一、目标函数
求二元高次函数的最小值。目标函数选择:

用于测试算法的简单的目标函数:
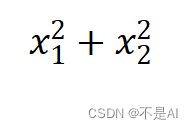
二、Python代码实现
python
import numpy as np
# 目标函数(2变量)
def objective_function(x):
return x[0] ** 2 + 2 * x[0] - 15 + 4 * 4 * 2 * x[1] + 4 * x[1] ** 2
# 测试:return x[0] ** 2 + x[1] ** 2
# 模拟退火
def simulated_annealing(objective_func, # 目标函数
initial_solution=np.array([0, 0]), # 初始解
temperature=100, # 初始温度
min_temperature=0.1, # 最小温度值
cooling_rate=0.90, # 冷却率(乘法系数)
iter_max=100, # 最大迭代次数
seed=0 # 随机种子
):
np.random.seed(seed)
current_solution = initial_solution
best_solution = current_solution
while temperature > min_temperature:
for j in range(iter_max):
# 生成新的解
new_solution = current_solution + np.random.uniform(-1, 1, len(current_solution))
# 计算新解与当前解之间的目标函数值差异
current_cost = objective_func(current_solution)
new_cost = objective_func(new_solution)
cost_diff = new_cost - current_cost
# 判断是否接受新解
if cost_diff < 0 or np.exp(-cost_diff / temperature) > np.random.random():
current_solution = new_solution
# 更新最优解
if objective_func(current_solution) < objective_func(best_solution):
best_solution = current_solution
# 降低温度
temperature *= cooling_rate
return best_solution
# 调用退火算法求解最小值
best_solution = simulated_annealing(objective_function)
print(f"函数最小值: {objective_function(best_solution)} 自变量取值:{best_solution}")代码参考博客:利用Python 实现 模拟退火算法
三、程序输出
测试函数输出:
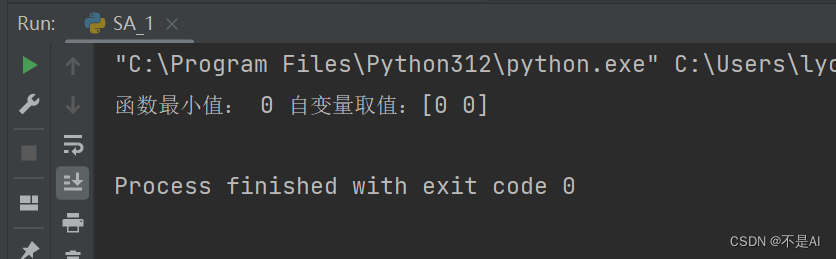
目标函数输出:

四、MatLab验证程序
参考博客:MATLAB求解二元(多元)函数极值
先定义目标函数(位于fun2_3.m中):
matlab
function f = fun2_3(x)
f = x(1) ^ 2 + 2 * x(1) - 15 + 32 * x(2) + 4 * x(2) ^ 2;模拟退火算法求极值:
matlab
clc, clear
[x, y]=meshgrid(-10:0.3:10,-10:0.3:10);
z = x.^2 + 2 * x -15 + 32 * y + 4 * y.^2;
figure(1)
surf(x,y,z)
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
zlabel('Z');
figure(2)
contour(x,y,z)
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
grid on;
x0=[-3,-3];
% [x,fmin]=fminsearch(@fun2_3,x0)
[x,fmin] = fminunc(@fun2_3,x0)程序输出:

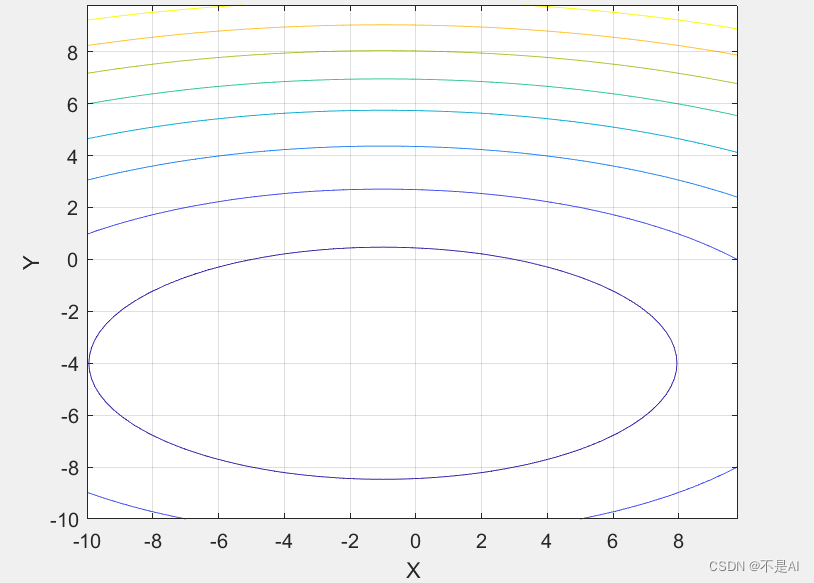
 可见,两种方法的求解结果基本相同。
可见,两种方法的求解结果基本相同。