水到绝处是风景
人到绝境是重生
目录

契子✨
我们之前不仅讲过 队列queue 还有 双端队列deque 而我们今天所讲的依旧是队列家族的成员 -- 优先队列priority_queue
顾名思义,priority_queue 是一个拥有权值观念的 queue ,它允许增删元素、访问元素等功能。由于这是一个 queue,所以只允许在低端加入元素,并从顶端取出元素,除此之外别无其他存取元素的途径

priority_queue 带有权值观念,其内的元素并非依照推入的顺序排序,而是自动依照元素的权值排序(权值通常以实值表示)。权值最高者,排在前面
大家想象一下,我们之前学过的数据结构有哪一种具有类似的性质?
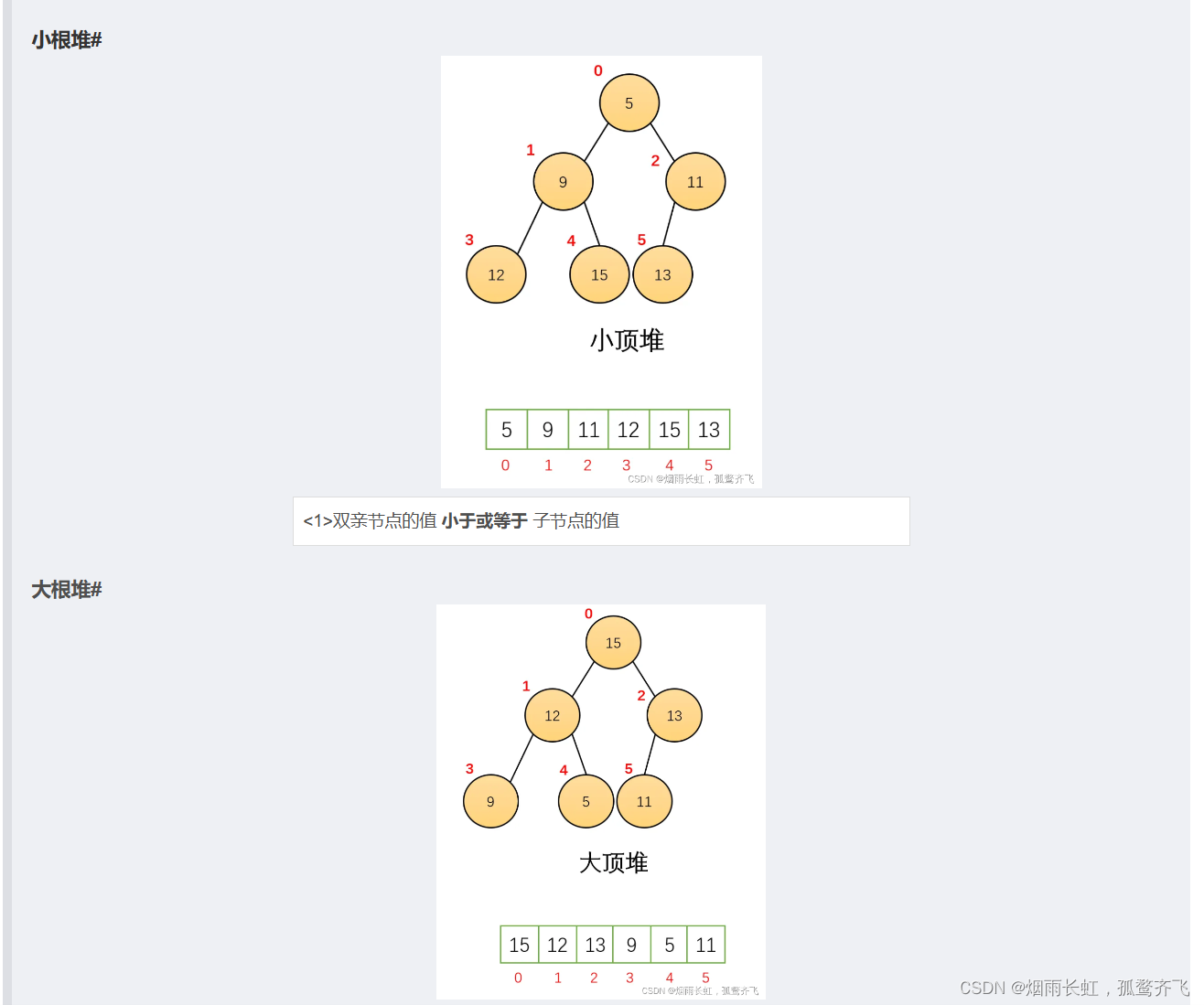
是不是像我们学过的 -- 堆(heap),我们可以利用 heap 的特性完成 [依权值高低自动递增排序] priority_queue
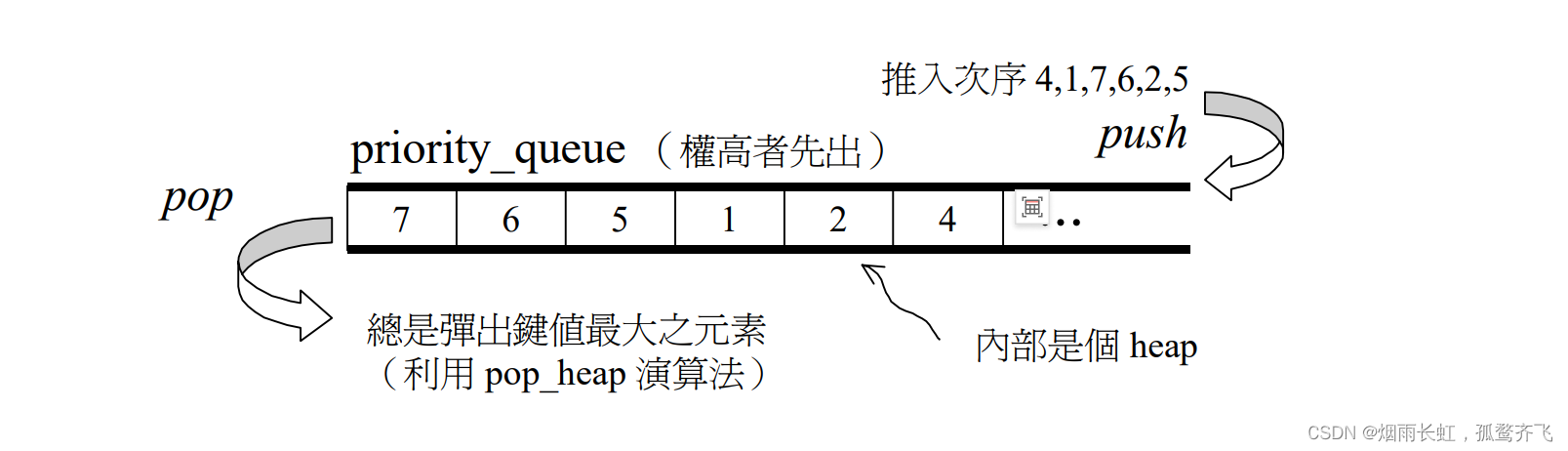
优先队列 priority_queue 是一种容器适配器,默认使用vector 作为其底层存储数据的容器,在 vector 上又使用了堆算法将vector 中元素构造成堆的结构,因此 priority_queue 就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用priority_queue 。注意: 默认情况下priority_queue是 大堆
priority_queue 没有迭代器
priority_queue 的所有元素,进出都有一定的规则,只有 queue 的顶端元素(权值最高元素),才有机会被外界取用,priority_queue 不提供遍历功能,也不提供迭代器功能
priority_queue的模拟实现
通过对 priority_queue的底层结构默认就是 vector ,然后我们处理一下形成堆,因此此处只需对对进行通用的封装即可。操作非常简单,源码很简短,这里就完整的列出吧 ~ 然后在讲一下细节

cpp
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::swap;
namespace Mack
{
template<class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T,class Sequence = vector<T>, class Comapre = less<T> >
class priority_queue
{
public:
priority_queue() = default;
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
c.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
for (int i = (c.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
const T& top() const
{
return c.front();
}
bool empty() const
{
return c.empty();
}
size_t size() const
{
return c.size();
}
void AdjustUP(size_t child)
{
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (comp(c[parent] , c[child]))
{
swap(c[parent], c[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& val)
{
c.push_back(val);
AdjustUP(size()-1);
}
void AdjustDown(size_t parent)
{
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size())
{
while (child + 1 < size() && comp(c[child] , c[child+1]))
{
child++;
}
if (comp(c[parent] , c[child]))
{
swap(c[parent], c[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void pop()
{
swap(c[0], c[size() - 1]);
c.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
private:
Sequence c;
Comapre comp;
};
}我们先来分析一下库里面的优先队列
对啦 ~ 头文件依然是**#include<queue>** 哦
源码剖析:
cpp
#include<queue>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void priority_queue_test()
{
priority_queue<int> str;
str.push(10);
str.push(30);
str.push(20);
str.push(50);
str.push(35);
while (!str.empty())
{
cout << str.top() << " ";
str.pop();
}
}
我们发现库里的优先队列默认排的是降序也就是大堆 ~
所以我们写优先队列时,也要按照大堆的方式去写
关于堆算法,老铁们可以借鉴一下这个:二叉堆
我们重点讲一下关于 priority_queue的自动排序,我们知道我们现在的优先队列排的是降序,那我们想排升序怎么办呢?难道要将堆中的比较符号都改一下吗?
我们先来看一下库里的算法:
cpp
#include<queue>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void priority_queue_test()
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>,greater<int>> str;
str.push(10);
str.push(30);
str.push(20);
str.push(50);
str.push(35);
while (!str.empty())
{
cout << str.top() << " ";
str.pop();
}
}
用惯排序 sort的老铁可能会有些不习惯,为什么中间还要加一个参数,因为库里就是以下的格式,就跟传缺省一样不能隔代相传
cpp
template<class T,class Sequence = vector<T>, class Comapre = less<T> >我们回到重点!!!

在我们我们 C语言 阶段的话频繁的比较大小我们一般都会写成一个函数
cpp
bool Compare(int x, int y)
{
return x < y;
}
int main()
{
int x = 0, y = 1;
if (Compare(x, y))
{
printf("y>x");
}
else
{
printf("y<x");
}
return 0;
}如果比较 int 我们写一个专门比较 int 类型的函数,char 类型则专门写一个char 类型的函数
当我们学了 C++ 就开摆了,编程的进步就是变懒的过程 -- 我们可以利用模板来控制类型的比较
而要使用模板的前提必须是一个类,或者类中的函数
cpp
template<class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};所以我们用一个类去包含比较函数在利用模板,而我们重载()的原因就是想写成这样一种函数的形式:Compare(x, y) -- 这样方便比较
我们调用类中的函数是不是都是 类对象+点运算符,我们将()重载便可以写成函数的形式
这样的函数形式我们称之为伪函数
为了让我们得初始化方便,库里提供了迭代器区间构造
有些老铁可能会疑惑,不是不提供迭代器吗,怎么还会有迭代器区间构造?
嘿嘿 ~ 其实我们的数组 也可以进行迭代的
cpp
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
c.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
for (int i = (c.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}先将数据尾插到对象中,在向下调整建堆,因为向下调整要找到第一个非叶子节点
这里放张动图以便老铁理解:
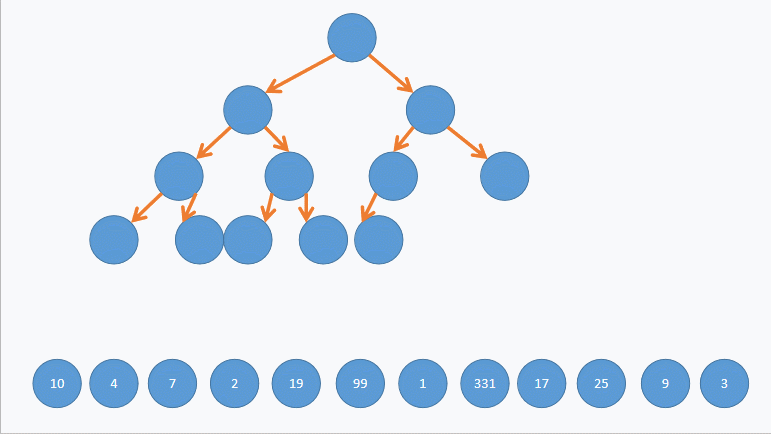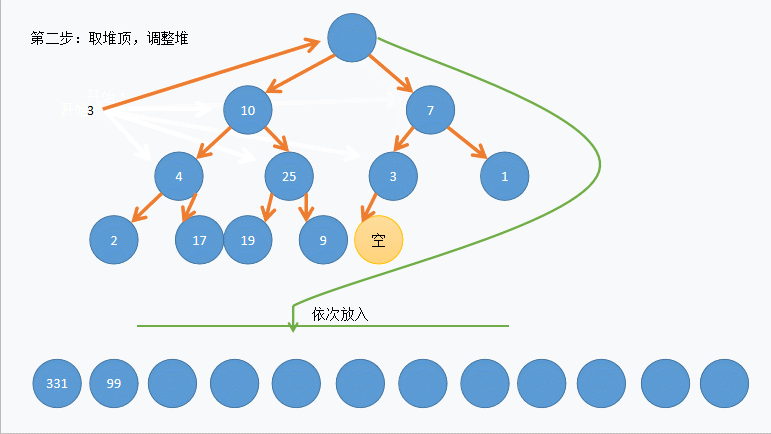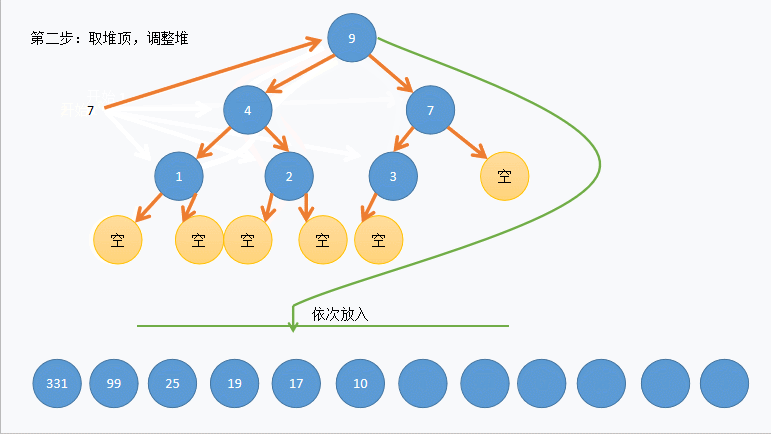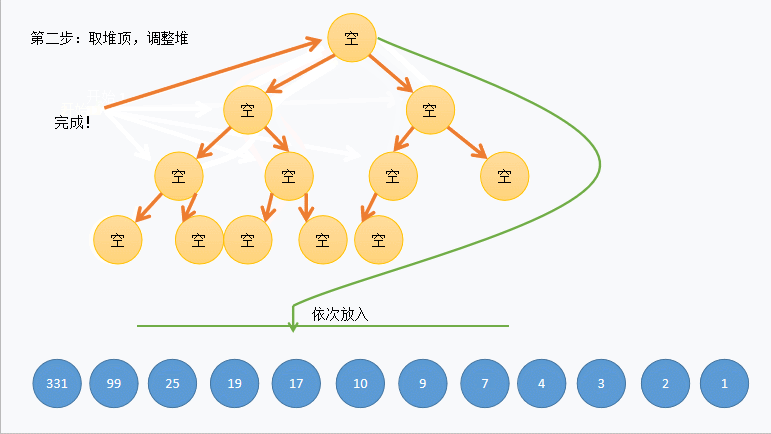
(_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2 的 _con.size() - 1 是找到最后一个节点,(_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2,则是套公式 parent = (child-1) /2 找到最后一个节点的双亲也就是第一个非叶子节点
代码测试:
别的不说先来测试一下代码,不要哔哔了一大段文字结果代码都是错的
cpp
void priority_queue_test()
{
int arr[] = {1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0};
priority_queue<int, vector<int>> str(arr, arr + 9);
while (!str.empty())
{
std::cout << str.top() << " ";
str.pop();
}
}
cpp
#include"priority_queue.h"
#include<iostream>
using std::iostream;
using std::ostream;
using namespace Mack;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
void TestPriorityQueue()
{
priority_queue<Date> q1;
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 29));
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 28));
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 30));
std::cout << q1.top() << std::endl;
priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date>> q2;
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 29));
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 28));
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 30));
std::cout << q2.top() << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
TestPriorityQueue();
std::cout << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

有问题的话可以提出来哦 ~
