文章目录
前言
在镜像中加入Git提交号,主要用于出现问题时,方便追溯。
环境介绍
硬件:T113
软件:全志Tina 5.0
思路
1、想办法获取当前的提交号。
2、将提交号写入一个头文件中,方便其它函数引用。
3、在cpuinfo或设备树中加入提交号信息,其中提交号从头文件获取即可。
内核cpuinfo中添加Git提交号
修改setup.c
我们知道在cat /proc/cpuinfo时,会打印关于CPU架构、型号、速度、缓存大小、功能等的详细信息,那就将Git提交号放到这里吧,最终效果如下图:
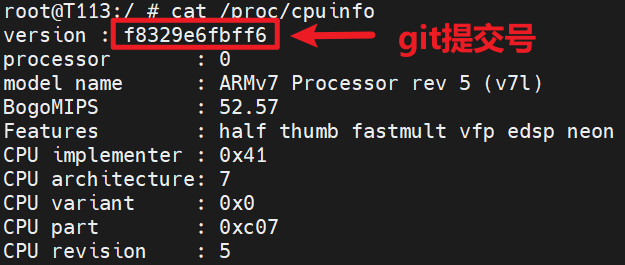
cpuinfo的实现在<SDK>/kernel/linux-5.4/arch/arm/kernel/setup.c中,定位到c_show()函数,在第11行加入打印:
c
/* setup.c */
...
...
static int c_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v)
{
int i, j;
u32 cpuid;
seq_printf(m, "version\t: %s\n", GIT_COMMIT_INFO); //打印提交号
for_each_online_cpu(i) {
/*
* glibc reads /proc/cpuinfo to determine the number of
* online processors, looking for lines beginning with
* "processor". Give glibc what it expects.
*/
seq_printf(m, "processor\t: %d\n", i);
cpuid = is_smp() ? per_cpu(cpu_data, i).cpuid : read_cpuid_id();
seq_printf(m, "model name\t: %s rev %d (%s)\n",
cpu_name, cpuid & 15, elf_platform);
#if defined(CONFIG_SMP)
seq_printf(m, "BogoMIPS\t: %lu.%02lu\n",
per_cpu(cpu_data, i).loops_per_jiffy / (500000UL/HZ),
(per_cpu(cpu_data, i).loops_per_jiffy / (5000UL/HZ)) % 100);
#else
seq_printf(m, "BogoMIPS\t: %lu.%02lu\n",
loops_per_jiffy / (500000/HZ),
(loops_per_jiffy / (5000/HZ)) % 100);
#endif
/* dump out the processor features */
seq_puts(m, "Features\t: ");
for (j = 0; hwcap_str[j]; j++)
if (elf_hwcap & (1 << j))
seq_printf(m, "%s ", hwcap_str[j]);
for (j = 0; hwcap2_str[j]; j++)
if (elf_hwcap2 & (1 << j))
seq_printf(m, "%s ", hwcap2_str[j]);
seq_printf(m, "\nCPU implementer\t: 0x%02x\n", cpuid >> 24);
seq_printf(m, "CPU architecture: %s\n",
proc_arch[cpu_architecture()]);
if ((cpuid & 0x0008f000) == 0x00000000) {
/* pre-ARM7 */
seq_printf(m, "CPU part\t: %07x\n", cpuid >> 4);
} else {
if ((cpuid & 0x0008f000) == 0x00007000) {
/* ARM7 */
seq_printf(m, "CPU variant\t: 0x%02x\n",
(cpuid >> 16) & 127);
} else {
/* post-ARM7 */
seq_printf(m, "CPU variant\t: 0x%x\n",
(cpuid >> 20) & 15);
}
seq_printf(m, "CPU part\t: 0x%03x\n",
(cpuid >> 4) & 0xfff);
}
seq_printf(m, "CPU revision\t: %d\n\n", cpuid & 15);
}
seq_printf(m, "Hardware\t: %s\n", machine_name);
seq_printf(m, "Revision\t: %04x\n", system_rev);
seq_printf(m, "Serial\t\t: %s\n", system_serial);
return 0;
}
...
...那问题来了,这个GIT_COMMIT_INFO宏在哪定义的?
c
seq_printf(m, "version\t: %s\n", GIT_COMMIT_INFO); //打印提交号获取Git提交号和生成GIT_COMMIT_INFO宏
在内核源码中,自带有一个setlocalversion脚本。它的主要作用是为内核版本号添加额外的本地或特定的标识符。当内核源码是从版本控制系统(如 Git)中检出的,并且不在某个特定的标签(tagged commit)上时,setlocalversion脚本会被调用,并在版本号后添加一个 "+" 号以及其他的本地版本信息。
简单概括就是该脚本已经实现了怎么获取提交号,当然使用一句简单的git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD命令也可以获取当前的提交号。我们主要借助现成的完善的可靠的已经经过验证的方法,仅此而已。
找到<SDK>/kernel/linux-5.4/scripts/setlocalversion脚本,主要关注scm_version()函数:
shell
/* setlocalversion */
...
...
scm_version()
{
local short
short=false
cd "$srctree"
if test -e .scmversion; then
cat .scmversion
return
fi
if test "$1" = "--short"; then
short=true
fi
# Check for git and a git repo.
if test -z "$(git rev-parse --show-cdup 2>/dev/null)" &&
head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; then
if [ -n "$android_release" ] && [ -n "$kmi_generation" ]; then
printf '%s' "-$android_release-$kmi_generation"
fi
# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore
# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.
if [ -z "`git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null`" ]; then
# If only the short version is requested, don't bother
# running further git commands
if $short; then
echo "+"
return
fi
# If we are past a tagged commit (like
# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.
if atag="`git describe 2>/dev/null`"; then
echo "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'
# If we don't have a tag at all we print -g{commitish}.
else
printf '%s%s' -g $head
fi
fi
# Is this git on svn?
if git config --get svn-remote.svn.url >/dev/null; then
printf -- '-svn%s' "`git svn find-rev $head`"
fi
# Check for uncommitted changes.
# First, with git-status, but --no-optional-locks is only
# supported in git >= 2.14, so fall back to git-diff-index if
# it fails. Note that git-diff-index does not refresh the
# index, so it may give misleading results. See
# git-update-index(1), git-diff-index(1), and git-status(1).
if {
git --no-optional-locks status -uno --porcelain 2>/dev/null ||
git diff-index --name-only HEAD
} | grep -qvE '^(.. )?scripts/package'; then
printf '%s' -dirty
fi
# All done with git
return
fi
# Check for mercurial and a mercurial repo.
if test -d .hg && hgid=`hg id 2>/dev/null`; then
# Do we have an tagged version? If so, latesttagdistance == 1
if [ "`hg log -r . --template '{latesttagdistance}'`" = "1" ]; then
id=`hg log -r . --template '{latesttag}'`
printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"
else
tag=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | cut -d' ' -f2`
if [ -z "$tag" -o "$tag" = tip ]; then
id=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | sed 's/[+ ].*//'`
printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"
fi
fi
# Are there uncommitted changes?
# These are represented by + after the changeset id.
case "$hgid" in
*+|*+\ *) printf '%s' -dirty ;;
esac
# All done with mercurial
return
fi
# Check for svn and a svn repo.
if rev=`LANG= LC_ALL= LC_MESSAGES=C svn info 2>/dev/null | grep '^Last Changed Rev'`; then
rev=`echo $rev | awk '{print $NF}'`
printf -- '-svn%s' "$rev"
# All done with svn
return
fi
}
...
...该函数被执行后,若使用Git管理,则会输出当前的提交号。若没使用Git管理,输出空。知道了该函数的作用后,我们自行在同级目录下,创建一个专门用于生成提交号的脚本scm_version.sh,将scm_version()函数复制进去。脚本的完整内容如下:
shell
#!/bin/bash
INFO_DIR=${LICHEE_KERN_DIR}/include/dt-bindings/cpuinfo.h
scm_version()
{
local short
short=false
cd "$srctree"
if test -e .scmversion; then
cat .scmversion
return
fi
if test "$1" = "--short"; then
short=true
fi
# Check for git and a git repo.
if head=$(git rev-parse --verify HEAD 2>/dev/null); then
# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore
# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.
if [ -z "$(git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null)" ]; then
# If only the short version is requested, don't bother
# running further git commands
if $short; then
# echo "+"
return
fi
# If we are past a tagged commit (like
# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.
if atag="$(git describe 2>/dev/null)"; then
echo "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d", $(NF-1))}'
fi
# Add -g and exactly 12 hex chars.
printf '%s' "$(echo $head | cut -c1-12)"
fi
# Check for uncommitted changes.
# This script must avoid any write attempt to the source tree,
# which might be read-only.
# You cannot use 'git describe --dirty' because it tries to
# create .git/index.lock .
# First, with git-status, but --no-optional-locks is only
# supported in git >= 2.14, so fall back to git-diff-index if
# it fails. Note that git-diff-index does not refresh the
# index, so it may give misleading results. See
# git-update-index(1), git-diff-index(1), and git-status(1).
if {
git --no-optional-locks status -uno --porcelain 2>/dev/null ||
git diff-index --name-only HEAD
} | read dummy; then
printf '%s' -dirty
fi
fi
}
commit_info="$(scm_version)"
if test -z "${commit_info}" ; then
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "null"
EOM
else
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "${commit_info}"
EOM
fi下面解释一下脚本各部分内容:
- 脚本开头定义了cpuinfo.h文件的路径,脚本最后会创建一个cpuinfo.h,并把
GIT_COMMIT_INFO宏写入该文件。可以发现该文件的路径在dt-bindings目录下,后续想要在设备树也添加git提交号的话,直接include该文件即可。【需要注意的是:cpuinfo.h需要加入到.gitignore忽略文件中,否则每次提交后的第一次编译都会检测到cpuinfo.h的修改】
shell
INFO_DIR=${LICHEE_KERN_DIR}/include/dt-bindings/cpuinfo.h
scm_version()
{
...
}
commit_info="$(scm_version)"
if test -z "${commit_info}" ; then
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "null"
EOM
else
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "${commit_info}"
EOM
fi- scm_version()函数也作了修改,第一处修改如下,修改前:
shell
...
scm_version()
{
...
if test -z "$(git rev-parse --show-cdup 2>/dev/null)" &&
head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; then
...
}
...- 修改后:
shell
...
scm_version()
{
...
if head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; then
...
}
...- 第二处修改如下,修改前:
shell
...
scm_version()
{
...
if $short; then
echo "+"
return
fi
...
}
...- 修改后:
shell
...
scm_version()
{
...
if $short; then
# echo "+"
return
fi
...
}
...至此,用于生成提交号的脚本已制作完成。
那我们的脚本怎么被执行?在setlocalversion脚本最后执行即可:
shell
/* setlocalversion */
...
sh ${LICHEE_KERN_DIR}/scripts/scm_version.sh因为在内核开始编译前,会先执行setlocalversion脚本。借此执行我们自己的脚本。
继续修改内核setup.c
前面已经在<SDK>/kernel/linux-5.4/arch/arm/kernel/setup.c中加了提交号的打印,现在需要引入头文件:
c
...
#include <dt-bindings/cpuinfo.h>
...验证
cat /proc/cpuinfo查看git提交号:
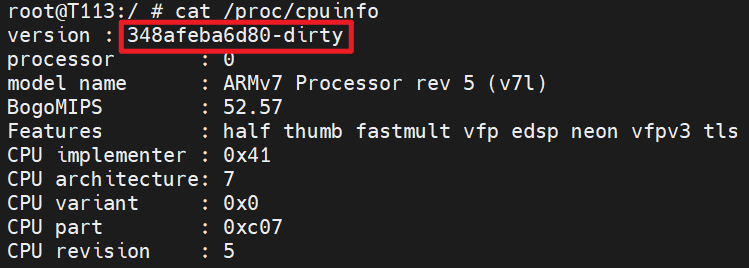
提交号后面还多了一个dirty字样,表明当前提交还存在未提交的文件,所以该提交号是最近一次提交的。
内核设备树中添加Git提交号
修改设备树
修改内核设备树<SDK>/device/config/chips/t113/configs/evb1_auto/linux-5.4/board.dts,直接引入头文件cpuinfo.h即可:
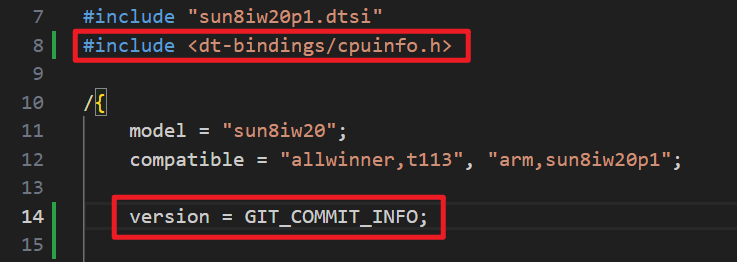
验证
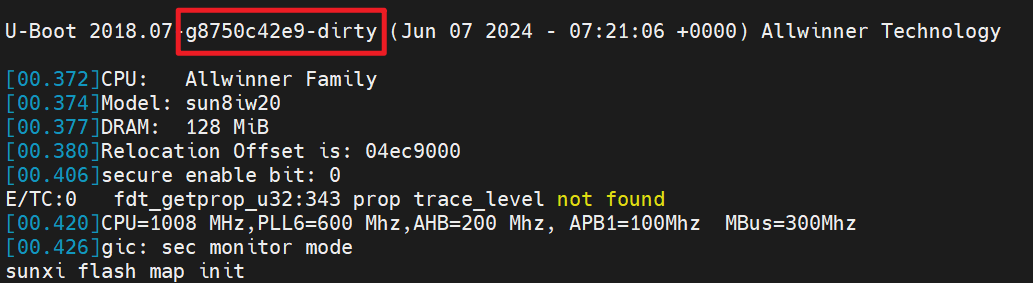
在uboot命令行执行fdt list /查看:
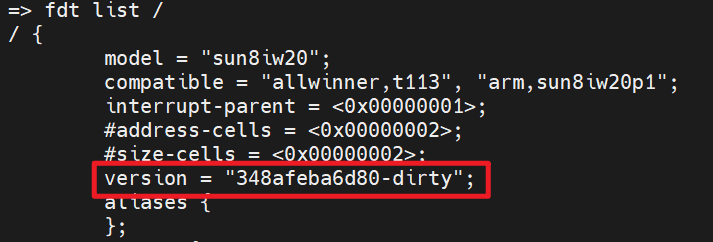
U-Boot版本号添加Git提交号
U-Boot配置
配置CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO=y
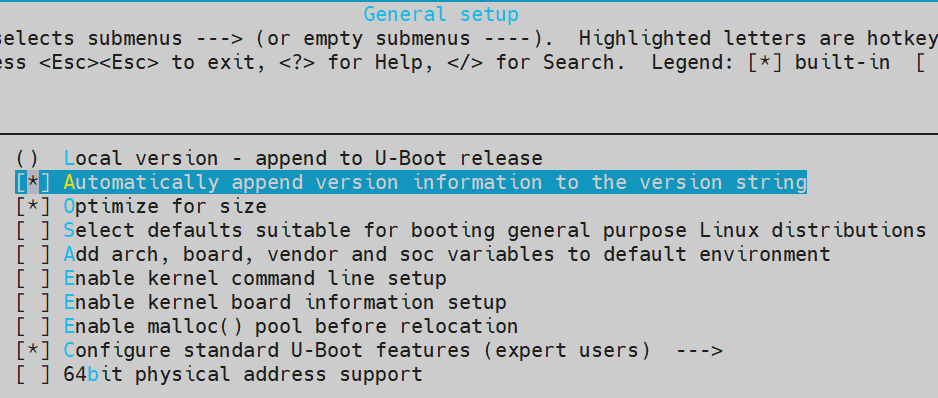
修改setlocalversion脚本
修改<SDK>/brandy/brandy-2.0/u-boot-2018/scripts/setlocalversion,主要修改其中的scm_version()函数,修改后的scm_version()函数如下:
shell
/* setlocalversion */
...
scm_version()
{
local short
short=false
cd "$srctree"
if test -e .scmversion; then
cat .scmversion
return
fi
if test "$1" = "--short"; then
short=true
fi
# Check for git and a git repo.
if head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; then
# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore
# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.
if [ -z "`git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null`" ]; then
# If only the short version is requested, don't bother
# running further git commands
if $short; then
# echo "+"
return
fi
# If we are past a tagged commit (like
# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.
if atag="`git describe 2>/dev/null`"; then
echo "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'
# If we don't have a tag at all we print -g{commitish}.
else
printf '%s%s' -g $head
fi
else
printf '%s%s' -g $head
fi
# Is this git on svn?
if git config --get svn-remote.svn.url >/dev/null; then
printf -- '-svn%s' "`git svn find-rev $head`"
fi
# Check for uncommitted changes
if git diff-index --name-only HEAD | grep -qv "^scripts/package"; then
printf '%s' -dirty
fi
# All done with git
return
fi
# Check for mercurial and a mercurial repo.
if test -d .hg && hgid=`hg id 2>/dev/null`; then
# Do we have an tagged version? If so, latesttagdistance == 1
if [ "`hg log -r . --template '{latesttagdistance}'`" == "1" ]; then
id=`hg log -r . --template '{latesttag}'`
printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"
else
tag=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | cut -d' ' -f2`
if [ -z "$tag" -o "$tag" = tip ]; then
id=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | sed 's/[+ ].*//'`
printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"
fi
fi
# Are there uncommitted changes?
# These are represented by + after the changeset id.
case "$hgid" in
*+|*+\ *) printf '%s' -dirty ;;
esac
# All done with mercurial
return
fi
# Check for svn and a svn repo.
if rev=`LANG= LC_ALL= LC_MESSAGES=C svn info 2>/dev/null | grep '^Last Changed Rev'`; then
rev=`echo $rev | awk '{print $NF}'`
printf -- '-svn%s' "$rev"
# All done with svn
return
fi
}
...验证