上一节说到请求url定位servlet的过程,tomcat会把请求url和容器的映射关系保存到MappingData中,org.apache.catalina.connector.Request类实现了HttpServletRequest,其中定义了属性mappingDataprotected final MappingData mappingData = new MappingData();用于保存映射关系,其是在CoyoteAdapter.java#service()方法中创建。定位servlet对请求进行处理的入口是connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);,先看张图总览下处理过程。
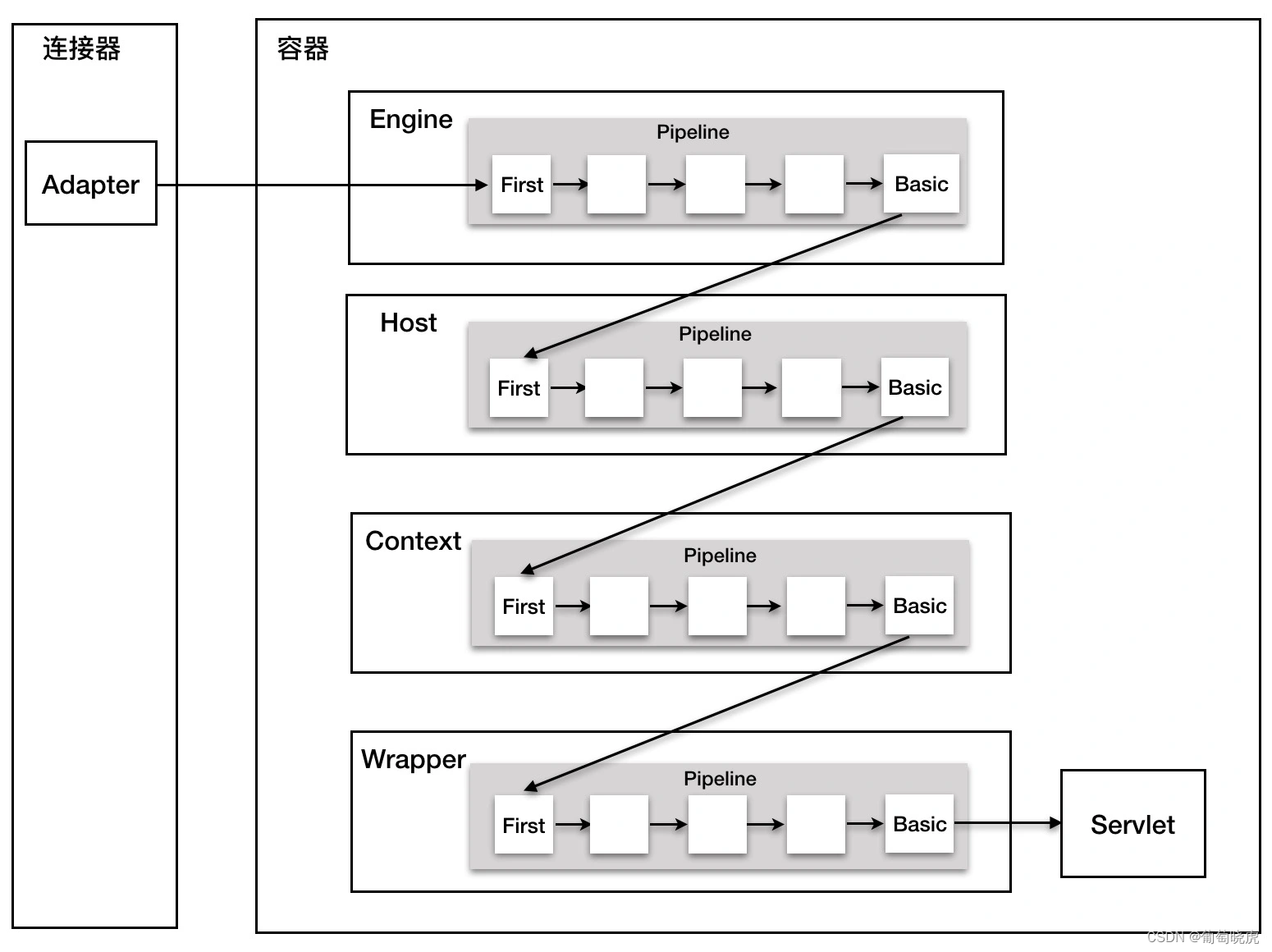
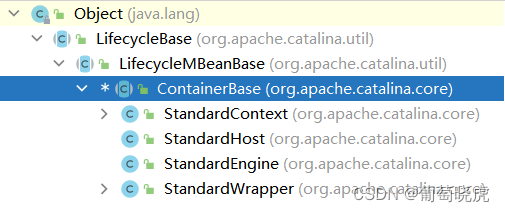
这里的逻辑就是调用Pipeline中的每个Valve进行处理。在ContainerBase.java抽象父类中声明了属性protected final Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline(this);,意味着ContainerBase的子类都会有一个管道Pipeline(StandardPipeline),查看类的继承关系可知,tomcat中ContainerBase的子类有四个:StandardEngine、StandardHost、StandardContext、StandardWrapper。
- StandardEngine
通过connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline()获取到Engine(StandardEngine)容器,再通过getPipeline().getFirst()获取Pipeline(StandardPipeline.java)中的第一个Valve,即使用StandardEngine中的StandardPipeline的第一个Valve进行处理,接下来看下这个Valve怎么来的。在Valve中有个属性protected Valve next = null;,用来指向下一个Valve,这就构建了一个链表,getFirst()时发现链条为空,则默认获取basic,而StandardEngine的pipeline中的basic是在StandardEngine的构造函数中生成的。
java
public Valve getFirst() {
if (first != null) {
return first;
}
return basic;
}
public StandardEngine() {
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardEngineValve());
......
}
public void setBasic(Valve valve) {
......
Valve current = first;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == oldBasic) {
current.setNext(valve);
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
this.basic = valve;
}搞清楚了这个Valve的由来了,再看他的处理逻辑:就是找到前面通过请求url定位的Host,获取Host的Valve进行处理。
java
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
......
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
public Host getHost() {
return mappingData.host;
}
}- StandardHost
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);的过程类似类似StandardEngine容器。
java
public StandardHost() {
super();
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardHostValve());
}不过Host容器的Valve要多一点。首先在server.xml中配置了一个AccessLogValve,这个在使用Digester解析时会添加到Host容器的Pipeline,既然是解析xml文件生成,那我们就可以在xml文件中自定义一些Valve了。
xml
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"
pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
</Host>同时在启动时会向Pipeline添加一个ErrorReportValve。
java
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
Valve valve = ErrorReportValve.class.getName().equals(errorValve) ? new ErrorReportValve() :
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass", errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}最终tomcat收到请求使用Host容器处理时,就会有三个Valve参与:AccessLogValve->ErrorReportValve->StandardHostValve。
接下来我们一个个看每个Valve的处理过程。
- AccessLogValve
好像没做什么正事,之后再看。
java
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (tlsAttributeRequired) {
request.getAttribute(Globals.CERTIFICATES_ATTR);
}
if (cachedElements != null) {
for (CachedElement element : cachedElements) {
element.cache(request);
}
}
getNext().invoke(request, response);
}- ErrorReportValve.java
这是在请求处理完的后置处理,用来报告错误的。
java
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Perform the request
getNext().invoke(request, response);
if (response.isCommitted()) {
if (response.setErrorReported()) {
// Error wasn't previously reported but we can't write an error
// page because the response has already been committed.
// See if IO is allowed
AtomicBoolean ioAllowed = new AtomicBoolean(true);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, ioAllowed);
if (ioAllowed.get()) {
// I/O is currently still allowed. Flush any data that is
// still to be written to the client.
try {
response.flushBuffer();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
// Now close immediately to signal to the client that
// something went wrong
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW,
request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION));
}
}
return;
}
Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// If an async request is in progress and is not going to end once this
// container thread finishes, do not process any error page here.
if (request.isAsync() && !request.isAsyncCompleting()) {
return;
}
if (throwable != null && !response.isError()) {
// Make sure that the necessary methods have been called on the
// response. (It is possible a component may just have set the
// Throwable. Tomcat won't do that but other components might.)
// These are safe to call at this point as we know that the response
// has not been committed.
response.reset();
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
// One way or another, response.sendError() will have been called before
// execution reaches this point and suspended the response. Need to
// reverse that so this valve can write to the response.
response.setSuspended(false);
try {
report(request, response, throwable);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
}- StandardHostValve
没有大的处理,还是把请求向后传递到Context容器的Valve。
java
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
Context context = request.getContext();
......
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
......
}- StandardContext
在tomcat启动时,StandardContext#startInternal()方法会添加一个NonLoginAuthenticator类型Valve到StandardContext的Pipeline中,然后设置basic(StandardContextValve)。StandardContextValve从请求中获取StandardWrapperValve进行请求的处理。 - StandardWrapperValve
前面铺垫了这么久,总算到正题了,请求的正式处理就是在StandardWrapperValve中进行的,前面的Valve做的还是对请求进行加工,没有进行正式的处理。怎么样,是不是看到熟悉的代码段,平时我们所说的过滤器链对请求过滤处理的代码!这块就是挨个调用每个过滤器Filter上的doFilter()方法进行处理。
java
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
......
Servlet servlet = null;
......
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
......
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
......
}还是慢慢看吧,首先在Wrapper容器中取出Servlet,然后创建用来处理请求的servlet过滤器链。依次调用每个过滤器的doFilter方法,最后会通过HttpServlet中的模板方法internalDoFilter()调用内置的service方法,就是根据请求方式处理请求啦,也就是我们写的过滤器中处理请求的方法。
java
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}总结下,tomcat使用valve处理请求是请求处理的最后一步。首先启动时会给每个容器的Pipeline添加一个基本valve,放在链条尾部,由这个valve找到下一个容器的valve,用来传递请求,最终传递到StandardWrapperValve后,取出servlet对请求进行处理。有不对的地方请大神指出,欢迎大家一起讨论交流,共同进步。