowdsourcing platform, online task assignment problem has been widely studied as a typical problem in spatial crowdsourcing. Most of the existing studies are based on a single-platform task assignment to maximize the platform's revenue. Recently, cross online task assignment has been proposed, aiming at increasing the mutual benefit through cooperations. However, existing methods fail to consider the data privacy protection in the process of cooperation and cause the leakage of sensitive data such as the location of a request and the historical data of cooperative platforms. In this paper, we propose Privacy-preserving Cooperative Online Matching (PCOM), which protects the privacy of the users and workers on their respective platforms. We design a PCOM framework and provide theoretical proof that the framework satisfies the differential privacy property. We then propose two PCOM algorithms based on two different privacy-preserving strategies. Extensive experiments on real and synthetic datasets confirm the effectiveness and efficiency of our algorithms.
随着空间众包平台的不断发展,在线任务分配问题作为空间众包中的典型问题被广泛研究。现有研究大多基于单平台任务分配,以实现平台收益最大化。最近,有人提出了交叉在线任务分配,旨在通过合作增加互惠互利。然而,现有方法未能考虑合作过程中的数据隐私保护,导致请求位置和合作平台历史数据等敏感数据泄露。在本文中,我们提出了保护隐私的合作在线匹配(PCOM),它能保护用户和工作者在各自平台上的隐私。我们设计了一个 PCOM 框架,并提供了该框架满足差分隐私属性的理论证明。然后,我们基于两种不同的隐私保护策略提出了两种 PCOM 算法。在真实和合成数据集上进行的大量实验证实了我们算法的有效性和效率。

Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p51-yang.pdf
3
Title:
L2chain: Towards High-performance, Confidential and Secure Layer-2 Blockchain Solution for Decentralized Applications
L2chain: 面向去中心化应用的高性能、保密和安全的2 层区块链解决方案
Authors:****

Abstract:****
With the rapid development of blockchain, the concept of decentralized applications (DApps), built upon smart contracts, has attracted much attention in academia and industry. However, significant issues w.r.t. system throughput, transaction confidentiality, and the security guarantee of the DApp transaction execution and order correctness hinder the border adoption of blockchain DApps. To address these issues, we propose L2chain, a novel blockchain framework aiming to scale the system through a layer-2 network where DApps process transactions in the layer-2 network and only the system state digest, acting as the state integrity proof, is maintained on-chain. To achieve high performance, we introduce the split-execute-merge (SEM) transaction processing workflow with the help of the RSA accumulator, allowing DApps to lock and update a part of the state digest in parallel. We also design a witness cache mechanism for DApp executors to reduce the transaction processing latency. To fulfill confidentiality, we leverage the trusted execution environment (TEE) for DApps to execute encrypted transactions off-chain. To ensure transaction execution and order correctness, we propose a two-step execution process for DApps to prevent attacks (i.e., rollback attacks) from subverting the state transition. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that L2chain can achieve 1.5X to 42.2X and 7.1X to 8.9X throughput improvements in permissioned and permissionless settings respectively.Sharding is a prominent technique for scaling blockchains.
随着区块链的快速发展,建立在智能合约基础上的去中心化应用程序(DApps)的概念引起了学术界和产业界的广泛关注。然而,系统吞吐量、交易保密性以及 DApp 交易执行和顺序正确性的安全保证等重大问题阻碍了区块链 DApps 的边界应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了 L2chain,这是一种新型区块链框架,旨在通过二层网络扩展系统,其中 DApp 在二层网络中处理交易,只有系统状态摘要(作为状态完整性证明)在链上维护。为了实现高性能,我们在 RSA 累加器的帮助下引入了拆分-执行-合并(SEM)事务处理工作流,允许 DApps 锁定和并行更新状态摘要的一部分。我们还为 DApp 执行器设计了见证缓存机制,以减少事务处理延迟。为了实现保密性,我们利用 DApp 的可信执行环境 (TEE) 在链外执行加密交易。为确保交易执行和顺序的正确性,我们为 DApp 提出了两步执行流程,以防止攻击(即回滚攻击)破坏状态转换。大量实验证明,在有权限和无权限设置下,L2chain 的吞吐量可分别提高 1.5 倍至 42.2 倍和 7.1 倍至 8.9 倍。

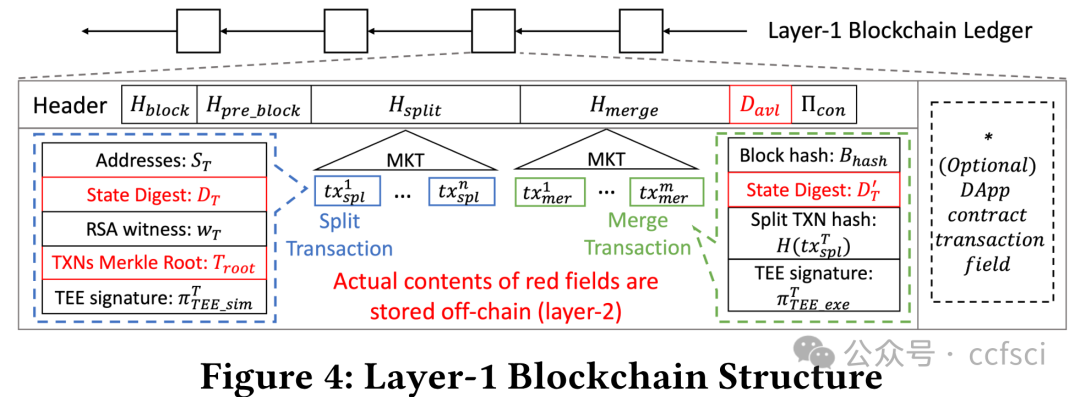
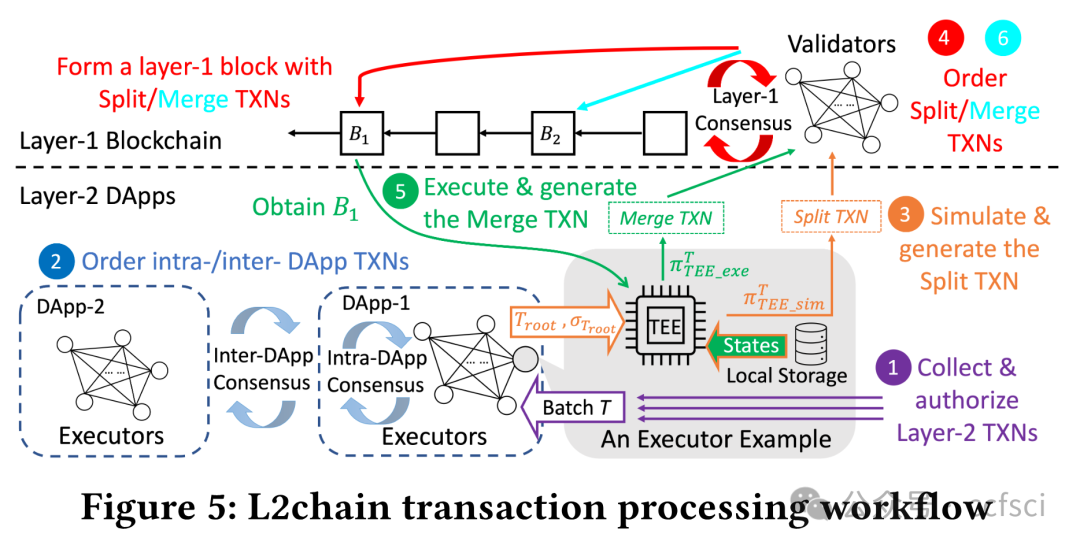
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p986-chen.pdf
4
Title:
Auto-Tuning with Reinforcement Learning for Permissioned Blockchain Systems
利用强化学习为许可区块链系统进行自动调整
Authors:****

Abstract:****
In a permissioned blockchain, performance dictates its development, which is substantially influenced by its parameters. However, research on auto-tuning for better performance has somewhat stagnated because of the difficulty posed by distributed parameters; thus, it is possible only with difficulty to propose an effective auto-tuning optimization scheme. To alleviate this issue, we lay a solid basis for our research by first exploring the relationship between parameters and performance in Hyperledger Fabric, a permissioned blockchain, and we propose Athena, a Fabric-based auto-tuning system that can automatically provide parameter configurations for optimal performance. The key of Athena is designing a new Permissioned Blockchain Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (PB-MADDPG) to realize heterogeneous parameter-tuning optimization of different types of nodes in Fabric. Moreover, we select parameters with the most significant impact on accelerating recommendation. In its application to Fabric, a typical permissioned blockchain system, with 12 peers and 7 orderers, Athena achieves a throughput improvement of 470.45% and a latency reduction of 75.66% over the default configuration. Compared with the most advanced tuning schemes (CDBTune, Qtune, and ResTune), our method is competitive in terms of throughput and latency.
在许可区块链中,性能决定了其发展,而性能又在很大程度上受其参数的影响。然而,由于分布式参数带来的困难,有关自动调整以提高性能的研究在一定程度上停滞不前;因此,很难提出有效的自动调整优化方案。为了缓解这一问题,我们首先在许可区块链 Hyperledger Fabric 中探索了参数与性能之间的关系,为我们的研究奠定了坚实的基础,并提出了基于 Fabric 的自动调整系统 Athena,该系统可以自动提供参数配置,以获得最佳性能。Athena 的关键在于设计一种新的许可区块链多代理深度确定性策略梯度(PB-MADDPG),以实现 Fabric 中不同类型节点的异构参数调整优化。此外,我们还选择了对加速推荐影响最大的参数。雅典娜应用于拥有 12 个对等节点和 7 个订购者的典型许可区块链系统 Fabric,与默认配置相比,吞吐量提高了 470.45%,延迟降低了 75.66%。与最先进的调整方案(CDBTune、Qtune 和 ResTune)相比,我们的方法在吞吐量和延迟方面都很有竞争力。


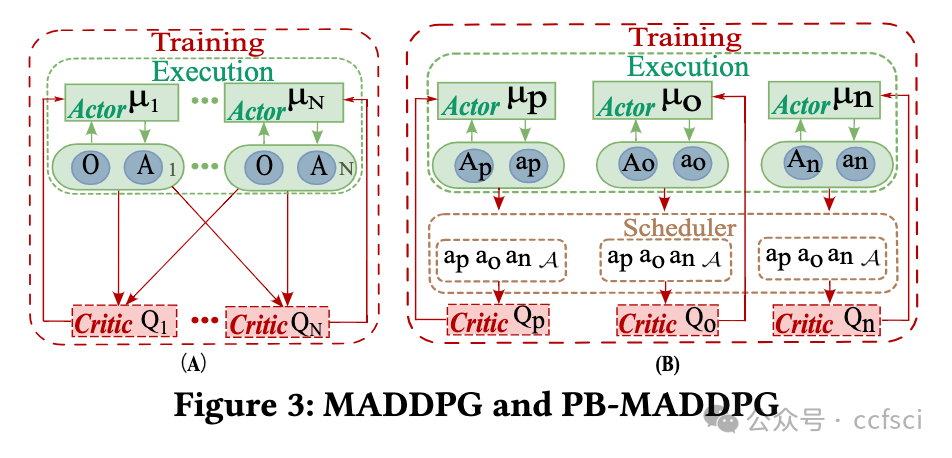
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p1000-li.pdf
5
Title:
GriDB: Scaling Blockchain Database via Sharding and Off-Chain Cross-Shard Mechanism
GriDB:通过分片和链外跨片机制扩展区块链数据库
Authors:****

Abstract:****
Blockchain databases have attracted widespread attention but suffer from poor scalability due to underlying non-scalable blockchains. While blockchain sharding is necessary for a scalable blockchain database, it poses a new challenge named on-chain cross-shard database services. Each cross-shard database service (e.g., cross-shard queries or inter-shard load balancing) involves massive cross-shard data exchanges, while the existing cross-shard mechanisms need to process each cross-shard data exchange via the consensus of all nodes in the related shards (i.e., on-chain) to resist a Byzantine environment of blockchain, which eliminates sharding benefits. To tackle the challenge, this paper presents GriDB, the first scalable blockchain database, by designing a novel off-chain cross-shard mechanism for efficient cross-shard database services. Borrowing the idea of off-chain payments, GriDB delegates massive cross-shard data exchange to a few nodes, each of which is randomly picked from a different shard. Considering the Byzantine environment, the untrusted delegates cooperate to generate succinct proof for cross-shard data exchanges, while the consensus is only responsible for the low-cost proof verification. However, different from payments, the database services' verification has more requirements (e.g., completeness, correctness, freshness, and availability); thus, we introduce several new authenticated data structures (ADS). Particularly, we utilize consensus to extend the threat model and reduce the complexity of traditional accumulator-based ADS for verifiable cross-shard queries with a rich set of relational operators. Moreover, we study the necessity of inter-shard load balancing for a scalable blockchain database and design an off-chain and live approach for both efficiency and availability during balancing. An evaluation of our prototype shows the performance of GriDB in terms of scalability in workloads with queries and updates.
区块链数据库已引起广泛关注,但由于底层区块链不可扩展,其可扩展性较差。虽然区块链分片是可扩展区块链数据库的必要条件,但它也提出了一个新的挑战,即链上跨分片数据库服务。每项跨分片数据库服务(如跨分片查询或分片间负载均衡)都涉及大量的跨分片数据交换,而现有的跨分片机制需要通过相关分片(即链上)所有节点的共识来处理每项跨分片数据交换,以抵御区块链的拜占庭环境,从而消除了分片的优势。为应对这一挑战,本文通过设计一种新型链外跨分片机制,提出了首个可扩展的区块链数据库 GriDB,以提供高效的跨分片数据库服务。借鉴链外支付的理念,GriDB 将大量跨分区数据交换委托给几个节点,每个节点从不同的分区中随机抽取。考虑到拜占庭环境,不受信任的委托人合作生成跨碎片数据交换的简洁证明,而共识只负责低成本的证明验证。然而,与支付不同,数据库服务的验证有更多要求(如完整性、正确性、新鲜度和可用性);因此,我们引入了几种新的验证数据结构(ADS)。特别是,我们利用共识扩展了威胁模型,并降低了传统的基于累加器的 ADS 的复杂性,以实现具有丰富关系运算符集的可验证跨分区查询。此外,我们还研究了可扩展区块链数据库跨区块负载平衡的必要性,并设计了一种离链和实时方法,以提高平衡期间的效率和可用性。对我们原型的评估显示了 GriDB 在查询和更新工作负载中的可扩展性能。
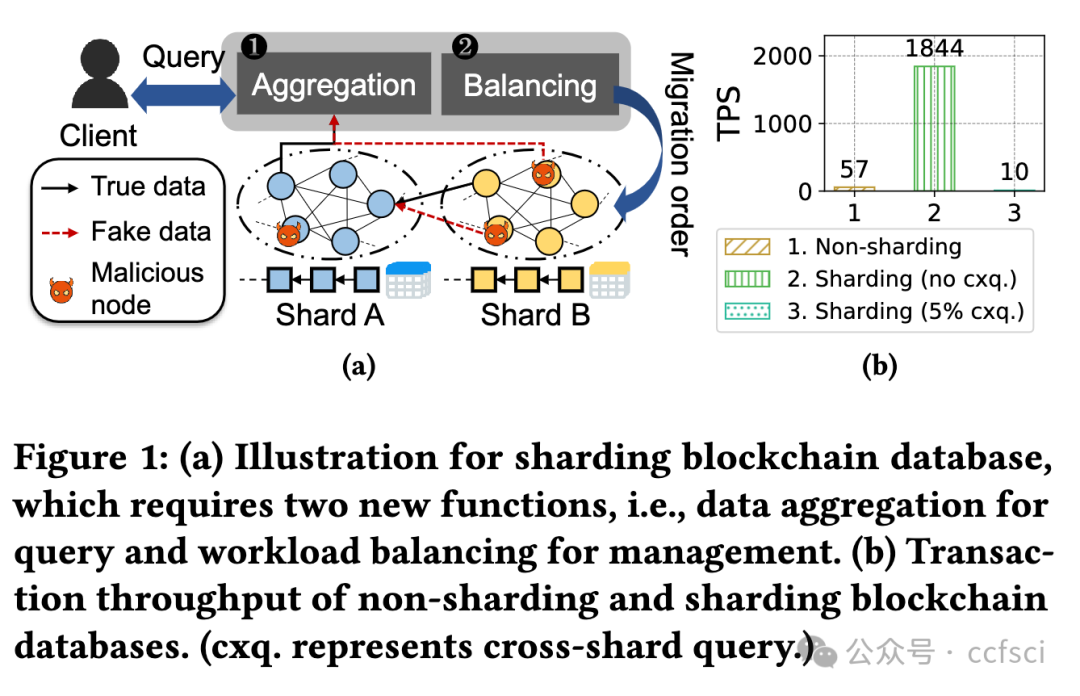
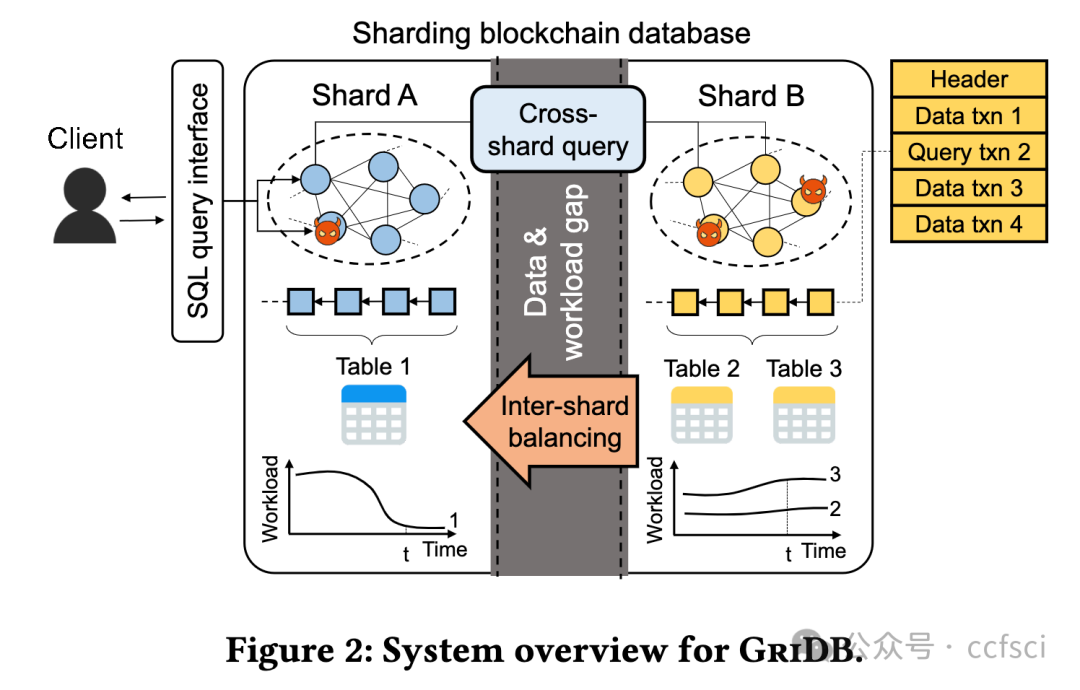
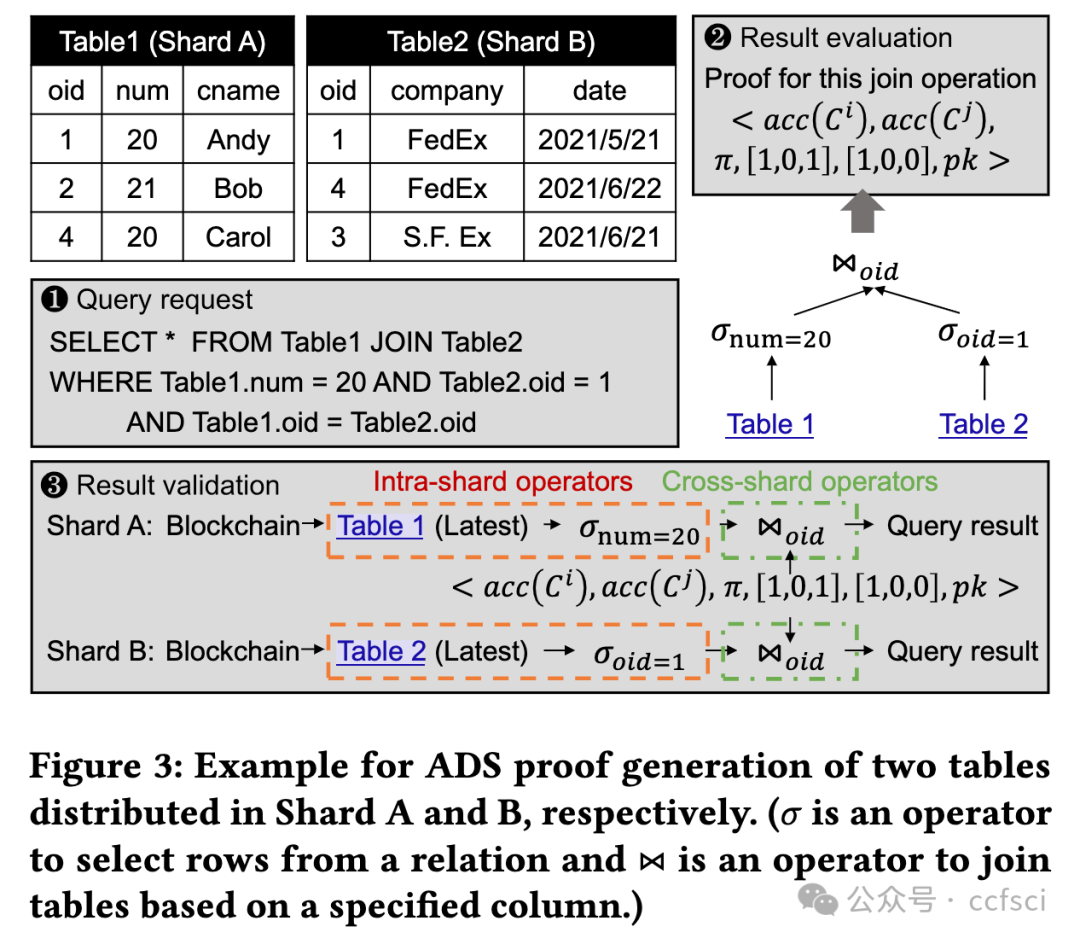
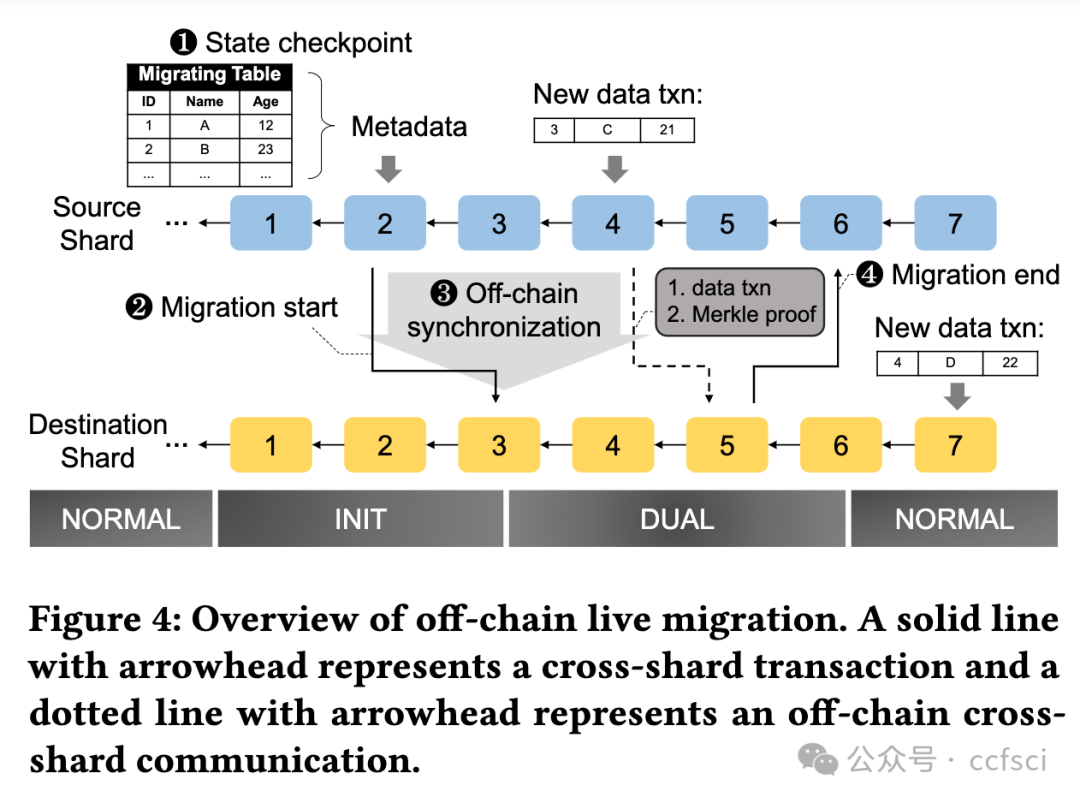
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p1685-hong.pdf
6
Title:
AdaChain: A Learned Adaptive Blockchain
AdaChain:学习型自适应区块链
Authors:****

Abstract:****
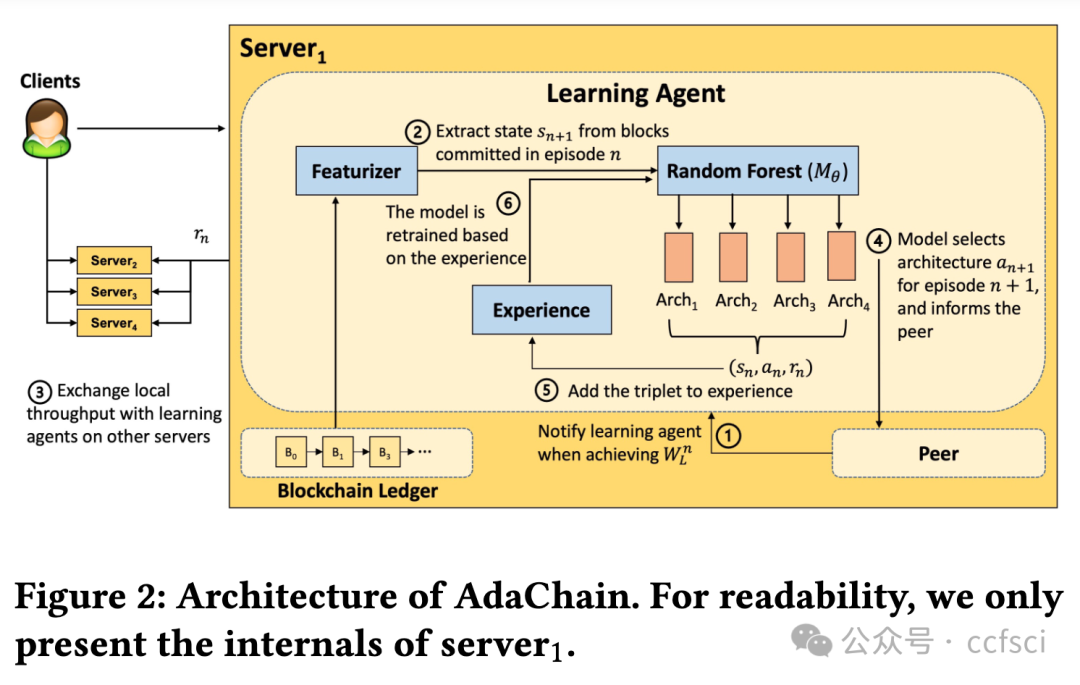
This paper presents AdaChain, a learning-based blockchain framework that adaptively chooses the best permissioned blockchain architecture to optimize effective throughput for dynamic transaction workloads. AdaChain addresses the challenge in Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) environments, where a large variety of possible smart contracts are deployed with different workload characteristics. AdaChain supports automatically adapting to an underlying, dynamically changing workload through the use of reinforcement learning. When a promising architecture is identified, AdaChain switches from the current architecture to the promising one at runtime in a secure and correct manner. Experimentally, we show that AdaChain can converge quickly to optimal architectures under changing workloads and significantly outperform fixed architectures in terms of the number of successfully committed transactions, all while incurring low additional overhead.
本文介绍了基于学习的区块链框架AdaChain,该框架可自适应地选择最佳许可区块链架构,以优化动态交易工作负载的有效吞吐量。AdaChain解决了区块链即服务(BaaS)环境中的难题,在这种环境中,部署了大量可能的智能合约,它们具有不同的工作负载特征。AdaChain 支持通过强化学习自动适应底层动态变化的工作负载。当发现有前景的架构时,AdaChain 会在运行时以安全、正确的方式从当前架构切换到有前景的架构。实验表明,在不断变化的工作负载下,AdaChain 可以快速收敛到最佳架构,并且在成功提交事务的数量方面明显优于固定架构,同时产生的额外开销也很低。
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p2033-wu.pdf
7
Title:
PSFQ: A Blockchain-Based Privacy-Preserving and Verifiable Student Feedback Questionnaire Platform
PSFQ:基于区块链的隐私保护和可验证学生反馈问卷平台
Authors:****

Abstract:****
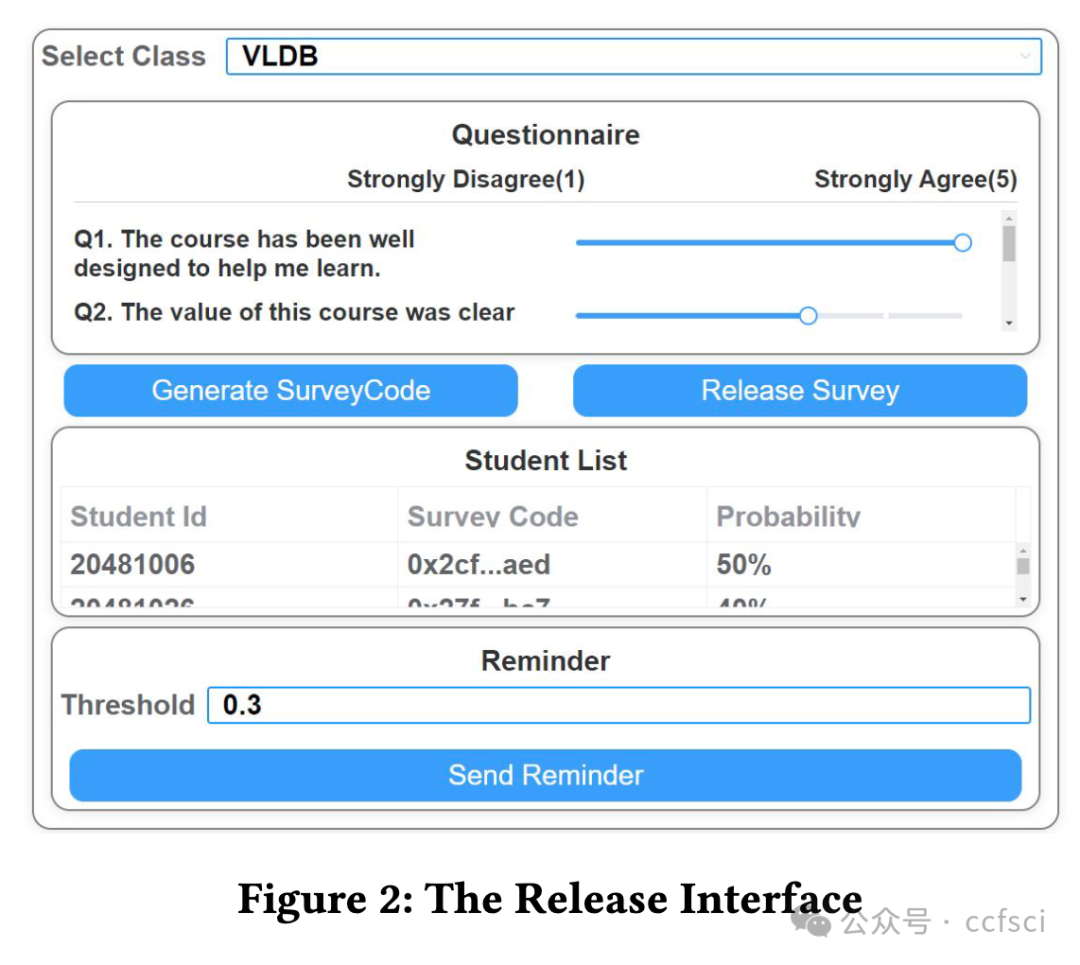
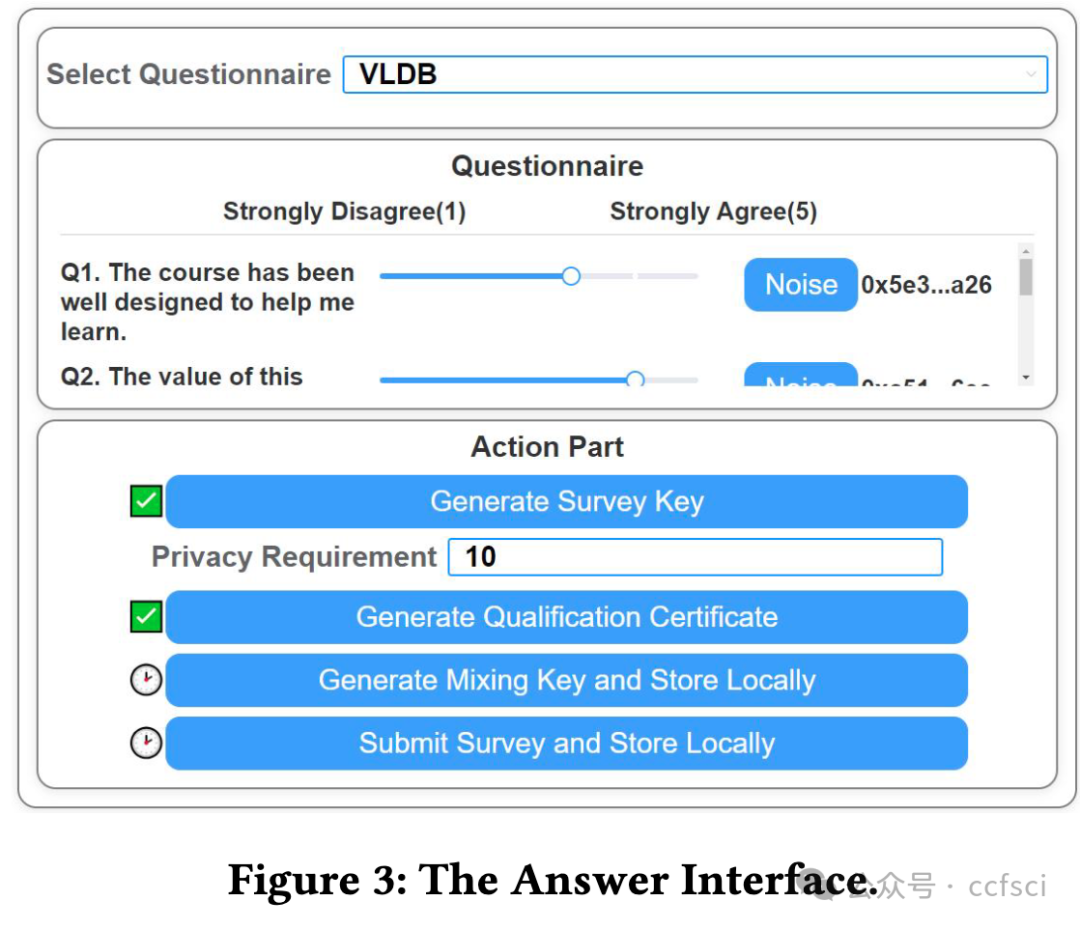
Recently, more and more higher education institutions have been using student feedback questionnaires (SFQ) to evaluate teaching. However, existing SFQ systems have two shortcomings. The first is that the respondent of an SFQ is not anonymous. The second is that the statistical report of SFQs can be manipulated. To tackle these two shortcomings, we develop a novel SFQ system, namely PSFQ. In PSFQ, the respondent of an SFQ is mixed with multiple users by a ring signature. PSFQ uses an advanced ring signature approach to minimize the size of a ring signature when anonymity satisfies the requirements. Thus, the first shortcoming has been overcome. Moreover, all answers are encrypted by homomorphic encryption and stored on the blockchain, enabling users to verify the correctness of the statistical reports. Our demonstration will showcase how PSFQ provides confidential SFQ responses while ensuring the correctness of statistical reports.
最近,越来越多的高等教育机构开始使用学生反馈问卷(SFQ)来评估教学。然而,现有的 SFQ 系统有两个缺点。一是 SFQ 的受访者不是匿名的。其次,SFQ 的统计报告可以被操纵。针对这两个缺点,我们开发了一种新型 SFQ 系统,即 PSFQ。在 PSFQ 中,SFQ 的应答者通过环签名与多个用户混合。PSFQ 采用先进的环签名方法,在满足匿名性要求的情况下最大限度地减小环签名的大小。因此,第一个缺点已被克服。此外,所有答案都经过同态加密并存储在区块链上,使用户能够验证统计报告的正确性。我们的演示将展示 PSFQ 如何在确保统计报告正确性的同时提供保密的 SFQ 答案。

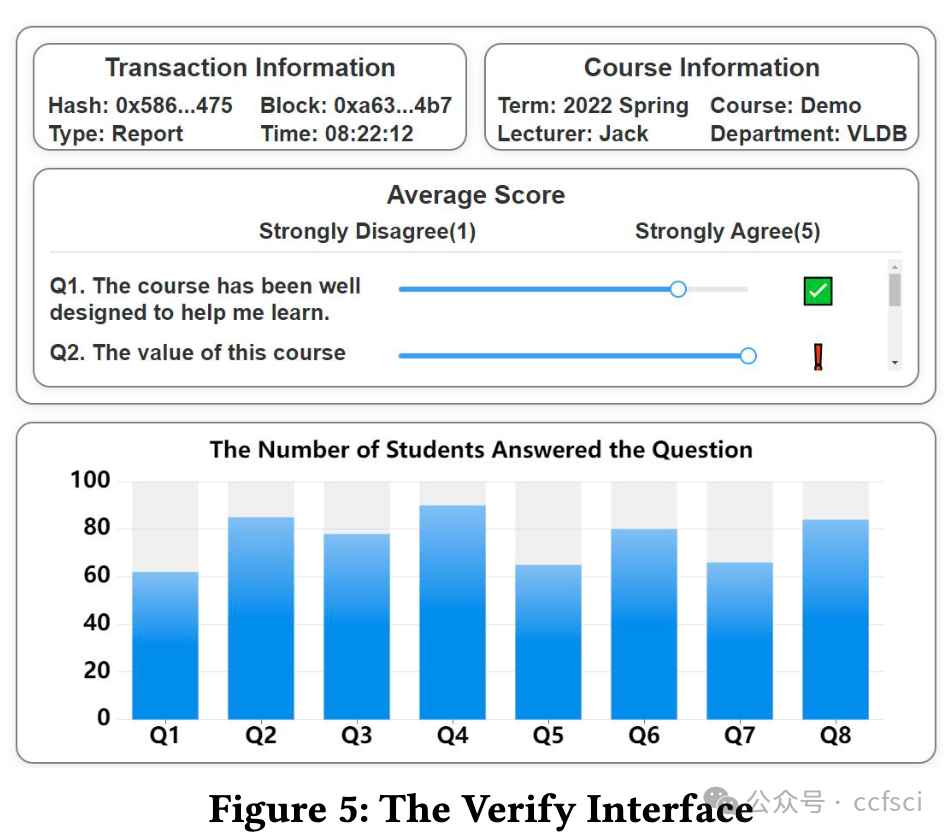
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p3918-ni.pdf
8
Title:
ChainDash: An Ad-Hoc Blockchain Data Analytics System
ChainDash:临时区块链数据分析系统
Authors:****

Abstract:****
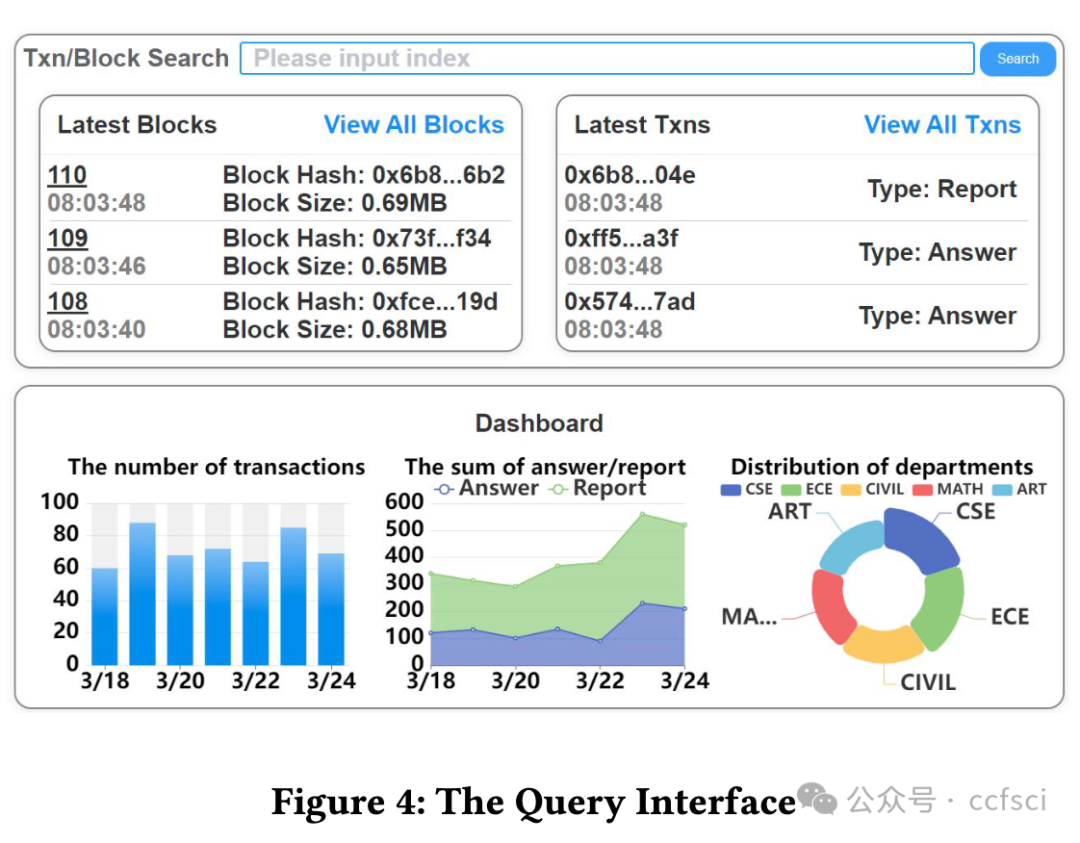
The emergence of digital asset applications, driven by Web 3.0 and powered by blockchain technology, has led to a growing demand for blockchain-specific graph analytics to unearth the insights. However, current blockchain data analytics systems are unable to perform efficient ad-hoc graph analytics over both live and past time windows due to their inefficient data synchronization and slow graph snapshots retrieval capability. To address these issues, we propose ChainDash, a blockchain data analytics system that dedicates a highly-parallelized data synchronization component and a retrieval-optimized temporal graph store. By leveraging these techniques, ChainDash supports efficient ad-hoc graph analytics of smart contract activities over arbitrary time windows. In the demonstration, we showcase the interactive visualization interfaces of ChainDash, where attendees will execute customized queries for ad-hoc graph analytics of blockchain data.Sharding is a prominent technique for scaling blockchains.
在 Web 3.0 和区块链技术的推动下,数字资产应用不断涌现,这导致对区块链特定图分析挖掘洞察力的需求不断增长。然而,当前的区块链数据分析系统由于数据同步效率低下和图形快照检索能力缓慢,无法在实时和过去的时间窗口内执行高效的临时图形分析。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了区块链数据分析系统 ChainDash,该系统专用于高度并行化的数据同步组件和检索优化的时序图存储。利用这些技术,ChainDash 支持对任意时间窗口内的智能合约活动进行高效的临时图分析。在演示中,我们将展示 ChainDash 的交互式可视化界面,与会者将执行定制查询,对区块链数据进行临时图分析。

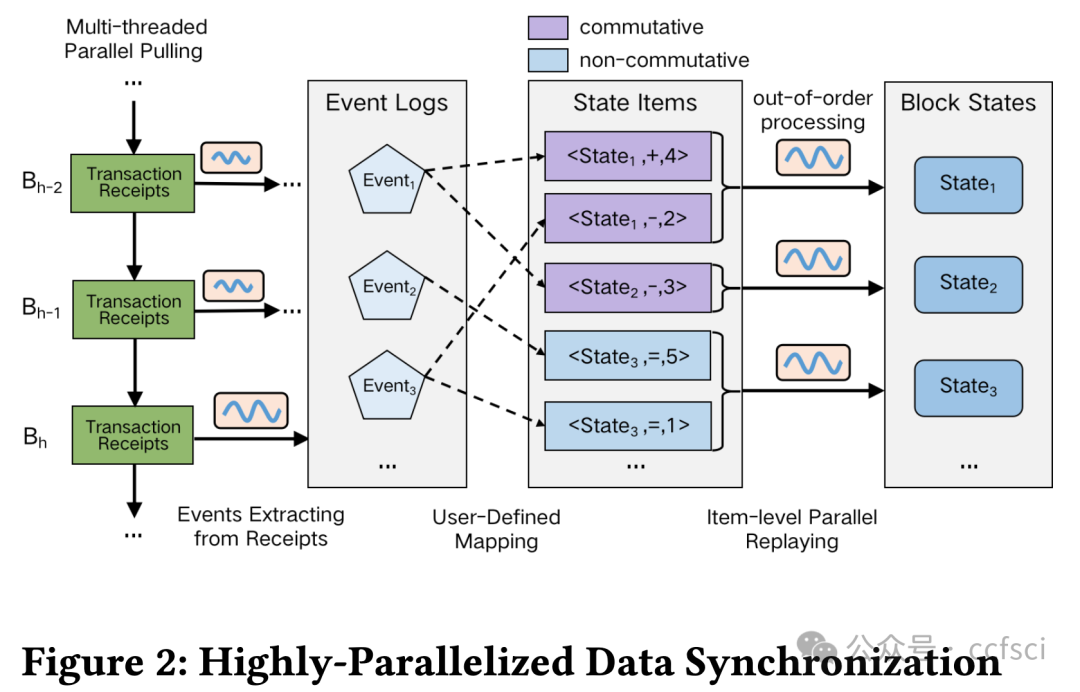

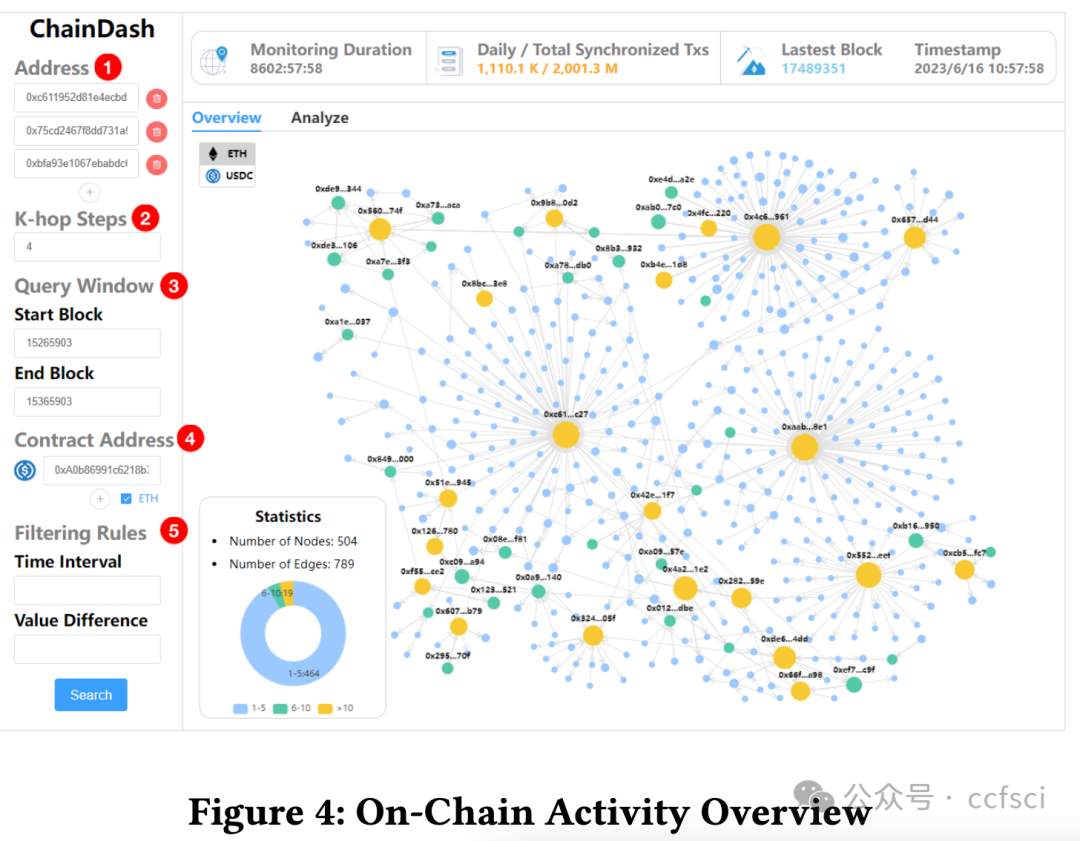
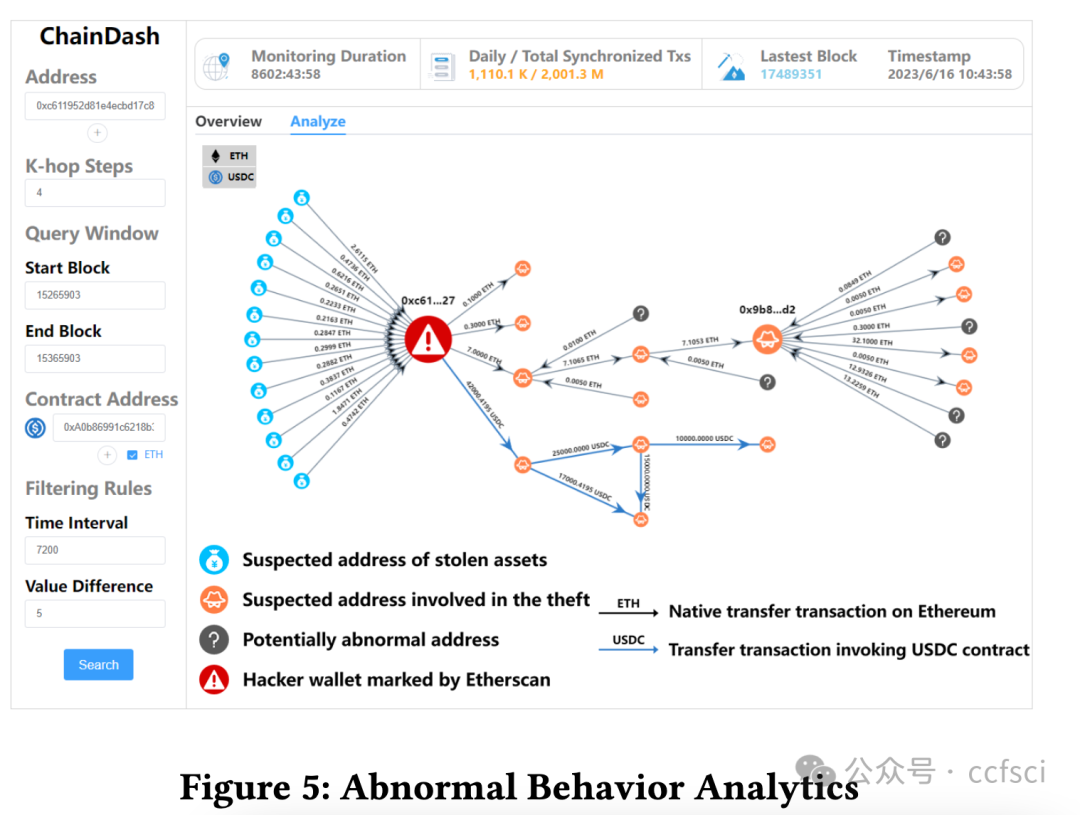
Pdf link:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol16/p4022-zhang.pdf

关注ccfsci,持续接收区块链最新论文
洞察区块链技术发展趋势
Follow us to keep receiving the latest blockchain papers
Insight into Blockchain Technology Trends